
Technologies for Reducing Greenhouse Gases
E. M. Ozdamirova
1
and D. S. Chankaeva
2
1
Kadyrov Chechen State University, 32 Sheripova Street, Grozny, Russia
2
Grozny State Oil Technical University named after M.D. Millionshchikov, Grozny, Russia
Keywords: Earth's atmosphere, gases, carbon dioxide, greenhouse effect.
Abstract: Of all the problems facing humanity, climate change is the most important, especially since the rate of its
change is increasing and, according to experts, the climate situation will worsen. Climate change is
inextricably linked to the degradation of the Earth's biosphere. The article discusses technologies for reducing
greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases are the collective name for a number of gases that can trap the planet's
thermal radiation. In the visible range, they remain transparent, while absorbing the infrared spectrum. There
is no definite formula for greenhouse gases. Some links between the energy sector and the rest of the economy
are taken into account. Like capital or labor, energy enters production functions in industrial sectors directly
as an end product and indirectly as a raw material.
1 INTRODUCTION
The problem of climate change and the danger of
global and regional impact has become one of the
most actively discussed topics in the world. However,
due to the novelty and unusual nature of the problem,
even ecologists find it difficult to understand all its
details. In addition, the sensationalism of many
newspaper publications and the linkage of the Kyoto
Protocol to various political issues, alas, do not help
to understand the essence of the problem.
The earth's atmosphere has the ability to let the
sun's rays through, while retaining thermal radiation
from the surface. The result is heat accumulation. The
accumulation of gases and other emissions in the
atmosphere exacerbates this process, triggering the
greenhouse effect mechanism.
This global problem has existed for a long time.
But with the development of technologies that
increase emissions into the atmosphere, with an
increase in the number of cars and a general
deterioration in the environment, it is becoming
increasingly relevant. According to statistics, the
average temperature of the planet has increased by
0.74° over the past century alone. At first glance, this
seems like quite a bit. But even such an increase has
already led to irreversible climate change (Korobova,
2020).
Who discovered the mechanism of the greenhouse
effect? For the first time this definition was used in
1827 by J. Fourier. On this topic, he even wrote a
voluminous article in which he considered various
schemes for the formation of the earth's climate. It
was Fourier who first put forward and confirmed the
idea that the optical properties of the earth's
atmosphere are similar to those of glass.
Later, the Swedish physicist Arrhenius, while
studying the infrared properties of water vapor and
carbon dioxide, put forward the theory that their
accumulation in the atmosphere can cause an increase
in the temperature of the entire planet. Subsequently,
on the basis of these studies, the concept of the
greenhouse effect arose.
2 MATERIALS AND
METHODS
Greenhouse gases are the collective name for a
number of gases that can trap the planet's thermal
radiation. In the visible range, they remain
transparent, while absorbing the infrared spectrum.
There is no definite formula for greenhouse gases.
Their percentage may change constantly. So what are
greenhouse gases?
The main greenhouse gases are:
1. Carbon dioxide. The longest living in the
atmosphere, as a result of this, its constant
accumulation occurs;
22
Ozdamirova, E. and Chankaeva, D.
Technologies for Reducing Greenhouse Gases.
DOI: 10.5220/0011553900003524
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Methods, Models, Technologies for Sustainable Development (MMTGE 2022) - Agroclimatic Projects and Carbon Neutrality, pages
22-25
ISBN: 978-989-758-608-8
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
2. Methane. Due to a number of properties, it has
a stronger activity. According to Wikipedia, its
level in the atmosphere has increased by more
than 150 times since 1750;
3. Nitrous oxide;
4. Perfluorocarbons - PFCs (Perfluorocarbons -
PFCs);
5. Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs);
6. Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6).
Greenhouse gases lead to significant climate
changes, by their nature, the sources of their
formation can be divided into 2 large groups:
Man-made. They are the main cause of the
greenhouse effect. These include various types of
industry that use the combustion of hydrocarbon
fuels, the development of oil fields, emissions from
automobile engines.
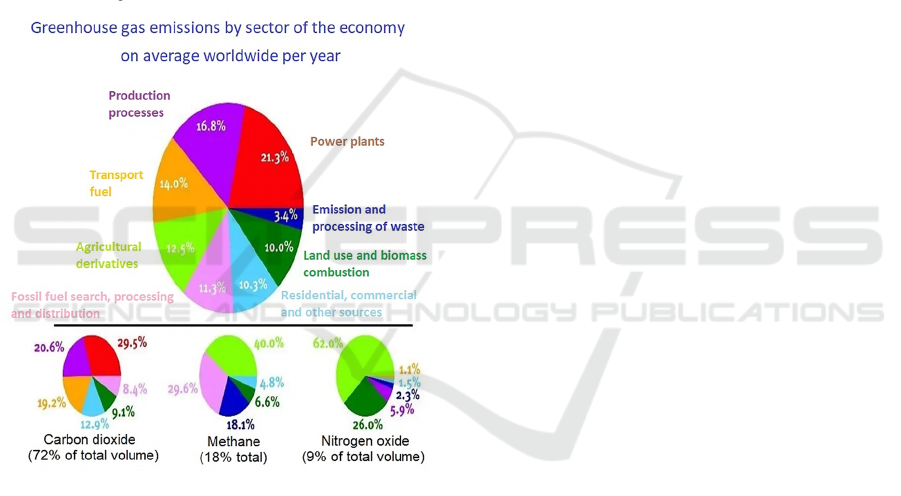
Figure 1: Greenhouse gas emissions by sectors of the
economy on average throughout the world per year.
Natural. They play a secondary role. Most of the
natural greenhouse gases enter the atmosphere during
volcanic eruptions. Also in this group can be
attributed evaporation of the oceans and large forest
fires.
The main reason for the development of the
greenhouse effect on Earth are gases accumulating in
the atmosphere. Exceeding their concentration leads
to a change in the heat balance.
Additionally, the ozone layer can also be
involved in this process. Under the influence of freon
and nitrogen oxides, which are also included in the
list of greenhouse gases, it begins to rapidly break
down and become thinner. As a result, the level of
hard ultraviolet radiation increases dramatically.
Thus, the greenhouse effect and the destruction of the
ozone layer are a chain of interrelated events that have
a significant impact on the biogeocenosis of the entire
planet (Temnov, 1987).
The main causes of the greenhouse effect include:
The rapid growth of industry using oil, gas and
other fossil hydrocarbons as energy sources. They
account for about half of all gas emissions.
Mass destruction of forests. In the process of
photosynthesis, trees absorb carbon dioxide and
produce oxygen, forests are the “lungs of the planet”,
their destruction is fraught with a sharp increase in the
amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Development of agriculture. As a result of the
decay of animal waste products, a large amount of
methane is produced, which is one of the most
aggressive greenhouse gases.
In addition to human activities, natural causes can
also contribute to the enhancement of the greenhouse
effect. For example, large volcanic eruptions or mass
burning of forests. An increase in temperature on the
Earth's surface as a result of the thinning of the ozone
layer leads to increased evaporation of moisture,
which also aggravates the situation. The relationship
between the greenhouse effect and the ozone layer
has long been proven. An increase in the
concentration of water vapor in the atmosphere is a
fundamental factor in the development of the problem
(Temnov, 2000).
Depending on the development scenarios, the
technological foundation of the global economy
needs to be fundamentally upgraded.
Below is a brief overview of recent research on
technological progress in key economic sectors.
Unfortunately, Russia lags far behind most
developed countries in terms of energy efficiency and
energy conservation. We have a huge potential to
reduce greenhouse gas emissions, which is a
relatively low-cost potential.
On the one hand, we must do it resolutely -
reducing emissions, because without that - the
President and the Administration will not be able to
achieve accelerated economic growth, economic
restructuring and doubling of GDP without
improving the energy efficiency of the Russian
economy.
Energy supply will continue to be dominated by
fossil fuels and traditional combustion technologies.
Improvements can be achieved by increasing the
efficiency of power plants, co-firing coal and
biomass, adding biogas to natural gas, replacing coal
fuel with natural gas, and more.
Technologies for Reducing Greenhouse Gases
23

The following technologies are considered the
most promising:
gas technology. Units based on a steam-gas
combined cycle (natural gas combined "cycle,
NGCC) or CCGT" GTU.
Use the gases produced during the combustion of
fuel
Used to generate steam to drive steam turbines to
generate electricity. Efficiency can be increased by as
much as 60% by increasing flame temperature and
steam pressure, as well as more complex steam
cycles. Main problems: high temperature materials,
efficient cooling system (Schreiber, 1977).
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
New corner technologies include steam parameters
for supercritical and ultra-supercritical (SSC)
circulating boiling technologies (up to 700°C and
37.5 MPa).
layer and efficiency over 50%.
Pre-gasification plants for various types of solid
hydrocarbon fuels (to produce synthesis gas
consisting of a mixture of hydrogen and carbon
monoxide), as well as conversion cycles similar to
CCGT "GTU" (yield up to 50%) can also have an
effect.
The problem with new materials that can work at
such temperatures and pressures.
The low-temperature swirling combustion
technology (LBT) is based on the aerodynamics of
the flow in the furnace - most of the fuel enters the
bottom of the furnace, and the air goes up.
The use of energy and heat pumps further
increases efficiency through the use of low
temperature thermal energy.
Micro and micro cogeneration. The modern way
of life of the population requires the effective use of
semi-autonomous decentralized power supply
systems based on micro and micro power plants /
CHP.
Their power ranges from a few kilowatts (for
small kitchen appliances such as refrigerators) to
multi-megawatt appliances for entire villages or
industrial sites. The calorific value can reach tens and
even hundreds of kilojoules per hour, and the overall
efficiency can exceed 75% (Egamov, 2015).
4 CONCLUSIONS
Energy is a crucial economic input circulating in most
economies, widely utilized as a production factor and
consumed in different forms by households. Due to
inter-sectoral linkages and the wide impact of energy-
related policies on the remaining sectors and all
economic agents, general equilibrium modelling is an
appropriate tool to assess energy and environmental
policy scenario.
Several linkages between energy sector and the
rest of economy are taken into consideration.
Similarly to capital or labor, energy enters production
functions in industrial sectors directly as a final
product and indirectly as a raw materials. In case of
households, energy consumption enters utility
function through housing and transport services.
Produced electricity is supplied only to a single sector
(electricity distribution) because nobody except this
single sector should buy electricity directly from
producers. Future modification of the model should
takes into account consider to implement bottom-up
part for heating sector, international trade,
unemployment, more disaggregated sectors
representation, prosumer energy, motor fuels black
market, distinguish between capital stock and land in
natural resources sectors, sectoral emission
coefficients (Porfiriev, 2010).
It is estimated that in European countries, about
95% of households use personal heating system.
there are various ways to solve the problem of the
greenhouse effect. The main thing is that the struggle
should be conducted at the international level. To
correct the current situation, the efforts of all mankind
are needed. Gas emissions are a global problem, it
concerns the entire planet as a whole, and not
individual countries.
In general, Russia has a huge and still unused
reserve for reducing the carbon footprint of products
due to existing protective and other categories of
forests on agricultural land. Forests located on
agricultural land are of great importance for the
absorption of greenhouse gases (Porfiriev, 2010).
REFERENCES
Korobova, O. S., 2020. Theoretical aspects of using the
potential to reduce greenhouse gases in coal-mining
regions. Publishing House of RUDN University.
Temnov, V. G., 1987. Structural systems in nature and
construction technology. Leningrad: Stroyizdat,
Leningrad. dept.
MMTGE 2022 - I International Conference "Methods, models, technologies for sustainable development: agroclimatic projects and carbon
neutrality", Kadyrov Chechen State University Chechen Republic, Grozny, st. Sher
24

Temnov, V. G., 2000. Automated end-to-end design as a
basis for resource-saving technologies for creating
buildings and structures. Materials 57 scientific. conf.
prof. lecturer, researcher worker, engineer university
SPbGAS.
Schreiber, A. K., 1977. Organization, planning and
construction management. Higher school.
Egamov, N. M., 2015. Application of information
technologies in design.
Porfiriev, B., 2010. Climate change: risks or development
factors Russia in global politics.
http://www.globalaffairs.ru/number/Atmosfera-i-
ekonomika-14886.
Nikoláeva, L. B., 2018. Latin American economy in the
face of climate changes. New priorities | [Economía
latinoamericana de cara a los cambios climáticos.
Nuevas prioridades]
.
Porfiriev, B., 2010. Climate change: risks or development
factors? Russia in global politics.
http://www.globalaffairs.ru/number/Atmosfera-i-
ekonomika-14886.
Nikoláeva, L. B., 2018. Latin American economy in the
face of climate changes. New priorities | [Economía
latinoamericana de cara a los cambios climáticos.
Nuevas prioridades] Iberoamerica (Russian
Federation)
.
Gonset, C., Vielle, M., 2012. Climate Impact Modeling
Changes in the Energy Sector: A Swiss Perspective,
Federal Polytechnic School of Lausanne.
Kassenberg, A., Snegotsky, A., 2015. W kierunku
niskoemisyjnejtransofromacji rynku pracy. Report 6.
Niskoemisyjna Polska 2050, Warsaw.
Kihuila, O., Rutherford, T. F., 2013. The Cost of Reducing
CO2 Emissions: Integrating abstaining technologies
into economic modelling. Environmental Economics.
Technologies for Reducing Greenhouse Gases
25
