
Situational Question Answering using Memory Nets
Joerg Deigmoeller
1
, Pavel Smirnov
1
, Viktor Losing
1
, Chao Wang
1
, Johane Takeuchi
2
and Julian Eggert
1
1
Honda Research Institute Europe, Carl-Legien-Straße 30, 63073 Offenbach am Main, Germany
2
Honda Research Institute Japan, 8-1 Honcho, Wako, Saitama 351-0114, Japan
Keywords:
Situational Question Answering, Knowledge Representation and Reasoning, Natural Language
Understanding.
Abstract:
Embodied Question Answering (EQA) is a rather novel research direction, which bridges the gap between
intelligence of commonsense reasoning systems and reasoning over actionable capabilities of mobile robotic
platforms. Mobile robotic platforms are usually located in random physical environments, which have to be
dynamically explored and taken into account to deliver correct response to users’ requests. Users’ requests
are mostly related to foreseeable physical objects, their properties and positional relations to other objects in
a scene. The challenge here is to create an intelligent system which successfully maps the query expressed in
natural language to a set of reasoning stems and physical actions, required to deliver the user a correct answer.
In this paper we present an approach called Situational Question Answering (SQA), which enforces the em-
bodied agent to reason about all available context-relevant information. The approach relies on reasoning over
an explicit knowledge graph complemented by inference mechanisms with transparent, human-understandable
explanations. In particular, we combine a set of facts with basic knowledge about the world, a situational mem-
ory, commonsense understanding, and reasoning capabilities, which go beyond dedicated object knowledge.
On top, we propose a Semantics Abstraction Layer (SAL) that acts as intermediate level between knowledge
and natural language. The SAL is designed in a way that reasoning functions can be executed hierarchically
to provide complex queries resolution. To demonstrate the flexibility of the SAL we define a set of questions
that require a basic understanding of time, space, and actions including related objects and locations. As an
outlook, a roadmap on how to extend the question set for incrementally growing systems is presented.
1 INTRODUCTION
The motivation of our work is to enable an Intelli-
gent Agent (IA) to interact with its environment in
a purposeful way as well as to pursue and reach its
own goals by utilizing its own resources. As this is a
quite abstract and high goal, we approach the problem
from top down and focus on the continuous refine-
ment of agent’s knowledge base via incorporation of
new facts extracted either from commonsense knowl-
edge graphs or from an agent’s perception of the en-
vironment. For speeding up the development, we use
a virtual environment, which first has to be explored
in order to let an agent to reason about it. This idea
is similar to Embodied Question Answering (EQA,
(Das et al., 2017)), which gets greater attention in re-
cent years. Here, an environment related question is
raised to an agent and the task is to explore the sur-
rounding until it finds the required information (usu-
ally using visual recognition) to answer the question.
The main difference to our work is that the reasoning
in not embedded into an end-to-end deep neural net-
work, but in a knowledge engine that combines world
knowledge with environment information into a sin-
gle graph representation. This gives use the advan-
tages to explicitly define general reasoning processes
as well as to allow for a transparent explanation of
internal reasoning steps. Another difference is, that
we leave the recognition task out of scope for this pa-
per and focus on the reasoning in a certain situation,
given the perception delivered by a simulator frame-
work. In this paper we put focus on the agent’s knowl-
edge engine system, which provides two main func-
tions: continuously store and retrieve complex struc-
tured and unstructured information about the environ-
ment and infer additional context relevant knowledge
in situations. Our previous work (Eggert et al., 2019;
Eggert et al., 2020) introduces the idea of Memory
Deigmoeller, J., Smirnov, P., Losing, V., Wang, C., Takeuchi, J. and Eggert, J.
Situational Question Answering using Memory Nets.
DOI: 10.5220/0011549200003335
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2022) - Volume 2: KEOD, pages 169-176
ISBN: 978-989-758-614-9; ISSN: 2184-3228
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reser ved
169

Net (MemNet), which provides a conceptual basis for
a knowledge engine that facilitates an agent to act in
a physical environment.
As a means to share knowledge with a user and
measure the reasoning performance, we attached a
natural language understanding to the knowledge en-
gine. Given an environment setting in the simulator
and a dedicated set of questions and answers, we can
enforce the agent to utilize and show its reasoning ca-
pabilities. Our focus is that the agent makes sense
out of a situation it is in by using its gained contex-
tual knowledge and making this process transparent.
We call this approach Situational Question Answer-
ing (SQA).
We are convinced, that real situational reason-
ing requires a detailed understanding of the seman-
tic meaning, which goes beyond usual language un-
derstanding. It requires a tight interaction between
language and semantic concepts embedded in a large
network. In the same way, observations need to be
part of that network, to utilize the full inference capa-
bilities. To allow an agent to act in an environment,
observed objects must be semantically separated into
objects that are manipulated and objects that are used
for manipulation (tool), as well as the changes an ob-
ject undergoes through an action. Such a context def-
inition is known from linguistics as verb semantics
(Baker et al., 1998), where each participant plays a
different role in an action. The most important roles
for our setting are the agent itself, the patient (object)
and the instrument (tool) that contribute to an action.
The novelty we present in this paper, especially in
relation to EQA, constitutes of two parts. First, the de-
tailed distinction between different action participants
(object, tool, subject, location) and their tight linkage
to the language understanding. In our work, we call
such context definitions action patterns which pro-
vide the key structure for situational reasoning. Sec-
ond, the embedding of observations and action pat-
terns into a large semantic network, combined with
commonsense information. We show both novelties
on the task of situational question answering.
In the reminder of this paper, we present our work
in the area of EQA and focus on knowledge represen-
tations that require situational aspects for the embod-
ied agent. In chapter 3, we explain the overall system
and how each component contributes to the overall in-
formation gain in a situation. Finally we evaluate the
system on a set question-answer pairs in chapter 4 and
conclude the paper with an outlook in chapter 5.
2 RELATED WORK
In recent years, the domain of Embodied Question
Answering (EQA) has rapidly grown in combination
simulators for home environment for executing high
level tasks (Puig et al., 2018; Kolve et al., 2019). The
focus of EQA (Das et al., 2017; Duan et al., 2022; Yu
et al., 2019) - sometimes also called Interactive Ques-
tion Answering (IQA) (Gordon et al., 2018) - is on ex-
ploring virtual environments by an agent and to finally
answer questions raised to the system. This direction
has set a new trend and provided great opportunities
for researchers interested in language grounding in
robotics (Tangiuchi et al., ) and question answering
(Pandya and Bhatt, 2019) by using simulated envi-
ronments. Even though the relation to SQA might be
obvious, the questions differ significantly in the sci-
entific direction, which enforces more consideration
of robotics and commonsense knowledge. The focus
in SQA is less on dedicated object information, but
rather on the embedding of objects in all day situa-
tions. Therefore, instead of reasoning on physical fea-
tures, we target for a contextual embedding of objects
in all day situations to broaden the scope of language
interaction.
The work that comes closest to our idea is de-
scribed in (Tan et al., 2021). They include common-
sense information into the EQA process by loosely
coupling semi-structured data from ConceptNet with
their scene graph. As they operate on graphs and not
on deep neural network (as all EQA approaches do),
they call their approach K-EQA (Knowledge-based
Embodied Question Answering). The performance is
estimated by comparing the question answering task
with and without visual recognition (scripted scene
information). The questions are generated automat-
ically from selected link types in ConceptNet, con-
nected with the simulator information to finally gener-
ate answers for training and testing. The step towards
using commonsense information in the question an-
swering is a remarkable contribution to the domain.
Nevertheless, the reasoning is performed on triplet
information like (‘Sports equipment’, ‘ReceivesAc-
tion’, ‘purchased at a sporting goods store’), which is
questionable that such text snippets provide any ma-
chine interpretable meaning. As already described
in the introduction, our approach further splits such
snippets like ‘purchased at a sporting goods store’ into
detailed information as ’purchased’ is the action and
’sporting goods store’ is the location where the ac-
tion takes place. Making these types explicit allows
for a real semantic understanding and embedding into
the agent’s context. We describe this approach in
section 3.3. Additionally, we combine commonsense
KEOD 2022 - 14th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
170

and scene graph information into a single knowledge
graph. This provides a strong connection between se-
mantic types and observations, as well as the storing
and correcting of context information in situations.
The detailed description of actions and their con-
tributors is also known from knowledge representa-
tions in robotics (Paulius and Sun, 2018; Thosar et al.,
2018). The goal is usually to execute a manipulation
task and to infer missing information that is required
for the successful execution (Beetz et al., 2018). Even
if a language interaction would be really helpful for
this domain, it has not been established so far, espe-
cially not for resolving situations on a high level, in-
cluding ambiguities coming from language. We dis-
tinguish ourselves from this domain as we operate on
a higher level in direct language interaction by devel-
oping further the idea of embodied question answer-
ing and situation understanding at the same time.
We think that SQA provides a novel direction to
bring the domains of question answering, common-
sense knowledge and robotics closer together to fi-
nally enable a natural interaction with agents, either
in simulation or in real.
3 SYSTEM OVERVIEW
In this section, we describe the overall system and go
into depth of each component in the sub-sections. The
core of the system is the knowledge engine that acts as
connecting component (see figure 1) that is synchro-
nized with the simulated environment. Other com-
ponents either allow to access the knowledge engine
via natural language (Semantic Parsing), inspect the
reasoning steps (Explainable AI) or insert externally
gathered knowledge (Knowledge Insertion). The in-
teraction between all, finally enables the task of SQA
using natural language and reasoning in specific situ-
ations.
3.1 Knowledge Engine
The knowledge engine consists of three main parts
(see figure 1 at bottom left), the knowledge graph, the
reasoning layer, and the Semantics Abstraction Layer
(SAL). Those layers are important to allow for mod-
ular access of the knowledge representation and rea-
soning. The SAL is the highest layer and describes as
orthogonal as possible access functions to scale well
by applying nested executions. This finally leads to
the idea of Inductive Functional Programming which
allows for various learning applications on top (Dia-
conu, 2020).
Figure 1: Overall system sketch with the knowledge engine
as core component. The simulated environment and the
semantic parsing allows for situational question answering
using externally gathered knowledge. The XAI facilitates
tracing of the reasoning steps in the knowledge engine.
3.1.1 Knowledge Graph
First we start with the lowest layer, the knowledge
graph. The representation is created according to
MemNet and covers four main columns of object,
subject, action and state hierarchies, as described in
(Eggert et al., 2020). The four columns are motivated
by verb semantics (Baker et al., 1998), which derive
from linguistics. In verb semantics, words acquire a
semantic role in the context of a verb, or here an ac-
tion. That means, each participant from one of the
four hierarchies in MemNet can jump into a role that
is dedicated to a specific action. For example, a knife
is no longer a simple object, but rather a tool if it con-
tributes to the action cut. In the same way, an agent
can become an actor or recipient in an action bring,
depending on the context. Such roles are reflected in
MemNet as action patterns using inheritance or even
multiple inheritance if required. For further reading,
we refer to our earlier papers (Eggert et al., 2019; Eg-
gert et al., 2020). The action patterns can be inserted
manually, in interaction or through accessing exter-
nal knowledge sources (cf. chapter 3.3). They pro-
vide the basis for situational reasoning, for example
if we are interested in objects that are usually related
to the action cutting, what objects are used for cutting
Situational Question Answering using Memory Nets
171

or which agent applied which tool for a certain ac-
tion. According to VerbNet (Schuler, 2005), the par-
ticipants in actions are arranged in a whole taxonomy,
starting with time, place, undergoer and actor on high-
est level. For our work we focus on actor, location
(place) and object/tool (undergoer), as it already cov-
ers the most obvious interactions. As initial hierarchy,
we reuse the WordNet (Fellbaum, 1998) inheritance
hierarchy and import it into MemNet. For simplicity,
we assign all nouns to the object column and all verbs
to the action column at first.
As will be explained later in chapter 3.4, phys-
ical instances in the simulator are inserted into the
knowledge graph as specializations of known object
concepts or subject in case of the agent. For each in-
stance, we manually identified the correct concept in
the graph and enriched the specialization with geo-
metric information, either position or shape.
3.1.2 Reasoning Layer
The reasoning layer provides basic methods to iden-
tify concepts in the graph from different entry points.
Each concept is embedded into related concepts, ei-
ther in a hierarchy (semantically related) or through
an action pattern (context related). This is a straight
forward inference by following paths in the graph.
Spatial reasoning is based on simple geometric inter-
pretations based on 2D shapes and points.
3.1.3 Semantics Abstraction Layer
The SAL provides an access to the knowledge engine
on a semantics level. This means, no deeper under-
standing of reasoning details is required when oper-
ating on this level. In a nutshell, the whole API is
based on getting or setting objects, locations, actions,
states, tools or combinations of those as action pat-
terns. All arguments can be either forwarded as ut-
terance, i.e. text or a unique ID of the concept node
in the graph. Further distinction is made between ab-
stract concepts and instances that are attached with
positions and shapes. Instances are provided with a
short term memory (STM) label for easy identifica-
tion in the graph. We focus on the most important
API calls for situational question answering, which
are the STM retrieving functions. A list of functions
is presented below with further explanation:
get action patterns(object, location, action, state, tool)
get stm objects(object, location, action, state, tool)
get stm locations(object, location, action, state, tool)
get stm actions(object, location, action, state, tool)
get stm subjects(object,location,action, state, tool)
get stm states(object, location, action, state, tool)
get stm tools(object, location, action, state, tool)
get count(object, location, action, state, tool)
The API can be read as following. For each se-
mantic type there is a getting function, while again the
arguments are the semantic types, where none, one
or multiple can be specified. By specifying a certain
type, the internal reasoning will also explore its spe-
cializations, i.e. its child concepts until they finally hit
a matching instance within the hierarchy. That means,
we could alternatively identify a banana by calling
get stm objects (object=”fruit”, state=”yellow”).
The only exception are spatial key words as state
argument, which are currently limited to in or on. For
example, identifying all objects on a table, we could
ask for
get stm objects (state=”on”, location=”table”).
In the same way, if contextual information has
been extracted from external knowledge sources,
tools could be identified that are used for the action
cut by
get stm tools (action=”cut”).
As return value, the functions always return the
corresponding concept IDs, which again can be for-
warded to any function, so that we can create a tree
of calls. This gives us a quite large flexibility, with
a comparably low number of functions. When we
talk about the translation from natural language to se-
mantic calls in chapter 3.2, such a flexibility and con-
ceptual interplay between grammar and semantics be-
comes very important to be able to check the validity
of natural language.
3.2 Semantic Parsing
The semantic parsing translates incoming natural lan-
guage requests into SAL calls. As a first step, the
incoming sentence is analyzed by the syntactic parser
spaCy (Honnibal and Montani, 2017), which returns
the grammatical structure of the text as a graph. The
advantage is that in addition to usual intent and slot
recognition known from natural language understand-
ing in chat-bot systems (Jiao, 2020), we additionally
get the relation between words from the dependency
parsing. By this, we can identify sub-clauses and can
group them into semantic closed sub-contexts. As an
example, if we look at ”where is something to drink”,
we can identify the pattern ”where is [object]” on a
high level. We use this pattern to map this to the func-
tion get
stm locations. Further, on a next level, the
[object] is further specified by the sub-clause ”some-
thing to drink”. The extracted structure by the syntac-
tic parser gives us all information we need to map this
KEOD 2022 - 14th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
172

sub-clause to the function get stm objects, where the
arguments are ”something” for the object and ”drink”
for the action.
Pursuing this idea, we applied a set of rules to map
words (tagged as parts-of-speech) and the dependency
tree to a sequence of SAL calls. The advantage here
is that this is a generic mapping, because it relies on
the syntactic tree and the SAL calls are generated au-
tomatically from the sentence structure.
3.3 Knowledge Insertion
In the reasoning process, we also aim to answer
common-sense questions such as ”What tool can I
use to cut an orange ?” or ”What tool can I cut using
the knife?”. To enable such reasoning we extracted
common-sense knowledge from ConceptNet (Speer
et al., 2017) and inserted it into our graph. In particu-
lar, we extracted action patterns as tool-action-object
triplets, e.g., knife-cut-orange, from the phrases of
the used for relation. We use the syntactic parsing
of spaCy (Honnibal and Montani, 2017) to extract
the action and object from the phrases. The tool is
given by the entity to which the used for relation is
assigned. More details about the extraction and an
analysis of its accuracy can be found in (Losing et al.,
2021). Altogether, we extracted 5887 action patterns.
As the extracted information is on text level,
we perform Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD)
(Bevilacqua et al., 2021) to obtain a mapping from
words to the synsets in our graph. In this regard, we
apply the state-of-the-art method CONSEC (Barba
et al., 2021), which phrases the WSD task as a
text extraction problem. The method is based on
the pre-trained Transformer model DEBERTA (He
et al., 2021), which was fine-tuned using the anno-
tated SEMCOR data (Miller et al., 1994).
3.4 Virtual Simulation
Capabilities of embodied question-answering have to
be demonstrated in a certain context in the way that
asked questions relate to objects located in a certain
environment. 3D-simulators like Virtual Home (Puig
et al., 2018) or AI2-THOR (Kolve et al., 2019) of-
fer a variety of flat-looking scenes, where a virtual
agent can be placed and manipulated via high-level
execution commands. Virtual Home has been cho-
sen because of it’s abstraction level, capability to add
multiple agents to the scene and return a subset of the
scene graph observed by a certain camera (mocking
the visual recognition part).
3.4.1 Interaction with Knowledge Engine
In order to facilitate a synchronization between vir-
tual simulator and the knowledge engine, an interme-
diate simulator-managing component is required. The
purpose of the component is to configure a desired
scene using the simulator’s API and initialize objects
as short-term instances in the knowledge graph. This
means that the relevance of inserted objects is re-
stricted by the current situation only. By combining
instances of the short-term memory with long-term
commonsense knowledge, the agent is able to rea-
son on the current environment. If the environment
gets changed (because of agent’s or human’s manip-
ulations) the simulator-managing component updates
corresponding short-term instances in the knowledge
engine, so that their latest state is taken into account
during the next reasoning operations.
3.5 XAI
Visualization of the knowledge graph, known as both
the human- and machine-readable format by its na-
ture, is widely used for increasing the explainability
of machine learning models (Tiddi and Schlobach,
2022). Therefore, a user-friendly Explainable Arti-
ficial intelligence (XAI) interface is demanded by ex-
perts for getting more insight into how our system
works in real-time (Spinner et al., 2019; Arrieta et al.,
2020; Tjoa and Guan, 2020). In our system, a web-
based graphical user interface (GUI), which combines
different modes and a dialogue box is designed and
implemented. There are three targets of the XAI in-
terface: 1) send commands to the system and receive
feedback from the agent, 2) visualize the reasoning
process of the agent to resolve the request for a user
and 3) supervise the current status and execution of
the agent.
We introduce the the whole procedure of the in-
teraction with our XAI interface by the following ex-
amples (Figure 2): Firstly, the user can type a natural-
language command into the dialog box. For exam-
ple, when a user asks ”how many breads are in the
kitchen?” (Figure 2 A), the front-end GUI will send
the raw language input to the Semantic Parsing and
translates it into the calls of the Semantics Abstrac-
tion Layer (see 3.1.3). After getting the results from
the knowledge graph, the output data is sent to the
front-end interface to visualize the whole process of
calling a sequence of functions. Then, as shown in
Figure 2 B, the natural language ”how many breads
are in the kitchen?” is translated into the pattern of
”counting objects” on a higher level, which matches
the function ’get count’ (Figure 2 b.5). This func-
Situational Question Answering using Memory Nets
173

tion requires the parameter of the related instances to
”count”. On a lower level, the system calls the func-
tion ’get stm objects in’ (Figure 2 b.2), with the ar-
guments ’bread’ as object and ’kitchen’ as location.
The outputs are the instances of the concept ”bread”,
which are displayed as pink circles (b.4). After the
instances are put as the parameter ”object” (Figure
2 b.2) and calling the function ’get count’, the fi-
nal result is returned (Figure 2 b.7) and answered in
the dialog box (Figure 2 b.8). At last, the user can
switch to the camera mode (Figure 2 D), which dis-
plays the video stream from the virtual home simu-
lator, by pressing the tab button (Figure 2 c.1) to ob-
serve what is the status of the agent in real-time. As
shown in Figure 2 C, when asked ”bring the book to
the kitchen”, the agent applies the action in the sim-
ulation. This allows for a real and transparent user
experience of the system beyond the SQA task de-
scribed in this paper.
4 EVALUATION
To evaluate our system, we used a set of question
types, known from state-of-the-art (Tan et al., 2021;
Das et al., 2017; Duan et al., 2022; Yu et al., 2019).
In comparison to the existing work, we added the se-
mantic types tool, location and action stored as action
patterns in the knowledge engine which are fed by ex-
tracted commonsense. This allows us to increase the
variations in phrasing questions and at the same time,
enforcing the system to show its capabilities related
to situational understanding.
To focus on the variations of questions, we stick
to a single environment, instead of using multiple en-
vironments, as related work does. Another reason for
this is that we don’t need a training phase, because we
answer questions using zero shot learning by relying
on extracted commonsense information (cf. chapter
3.3) or predefined standard operations as discussed in
chapter 3.1. The environment is a modified setup de-
livered by Virtual Home (Puig et al., 2018) and lim-
ited to 2 rooms.
As already discussed in chapter 2, our work is
coming closest to the approach (Tan et al., 2021). Un-
fortunately, it is hard to judge the impact of common-
sense information, which we think is a key factor in
free interaction with the user. It seems that the com-
monsense information requested in (Tan et al., 2021)
is prompted using the same phrasing as it is available
in ConceptNet. This finally does not require much
reasoning and is rather a pattern matching without se-
mantic interpretation.
We created a set of questions for locating, count-
ing and enumerating objects, as well as asking for
their existence in the environment. The types of ques-
tions are listed in table 1. Each question type can
again refer to either an action pattern or directly re-
fer to an instance. We estimated the accuracy of
a question by comparing the answers delivered by
the system against the ground truth answers from the
scene. As it can happen that multiple answers exist,
we need to compare every possible ground truth an-
swer against every system answer and vice versa.
To give a better insight, we first evaluated each
question type individually (see columns 1 and 3 in ta-
ble 2). Then we tested the influence of extracted com-
monsense information on the whole set (see columns
2 and 3 in table 2, all questions). The main mes-
sage of table 2 is that the performance increases from
77% to 91% on the complete questions set, if we add
commonsense information to the knowledge engine
(columns 2 and 3). This shows the importance of ac-
tion pattern information for situational reasoning.
The instance questions (column 1) refer directly to
instances in the environment, without any context in-
formation extracted from commonsense, which is the
usual way in Embodied Question Answering. That
means, this set measures the basic reasoning capabil-
ities without the need to query action patterns. This
also shows the drop of performance (from 94% to
77%) once we add questions that require context in-
formation by applying the complete set.
5 CONCLUSION
We proposed Situational Question Answering (SQA),
which is a new direction based on Embodied Question
Answering with the addition of situational reasoning.
The main intention is to enforce an agent to show its
abilities to reason on all day situations and infer con-
textually related items in its environment.
The novelty of this paper can be divided into two
parts. First, the introduction of action patterns for
question answering and the tight linkage to language
understanding. Second, the embedding of observa-
tions and action patterns that are fed by commonsense
information into a single semantic network.
We showed the need to distinct between semantic
types from the view of an agent to allow for realis-
tic decision making in situations. We investigated the
influence of extracted commonsense information on
questions that require such contextual semantic un-
derstanding. This was reflected by an improvement
from 94% to 77% on a large questions set using com-
monsense information.
As an outlook, we plan to extend the extracted
KEOD 2022 - 14th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
174
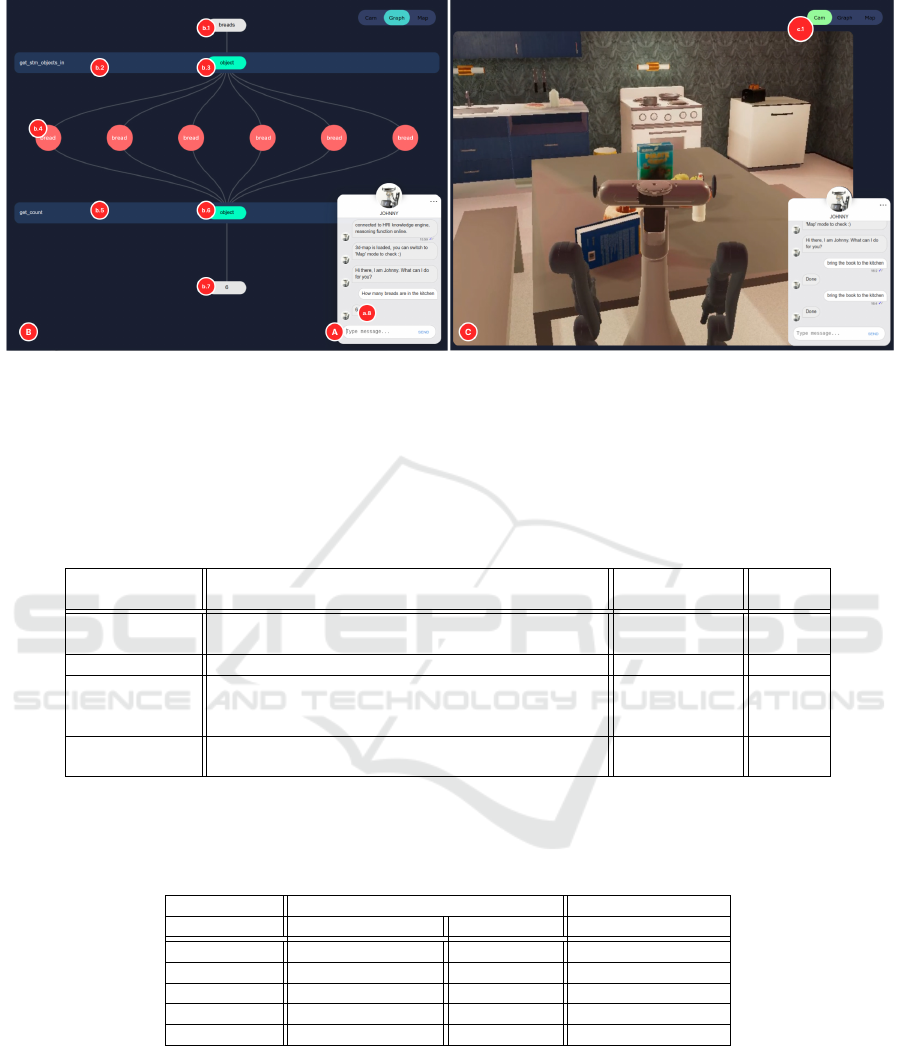
Figure 2: The XAI interface. (A) the dialogue box, which enables the end-user to type in natural-language commands and the
agent will provide answers. (B) Graph Mode, which visualizes the internal computation process of the system. (C) Camera
Mode, which displays the video stream from the virtual home simulator.
Table 1: Templates for different question types ranging from locating, counting and enumerating to asking for the existence of
an object in the simulated environment. Overall, we had 53 objects (such as apple, milk, pillow, remote control, microwave,
etc.) represented by additional 78 upper-class lemmas (such as food, drinks, furniture, etc.). Additionally, we had 12 locations
(e.g. sofa, fridge or dining table), 38 actions (such as drink, sit, cut, eat) and 28 tools related to specific actions (e.g. fork,
knife, plate or microwave). Column 3 of the table reflects the different kinds of knowledge used in the templates. The final
column is the semantic type that is returned by the question.
Question Types Question Templates
Required
Knowledge
Return
Types
Locating
”Where is [object]?”
”Where is something to [action]?”
instances
action patterns
location
location
Counting
”How many [object] are on/in [location]?” instances number
Enumerating
”What is in/on [location]?”
”What tool can I use to [action] an [object]?”
”What object can I [action] with a [tool]?”
instances
action patterns
action patterns
object
tool
object
Existence
”Is there [object] on/in the [location]?”
”Is there something to [action] on/in the [location]?”
instances
action patterns
bool
bool
Table 2: Accuracy for the different question types from table 1 using no extracted commonsense information about object-
action-tool relations (column 1 and 2) and using commonsense information in column 3. Columns 1 and 2 shows the difference
between the question sets referring to instances directly and questions that require action pattern information. The number in
brackets are the number of questions. The overall count was 321 questions for the complete set.
without commonsense with commonsense
instance questions all questions all questions
Locating 0.86 (48) 0.76 (51) 0.80 (51)
Counting 0.92 (96) 0.92 (96) 0.92 (96)
Enumerating 0.97 (11) 0.71 (44) 0.90 (44)
Existence 1.0 (96) 0.73 (130) 1.0 (130)
Overall 0.94 (291) 0.77 (321) 0.91 (321)
commonsense information to also tackle questions re-
ferring to usual object properties, like taste or consis-
tency. The goal is to step by step improve the situ-
ational interpretation capabilities of an agent by in-
creasing the detailed semantic understanding.
It is also obvious that some situations might be
ambiguous, so that the agent should have the chance
to request more information from the user using di-
alog. Therefore, we also want to extend the set by
ambiguous questions to enforce the agent to raise a
query to the user to finally resolve a situation.
Situational Question Answering using Memory Nets
175

REFERENCES
Arrieta, A., Diaz-Rordiguez, N., Ser, J. D., Bennetot, A.,
Tabik, S., Barbado, A., Garcia, S., Gil-L
´
opez, S.,
Molina, D., and Benjamins, R. (2020). Explainable
artificial intelligence (xai): Concepts, taxonomies, op-
portunities and challenges toward responsible ai. In
Information Fusion.
Baker, C., Fillmore, C., and Lowe, J. (1998). The berkeley
framenet project. In In Proceedings of the Coling-Acl.
Barba, E., Procopio, L., and Navigli, R. (2021). Consec:
Word sense disambiguation as continuous sense com-
prehension. In Conference on Empirical Methods in
Natural Language Processing.
Beetz, M., Bessler, D., Haidu, A., Pomarlan, M.,
Bozcuoglu, A. K., and Bartels, G. (2018). Know rob
2.0 — a 2nd generation knowledge processing frame-
work for cognition-enabled robotic agents. In Inter-
national Conference on Robotics and Automation.
Bevilacqua, M., Pasini, T., Raganato, A., and Navigli, R.
(2021). Recent trends in word sense disambiguation:
A survey. In International Joint Conference on Artifi-
cial Intelligence.
Das, A., Datta, S., Gkioxari, G., S. Lee, D. P., and Ba-
tra, D. (2017). Embodied question answering. https://
arxiv.org/abs/1711.11543. Accessed:2022-07-11.
Diaconu, A. (2020). Learning functional programs
with function invention and reuse. https://
arxiv.org/abs/2011.08881. Accessed: 2022-07-11.
Duan, J., Yu, S., Tan, H. L., Zhu, H., and Tan, C. (2022). A
survey of embodied ai: From simulators to research
tasks. https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.04918. Accessed:
2022-07-11.
Eggert, J., Deigmoeller, J., Fischer, L., and Richter, A.
(2019). Memory nets: Knowledge representation for
intelligent agent operations in real world. In 11th
International Conference on Knowledge Engineering
and Ontology Development. SCITEPRESS.
Eggert, J., Deigmoeller, J., Fischer, L., and Richter, A.
(2020). Action representation for intelligent agents
using memory nets. In Communications in Computer
and Information Science. SPRINGER.
Fellbaum, C. (1998). WordNet: An Electronic Lexical
Database. Bradford Books.
Gordon, D., Kembhavi, A., Rastegari, M., Redmon,
J., Fox, D., and Farhadi, A.(2018). Iqa: Vi-
sual question answering in interactive environments.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.03316. Accessed: 2022-07-
11.
He, P., Liu, X., Gao, J., and Chen, W. (2021). Deberta:
Decoding-enhanced bert with disentangled attention.
In Conference on Learning Representations.
Honnibal, M. and Montani, I. (2017). spaCy 2: Natural lan-
guage understanding with Bloom embeddings, con-
volutional neural networks and incremental parsing.
https://sentometrics-research.com/publication/72.
Accessed: 2022-07-11.
Jiao, A. (2020). An intelligent chatbot system based on en-
tity extraction using rasa nlu and neural network. In J.
Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Kolve, E., Mottaghi, R., Han, W., VanderBilt, E., Weihs,
L., Herrasti, A., Gordon, D., Zhu, Y., Gupta,
A., and Farhadi, A. (2019). Ai2-thor: An in-
teractive 3d environment for visual ai. https://
arxiv.org/abs/1712.05474.Accessed: 2022-07-11.
Losing, V., Fischer, L., and Deigmoeller, J. (2021). Extrac-
tion of common-sense relations from procedural task
instructions using BERT. In Proceedings of the 11th
Global Wordnet Conference.
Miller, G. A., Chodorow, M., Landes, S., Leacock, C., and
Thomas, R. G. (1994). Using a semantic concordance
for sense identification. In Human Language Technol-
ogy: Proceedings of a Workshop held at Plainsboro.
Pandya, H. A. and Bhatt, B. S. (2019). Question answer-
ing survey: Directions, challenges, datasets, evalua-
tion matrices. https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.03572. Ac-
cessed: 2022-07-11.
Paulius, D. and Sun, Y. (2018). A survey of knowledge rep-
resentation in service robotics. In Robotics and Au-
tonomous Systems.
Puig, X., Ra, K., Boben, M., Li, J., Wang, T., Fidler, S.,
and Torralba, A. (2018). VirtualHome: Simulating
household activities via programs. In Conference on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.
Schuler, K. K. (2005). VerbNet: A Broad-Coverage, Com-
prehensive Verb Lexicon. University of Pennsylvania.
Speer, R., Chin, J., and Havasi, C. (2017). Conceptnet 5.5:
An open multilingual graph of general knowledge. In
Proceedings of AAAI-31.
Spinner, T., Schlegel, U., Sch
¨
afer, H., and El-Assady, M.
(2019). explainer: A visual analytics framework for
interactive and explainable machine learning. In IEEE
Transactions On Visualization And Computer Graph-
ics.
Tan, S., Ge, M., Guo, D., Liu, H., and Sun, F.
(2021). Knowledge-based embodied question an-
swering. https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.07872. Accessed:
2022-07-11.
Tangiuchi, T., Mochihashi, D., Nagai, T., Uchida, S., Inoue,
N., Kobayashi, I., Nakamura, T., Hagiwara, Y., Iwa-
hashi, N., and Inamura, T. Survey on frontiers of lan-
guage and robotics. https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.03572.
Accessed: 2022-07-11.
Thosar, M., Zug, S., Skaria, A. M., and Jain, A. (2018).
A review of knowledge bases for service robots in
household environments. In 6th International Work-
shop on Artificial Intelligence and Cognition.
Tiddi, I. and Schlobach, S. (2022). Knowledge graphs as
tools for explainable machine learning: A survey. In
Artificial Intelligence.
Tjoa, E. and Guan, C. (2020). A survey on explainable arti-
ficial intelligence (xai): Toward medical xai. In IEEE
Transactions On Neural Networks And Learning Sys-
tems.
Yu, L., Chen, X., Gkioxari, G., Bansal, M., Berg, T. L., and
Batra, D. (2019). Multi-target embodied question an-
swering. https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.04686. Accessed:
2022-07-11.
KEOD 2022 - 14th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
176
