
Big Data Aanalytics in Higher Education
Irina Vdovychenko
1a
, Valentyna Khotskina
2b
, Serhii Hushko
2 c
, Victoria Solovieva
2 d
and Sergiy Tkalichenko
2e
1
National University, Vitaly Matusevich str., 11, Kryvyi Rih, 50027, Ukraine
2
State University of Economics and Technology, Medychna Str., 16, Kryvyi Rih, 50005, Ukraine
tsw1966@ukr.net
Keywords: Big Data Technologies, Higher Education System, Information Arrays, Analytics, Student Subjects
Olympiads.
Abstract: The article offers an overview of the means and methods of one of the most demanded modern Big Data
technologies for the use in the higher education system. The paper presents an analysis of publications on
similar studies. A brief description of Big Data technology is given in it. The article highlights various
information arrays in the archives of universities, which are systematically replenished. The use of Big Data
technology examples in American universities are considered. The research results of correlations and links
with characteristics of student subjects Olympiad’s winners were represented in the work. The purpose of the
article was to substantiate and propose certain directions for researching processes in the higher education
system using big data analytics. The authors propose the tasks, by solving which it would allow improving
significantly the educational process in universities.
1 INTRODUCTION
The system of higher education is constantly forming
and accumulating huge amounts of information.
These are the data about students and materials,
educational literature, curricula, laboratories and
classrooms, educational practices, diplomas and
coursework, and much more. And all this
information, accumulating, changing and
replenishing, is stored for decades.
To process these archives, new technologies are
required, one of which is Big Data technologies.
The volumes of information are steadily growing
and transforming. The replacement of classical
methods of data analysis with technologies such as
Big Data is becoming relevant.
In view of the fact that data arrays, the size of
which exceeds the potential of reference databases for
their research, processing and storage, require new
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0953-655x
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8963-4189
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4833-3694
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8090-9569
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1798-8073
tools and methods of analysis, they are increasingly
appealing to Big Data technology.
The need for Big Data arose a few years ago.
Clifford Lynch, editor of Nature, first introduced the
“big data” concept in 2008. Some scientists were
already interested in the problem of the information
rapid growth at the global scale. It should be noted
that big data has existed before. Today, the Big Data
category includes significant data flows over 100 GB
per day. In our time, the concept of Big Data has
already thoroughly entered the list of the technologies
in demand around the world. It penetrates and is
actively used in various spheres of life: technology,
business, video, sociology, medicine, education,
space, finance, etc.
Big Data is a combination of approaches,
methods, tools applied for the work with structured
and unstructured data of large volumes and diversity.
Most often, the technology is used for solving
intellectual problems. It is necessary in situations of
continuous growth of information. As the analysis
436
Vdovychenko, I., Khotskina, V., Hushko, S., Solovieva, V. and Tkalichenko, S.
Big Data Aanalytics in Higher Education.
DOI: 10.5220/0011364200003350
In Proceedings of the 5th International Scientific Congress Society of Ambient Intelligence (ISC SAI 2022) - Sustainable Development and Global Climate Change, pages 436-445
ISBN: 978-989-758-600-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

showed, Big Data is an alternative to classical
database management systems and solutions within
Business Intelligence. Big data tools that allow
distributed processing of information are used both
for incredibly large data (all pages of the global
network) and for small ones. To make a more
efficient decision, to identify hidden patterns, it is
necessary to submit a larger amount of input data for
processing, in these conditions Big Data is simply
necessary.
Currently, to process large arrays of "raw" data,
Big Data is used as the ideology of information
processing. At first, conventional computational
methods were used, which made it possible to process
huge amounts of input data, but today, Big Data is a
self-learning algorithm that can independently
expand and improve itself. The technology is making
a leap from simple processing of large information
arrays to a fundamentally new intellectual form. Big
Data technologies open up new approaches and
application possibilities (Vdovychenko, 2018)..
An important aspect that speaks in favor of Big
Data is the statement of analysts that education and
medicine will be promising areas for growth in the
use of the technology. With a small investment in
“big data”, they immediately begin to give tangible
returns. According to a number of experts, the
massive introduction of Big Data in these industries
can improve the life quality of people in the shortest
possible time (Savchuk, 2014).
2 THE ANALYSIS OF RECENT
RESEARCH AND
PUBLICATIONS
A lot of research has been carried out recently in the
field of education using Big Data technology, but the
results are scattered, and yet answers to many
questions have not been received. The trends and
results of some researches are considered as it
follows.
The group of scientists led by J. Okumpau,
analyzing Big Data, come to the conclusion that the
revealed patterns, taken mainly from one
demographic group, do not generalize the results
taken from other demographic groups. For example,
the patterns found for urban students are not similar
to the patterns built for rural students (Ocumpaugh et
al., 2014).
In their work, M. Nasiri, B. Minai, F. Wafai
consider a forecasting model for academic success
through monitoring and support the first-year
students (Nasiri et al., 2012). In the works of O.
Moscozo-Ts ea, M. Fitzkaino, S. Luyan-Mora, the
analysis of Big Data methods was carried out in terms
of two indicators of educational efficiency: student
dropout and student graduation (Moscoso-Zea et al.,
2017).
The work of I. Jugo, B. Kovacic and V. Slavui,
represents an interest, which describes the experience
of creating adaptive e-learning systems that use data
intellectual analysis tools to improve the adaptability
of the learning system (Jugo et al., 2016).
R. Asif, analyzing Big Data, found that the
concentration of pedagogical efforts on analytics and
learning results accounting in a small number of
specialized academic disciplines can contribute to the
effectiveness of learning (Asif et al., 2017).
In the works of K. Khare, H. Lam, A. Khare, the
analytics of students' success using massive online
courses is considered, which allows scientists to
predict the probability of refusal to study the course
(Khare et al., 2017).
In their researches, scientists consider Big Data
aspects related to the interaction of learning subjects.
G. Mobasher, A. Shawish, O. Ibrahim describe the
structure of a large database in education, which,
among other things, contains the demographic data of
students, the psychological characteristics of
students, teachers and parents (Mobasher et al.,
2017). In the works of V. Tem, an approach to the
joint learning organization is described, which makes
it possible to identify educational patterns based on a
varied set of educational online resources (Tam et al.,
2016).
Based on the analysis of many approaches and
models in his statements, I.D. Frumin identifies three
Big Data major areas:
1. Associated with thinking (primarily critical and
creative);
2. Associated with interaction with others
(communication and collaboration);
3. Associated with interaction with oneself (self-
regulation, reflexivity, self-organization).
It is clear that the results of analytics in these areas
are most valuable when they reveal abnormal and
borderline states of the educational system
(Liebowitz, 2016). R. Asif when analyzing Big Data,
found that the concentration of pedagogical efforts on
analytics and accounting the results of learning in a
small number of specialized academic disciplines can
contribute to the effectiveness of learning.
Consequently, the development of Big Data
technology in education is considered by many
scientists, but these are disparate approaches, there is
Big Data Aanalytics in Higher Education
437
no data systematic analysis on the use of Big Data
for the development of the education system. The
research results application for positive changes in the
development of higher education system were not
noted. We consider it important and relevant to
substantiate and propose certain trends of processes
research in higher education system using big data
analytics. In our opinion, these are the tasks having
solved them it is possible to significantly improve the
educational process in universities.
3 PRESENTATIONS OF THE
MAIN MATERIAL
If Big Data technology used, then the information
accumulated in the higher education system is
considered and analyzed would be a colossal source
of a unique new information. With its help, it is
possible to improve, transform the training system,
rethink approaches, reduce the time and efforts for
solving standard problems, and introduce ready-made
experience that gives the best result. We propose to
highlight the following arrays of information in
universities:
Methodical information.
Educational literature.
Archives (diplomas, coursework, practical
works).
Personal data of students (biographical data, data
on academic performance and attendance.
Personal data of university employees
(biographical data, scientific, educational and
administrative work).
Administrative data.
Current information.
Results of sessions.
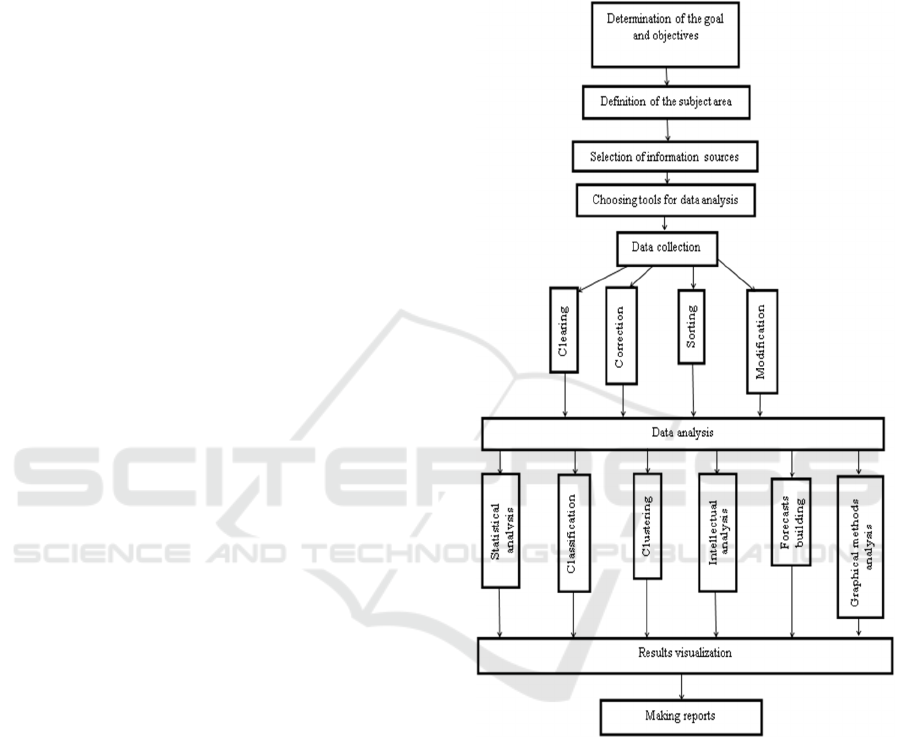
Logical-functional diagram of Big Data processes in
the education system is shown in Fig.1.
Big Data technologies develop analytic indicators on
the base of this information. The following types of
analytic indicators are defined:
descriptive analytics;
predictive analytics;
prescriptive analytics.
The point of descriptive analytics is to compose an
objective and most accurate description of the current
situation using the available data.
Descriptions are usually visualized through
graphs, charts, infographics, according often to
averaged data. The task is to turn huge arrays of
numbers and graphs into accessible, understandable
and easily perceived information.
The purpose of the models used in predictive
analytics is to predict events based on a comparison
of historical and current data. Most often, predictive
analytics is used to identify in advance students who
are inclined to abandon their studies and therefore
need special attention from the teacher.
Figure 1: Logical-functional diagram of Big Data processes
in the education system.
Prescriptive analytics answers the question
"what’s to be done?" Such reports not only indicate
which of students is worth paying attention to and
what exactly he is not coping with, but also give
recommendations for what direction is to change the
educational trajectory. For this, the algorithms use
generalized information about the actions of previous
users with similar characteristics (Leviev, 2021).
Let's look at examples of using Big Data
technology in universities in different countries.
According to statistics, 400,000 students in the
United States are expelled annually. The outflow of
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
438

students negatively affects the educational
institutions themselves: the greater the outflow, the
less profits and the state’s financial support. The
college's position in national rankings is falling.
To solve the problem, the University of the
Commonwealth of Virginia, together with the
Education Advisory Board, conducted a study that
made it possible to identify students at risk and help
them. At the University a platform was created, which
aggregates all student grades and searches for the
problems. As a result of the use of Big Data, within
one semester the number of students who completed
the course increased by 16%, and the number of
students who were promoted to the next course of
study increased by 8 percent.
Nottingham Trent University of England
implemented an interactive system of descriptive
analytics of student results in the form of a dashboard
that showed data on student engagement in the
educational process. The dashboard was designed to
reduce student dropout rates, improve attendance and
increase a sense of membership of the university
community.
The monitor panel, which is available to students,
teachers and curators (tutors), displays the indicators
of the involvement of each student in comparison
with his classmates:
frequency of work with at the library,
information of the courses studied,
attendance,
participation in competitions,
and other educational indicators.
Thus, any student can watch his own activity and
compare himself with fellow students in order to
understand how much he is involved in the
educational process and the life of the university as a
whole, and to what aspect should be paid more
attention. If a student does not show signs of activity
within two weeks, the platform sends notifications to
tutors so that they can quickly contact the student and
support him. 3 years after the implementation of the
system, the results of a university survey showed that
72% of freshmen used this Big Data student
dashboard and it inspired them to increase the amount
of time spent for studying.
At the American Austin Pie University, a referral
system was introduced which helps students choose
and be enrolled in educational courses. The inputs
used are the learning outcomes of previous students
for a specific course, the performance of each student,
and information about students with similar profiles
and interests. Based on the analysis of this Big Data
information, the system using Machine Learning
algorithms, selects training courses that best match
the interests, abilities and curriculum of an individual
student. The accuracy of the recommendations is
estimated at 90% (Leviev, 2021).
Ball State University in Indiana uses Big Data to
analyze student participation in a variety of campus
activities. This parameter is considered to be the key
in terms of academic success. The University
monitors the frequency of campus visits and events.
This approach has contributed to improved learning
results. And there are many similar examples.
At the North Carolina University (USA) in early
2020, a multitasking learning system was presented,
where Big Data models of the system predict the
probability of a student's correct answer based on his
previous behavior in the educational process. This is
useful for informing teachers in case a student may
need additional instructions and it facilitates adaptive
learning functions. Such as changing the storyline, or
prompts, etc., for example (Geden, 2020). And there
are many of such examples.
In recent years, a fundamentally new effect of the
massive application of this approach in data
processing has begun to manifest itself. Scientists are
looking for hidden correlations between the studied
phenomenon (object, process) and thousands of other
factors, where huge statistics accumulated over the
years were used as the initial data. The use of these
empirically discovered patterns promises the progress
in the development of many scientific directions.
Complex modern Big Data models more and more
often reveal some seemingly irrational and fantastic
dependencies, allowing to have a look far beyond the
known scientific picture of the world (Tyndall, 2012).
In this regard, Big Data is sometimes called the "new
astrology of the XXI century." And this is the result
of a smooth transition from the amount of information
to its quality, when machines become capable of
identifying fundamentally new dependencies that
were previously inaccessible to human limited
awareness.
One of the applications of big data is predictive
modeling. By studying the potential university
entrants, it is possible to get important data. Based on
the analysis of this information, the Big Data system
selects a specialty and university that best suits the
interests, experience and personal qualities, abilities,
level of knowledge and financial capabilities of a
particular future student. It is possible to determine
which psycho-type of a student is suitable for
acquiring the specialty, and which one is not. The
accuracy of the recommendations is about 92%.
Those students who want and who are able to get this
University’s specialties, they will come to the
University. This will reduce the percentage of
Big Data Aanalytics in Higher Education
439

dropping out from the university, ensure the quality
of graduates, enterprises will receive good specialists.
Big data analytics will help understand better the
students’ abilities and capabilities. Studying the
psychological peculiarities, behavior, social status,
family customs, national features, cultural level,
emotional personality type and other characteristics,
it is possible to personally select additional
instructions, leading questions, prompts, similar
examples, visualizations, etc., when organizing
distance learning. This will significantly increase its
efficiency, the interest of students in educational
material.
Mikhail Leviev, head of Algo Most, offers his 5
ways of using Big Data in education:
1. Big Data and economy;
2. Personalization of training;
3. Improving the quality of teaching;
4. Choice a future profession;
5. Virtual campus.
These are the most common areas of scientific
research on the use of Big Data in education. We
propose in new directions to find explicit and implicit
reasons, features, coincidences of circumstances and
coincidence of factors that give unique results. These
results must be found, identified, recorded and
repeated for developing the education system,
training highly qualified specialists in various fields,
as well as "heaven-born" teachers who can teach and
transfer knowledge and experience in a qualitative
manner.
In identifying such new directions, we paid
attention to student Olympiads. They are held with
the aim of enhancing the educational and cognitive
activity of students, intensifying and improving the
educational process, stimulating the needs for
creative mastery of knowledge, with the aim of
developing future graduates, identifying and realizing
their creative abilities and scientifically gifted, truly
talented youth. Knowing that the goal of the student
Olympiad is to improve the quality of training
qualified specialists, to search for gifted student
youth, to stimulate their creative work, we understand
that they are the best ones suited for the analysis.
While studying the participants and winners of
student Olympiads, it is necessary to accumulate
explicit and less explicit patterns. This will make it
possible to identify the most effective methods of
preparing for the Olympiads, the most efficient
teaching techniques of certain disciplines, as well as
innovative teachers who are able to convey
knowledge and skills to students in the best possible
way. When studying the results of the Olympiads, it
is necessary to pay attention to the following
questions:
To identify the universities, the students of
which most often become the winners.
To identify the universities whose students are
often not included in the top 10.
Which academic disciplines are the worst
covered by students?
What topics of learning material are the worst
covered by students?
To reveal the presence / absence of students’
success growth with re-participation.
To study the dependence of success at the
Olympiad on the course, gender, social living
conditions, etc.
To find out if there is a connection between
victories at the Olympiads and the kind of sport the
student is engaged in.
To take into account gender, height, age,
heredity, psychologic type and other explicit and
implicit features of the winners of student subject
Olympiads.
To conduct a study of this issue, information
about students was collected, winners of the second
round of the All-Ukrainian Student Olympiads. The
student Olympiads on technical disciplines were
under consideration as follows:
1. Life safety;
2. Power engineering, electrical engineering and
electro-mechanics;
3. Energy management and engineering;
4. Fundamentals of labor protection;
5. Energy saving and energy management;
6. Civil protection;
7. Casting production;
8. Materials science;
9. Physical metallurgy;
10. Metals heat treatment;
11. Non-metallic materials;
12. Welding;
13. Programming processing on numerically
controlled machines;
14. Computer-aided design and computer modeling
systems in mechanical engineering;
15. Engineering technology;
16. Interchangeability, standardization and technical
measurements;
17. Theoretical mechanics;
18. Resistance of materials;
19. Applied Mechanics;
20. Mechatronics;
21. Machine parts and design bases;
22.Metrology and information-measuring
technology;
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
440
23. Metrology, standardization and certification;
24. Radio engineering;
25. Electronic devices;
26. General electrical engineering;
27. Theoretical foundations of electrical engineering;
28. Descriptive geometry and geometric modeling on
a PC;
29. Mathematics;
30. Programming;
31. System programming.
The input information array was based on
information about students of universities in the city
of Krivoy Rog, engineering specialties, such as:
transportation engineer, mechanical engineer,
road transport engineer, heat and power engineer,
electrical engineer, builder, mechanical engineer,
metallurgist, electro-mechanical engineer, process
engineer, programmer, systems engineer, automated
control system engineer, electronics engineer,
electrician, analyst, miner, ore dressing engineer.
The information was collected from 2010 to
2021. The following fields in the database were
obtained after systematization:
sequential number, university, specialty, course,
gender, age, height, weight, hair color, eye color,
nationality, psychological type, type of
temperament, chronic diseases, parents' age (f/ m),
parents' (f/m), living conditions, marital status, sport,
music education, art education, participation in
amateur performances, gastronomic priorities,
hobbies, favorite color, favorite season, favorite
flower, pets available. As an example, partially
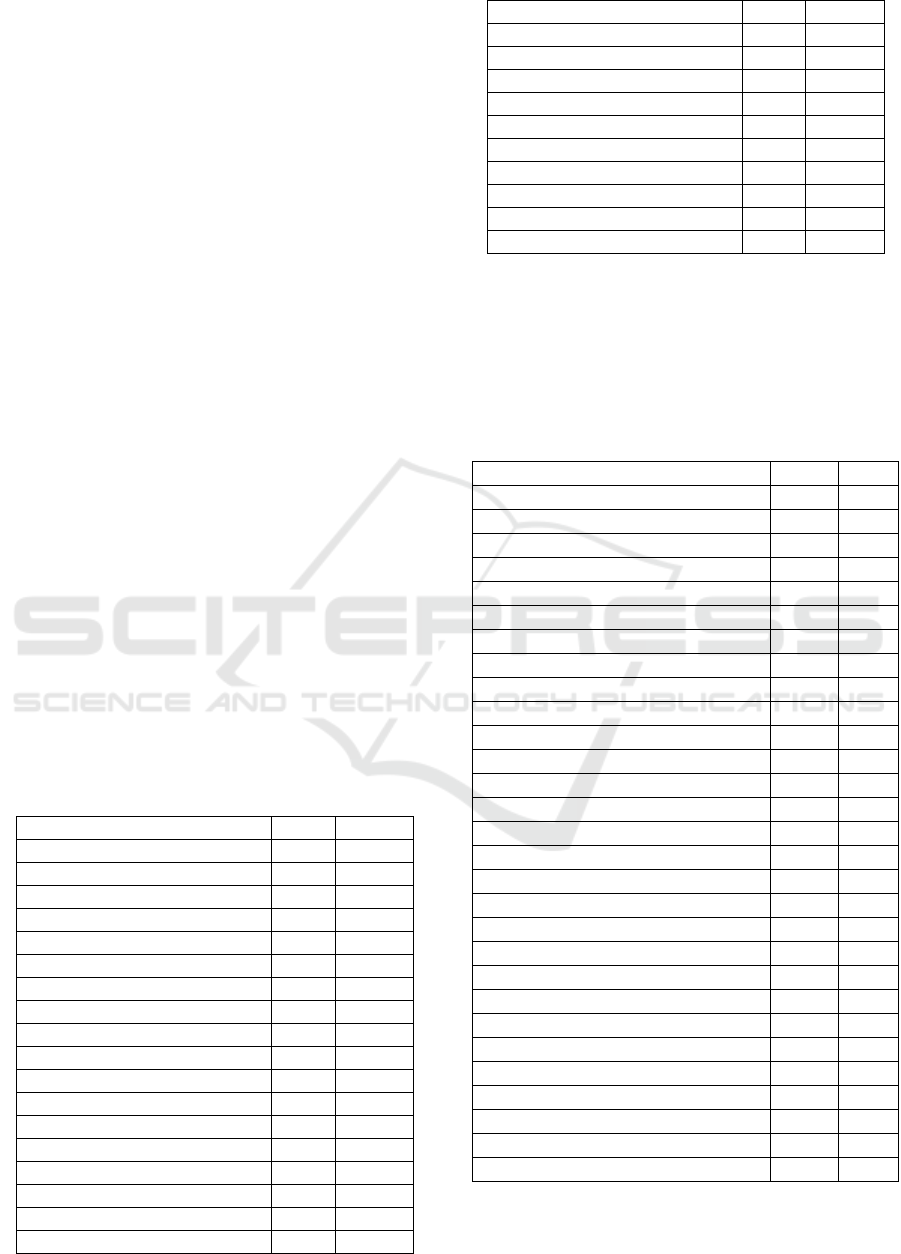
collected information is represented in Table 1.
Table 1: Information for analysis.
S/No 1 2
University knu knu
Specialty komп meh
Course 4 3
Gender g m
Age 21 20
Height 168 183
Height 57 78
Hair color sv.r shat
Eye color ser kar
Nationality ukr ukr
Psychological type int ekst
Type of temperament mel hol
Chronic diseases - -
Father’s age 45 47
Mother’s age 42 41
Father’s education vis sr.t
Mother’s education vis vis
Living conditions otl otl
Marital status holl holl
Sport voll box
Music education - -
Art education + -
Participation in amateur + +
Gastronomic priorities sl ostr
Hobbies put bok
Favorite color roz kr
Favorite season leto leto
Favorite flower liliy rom
Pets available + +
The information was processed, qualitative
indicators were converted into quantitative ones,
ranked and received input data for analysis using the
R programming language, as one of the leading tools
for Big Data technology. An example of some data
obtained is presented in Table 2.
Table 2: Modified information for analysis.
S/No 1 2
University 1 2
Specialty 4 8
Course 4 3
Gender 1 2
Age 21 20
Height 168 183
Height 57 78
Hair color 5 3
Eye color 4 1
Nationality 1 1
Psychological type 2 1
Type of temperament 1 3
Chronic diseases 0 0
Father’s age 45 47
Mother’s age 42 41
Father’s education 1 2
Mother’s education 1 1
Living conditions 1 1
Marital status 1 1
Sport 6 4
Music education 0 0
Art education 1 0
Participation in amateur 1 1
Gastronomic priorities 1 4
Hobbies 2 5
Favorite color 7 6
Favorite season 3 3
Favorite flower 4 8
Pets available 1 1
Some information was obtained by questioning
Olympiad’s winners.
Big Data Aanalytics in Higher Education
441

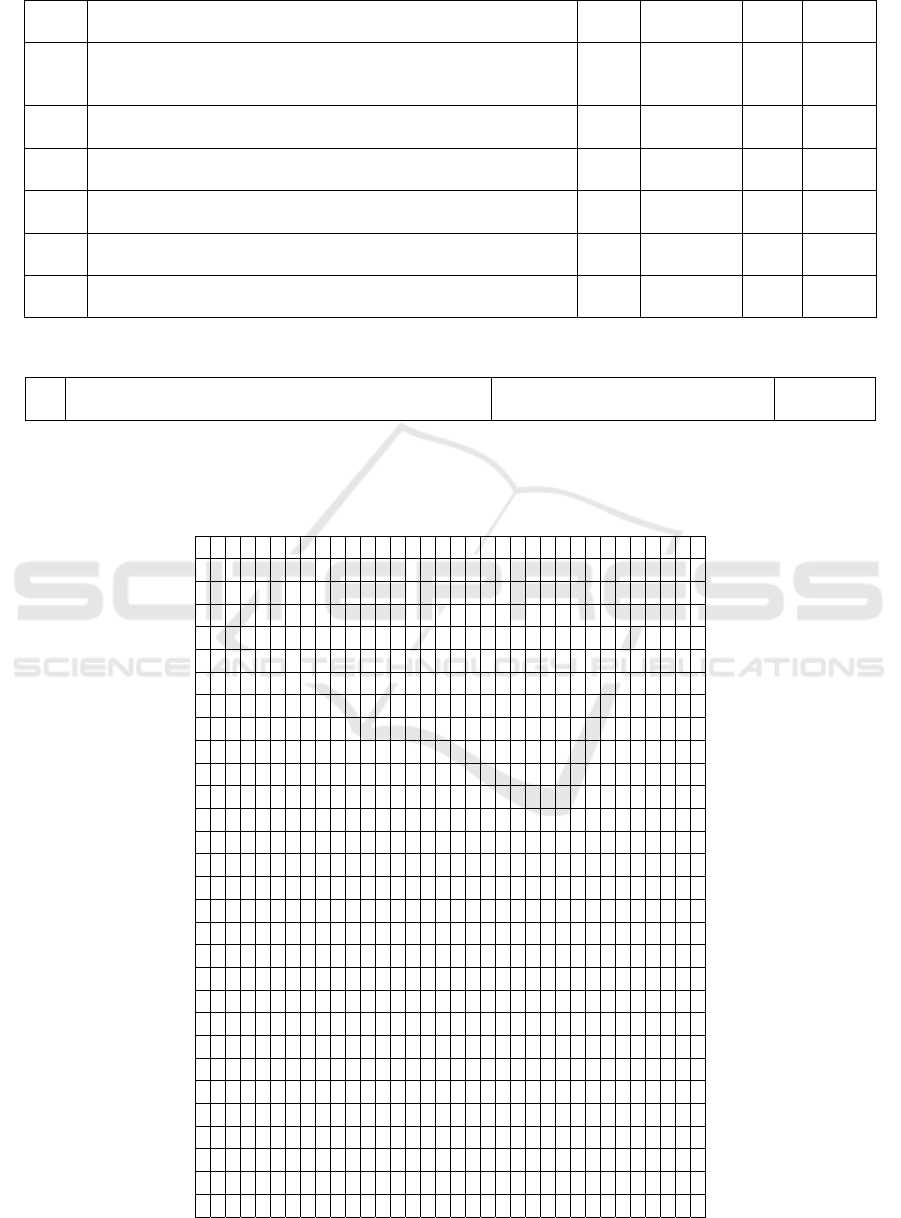
QUESTIONNAIRE FORM
We ask you to take part in the research in order to assess, with your help, the real state of affairs in this area
and to suggest proposals for the future. The profile is anonymous. The research data will be used for scientific
purposes only and in a generalized form. We are sincerely grateful for your cooperation!
А. Please, rate the weight of the indicated factors of the problem of Olympiads organization and holding them
on a scale from 0 - none, 1 - the least, etc., to "5" - the highest.
S/N
o
Factors Factor
wei
g
ht
Choic
e
1. Com
p
lexit
y
of or
g
anizin
g
Ol
y
m
p
iads for the entire education s
y
ste
m
0 1 2 3 4 5
2. Com
p
lexit
y
of conductin
g
Ol
y
m
p
iads for individual universities 0 1 2 3 4 5
3. Difficulty of conducting Olympiads for teachers 0 1 2 3 4 5
4. Difficulty of holding Olympiads for students 0 1 2 3 4 5
5. To what extent will the holding Olympiads improve the quality of specialists
training?
0 1 2 3 4 5
6. To what extent will the holding Olympiads increase the competitiveness of
Ukrainian s
p
ecialists in the world?
0 1 2 3 4 5
7. To what extent will the holding Olympiads increase the flow of students to
Ukrainian universities from other countries?
0 1 2 3 4 5
8. To what extent will the holding Olympiads increase the accessibility of higher
education for all segments of the population?
0 1 2 3 4 5
9. o what extent will the holding of Olympiads contribute to the democratic reforming
of the education s
y
stem?
0 1 2 3 4 5
10. To what extent does Ukrainian le
g
islation stimulate the holdin
g
of Ol
y
m
p
iads? 0 1 2 3 4 5
11. What is the degree to which it is necessary to introduce assessment of students'
knowled
g
e at Ol
y
m
p
iads on a uniform Euro
p
ean scale?
0 1 2 3 4 5
12. To what extent does the holding of Olympiads activate the atmosphere of novelty
and innovation in the work of teachers?
0 1 2 3 4 5
13. To what extent does the holding of Olympiads activate the atmosphere of novelty
and innovation in the work of students?
0 1 2 3 4 5
14. To what extent will the holding of Olympiads contribute to the implementation of a
creative a
pp
roach to learnin
g
?
0 1 2 3 4 5
15. To what extent will Olympiads increase the competitiveness of specialists in the
Ukrainian market?
0 1 2 3 4 5
16. To what extent is the current level of a student's preparation for the Olympiad
determined by knowledge and competence, but not by the time spent for
conventional trainin
g
and learnin
g
?
0 1 2 3 4 5
17. To what extent does Olympiad holding guarantee a coordinated approach to quality
standards for transnational learning?
0 1 2 3 4 5
18. To what extent will a wide European market be accessible for Ukrainian students
mobility after winning Olympiad?
0 1 2 3 4 5
19. To what extent will victories at Olympiad affect the competitiveness of students in
the world?
0 1 2 3 4 5
20. What degree of reforming the higher education system will be achieved by active
and systematic of Olympiads holding in Ukraine?
0 1 2 3 4 5
21. To what extent is it necessary to involve students in the development of a working
concept for holding Olympiads in Ukraine?
0 1 2 3 4 5
22. How profitable is the European higher education system influence on the national
conce
p
t of Ol
y
m
p
iads for Ukraine?
0 1 2 3 4 5
23. To what extent will the reduction in the volume of Olympiads affect the level of
trainin
g
of s
p
ecialists?
0 1 2 3 4 5
24. To what extent will internationally funds and grants for the development of
education stimulate the holding of Olympiads in Ukraine?
0 1 2 3 4 5
25. To what extent should the student community take part in running Olympiads on
the basis of e
q
ual
p
artnershi
p
?
0 1 2 3 4 5
26. To what extent is the European higher education system a guarantee for intellectual
learnin
g
?
0 1 2 3 4 5
27. To what extent will
y
ou contribute to the
p
rocess of holdin
g
Ol
y
m
p
iads in Ukraine? 0 1 2 3 4 5
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
442
B. Do you agree with the statements presented?
No Difficult
to sa
y
Yes Choice
1. Innovations in the concept of holding Olympiads in Ukraine is a
key issue, with the adoption of which cardinal changes in the
development of higher education in Ukraine will begin.
0 2 5
2. Will the independent assessment of the Olympiads ensure the
p
artici
p
ation of international ex
p
erts?
0 2 5
3. Is it realistic to form a uniform European space for holding
Olympiads in higher education?
0 2 5
4. Do the disciplines and tasks that are submitted for Olympiads
meet the requirements of the Ukrainian labor market?
0 2 5
5. Do you approve the expression: "Education is a public
p
ro
p
ert
y
"?
0 2 5
6. Is the foreign expert’s participation obligatory in assessing the
q
ualit
y
of Ol
y
m
p
iads in Ukraine?
0 2 5
C. If the level of the Olympiads in the European Union is taken as 5 points, then what level
1 Conducting Olympiads in engineering and technical
disciplines in Ukraine
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
An example of a part of the obtained results of questioning the Olympiads winners on the problems of holding
student Olympiads in Ukraine are presented in Table 3.
Table 3: Part of the final array with the survey results.
433 1 5 2 3 2 3 3 115214442433333422025553
432 1 1 3 2 4 2 2 034454343222112232525053
252 1 4 0 0 0 3 0 032301105112111210522050
444 3 5 0 0 3 2 3 324502200552245122520000
545 2 4 0 0 0 2 0 023010000221004300022010
544 4 5 2 4 2 3 3 242454453014355330525558
543 1 2 2 0 0 4 0 034400000201005500002024
434 5 5 1 0 2 0 0 123001002100001315002006
555 5 1 0 0 0 3 0 011510003530013000500200
345 2 5 3 5 3 4 5 255315534342245040500555
444 2 4 2 4 2 3 3 254454332123343310522247
333 3 4 3 3 2 5 3 333433333333333335502255
445 3 4 0 3 0 1 0 354054440143044322500525
555 5 5 1 0 2 3 1 120500000012211212002503
543 4 4 2 4 2 3 5 241452443342434532525555
112 1 3 0 1 0 2 0 053351111443251120502206
222 2 4 3 2 2 2 3 003332224112344440502225
222 2 5 4 5 3 3 4 424453341324353142522255
555 5 3 0 0 0 4 0 012503331011005012200008
000 0 5 3 3 5 5 5 354255555435555342255555
334 2 2 2 0 3 1 3 241224453232324325525256
453 5 3 5 5 3 3 4 434235554353334442525503
232 4 1 2 1 1 2 1 225212222322334110522003
433 5 4 3 1 2 0 1 232133322221122322000223
133 4 2 5 3 2 2 1 455355555455555345255553
555 5 3 3 3 1 1 3 042334443235555442522025
334 4 3 5 5 5 2 0 021443432342122220002225
434 5 3 2 2 3 3 0 022224443343223410250528
222 4 2 1 0 0 0 0 032000000200000000000003
444 3 5 2 2 2 0 0 033443543344554132505023
Big Data Aanalytics in Higher Education
443

In the result of our research, a large amount of
data was obtained, among which the following are
the most interesting:
1. At least one of the parents of the Olympiad
winners has a higher education.
2. The age difference between father and mother
of 75% was more than three years.
3. Hair color - predominantly brunette.
4. Psychological type - mostly introverts.
5. Type of temperament - mostly sanguine.
6. The kind of sport is tough single combats
(boxing, karate, etc.)
7. 46% have art, music or choreographic
education.
8. 62% participate in amateur performances.
9. 72% named red as their favorite color.
10.51% have pets.
From this array, you can find overlapping
dependencies, coinciding "chances" and many other
indicators with which you can determine a potential
winner of Olympiad, devote more time to him for
preparation.
Considering that this is the beginning of a large
study, we hope that Big Data technology will
provide an opportunity to identify many important
and interesting connections.
The results of this information analysis can be
used for serious changes in the educational process.
It is very interesting to use Big Data to analyze
teaching staff. To do this, among others, you can pay
attention to such questions: to identify the age
characteristics of teachers.
To determine from which universities:
the graduates do not change their qualifications;
the largest percentage of graduates get a job in
their specialty;
the largest number of graduates become
lecturers (teachers) with scientific degrees (the
highest category).
To study the peculiarities of teaching in these
universities, the experience of their best teachers, the
atmosphere in the educational institution and much
more, which seems less significant, but in the end, it
solves a lot.
It is very important to use Big Data technologies
to identify patterns and characteristics of families
formed by teacher’s dynasties. This technology will
be able to disclose those connections, which are
invisible to man, characteristics, features that form a
true teacher "from God."
By studying the pedagogical universities
applicants, Big Data will make it possible not to
invite random people who cannot be good teachers
in terms of their spiritual qualities, or their outlook,
or professional knowledge.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The considered Big Data technology, with the help of
which the patterns in the development of higher
education system are revealed, in such a small part of
it as student subject Olympiads, gives great
opportunities and hopes.
The presented results of the study of the student
subject Olympiads winners’ characteristics using Big
Data technology, as well as their opinions on the
importance of student Olympiads, obtained through
the questionnaire survey, provide information for
thought and application.
The results of Big Data application to the huge
amount of data accumulated in the higher education
system will give grounds for changing curricula, the
requirements, methods and approaches to teaching
students. Having implemented the proposed research
directions in the work, it allows getting a colossal
source of unique, new and useful data, on the base of
which it is possible to change the educational system
for the better.
REFERENCES
Asif, R., Merceron, A., Ali, S. and Haider, N. (2017).
Analyzing undergraduate students' performance using
educational data mining // Computers and Education.
2017. № 113. pages 177-194.
Geden, M, (2020).
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2020/02/20020
5132409.htm.
Jugo, I., Kovacic, B. and Slavuj V. (2016). Increasing the
adaptivity of an intelligent tutoring system with
educational data mining: A system overview //
International Journal of Emerging Technologies in
Learning. № 11(3). pages 67-70.
Khare, K., Lam, H. and Khare, A. (2017). Educational data
mining (EDM): Researching impact on online business
education // On the line: Business education in the
digital age. 2017. pages 37-53.
Leviev, M. (2021). 5 ways to apply big data in education
http: //www.edutainme.ru/post/learning-analytics/.
Liebowitz, J. (2016). Thoughts on recent trends and future
research perspectives in big data and analytics in higher
education // Big data and learning analytics in higher
education: Current theory and practice. – January,
2016. pages 7– 17.
Mobasher, G., Shawish, A. and Ibrahim, O. (2017).
Educational data mining rule-based recommender
systems // Paper presented at the CSEDU 2017 -
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
444

Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on
Computer Supported Education. 2017. № 1. pages 292-
299.
Moscoso-Zea, O., Vizcaino, M. and Lujan-Mora, S. (2017).
Evaluation of methods and algorithms of educational
data mining // Paper presented at the 2017 Research in
Engineering Education Symposium, REES 2017.
Nasiri, M., Minaei, B. and Vafaei, F. (2012). Predicting
GPA and academic dismissal in LMS using educational
data mining: A case mining // Paper presented at the 3rd
International Conference on eLearning and eTeaching,
ICeLeT. pages 53-58.
Ocumpaugh, J., Baker, R., Gowda, S., Heffernan, N., and
Heffernan, C. (2014). Population validity for
educational data mining models: A case study in affect
detection / British Journal of Educational Technology.
№ 45(3). pages 487-501.
Savchuk, I. (2014). Big Data is a technology that gives birth
to a new type of business. Bit magazine. No. 3 (36).
Tam, V., Lam, E., Fung, S., Fok, W. and Yuen, A. (2016).
Enhancing educational data mining techniques on
online educational resources with a semi-supervised
learning approach. // Paper presented at the Proceedings
of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Teaching,
Assessment and Learning for Engineering, TALE 2015.
2016. pages 203-206.
Tyndall, S. (2012). Big data: everything you need to know.
PC Week / RE, 2012, No. 25 (810).
Vdovychenko, I. (2018). Big Data technologies and their
application for the analysis of network users. ІІІ
International Scientific and Practical Conference
“Information Security and Computer Technologies.
The city of Kropyvnitsky. pages 189-191.
Big Data Aanalytics in Higher Education
445
