
Deep-vacuity: A Proposal of a Machine Learning Platform based on
High-performance Computing Architecture for Insights on Government
of Brazil Official Gazettes
Leonardo R. De Carvalho
1 a
, Felipe S. Lopes
1 b
, Jefferson Chaves
1 c
, Marcos C. Lima
2 d
,
Fl
´
avio E. Gomes De Deus
3 e
, Alet
´
eia P. F. A. von Paungarthem
1 f
and Flavio De Barros Vidal
1 g
1
Department of Computer Science, University of Brasilia, Brasilia, DF, Brazil
2
Department of Federal Police, Brasilia, DF, Brazil
3
Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Brasilia, Brasilia, DF, Brazil
Keywords:
Machine Learning, High Performance Computing, Government of Brazil, Official Gazette.
Abstract:
Brazil publishes region information, public tenders for the hire of civil servants, and also government contracts
with companies in its Official Gazettes. All this volume of information can contain interesting relationships
that reveal unique characteristics of the government, such as the effectiveness of public policies and even the
existence of illegal schemes. Establishing these relationships is not a trivial task and requires great effort.
Therefore, this work proposes the Deep Vacuity platform, which, by using a High-Performance Computing
architecture along with Machine Learning techniques, can collect, depurate, consolidate and analyze the data,
offering a friendly interface for decision-makers.
1 INTRODUCTION
Information is power (Freund, 1982). Even in the
1980s, a researcher had already noted this fact that
today seems so obvious. However, only if it is trans-
formed into knowledge can information be effectively
transformed into action (Connolly and Matarazzo,
1998). Brazil is one of the major countries in Latin
America. With a population of around 210 million
people, as described in (Instituto Brasileiro de Ge-
ografia e Estat
´
ıstica, 2020), spread across its 5,570
cities, this country has a governmental structure full
of information.
Considering that the government should be able
to guide the direction of a country, it is extremely im-
portant that the actions of this government are both
widely publicized and also understood at a deeper
level. In other words, it is necessary to understand
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7459-281X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6568-4541
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8459-5248
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3565-9924
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7953-6227
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4645-6700
g
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6317-218X
the repercussions of the acts, as well as the interrela-
tionships, be they occasional, accidental, intentional,
strategic or even fraudulent. Brazil presents an ex-
citing challenge of extracting knowledge about the
range of information that the Brazilian government
publishes in its state press structure. Each munic-
ipal, state and federal entity has a different way of
publicizing government acts. In this context, infor-
mation technology can be made available to all citi-
zens. Using several high-performance computer pro-
cessing techniques, coupled with the execution struc-
tures of models based on machine learning, this work
proposes a platform architecture for the collection and
processing of information published in the various
brazilian official gazettes, whether in the municipal,
state or federal field. This processing uses artificial
intelligence models designed to explore specific con-
cepts according to the objectives of each usage profile,
with the platform itself being agnostic in this respect.
The manuscript is organized as follows: In Sec-
tions 2 and 3 information about the official gazettes
in Brazil is presented, followed by a detailed com-
pilation of related works on fraudulent collusion in
public works contracts in official texts. Section 4 ex-
plains our proposed architecture. Section 5 describes
the preliminary results and a discussion about the pro-
136
R. De Carvalho, L., Lopes, F., Chaves, J., Lima, M., Gomes De Deus, F., von Paungarthem, A. and Vidal, F.
Deep-vacuity: A Proposal of a Machine Learning Platform based on High-performance Computing Architecture for Insights on Government of Brazil Official Gazettes.
DOI: 10.5220/0011532500003318
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST 2022), pages 136-143
ISBN: 978-989-758-613-2; ISSN: 2184-3252
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

posed architecture. Section 6 provides conclusion
points and further work.
2 BACKGROUND
Brazilian law defines the Official Press as the offi-
cial vehicle for public administration (Brasil, 1993) to
offer universal access, making the knowledge about
official acts available, and validating them. Official
Gazettes are very rich sources of governmental infor-
mation, as it is through them that official acts are not
only made public but are also considered valid (Mar-
tano, 2015). In other words, they are only applicable
from the moment they are published or, in cases spec-
ified in the acts themselves, within periods that fol-
low from those publications. Naturally, this type of
publication has been impacted by the arrival of new
information technologies and communication, so that
most public agencies that publish Official Gazettes
in Brazil nowadays offer them both printed and on-
line. However, the digital version of these documents
is usually offered in PDF format, which makes auto-
mated reuse of published information difficult.
The Diario Oficial da Uni
˜
ao (DOU) is one of the
means of communication through which the National
Press must make public any and all matters of fed-
eral scope (Rocha, 2011). The DOU, for more than
148 years, has fulfilled its governmental role by serv-
ing the interests of all stakeholders in official deci-
sions. The mission of DOU is to publicize and carry
out knowledge management on information from offi-
cial acts for society and provide strategic graphic ser-
vices to the Federal Public Administration (BRASIL,
2020). DOU is published in PDF format as shown in
Figure 1 and is divided into 3 parts: Section 1: in this
section, regulating acts with national coverage such
as laws and norms are published; Section 2: in this
section, acts related to public workers such as hiring,
promotions and resignations are published; Section
3: in this section, signed contracts between the gov-
ernment and other companies, including duration and
amount of money involved in the transaction are pub-
lished. Another way to obtain DOU data from the Na-
tional Press is shown in Figure 2. The National Press
delivers DOU data in XML format through open data
format.
Brazil is divided into 26 states, and plus the Fed-
eral District where the capital, Brasilia, is located.
Each state has its own way of organizing and pub-
lishing communications. The state S
˜
ao Paulo, for ex-
ample, has a platform called Imprensa Oficial. The
publications are divided into sections and subsections.
Unlike DOU, the Official Gazette of S
˜
ao Paulo does
Figure 1: DOU PDF Example.
Figure 2: DOU XML Example.
not have a data format version, such as XML. In this
case, in order to obtain the data it is necessary to open
each PDF file provided and parse the file. Besides the
three most populous states, the other 23 states and the
Federal District have their own platforms for publish-
ing official gazettes. Each one is structured in a dif-
ferent format with several sections and subsections.
The municipal scenario is more complex than the
state ones. Brazil has 5,570 cities according to its
Geography and Statistic Institute (IBGE) (Instituto
Brasileiro de Geografia e Estat
´
ıstica, 2020). Many
of these cities have their own web platform to pub-
lish Official Gazettes. Each of these platforms has
a different system for organizing the publications.
Besides this, some cities do not even have an elec-
tronic platform and publish their acts in paper format,
such as printed journals and in extreme cases there
are publications that appear only on bulletin boards
that are within the public bodies. That reinforces the
presumption of universal access possibilities, which
means that the Official Gazette is unquestionably pre-
sented as the organism in which official acts are pub-
lished, giving them legal validity, that is, existence in
the real world. In the Official Gazette of S
˜
ao Paulo
city, about 800 articles are published per day, dis-
tributed in approximately 90 pages, and it is estimated
that, during its existence, approximately 30 million
pages have been published (Martano, 2015). When
projecting this for the other 5,569 cities, as well as
the 26 states and the Federal District, and also adding
DOU publications, there is a huge volume of infor-
mation related to the government being created daily.
This enormous volume of data contains precious in-
Deep-vacuity: A Proposal of a Machine Learning Platform based on High-performance Computing Architecture for Insights on Government
of Brazil Official Gazettes
137

formation that has relationships in a wide scope.
Collecting, purifying, consolidating and extract-
ing these relationships is, in itself, a great challenge.
The collection process alone is a great challenge due
to the high number of data sources, with different de-
livery formats of the data. Once in possession of the
data, the second step of data extraction can be almost
impossible, because of the different methods used to
publish the same information. This is due to the fact
that there is no standardization for these publications.
This allows the same company to be published in dif-
ferent ways between different journals and even in
different publications within the same journal. As-
suming that the challenges of collecting, purifying
and consolidating data have been overcome, then an
equally complex phase comes: finding relationships
between publications. For this activity, given the large
volume of data, a computational technique that aims
to extract intelligence from this mass of disconnected
data, Machine Learning, enters the scene.
2.1 High Performance Computing
The recent development of technology is recently be-
ing associated with the growth of the problem size
that has to be handled. The problem size is increas-
ing exponentially and physical machines cannot sup-
port a huge range of users on different operation en-
vironments simultaneously. That is one of the rea-
sons leading to the advent of cloud computing and
virtualization technology (Chung et al., 2016). The
complexity of application and system software con-
tinues to grow in several dimensions. Firstly, as
computational performance increases, scientists are
developing more complex applications that incorpo-
rate more sophisticated temporal and spatial scales,
more complex physics and (increasingly) data assim-
ilation (Geist and Reed, 2017).
A desirable feature of high-performance appli-
cations is performance portability, where using the
same application code can result in high performance
across a diversity of architectures (Balaprakash et al.,
2018). There are two models that allow virtualized
instances to be deployed. They are hypervisor-based
and container-based platforms. For virtual machines,
a hypervisor, known as a layer, deploys and allocates
the operation space of instances (Chung et al., 2016).
As a simple example, consider the special case of two
different job configurations. This could correspond to
either (a) two different node parallel levels or (b) use
of nodes with or without accelerators (e.g., GPUs).
In an energy- or cost-constrained environment, one or
the other might be preferred, based on the characteris-
tics of the jobs in the batch queue and the speedup as
a function of node type and number (Geist and Reed,
2017). Another relevant aspect related to HPC sys-
tems is resilience and fault tolerance. The amount of
data expected to be processed by the platform pro-
posed by this work can eventually reach the level
of petabytes. Given this data volume, only a high-
performance computing environment would be able
to process the data and generate the desired informa-
tion. Therefore, this proposal adopted an HPC ori-
ented approach in the elaboration of the architecture
for the solution. Concerns about scalability and elas-
ticity were taken into account when designing this
proposal.
3 RELATED WORKS
The Brazilian Federal Police is consistently aspiring
to improve its fraud detection mechanisms, there-
fore (Vallim, 2020) focused on paving works con-
tracts, which are one of the most budget consuming
services at state or city level and the focus of criminal
activities, to make a CBR model of paving services
in the Parana State. Procurement, enterprises, con-
tract, and georeferenced data were used, with the aim
of classifying collusion cases.
Another way to prove and identify procurement
collusion is by using statistics and probability. Those
methods were explored in several Federal Police
studies and were based on joint behavior analysis
of competitors who act to achieve bid-rigging. It
was successfully applied to oil-related contracts us-
ing Operac¸
˜
ao Lava Jato information (Signor et al.,
2020a) and for infrastructure projects (Signor et al.,
2020b) with capped first-price auctions. The Brazil-
ian General Controllership of the Union (CGU), a
national auditing public agency, also has several ini-
tiatives to reach a reliable classifier for procurement
fraud. (Ralha and Silva, 2012) elaborated a not super-
vised evaluator that, using priori rules, computed the
possibility of a certain group being selected in a given
tender. The article (Balaniuk et al., 2012) focused
on the evaluation of fraud risk in government agen-
cies using Naive Bayes Classifiers for audit planning,
using structured data and fraudulent activity patterns.
In (Sun and Sales, 2018) traditional neural networks
and deep neural networks (DNN) are used to elabo-
rate an early alarm system.
In (Carvalho and Carvalho, 2016) the author
achieved reasonable results using Bayesian Models
with structured data of penal sanction of federal civil
servants, civil servants’ roles and income, number of
accounts judged irregular and number of regularity
certificates or an agency unit and affiliated civil ser-
WEBIST 2022 - 18th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
138
vants of each management unit.
The paper (Anysz et al., 2019) uses ANN and
structured data on Poland’s highway procurements.
They used the number of enterprises, price differ-
ences, contract orders in the same place, and set
of propositions to assess its fraud risk. Using TF-
IDF in procurement documentation, (Rabuzin and
Modru
ˇ
san, 2019) tested Logistic Regression, SVM
and Naive Bayes on potential corruption. Their model
had no annotated data, so it was focused on find-
ing one bid tenders which “could be potentially sus-
picious”. Natural Language Processing is not often
used to classify procurement documents for risk or
fraud (Lima et al., 2020). The technology is used for
assessing fraud risk in health care claims (Popowich,
2005; Van Arkel et al., 2013), and financial re-
ports (Seemakurthi et al., 2015; Goel and Uzuner,
2016).
In the article (de Bessa Lins, 1976), the author
conducted research from August 1974 to March 1976
regarding the official gazettes of the Brazilian states.
Questionnaires were sent to the Official Press, pub-
lic libraries or archives, assembly libraries, librarians,
journalists, and teachers, looking for copies of each
of the gazettes at legislation concerning them and per-
sonal consultation with specialized technicians. The
analysis of the results shows that in the first stage, as
much information as possible about each gazette was
collected without adequate concern. Subsequently,
the idea was improved and, through a comparative
study, the urgent need for renewal, a revision of “of-
ficial journalism” in the country was shown, as many
ends up not reading or knowing this information, only
those who have an obligation (for example, imposed
by their work) read the official gazettes.
In the paper (Luz de Araujo et al., 2020) the
authors use Universal Language Model Fine-Tuning
(ULMFiT) to leverage information contained in a un-
labeled language model dataset consisting of 2,652
texts extracted from the Official Gazette of the Fed-
eral District of Brazil. They compare the perfor-
mance of ULMFiT with simple bag-of-words base-
lines and perform an ablation analysis to identify the
impact of gradual unfreezing, language model fine-
tuning and the use of the fine-tuned language model
as a text feature extractor. The results analysis shows
that the combination of language model fine-tuning
and gradual unfreezing is extremely beneficial. It also
suggests that language models, even after being fine-
tuned on domain data, are not good feature extractors
and should be trained also on classification data.
In the article (Xavier et al., 2015), the authors use
a hybrid architecture for indexing documents in the
Official Gazette of the Brazilian city of Cachoeiro
de Itapemirim located in the state of Espirito Santo,
Brazil. They use text mining techniques to identify
indexes that adequately represent the context of the
document. In addition, the architecture features com-
ponents of transactional systems for validating and
storing information, as well as elements of text min-
ing for transforming unstructured information into a
set of structured objects, capable of being maintained
in databases. For the indexing user, it is extremely
important that the proposed tool retrieves all the doc-
uments involved in the concept being sought, bringing
as few documents as possible that are not relevant to
the context.
In the article (de Sousa, 2014), the author exam-
ines the conditions in which the Official Gazette of
the State of Goias offers access to the information it
conveys and creates a proposal for information archi-
tecture requirements for official digital information
representation provided by the state. The author also
analyzes the usability of that gazette for what it pro-
poses, presenting requirements for organizing infor-
mation for the representation of its data, so that the
principle of publicity of official acts is effectively met.
4 THE DEEP VACUITY
ARCHITECTURE
Collecting, processing and inferring useful knowl-
edge about the whole mass of data generated by the
Brazilian government is a very audacious mission,
and, this paper proposes the Deep Vacuity platform.
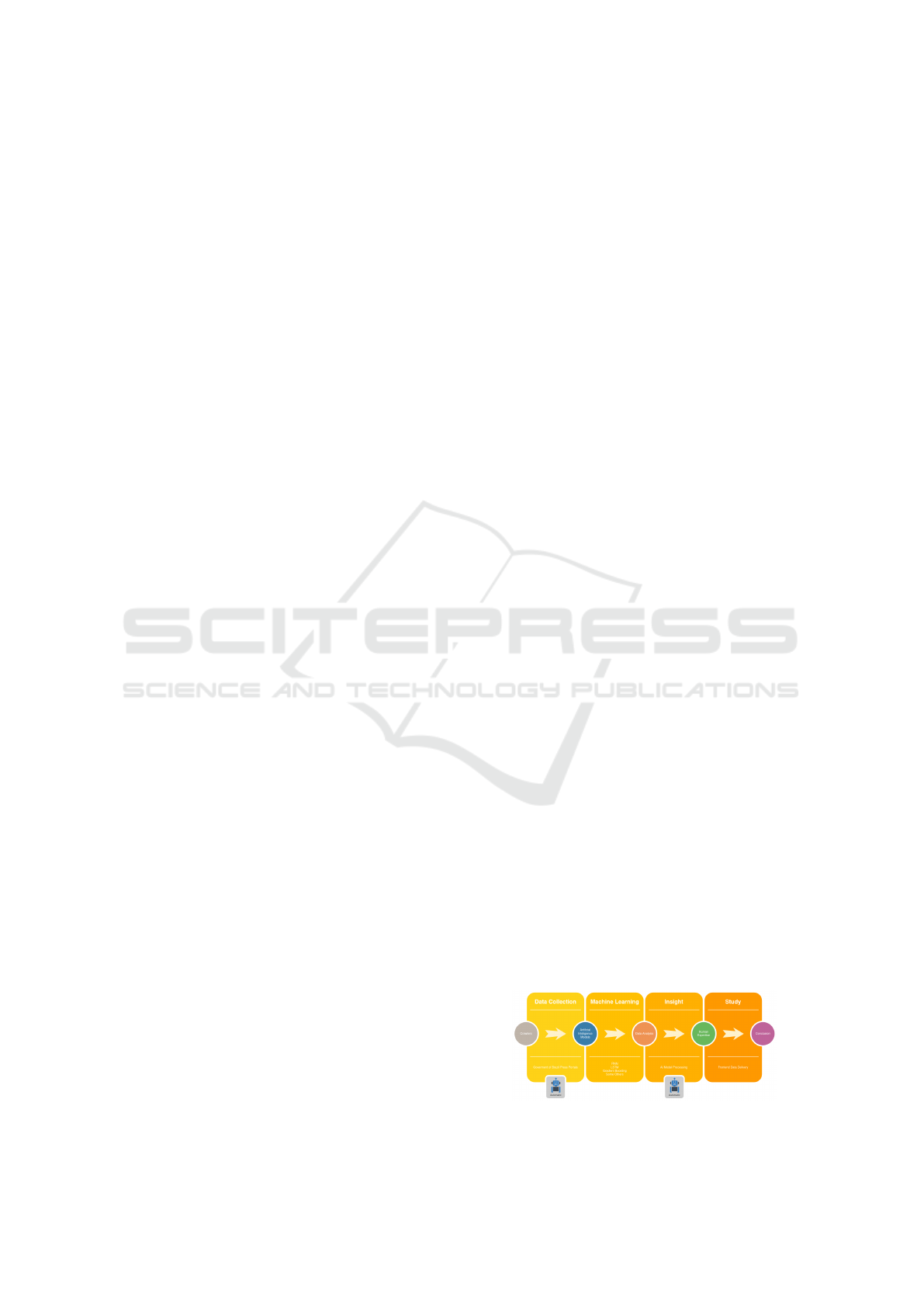
Figure 3 shows the general flow of Deep Vacuity.
It is possible to verify that the process begins with
the “Data Collection” phase in which entities called
“Crawlers” capture data in the various data sources
provided by the Brazilian government. Then artifi-
cial intelligence models are applied to these data in
the “Machine Learning” phase. Eventually, from the
data analysis, the platform will automatically reach an
“Insight”, that is, it will obtain new knowledge about
the data, which was not previously known. This new
knowledge will be presented through a frontend to a
human, whose knowledge in the area where the plat-
form is being used is extensive, and this expert will
make a conclusive study of the discovery.
Figure 3: Deep Vacuity Workflow.
Deep-vacuity: A Proposal of a Machine Learning Platform based on High-performance Computing Architecture for Insights on Government
of Brazil Official Gazettes
139

Considering the magnitude of the challenge, Deep
Vacuity has an architecture that allows its construc-
tion to occur gradually in order to accommodate any
changes that occur in the data sources. As shown in
Figure 4, there are eleven components that make up
the platform’s architectural solution.
Orchestration Component: This component is re-
sponsible for controlling data collection, as well
as triggering the processing of artificial intelligence
models. It should be automatically triggered peri-
odically by means of routines that are triggered by
scheduling operating system tasks, such as crontab
records. Its operation will use parameters defined in
the database. Area 1 in Figure 4 shows the Orchestra-
tion Component of Deep Vacuity Middleware.
Figure 4: Deep Vacuity Architecture.
Data Collection Component: This component ab-
stracts and isolates the specifics of each data source.
Applications denominated Crawlers obtain data from
sources. This process can be done by just request-
ing and receiving files in formats such as XML and
JSON, or parsing the web pages of the data sources.
There is a Crawler for each source and some sources
can share the same Crawler just by filling in their pa-
rameters. Therefore, in the case of sources that share
the same data delivery format, it is not necessary to
create a Crawler specifically for each source. When
requesting a collection, Data Broker must iterate over
the pool of active Crawlers as shown in Area 2 of Fig-
ure 4 and perform the extractions in parallel (respect-
ing an established concurrence limit). Considering
the diversity of ways to obtain primary data, it is es-
sential that the data collection flow is flexible enough
to suit the specificities of the data sources. In order to
achieve this, each type of data source will have its as-
sociated Crawler. The Crawler is the application that
knows the format of the data delivery by the source
and knows how to capture and properly handle that
data. Areas 2 and 3 of Figure 4 show the symbiotic
relationship between primary data sources and their
Crawlers inside a Deep Vacuity context.
Primary Data Sources Component: Each federa-
tive entity of the government of Brazil has its own
channel to publish its acts that need wide dissemina-
tion, such as calls for tenders, signing of contracts,
among other governmental acts. At national level,
these publications are made using the tool called
“Di
´
ario Of
´
ıcial da Uni
˜
ao” (DOU), which generally
provides publications daily, except for weekends and
holidays. At state level, each state has a different plat-
form for making these publications available. Each
one has its own particular format, following the struc-
ture defined by the government of each state. As well
as the structure, the way in which data is made avail-
able also varies between states. At municipal level,
there are several different realities. Brazil currently
has 5570 cities. Some of those cities publish their
gazettes electronically on their portals, however there
are still situations where notifications are made on pa-
per and even displayed on boards at city halls.
Storage Component: This component aims to
store the data collected by Crawlers for processing by
the Machine Learning Engine. It consists of several
standalone storage instances (Area 4 of Figure 4) that
are selected by Orchestrator to receive data at the time
of collection. Each storage component has a Network
File System (NFS) directory where the data is stored,
and which is mounted on the Machine Learning En-
gine instances. The data can be classified as “perma-
nent” or “transient”. If the data is transient, it will be
removed when the Machine Learning Engine ends its
activities on that data.
Machine Learning Component: This component
applies artificial intelligence models to the collected
data and generates new data that are loaded into the
database. A model can load pre-existing models in
the database to use in its processing, as well as other
essential parameters for the model’s execution. Each
model is related to many data sources. When Or-
chestrator triggers this component and there is a new
collection awaiting processing, the models related to
the respective source are loaded. Each model will re-
ceive an instance of the pool to perform its work. If
there are no available instances or the limit of com-
peting instances is reached, the model will wait in a
queue for processing. The parameters of pool limits
are stored in the database and queried by Orchestrator
during its process. Once in possession of the instance
for execution, the model obtains its parameters from
the database, as well as the respective related models.
WEBIST 2022 - 18th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
140

If related models exist, they will be created in Stor-
age. Then the model will be processed. At the end
of this processing, the model’s output will be stored
in the database. As shown in Area 5 of Figure 4 this
component is composed of several instances in which
the machine learning process occurs.
Database Component: Considering the expecta-
tion of data growth, this component is composed of
a cluster of some servers, so that its scalability is vi-
able over time as shown Figure 4 (Area 6). As the
maximum load of the servers is reached, new servers
can be added to the cluster in order to expand its ca-
pacity. The selection of models for analysis and re-
porting can involve a large volume of data and in or-
der to make the processing of these requests more ag-
ile, this component has data distributed in the cluster.
This mechanism uses high parallelism in loading data
to process large volumes of data more quickly than
occurs in centralized database systems. On the other
hand, queries involving smaller data volumes will be
penalized due to the need to perform additional tasks
related to data distribution that would not be neces-
sary in centralized systems.
Presentation Component: This component is the
interface from which the end user can obtain informa-
tion in several formats such as: HTML pages, XML
and JSON files. HTML pages have dynamic con-
tent processed via JavaScript using data loaded from
a REST API. It is prepared for an eventual increase
in number of users, as it has a load balancer service
that distributes requests among the various applica-
tion servers. It can be noticed in Area 7 of Figure 4
that all requests are made to the load balancer acting
as a reverse proxy to the instances running the fron-
tend application. Considering the diversity of ways to
deliver the data produced by the platform, the backend
REST API is stateless. Figure 5 shows a prototype of
a configuration page for artificial intelligence model
listing and upload of Deep Vacuity.
Figure 5: Deep Vacuity Frontend Prototype.
Request Processing Component: This component
(Area 9 of Figure 4) is responsible for receiving, han-
dling and responding to requests from the frontend
through a REST API. Some heavy processing can
be sent to the Request Queue before they are effec-
tively dealt with in order to prevent eventual overload
events in this component. It is prepared for an even-
tual growth in number of users, as it has a load bal-
ancer service that distributes requests among the vari-
ous application servers. Figure 4 shows, in Area 8, the
pool of instances that composes the backend. Those
instances run the backend application and are state-
less. The backend application uses data queried in the
Database to process the requests. The instances are
reachable through a reverse proxy that is responsible
for balancing the load allocated to each instance.
Request Queue Component: This component acts
as a solution processing scheduler. It queues requests
and triggers their execution at the appropriate time
following previously established metrics. An addi-
tional component is part of those processes where the
processing time is usually long. This mechanism al-
lows the user to request a processing and follow its ex-
ecution asynchronously and be notified when its pro-
cessing is finished. Additionally, it prevents backend
downtime caused by overload coming from excessive
frontend requests.
Monitoring Component: Considering the number
of components that make up the solution, this el-
ement monitors the functioning of the components,
their integration and prevents possible disaster sce-
narios. It has acceptable thresholds for each moni-
tored aspect. Once this limit is exceeded, the alert
system sends notifications to the service´s responsi-
ble in order to call attention to that component. The
Area 10 of Figure 4 illustrates the composition of this
component. There are three instances: Metric col-
lector: service responsible for obtaining and storing
established metrics from each monitored component;
Monitoring Dashboard: graphical application to vi-
sualize and analyze monitored component behavior
over time; Alert manager: service in which thresh-
olds are inputted and used to automatically monitor
component metrics.
Authentication and Authorization Component:
Deep Vacuity platform offers user interfaces through
its main frontend and the monitoring system. In both
cases it is necessary to have a system of authentication
and authorization of users based on roles, since there
will be segregation of functions both in the presenta-
tion component and in the monitoring tool. For this,
the platform has a segregated infrastructure whose
specific function is to house an application for the
Deep-vacuity: A Proposal of a Machine Learning Platform based on High-performance Computing Architecture for Insights on Government
of Brazil Official Gazettes
141

management of these authorizations, as well as meet-
ing authentication requests from the frontend and the
monitoring system. In Area 11 of Figure 4, it is possi-
ble to observe that in addition to the instance responsi-
ble for executing the application of this system, there
is also an instance in which the solution database is al-
located, which is completely separated from the main
platform database. In addition to authentication and
authorization, this system allows single sign on, that
is, once authenticated from one of the tools (frontend
or monitoring system) the user will be able to access
the other tool without having to perform a new login
process. within an established time window.
5 PRELIMINARY RESULTS
Deep Vacuity can be used for a number of purposes,
as once the data obtaining process is ready, it is sim-
pler for a work group to invest in the building of their
intelligence models, load them into the platform and
then obtain their “insights”. Some use cases that can
be performed using this tool will be described here.
For example, law enforcement officials responsible
for combating the crime of corruption in public con-
tracts could consolidate their knowledge of how a par-
ticular type of crime works and then upload to Deep
Vacuity for training on the data collected by the plat-
form, and from the insights collected, tools to con-
duct investigations into suspicious cases. Another use
case is the validation of the execution of public pol-
icy strategies. In this use case, a public manager, in
a broader scope, such as a federal one, for example,
could verify whether a particular public policy is be-
ing passed on to lower levels by applying smart mod-
els that verify the occurrence of local government acts
in that location. Still for public managers, another use
case would be an automated price quote. In this use
case, a finance manager from a public agency could
use Deep Vacuity to establish the value of a particular
item they wish to purchase or service they intend to
hire by applying an intelligent model on the data col-
lected by the platform, whether globally or regionally,
depending on interest.
Undue transfers of public officials that aim to re-
ceive compensation money, can be detected through
Deep Vacuity. For this, human resources managers
would need to implement intelligence models capa-
ble of isolating these cases in the universe of transfers
published across the country, including using the plat-
form itself as a training environment. These are just a
few examples of use cases that serve to illustrate the
potential that this architecture has.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This article showed the proposal for the Deep Vacu-
ity, which proposes to collect data from the Brazilian
government, process it and offer insights through a
friendly graphical interface so that they can be ana-
lyzed by experts. Although the challenge of this plat-
form seems arduous, the description of the architec-
ture, based on HPC, allows the conclusion that its vi-
ability is guaranteed. Likewise, the strategy of using a
generic artificial intelligence model for data process-
ing and generating insights has proved to be an appro-
priate approach to make architecture adhere to a wide
range of scenarios.
Deep Vacuity presents itself as a prominent tool
for analyzing government data, especially in the
Brazilian context. Beyond that, this tool can serve as
a starting point for a transformation in the Brazilian
management model, which has a history of reactivity.
Following the adoption of Deep Vacuity, it can reach
a level of predictability of events that could provide
government entities the time needed to prepare com-
bat or contour actions. The flow and the architecture
of the platform are already consolidated, as well as the
prototype of the frontend. The next steps are to build
the data collection structures, the integration track for
processing the smart models and the application back-
end. From that point on, tests can be carried out with
real data, which will allow the performance of the
platform to be evaluated in a productive environment.
Once reaching the aforementioned point, several arti-
ficial intelligence models can be developed that meet
the different use cases to which the platform will be
applied. The role of these models may be increased as
the use of the platform changes the demand for new
intelligent ways of data processing.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are grateful for supporting this research
through the Applied Research of Technological In-
novations project in the Federal Criminal Forensics
(DITEC/PF) through Public Call UNB-DITEC 01-
2021 and University of Brasilia.
REFERENCES
Anysz, H., Foremny, A., and Kulejewski, J. (2019). Com-
parison of ann classifier to the neuro-fuzzy system for
collusion detection in the tender procedures of road
construction sector. In IOP Conference Series: Ma-
terials Science and Engineering, volume 471, page
112064. IOP Publishing.
WEBIST 2022 - 18th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
142

Balaniuk, R., Bessiere, P., Mazer, E., and Cobbe, P. (2012).
Risk based Government Audit Planning using Na
¨
ıve
Bayes Classifiers. In Advances in Knowledge-Based
and Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems,
Spain.
Balaprakash, P., Dongarra, J., Gamblin, T., Hall, M.,
Hollingsworth, J. K., Norris, B., and Vuduc, R.
(2018). Autotuning in high-performance computing
applications. Proceedings of the IEEE, 106(11):2068–
2083.
Brasil (1993). Lei 8666. http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil
03/leis/l8666cons.htm, visited 2020-05-16.
BRASIL (2020). Di
´
ario oficial da uni
˜
ao. http://www.in.gov.
br, visited 2020-05-16.
Carvalho, R. S. and Carvalho, R. N. (2016). Bayesian mod-
els to assess risk of corruption of federal management
units. In BMA@ UAI, pages 28–35.
Chung, M. T., Quang-Hung, N., Nguyen, M., and Thoai, N.
(2016). Using docker in high performance computing
applications. In 2016 IEEE Sixth International Con-
ference on Communications and Electronics (ICCE),
pages 52–57.
Connolly, S. and Matarazzo, J. (1998). Knowledge and Spe-
cial Libraries. Routledge.
de Bessa Lins, M. I. (1976). Di
´
arios oficiais dos estados
brasileiros. https://www.brapci.inf.br/ repositorio/
2010/02/pdf d7a5189ebe 0008270.pdf, visited 2020-
05-16.
de Sousa, S. R. (2014). Di
´
ario oficial do estado de
goi
´
as: uma proposta de requisitos de arquitetura da
informac¸
˜
ao para representac¸
˜
ao da informac¸
˜
ao oficial
digital.
Freund, G. E. (1982). Impactos da tecnologia da
informaC¸
˜
Ao.
Geist, A. and Reed, D. A. (2017). A survey of high-
performance computing scaling challenges. The In-
ternational Journal of High Performance Computing
Applications, 31(1):104–113.
Goel, S. and Uzuner, O. (2016). Do sentiments matter in
fraud detection? estimating semantic orientation of
annual reports. Intelligent Systems in Accounting, Fi-
nance and Management, 23(3):215–239.
Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estat
´
ıstica
(2020). Estimativas da populac¸
˜
ao. https:
//www.ibge.gov.br/estatisticas/sociais/populacao/
9103-estimativas-de-populacao.html?=&t=
resultados, visited 2020-05-16.
Lima, M., Silva, R., Lopes de Souza Mendes, F., R. de
Carvalho, L., Araujo, A., and de Barros Vidal, F.
(2020). Inferring about fraudulent collusion risk on
Brazilian public works contracts in official texts us-
ing a Bi-LSTM approach. In Findings of the Associ-
ation for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2020,
pages 1580–1588, Online. Association for Computa-
tional Linguistics.
Luz de Araujo, P. H., de Campos, T. E., and Magalh
˜
aes
Silva de Sousa, M. (2020). Inferring the source of
official texts: Can svm beat ulmfit? In Quaresma,
P., Vieira, R., Alu
´
ısio, S., Moniz, H., Batista, F.,
and Gonc¸alves, T., editors, Computational Process-
ing of the Portuguese Language, pages 76–86, Cham.
Springer International Publishing.
Martano, A. M. R. (2015). Di
´
ario livre: co-criac¸
˜
ao
de uma ferramentapara publicac¸
˜
ao de um di
´
ario
oficial em formato aberto. Master’s thesis,
Escola de Artes, Ci
ˆ
encias e Humanidades.
https://teses.usp.br/teses/disponiveis/100/100131/
tde-21122015-091757/publico/dissertacao.pdf,
visited 2020-05-16.
Popowich, F. (2005). Using text mining and natural lan-
guage processing for health care claims processing.
ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter, 7(1):59–66.
Rabuzin, K. and Modru
ˇ
san, N. (2019). Prediction of public
procurement corruption indices using machine learn-
ing methods.
Ralha, C. G. and Silva, C. V. S. (2012). A multi-agent data
mining system for cartel detection in brazilian govern-
ment procurement. Expert Systems with Applications,
39(14):11642 – 11656.
Rocha, J. P. L. (2011). Intelig
ˆ
encia de fontes abertas: um es-
tudo sobre descoberta de conhecimento no di
´
ario ofi-
cial da uni
˜
ao. https://bdtd.ucb.br:8443/jspui/handle/
123456789/1336, visited 2020-05-16.
Seemakurthi, P., Zhang, S., and Qi, Y. (2015). Detection
of fraudulent financial reports with machine learning
techniques. In 2015 Systems and Information Engi-
neering Design Symposium, pages 358–361. IEEE.
Signor, R., Love, P. E., Belarmino, A. T., and Al-
fred Olatunji, O. (2020a). Detection of collusive ten-
ders in infrastructure projects: Learning from opera-
tion car wash. Journal of Construction Engineering
and Management, 146(1):05019015.
Signor, R., Love, P. E., Oliveira Jr, A., Lopes, A. O.,
and Oliveira Jr, P. S. (2020b). Public infrastruc-
ture procurement: Detecting collusion in capped first-
priced auctions. Journal of Infrastructure Systems,
26(2):05020002.
Sun, T. and Sales, L. J. (2018). Predicting Public Pro-
curement Irregularity: An Application of Neural Net-
works. Journal of Emerging Technologies in Account-
ing, 15(1):141–154.
Vallim, J. J. d. C. B. (2020). Uso do Modelo de Racioc
´
ınio
Baseado em Casos Para Monitoramento de Conluio
em Licitac¸
˜
oes de Obras de Pavimentac¸
˜
ao Urbana.
Master’s thesis, Universidade Federal do Paran
´
a, Cu-
ritiba.
Van Arkel, J. H., Wagner, J. J., Schweyen, C. L., Mahone,
S. M., Curtis, T. J., HAGINS, S., et al. (2013). Pre-
dictive modeling processes for healthcare fraud detec-
tion. US Patent App. 13/536,414.
Xavier, B. M., da Silva, A. D., and Gomes, G. R. R. (2015).
Uma arquitetura hibrida para a indexac¸
˜
ao de docu-
mentos do di
´
ario oficial do munic
´
ıpio de cachoeiro de
itapemirim.
Deep-vacuity: A Proposal of a Machine Learning Platform based on High-performance Computing Architecture for Insights on Government
of Brazil Official Gazettes
143
