Root Cause Classification of Temperature-related Failure Modes in a
Hot Strip Mill
Samuel Latham and Cinzia Giannetti
a
Faculty of Science and Engineering, Swansea University, Fabian Way, Swansea, Wales
Keywords: Root Cause Analysis, Machine Learning, Classification, Data Analytics, Knowledge Integration, Hot Strip
Mill, Steel Industry.
Abstract: Data is one of the most valuable assets a manufacturing company can possess. Historical data in particular
has much potential for use in automated data-driven decision-making which can result in more efficient and
sustainable processes. Although the technology and research behind data-driven systems for Root Cause
Analysis has developed vastly over decades, their use for real time automated detection of root causes within
steel manufacturing has been limited. Typically, root cause analysis still involves a lot of human interaction
both in the pre-processing and data analysis phases, which can lead to variability in results and cause delay
when devising corrective actions. In this paper, an application for automated Root Cause Analysis in an Hot
Strip Mill is proposed for the purpose of demonstrating the effectiveness of such an approach against a manual
approach. The proposed approach classifies temperature defects of steel strip Width Pull using a variety of
machine learning algorithms in conjunction with k-fold cross validation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Each year, millions of tonnes of steel are rolled by
steel companies across the globe. While steel-making
plants strive to produce high quality steel strip and
limited waste, various defects still occur on a regular
basis and thousands of these are recorded by
operators each year. Width-related defects account
for a large portion of these.
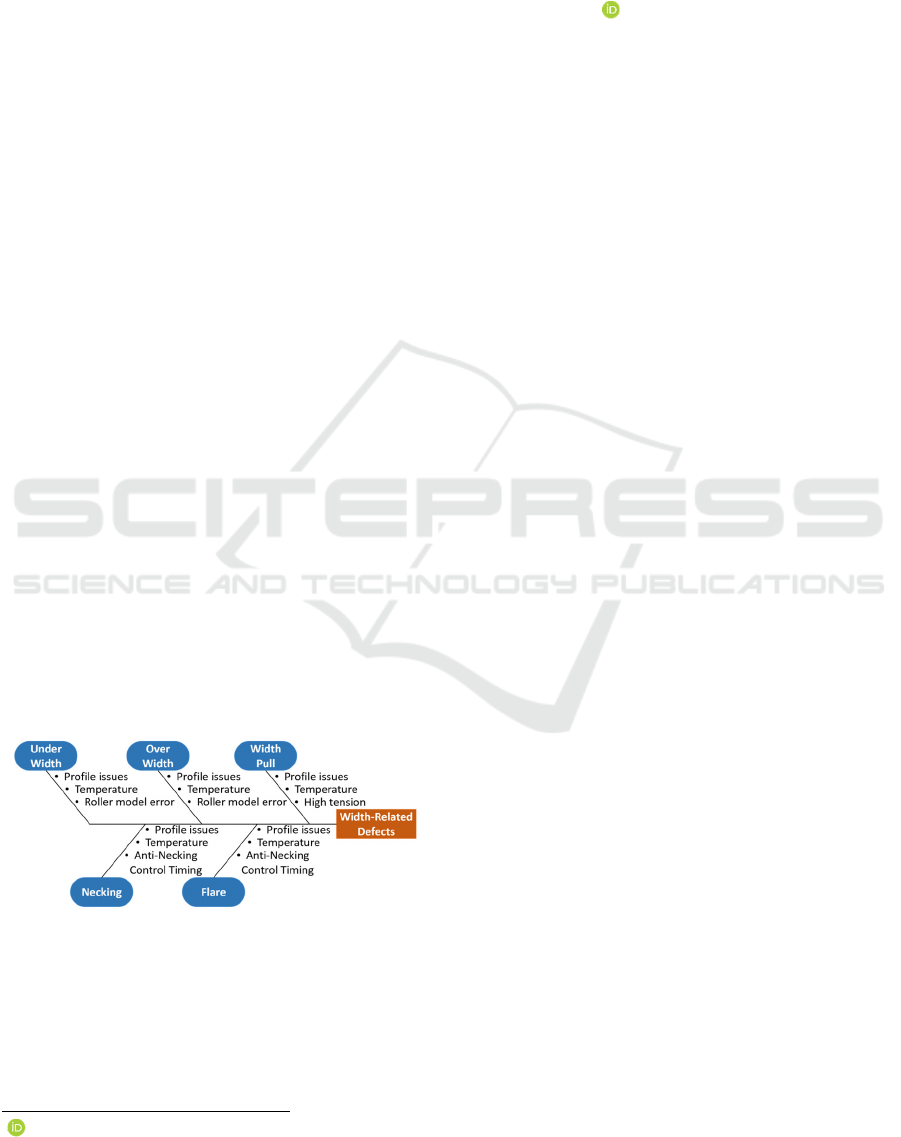
Figure 1: A fishbone diagram showing the causes of Width
Pull throughout an HSM.
There are several width-related defects, each with
a number of failure modes with potential origins from
various Hot Strip Mill (HSM) sub-processes,
including bar specification issues, temperature
fluctuations, and erratic tension control.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0339-5872
The current procedures used to determine the
causes of width-related defects, however, are mostly
manual and require human interaction before the
issue can be resolved, sometimes even including
simple true or false condition checks. This creates an
inconsistent timescale in which defects may go
unrecognised and successive products are therefore
negatively affected. These problems can occur not
only when defective behaviour is identified at a later
time, but also if defective behaviour is missed and
therefore goes unrecorded. Although human error is
thought to be the main concern associated with
manual processes, fast-paced and critical decision-
making and resource allocation are also primary
concerns (Janssen et al., 2019; Sheridan &
Parasuraman, 2000).
In recent decades, root cause analysis (RCA)
methodologies have adopted more up-to-date and
relevant technologies including automation and
machine learning (Mahto & Kumar, 2008).
Automation has proven to be a powerful approach in
manufacturing operations and RCA, dramatically
reducing the time between the occurrence of physical
events and digital analysis and visualisation
(e
Oliveira et al., 2022), usually without the need for
36
Latham, S. and Giannetti, C.
Root Cause Classification of Temperature-related Failure Modes in a Hot Strip Mill.
DOI: 10.5220/0011380300003329
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Innovative Intelligent Industrial Production and Logistics (IN4PL 2022), pages 36-45
ISBN: 978-989-758-612-5; ISSN: 2184-9285
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

human interaction. Machine learning also enables
RCA systems to learn patterns in data which can be
too ambiguous for a human to perceive and provides
the ability to re-train a system to adapt to new or
unforeseen behaviour (Wiering & van Otterlo, 2012;
Wuest et al., 2016). Within the steel rolling industry,
RCA, particularly with machine learning, is not yet
mainstream outside of its use in applications for
surface defect detection and roller model
optimisation. Currently, such applications have also
not been embedded into a larger RCA system
spanning multiple sub-processes in an HSM, which is
a future aim of this study.
By increasing the scope of machine learning
applications in an HSM setting, it is possible to create
a broad set of RCA tools for the identification of
failure modes which can be used to improve the
current process and reduce workload on team
members, allowing them to focus on other more
meaningful tasks. In the future, it would also be
beneficial to combine these tools into a broad system
to identify both the cause and origin of a defect
throughout a number of HSM sub-processes. This
would provide quick access and a simple but detailed
overview of the process with regards to process
performance and RCA.
In this paper, a proposition is made for an
automated RCA application which utilises machine
learning to classify the root cause of Width Pull in an
HSM. This aims to show that there is potential for a
series of this type of application to be created in a
steel industry setting and, in future, compiled into a
final system which can broadly monitor the HSM
process. The resulting application aims to save time
and boost productivity of both the HSM process and
analysts and reduce the overall number of defects that
occur in the future. In section 2, an insight into the
current issues and analysis procedures used in
existing HSMs is highlighted and a deeper
understanding into the background of RCA systems
and machine learning both in general and in the steel
industry is provided. The data pre-processing steps
taken and the methodology used to carry out
classification experiments are then outlined in section
3. The results of these experiments are then evaluated
against a manual approach to the described problem
in the penultimate section before concluding on the
proposed approach’s performance, the optimal
machine learning model, and how it might be
improved in the final section. Future work aims to
discuss the need and integration of such an
application in a broader RCA system spanning the
entire HSM process. This will be in conjunction with
a previous work in which an RCA application was
created for failure mode classification in an HSM
(Latham & Giannetti, 2021).
2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Root Cause Analysis in
Manufacturing and the Steel
Industry
2.1.1 Early Stages of Root Cause Analysis
Having only been around since the 1950s and only
becoming mainstream after the creation of Lean 6
Sigma in the 1980s, RCA has played a major part in
the push towards a better understanding of faults that
occur in manufacturing processes (Arnheiter &
Greenland, 2008; Ohno & Bodek, 1998). The aim of
RCA was originally to identify the cause of a known
issue so that an appropriate solution can then be
determined. However, the methodologies used to
achieve this goal has evolved over the years
(Arnheiter & Greenland, 2008) to make this process
more streamline and beneficial. Some examples
include the inclusion of expert knowledge, prescribed
solutions and, more recently, automation (Diez-
Olivan et al., 2019; Giannetti et al., 2015).
The first major example of a practical RCA
approach was the use of the 5 Whys methodology,
created in the 1930s by Toyota engineers
(Serrat,
2017), but becoming popular later in the century as
part of the Lean 6 Sigma framework . While Lean 6
Sigma is used to improve general business efficiency,
its techniques are often applied in the manufacturing
industry (Sreedharan & Raju, 2016). The 5 Whys
approach encourages further investigation into why
faults occur (Serrat, 2017), which, as mentioned, is
the main aim of RCA. The next major step in
developing RCA was to further include expert
knowledge such that analysts could make a guided
diagnosis of the issue (Sarkar, Mukhopadhyay, &
Ghosh, 2013). These expert systems eventually
included further knowledge such that a prescribed
solution could be given depending on the diagnosis
and inputs (Cao et al., 2022; Kalantri & Chandrawat,
2013). These were the first major steps towards
introducing artificial intelligence into RCA
methodologies.
2.1.2 Root Cause Analysis and Machine
Learning
Over the last few decades, the amount of data
collected in manufacturing processes has been
Root Cause Classification of Temperature-related Failure Modes in a Hot Strip Mill
37

increasing at such a rate that it is becoming an
increasingly important challenge to make use of this
data in an efficient manner (Yaqoob et al., 2016).
However, the infrastructures in which such vast
amounts of data are stored are often unorganised and
require a number of processing steps (Madden, 2012)
before data is transformed into a suitable standard for
analysis. The inclusion of artificial intelligence has
propelled the development of RCA tools and
methodologies such that it is now possible to quickly
and efficiently process large amounts of information.
There are many examples which demonstrate such
tools which include the use of neural networks,
regression models, and other more traditional analysis
models such as control charts for automated RCA in
a variety of industries
(Oliveira et al., 2022; Giannetti
et al., 2014a, 2014b). However, some argue that
further development is still required to maximise its
potential (Zhang et al., 2020).
In the last several decades, machine learning has
become a very popular tool for quick and automated
analysis and feedback in manufacturing processes
(Cinar et al., 2020; Dogan & Birant, 2021; Essien &
Giannetti, 2019; Giannetti & Essien, 2022). The
premise of machine learning is to learn patterns from
the features of a given set of historical data and use
this information to create a model that can identify
these patterns in new, unseen data. This approach
attempts to automate manual RCA operations and
provide quick, if not immediate, feedback
(Steenwinckel, 2018).
There are many applications of RCA which utilise
machine learning in the manufacturing industry
(Weichert et al., 2019), and many unique approaches
have been taken to develop them. One such example
is the use of machine learning-based anomaly
detection methods, including K-Nearest Neighbour
(KNN) and Local Outlier Factor (LOF), to detect
failure modes in assembly equipment (Abdelrahman
& Keikhosrokiani, 2020). Another application
includes the use of machine learning, specifically
neural networks, for quality monitoring in an
injection moulding process (Nam, Van Tung, & Yee,
2021). One more example is the use of supervised
methods such as K-Means Clustering and decision
trees for the detection of root causes of defects in
semiconductors (Tan et al., 2021). It is worth noting
that some approaches argue that a knowledge-based
approach can sometimes be more suitable than
machine learning depending upon the scenario
(Martinez-Gil et al., 2022; Roshan et al., 2014). It is
clear that some solutions are chosen to cater to the use
case addressed by the application but have the
common goal of using information from a process to
provide useful feedback for the purpose of improving
a process (Weichert et al., 2019).
2.1.3 Root Cause Analysis in the Steel
Rolling Industry
Within the steel rolling industry machine learning
and, especially, RCA is not yet mainstream and has
only seen analytics for RCA used on a niche scale.
While there has been much development for existing
applications of machine learning, areas of focus in
research are largely limited to surface defect detection
(Huang, Wu, & Xie, 2021) and roller model
optimisation (Li, Luan, & Wu, 2020). While it may
be difficult to introduce new technologies into an
operation of such a scale, machine learning has
untapped potential with regards to RCA in the steel
industry as it would enhance the automation of such
analyses. Time and resources spent on conducting
this process manually would therefore be saved and
workers who would normally be tasked with this
could devote more time to other workloads or more
complex projects in which human interaction is a
necessity.
2.2 Width Pull and Current HSM
Procedures
2.2.1 Width Pull in the HSM
When Width Pull occurs, the head end of a steel bar
either elongates or becomes under width specification
as a result of sudden tension in the strip (Khramshinet
al., 2015; Radionov et al., 2020). This defect can
occur for an array of reasons, including wrong bar
specifications, high or low temperatures, and erratic
tension.
Figure 2: A graph showing the width deviation of a strip
with Width Pull.
IN4PL 2022 - 3rd International Conference on Innovative Intelligent Industrial Production and Logistics
38
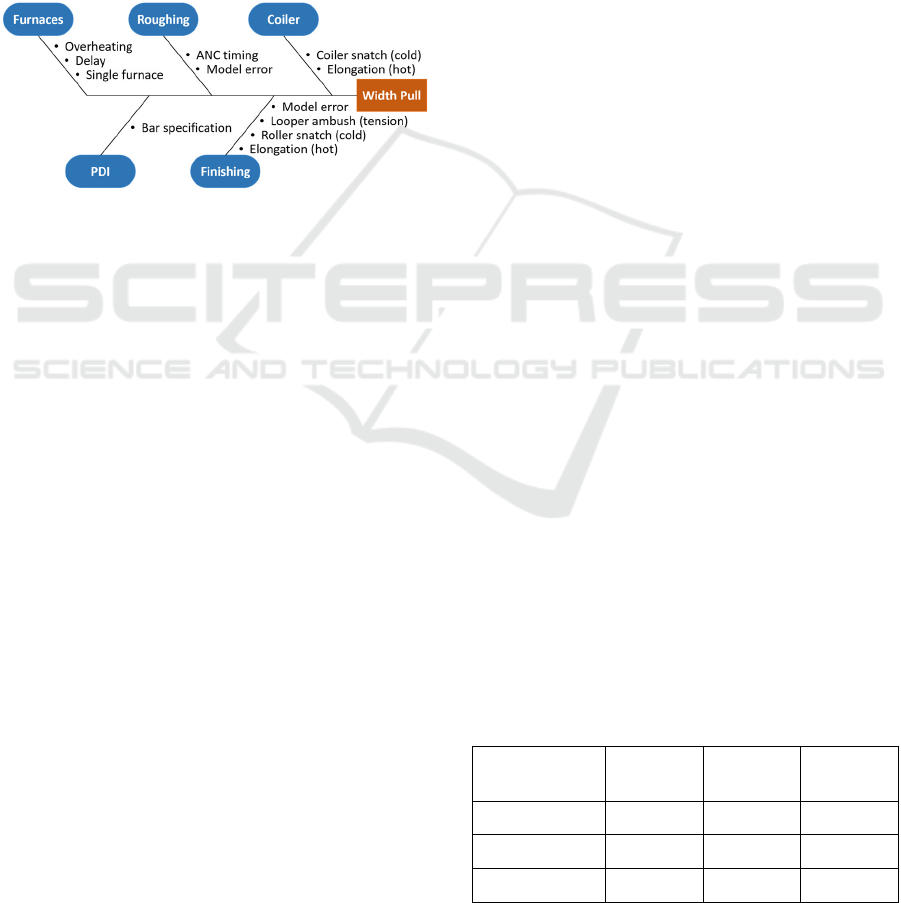
Currently, when Width Pull occurs in the HSM,
the root cause is determined via a manual analysis of
the defective sample. There are many causes of Width
Pull and, although there is a workflow in place to
determine basic causes, the data examined to
determine other causes can be quite ambiguous
making them difficult to draw conclusions on.
Although temperature-related causes normally
originate from the furnace (as shown in Figure 3), it
is important to note that the issue is originally
identified in a later part of the HSM process such as
Roughing or Finishing. Many failure modes of width-
related defects in the HSM process are temperature-
related (as shown in Figure 1).
Figure 3: A fishbone diagram showing the causes of Width
Pull throughout a HSM.
2.2.2 Current HSM Procedures
Width Pull, as well as other defects that occur in the
HSM, can have damaging effects both in the short-
term and long-term. Depending on the severity of the
under width caused by Width Pull or other defects, a
follow-up action is carried out. The first possible
action is a cutback in which the under width portion
of the strip is cut off. This results in a shorter strip
length and scrap which is melted for use in later strips,
requiring further processing which is both time-
consuming and unresourceful. Another action is to
make a concession in which the customer is offered
the defective strip at a negotiated lower price.
Although this action does not always require further
processing, potential profit is still lost. This however
does not mean that cutbacks do not occur before or
after concessions are made. In the worst-case
scenario, the strip is scrapped altogether. In the long-
term, all follow up actions require either further
resources and cost time and money, or result in
wasted material, ultimately producing business waste
(Sarkar, Mukhopadhyay, & Ghosh, 2013; Sreedharan
& Raju, 2016).
The effects of these defects can also be derived
not just from the defect itself but from the manual
analysis process that is currently used to determine
their root causes. Issues are often caught or resolved
long after immediate and, sometimes, lasting impacts
that are created by defective behaviour. For example,
some causes of Width Pull can affect a sequence of
strips if left unresolved (Khramshin et al., 2015). A
build-up of unresolved issues also suggests that the
information collected about root causes is analysed
too late to have a meaningful impact on the process,
resulting in a less productive system. Lastly, manual
analysis is time-consuming for analysts themselves. It
is a trivial task which, if automated, would enable
them to focus on more complex tasks and other
responsibilities, thus boosting their productivity.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Problem Statement
In the following experiments, the potential of
machine learning for automating RCA in an HSM
setting is demonstrated by classifying temperature-
related failure modes of steel strips which have
suffered from Width Pull. This application is planned
to be part of a greater work which will combine such
applications and determine the failure mode and
origin of identified strips with Width Pull throughout
the HSM.
3.2 Dataset
The number of steel strips affected by low
temperature, or ‘undersoaking’, accounts for a larger
percentage of samples, overall making the dataset
used in this study unbalanced. At the time of data
collection, a total of 166 samples were available, 111
of which were undersoaked and 55 of which were
high temperature. Despite the imbalance, the
available dataset still had a limited number of
samples. It was therefore decided to use the whole
dataset for this experiment rather than reducing the
amount of undersoaked samples to account for
balance, which would limit the quality of training
during machine learning.
Table 1: A table showing the split of labelled data used in
this experiment.
Training
Dataset
Testing
Dataset
Total
(Label)
Undersoaked 78 33 111
High Temp 39 16 55
Total (Dataset) 117 49 166
Root Cause Classification of Temperature-related Failure Modes in a Hot Strip Mill
39
Each sample is derived from two temperature
signals which are pre-processed and compared to
evaluate their representation of the root cause. This is
achieved through a series of transformations which
eliminate redundant data and account for differing
temperature ranges between different product
specification and comparing the range of values
between different product specifications and
comparing the range of values between the two
signals following these transformations. Statistical
features are then chosen to represent the samples
during the training stage of machine learning. These
features help the chosen machine learning algorithms
to distinguish between the behaviour of undersoaking
and high temperature.
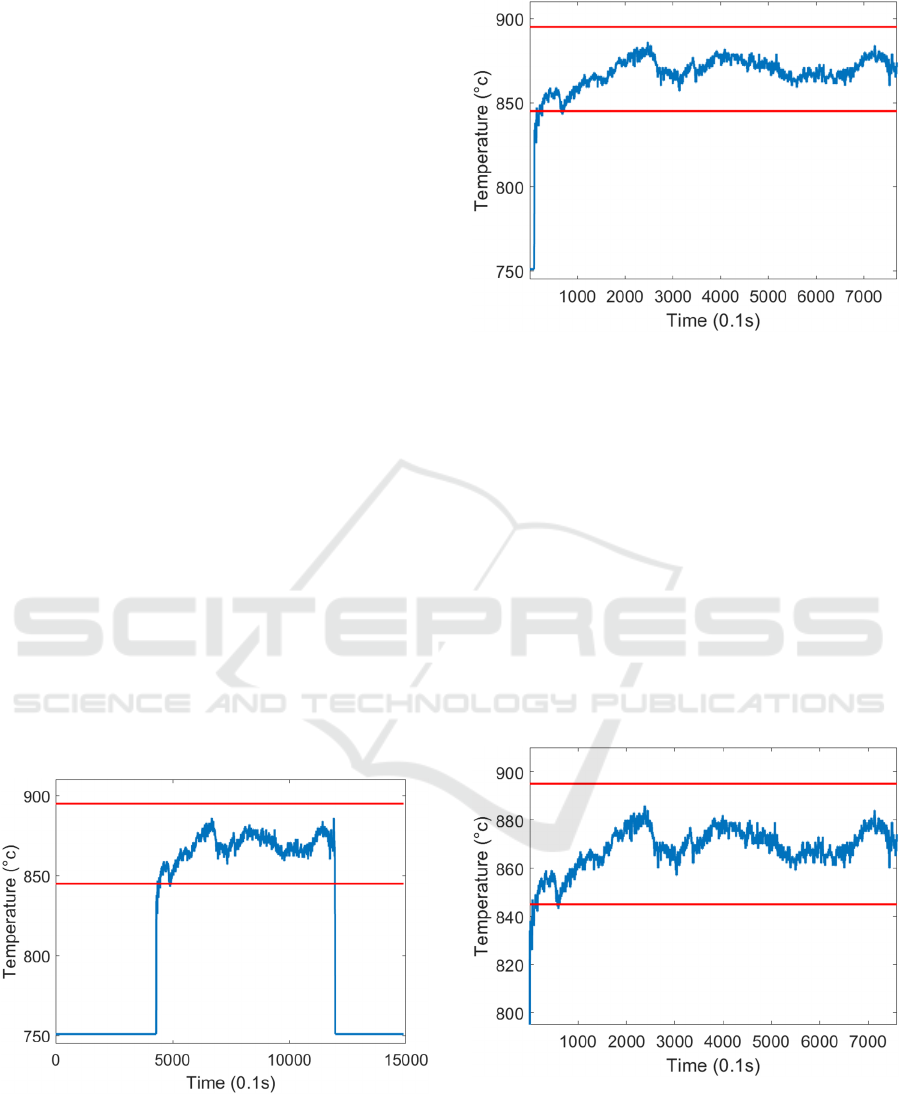
3.3 Pre-processing and Labelling
In order to analyse the signal data both manually and
using machine learning, redundant data must first be
eliminated and, if it is not already, the remaining data
must be processed into a readable format. By cleaning
signal data like this, a more relevant perspective of
our data is shown, making data from different classes
more distinct during the feature extraction stage. The
first step is to eliminate irrelevant measurements in
the signal which occur when the bar is not present in
the Finishing Mill (as shown in Figure 4). A binary
Metal-In-Mill (MIM) signal displays whether or not
the bar is present in the mill. The second step is
completed by extracting the temperature signal
measurement where the MIM signal is activated (as
shown in Figure 5).
Figure 4: Temperature signal of an undersoaked strip before
pre-processing.
Figure 5: Temperature signal of an undersoaked strip where
MIM signal is activated.
The second step is to pad outlier measurements to
sensible values (as shown in Figure 6). Measurements
above a strip temperature’s upper tolerance plus 50°c
are set to this value. Alternatively, measurements
below a strip temperature’s lower tolerance minus
50°c are set to this value. Outlier values alone are not
enough to distinguish whether Width Pull is caused
by temperature. This is because these values may be
caused by erroneous sensor readings and, very
commonly, noise upon the strip’s entrance into the
Finishing Mill. Data representing this behaviour is
therefore eliminated from the beginning of the signal
to remove redundant values that may misrepresent
failure modes during training.
Figure 6: Temperature signal of an undersoaked strip after
outliers are removed.
The next step in narrowing down on this
information is to segment first 10% of the signal,
representing the head end of the strip (as shown in
Figure 7). This is because Finishing Mill Width Pull
IN4PL 2022 - 3rd International Conference on Innovative Intelligent Industrial Production and Logistics
40
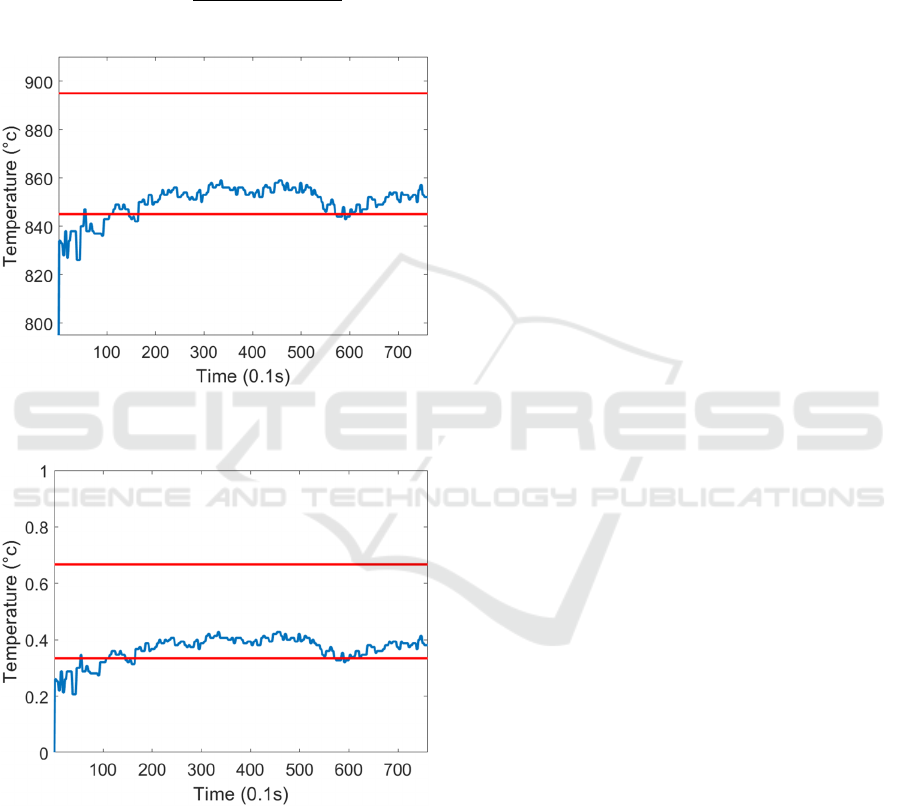
instances typically occur in the head end of the bar.
The final step maps each signal to a comparable scale
such that measurement ranges are mapped to the
sample values. A standard peak normalisation
formula (1) is used with the minimum and maximum
values of each signal to map all values of all signals
between 0 and 1 (as shown in Figure 8).
𝑃𝑒𝑎𝑘 𝑁𝑜𝑟𝑚.
𝑥min
𝑥
max
𝑥 min
𝑥
(1)
Figure 7: Temperature signal representing the head end of
an undersoaked strip.
Figure 8: Temperature signal of an undersoaked strip after
peak normalisation.
Although basic labels exist to show simply
whether or not a steel strip sample is has Width Pull,
the data required for this application must be specific
to the root cause of the defect. Using a combination
of the existing manual analysis process, the extracted
data, and a series of plots displaying the now cleaned
signal data, the root causes of the extracted Width
Pull samples were manually labelled, creating further
labels used to train and test the final machine learning
algorithms.
3.4 Feature Selection
A collection of statistical features was extracted from
the pre-processed data for use in the chosen machine
learning algorithms. These include several quartile
values, mean, peak value, root mean square, and
standard deviation. Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient
was then used to determine which of these features
would be used during training. More specifically, the
averages of each feature after being applied to this
formula were used as a guide to eliminate features
which correlated too closely and would therefore
become redundant or counterproductive during
training (Schober, Boer, & Schwarte, 2018). The
result of this methodology is a feature set which is
combined with the labels to create a final dataset
which can be used to train and test the machine
learning model appropriately.
3.5 Machine Learning Algorithms
A variety of classic machine learning algorithms has
been selected for training and testing in this
experiment. This subsection briefly describes each
model and their parameters.
3.5.1 Trees
A classification tree is a linear graph in which each
node is assigned a value based on training features.
These values are used as a foundation for decision-
making when classifying new samples.
3.5.2 Naïve Bayes
Naïve Bayes also uses probabilities based on training
features to determine classification labels. However,
the Naïve Bayes algorithm bases these probabilities
on the frequency of each value, meaning that more
prominent features are dominant in classification.
3.5.3 K-Nearest Neighbour
The KNN algorithm creates a dimensional space in
which samples are plotted based on the values of their
features. New samples are plotted in this space and
compared to a chosen number, k, of neighbours. The
class of a new sample is chosen based on the class of
the majority of its k neighbours. It should be noted
that the numbers k in KNN and k-fold cross validation
are unrelated.
Root Cause Classification of Temperature-related Failure Modes in a Hot Strip Mill
41
3.5.4 Support Vector Machines
A Support Vector Machine (SVM) also plots feature
values into a dimensional space, although rather than
comparing new samples to a distribution, this
algorithm attempts to create a new, separating
hyperplane. New samples are classified based on their
position relative to this hyperplane.
3.5.5 Artificial Neural Networks
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are made up of
neurons which are combined to form a number of
layers. Each neuron has a weight which is updated
during training based on the inputted features. An
ANN’s width and depth is determined by the number
of neurons and layers it contains.
3.5.6 Ensembles
An ensemble combines the result of more than one
machine learning algorithm. The ensembles used in
this experiment combines several tree algorithms.
3.6 K-fold Cross Validation
K-fold cross validation is used to estimate the
generalisation error of a machine learning model. In
this experiment, k = 5 has been chosen such that each
machine learning algorithm is run five times using
80% of the training dataset. For each of the five runs,
20% is not used during training.
4 RESULTS
4.1 Full Training Dataset
A total of 13 machine learning algorithms were used
in the training stage of this experiment. Accuracy,
precision, recall, and F1 score metrics are used to
evaluate the performance of each model. Accuracy
simply calculates the overall percentage of correctly
labelled samples. Precision describes the percentage
of samples which are labelled as a given class that
truly belong to this class while recall describes the
percentage of samples which belong to this class that
are classified correctly. Although accuracy is still an
informative metric, F1 score is derived from precision
and recall, and evaluates the performance of
classification models more reliably. In the following
results, F1 score is represented as a percentage for
consistency among metrics.
Table 2: Performance of each machine learning algorithm
when trained on the full training dataset.
Algorithm
Accuracy
(%)
Precision
(%)
Recall
(%)
F1
Score
(%)
Coarse
Gaussian
SVM
93.88 88.24 93.75 90.91
Coarse
Tree
95.92 93.75 93.75 93.75
Fine
Gaussian
SVM
81.63 81.82 56.25 66.67
Fine KNN 87.76 85.71 75 80
Fine Tree 95.92 93.75 93.75 93.75
Gaussian
Naïve
Bayes
93.88 84.21 1 91.43
Kernel
Naïve
Bayes
95.92 88.89 1 94.12
Linear
SVM
91.84 87.5 87.5 87.5
Narrow
ANN
93.88 93.33 87.5 90.32
Opt.
Ensemble
91.84 87.5 87.5 87.5
Opt. ANN 93.88 93.33 87.5 90.32
Quadratic
SVM
91.84 87.5 87.5 87.5
Wide ANN 89.8 86.67 81.25 83.97
From the results shown in Table 2, it can be seen
that a majority of the trained models can be used
appropriately for the classification task. However,
only a handful show consistent scores between the
performance metrics. In particular, the Coarse and
Fine Tree models have been shown to perform best
with accuracies and F1 scores of above 93%. These
models are generally quick to train and thus easier to
retrain when more data becomes available. Although
the Kernel Naïve Bayes model provides a better
accuracy, recall, and F1 score, its precision falls
behind the two Tree models, suggesting it does not
perform as well when labelling a particular class.
4.2 K-fold Cross Validation
After 5-fold cross validation, the models show
slightly decreased but similar performance to the
previous test results (as shown in Table 3). This
means that although each algorithm was given less
information during training, the models were still able
IN4PL 2022 - 3rd International Conference on Innovative Intelligent Industrial Production and Logistics
42

to generalise data relatively well, resulting in stable
training and thus reliable and consistent models.
Table 3: Performance of each machine learning algorithm
in 5-fold cross validation.
Algorithm
Accuracy
(%)
Precision
(%)
Recall
(%)
F1
Score
(
%
)
Coarse
Gaussian
SVM
85.31 79.01 75 76.88
Coarse
Tree
88.37 83.8 80 81.73
Fine
Gaussian
SVM
87.89 82.78 79.58 81.06
Fine KNN 88.16 82.55 80.94 81.63
Fine Tree 88.82 83.76 81.75 82.62
Gaussian
Naïve
Ba
y
es
88.64 82.59 83.13 82.64
Kernel
Naïve
Ba
y
es
88.57 81.94 83.93 82.7
Linear
SVM
88.47 81.76 83.75 82.55
Narrow
ANN
88.57 82.55 83.19 82.54
Opt.
Ensemble
88.86 82.69 84 83.03
Opt. ANN 88.79 82.47 84.09 82.98
Quadratic
SVM
88.74 82.46 83.85 82.87
Wide ANN 88.73 82.72 83.46 82.78
While it is beneficial to determine whether a
machine learning model generalises well, as has been
shown in this experiment, the Tree-based models
would be likely to be selected for use in this
application based on their superior performance in the
full training experiment (as shown in Table 2). In this
particular cross validation experiment, the
Optimisable Ensemble performed marginally better
than other models, but would not be selected for use
in the final application based on its performance when
trained on the full dataset.
At the current time, the small dataset used in this
experiment is suitable for the application of
classifying temperature-related root causes of Width
Pull. However, using the best performing machine
learning algorithms in this experiment, it will be both
time and cost-efficient to retrain with more data at a
later date.
5 CONCLUSION
A digitised version of the current RCA system for
Width Pull in an existing HSM has been proposed and
has shown to perform acceptably for the given task. It
is capable of providing almost immediate results and
feedback, dramatically reducing the time between a
defect occurring and its root cause being identified.
There would be several benefits of adopting this
application into an HSM setting. Time would be
saved on performing unnecessary analyses, reserving
efforts for productivity elsewhere. This application
also showcases the potential of combining data
sources with the aim of repurposing data to create
new tools and maximise the value of data resources.
This application is a step towards further automation
and digitisation of basic HSM analyses and shows
this approach has the potential to reduce workload on
analysts such that human interaction can be directed
towards more complex issues in the HSM. In future
work, there may also be potential in applying this
methodology to other steel strip manufacturing
processes, such as casting and cold rolling, and
linking the analyses of root causes between these
processes.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to acknowledge the M2A
funding from the European Social Fund via the Welsh
Government (c80816) and Tata Steel Europe that has
made this research possible. Prof. Giannetti would
like to acknowledge the support of the UK
Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council
(EP/V061798/1). All authors would like to
acknowledge the support of the IMPACT and
AccelerateAI projects, part-funded by the European
Regional Development Fund (ERDF) via the Welsh
Government.
REFERENCES
Abdelrahman, O., & Keikhosrokiani, P. (2020). Assembly
Line Anomaly Detection and Root Cause Analysis
Using Machine Learning. IEEE Access, 8(1), 189661–
189672.
Arnheiter, E. D., & Greenland, J. E. (2008). Looking for
root cause: a comparative analysis. In The TQM
Journal, 20(1), 18–30.
Cao, Q., Zanni-Merk, C., Samet, A., Reich, C., de Beuvron,
F., Beckmann, A., & Giannetti, C. (2022). KSPMI: A
Knowledge-based System for Predictive Maintenance
Root Cause Classification of Temperature-related Failure Modes in a Hot Strip Mill
43

in Industry 4.0. Robotics and Computer-Integrated
Manufacturing, 74(11), 1–15.
Cinar, Z., Nuhu, A., Zeeshan, Q., Korhan, O., Asmael, M.,
& Safaei, B. (2020). Machine Learning in Predictive
Maintenance towards Sustainable Smart Manufacturing
in Industry 4.0. Sustainability, 12(19), 1–36.
Diez-Olivan, A., Del Ser, J., Galar, D., & Sierra, B. (2019).
Data fusion and machine learning for industrial
prognosis: Trends and perspectives towards Industry
4.0. Information Fusion, 50(1), 92–111.
Dogan, A., & Birant, D. (2021). Machine learning and data
mining in manufacturing. Expert Systems with
Applications, 166(2), 11–19.
Essien, A., & Giannetti, C. (2019). A Deep Learning
Framework for Univariate Time Series Prediction
Using Convolutional LSTM Stacked Autoencoders.
IEEE International Symposium on Innovations in
Intelligent Systems and Applications, 1–6.
Giannetti, C., & Essien, A. (2022). Towards Scalable and
Reusable Predictive Models for Cyber Twins in
Manufacturing Systems. Journal of Intelligent
Manufacturing, 33(2), 441–455.
Giannetti, C., Ransing, M. R., Ransing, R. S., Bould, D. C.,
Gethin, D. T., & Sienz, J. (2015). Organisational
Knowledge Management for Defect Reduction and
Sustainable Development in Foundries. International
Journal of Knowledge and Systems Science, 6(3), 18–
37.
Giannetti, C., Ransing, M., Ransing, R., Bould, D. C.,
Gethin, D. T., & Sienz, J. (2014a). Product specific
process knowledge discovery using co-linearity index
and penalty functions to support process FMEA in the
steel industry. CIE 2014 - 44th International
Conference on Computers and Industrial Engineering
and IMSS 2014 - 9th International Symposium on
Intelligent Manufacturing and Service Systems, Joint
International Symposium on "The Social Impacts of
Developments in Information. 1–15.
Giannetti, C., Ransing, R., Ransing, M. R., Bould, D. C.,
Gethin, D. T., & Sienz, J. (2014b). A novel variable
selection approach based on co-linearity index to
discover optimal process settings by analysing mixed
data. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 72(1), 217–
229.
Huang, Z., Wu, J., & Xie, F. (2021). Automatic recognition
of surface defects for hot-rolled steel strip based on
deep attention residual convolutional neural network.
Materials Letters, 293(1), 3049–3055.
Janssen, C. P., Donker, S. F., Brumby, D. P., & Kun, A. L.
(2019). History and future of human-automation
interaction. International Journal of Human-Computer
Studies, 131(1), 99–107.
Kalantri, R., & Chandrawat, S. (2013). Root Cause
Assessment for a Manufacturing Industry: A Case
Study. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology
Review, 6(1), 62–67.
Khramshin, V. R., Evdokimov, S. A., Yu, A. I., Shubin, A.
G., & Karandaev, A. S. (2015). Algorithm of no-pull
control in the continuous mill train. 2015 International
Siberian Conference on Control and Communications
(SIBCON). 1–5.
Latham, S., Giannetti, C. (2021). Pre-Trained CNN for
Classification of Time Series Images of Anti-Necking
Control in a Hot Strip Mill. The 9
th
IIAE International
Conference on Industrial Engineering 2021
(ICIAE2021). 77–84.
Li, X., Luan, F., & Wu, Y. (2020). A Comparative
Assessment of Six Machine Learning Models for
Prediction of Bending Force in Hot Strip Rolling
Process. Metals, 10(5), 1–16.
Madden, S. (2012). From Databases to Big Data. In IEEE
Internet Computing, 16(3), 4–6.
Mahto, D., & Kumar, A. (2008). Application of root cause
analysis in improvement of product quality and
productivity. Journal of Industrial Engineering and
Management, 1(2), 16–53.
Martinez-Gil, J., Buchgeher, G., Gabauer, D.,
Freudenthaler, B., Filipiak, D., & Fensel, A. (2022).
Root Cause Analysis in the Industrial Domain using
Knowledge Graphs: A Case Study on Power
Transformers. Procedia Computer Science, 200(3),
944–953.
Murugaiah, U., Benjamin, S. J., Marathamuthu, M. S., &
Muthaiyah, S. (2010). Scrap loss reduction using the 5-
whys analysis. International Journal of Quality &
Reliability Management, 27(5), 527–540.
Nam, D. N. C., Van Tung, T., & Yee, E. Y. K. (2021).
Quality monitoring for injection moulding process
using a semi-supervised learning approach. IECON
2021 – 47th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial
Electronics Society. 1–6.
Ohno, T., & Bodek, N. (1988). Toyota Production System:
Beyond Large-Scale Production (1st Edition).
Productivity Press. 136–142.
Oliveira, E., Miguéis, V. L., & Borges, J. (2022). Automatic
root cause analysis in manufacturing: an overview &
conceptualization. Journal of Intelligent
Manufacturing, 33(5), 1–18.
Radionov, A. A., Gasiyarov, V. R., Karandaev, A. S.,
Usatiy, D. Y., & Khramshin, V. R. (2020). Dynamic
Load Limitation in Electromechanical Systems of the
Rolling Mill Stand during Biting. 2020 IEEE 11
th
International Conference on Mechanical and
Intelligent Manufacturing Technologies (ICMIMT).
149–154.
Roshan, H., Giannetti, C., Ransing, M., & Ransing, R.
(2014). "If only my foundry knew what it knows…" : a
7Epsilon perspective on root cause analysis and
corrective action plans for ISO9001:2008. 71st World
Foundry Congress: Advanced Sustainable Foundry,
WFC 2014. 1–15.
Sarkar, A., Mukhopadhyay, A., & Ghosh, S. (2013). Root
cause analysis, Lean Six Sigma and test of hypothesis.
The TQM Journal, 25(2), 170–185.
Schober, P., Boer, C., & Schwarte, L. A. (2018).
Correlation coefficients: appropriate use and
interpretation. Anesthesia & Analgesia, 126(5), 1763–
1768.
IN4PL 2022 - 3rd International Conference on Innovative Intelligent Industrial Production and Logistics
44

Serrat, O. (2017). The Five Whys Technique. Knowledge
Solutions (1st Edition). Springer. 307–310.
Sheridan, T., & Parasuraman, R. (2000). Human Versus
Automation in Responding to Failures: An Expected
Value Analysis. Human Factors, 42(3), 403–407.
Sreedharan, V. R., & Raju, R. (2016). A systematic
literature review of Lean Six Sigma in different
industries. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma,
7(4), 430–466.
Steenwinckel, B. (2018). Adaptive anomaly detection and
root cause analysis by fusing semantics and machine
learning. European Semantic Web Conference. 272–
282.
Tan, D., Xu, X., Yu, K., Zhang, S., & Chen, T. (2021).
Multi-Feature Shuffle Algorithm for Root Cause
Detection in Semiconductor Manufacturing. 2021 IEEE
Intl Conf on Dependable, Autonomic and Secure
Computing, Intl Conf on Pervasive Intelligence and
Computing, Intl Conf on Cloud and Big Data
Computing, Intl Conf on Cyber Science and Technology
Congress (DASC/PiCom/CBDCom/CyberSciTech).
130–136.
Weichert, D., Link, P., Stoll, A., Rüping, S., Ihlenfeldt, S.,
& Wrobel, S. (2019). A review of machine learning for
the optimization of production processes. The
International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing
Technology, 104(9), 1889–1902.
Wiering, M., & van Otterlo, M. (2012). Reinforcement
Learning: State-of-the-Art (2012 Edition). Springer. 3–
32.
Wuest, T., Weimer, D., Irgens, C., & Thoben, K.-D. (2016).
Machine learning in manufacturing: Advantages,
challenges, and applications. Production &
Manufacturing Research, 4(1), 23–45.
Yaqoob, I., Hashem, I. A. T., Gani, A., Mokhtar, S.,
Ahmed, E., Anuar, N. B., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2016).
Big data: From beginning to future. International
Journal of Information Management, 36(6), 1231–
1247.
Zhang, J., Arinez, J., Chang, Q., Gao, R., & Xu, C. (2020).
Artificial Intelligence in Advanced Manufacturing:
Current Status and Future Outlook. Journal of
Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 142(1), 1–53.
Root Cause Classification of Temperature-related Failure Modes in a Hot Strip Mill
45
