
Electrostatic Fiber-reinforced Concrete: New Opportunities in
Construction
Magomed Nakhaev
1a
and Madina Salamanova
2b
1
Chechen State University, Grozny named after A.A. Kadyrova, Grozny, Russian Federation
2
Grozny State Oil Technical University named after Academician M. D. Millionshchikov, Grozny, Russian Federation
Keywords: Construction, additive technology, electrostatic deposition, shaping frame, dry mix concrete, strong fibers.
Abstract: A new type of additive technology in construction is proposed - the so-called electrostatic molding of products
and structures from fiber-reinforced concrete. The peculiarity of the method is that the electrostatic deposition
of layers of dry concrete mix and reinforcing fibers on the shaping frame occurs without impact and noticeable
mechanical impact, in contrast to the coating technology, for example, with shotcrete. A layer of fiber-
reinforced concrete electrostatically deposited on the frame, after moistening and a short time delay, increases
the strength of the shaping frame. As the number of layers of concrete increases, the strength of the frame
increases, many times ahead of the load from an increase in the mass of concrete. Therefore, the shaping
frame can be made lightweight. This greatly simplifies its production. Therefore, reinforcing wire, wire mesh
and thinned coarse fabric made of hydrophilic fibers can be used for the frame of the structure. This is a
significant advantage of the new technology. When, after some time, the electrostatic concrete gains the
necessary strength, the structure is covered with glass fiber reinforced concrete from the inside using shotcrete.
It is necessary to carry out studies to determine the limits of applicability of the method in various areas of
construction.
1 INTRODUCTION
Apparently, the first truly additive technology in the
world was electroplating, discovered by B.S. Jacobi
in 1837. In electroforming, a new object is created
due to metal ions, which, under the action of an
electric field, purposefully move and settle on the
cathode, repeating its relief to the smallest detail (Dr.
Jacobi, 1840). In recent decades, additive
technologies based on the layer-by-layer growth of
three-dimensional objects using computer 3D
technologies have been increasingly used. This
applies to products made from a variety of materials.
One of the first additive technologies for builders
can be considered the technology of shotcrete, which
appeared at the beginning of the 20th century. This is
a productive method, but application of shotcrete
requires a solid wall, forming surface, or single-sided
formwork. Despite the fact that the concrete jet is
highly dispersed, upon impact, the high-speed jet
exerts strong pressure on the barrier (Bazhenov,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2589-6662
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1293-7090
1984). Therefore, shotcrete is used where there is a
solid foundation - for repairing destroyed reinforced
concrete, strengthening the walls of pits, tunnels and
foundations, restoring hydraulic structures, etc. The
construction 3D printer that appeared at the end of the
20th century is another example of additive
technology in construction (Dominguez, 2013;
Fedorov, 2017). Despite all its shortcomings, the
construction 3D printer has already proven itself as an
economical way to build low-rise housing.
For more than half a century abroad, especially in
Germany and the USA, and later in Russia, tents and
tent coverings made of film-fabric materials have
been used. Their disadvantage is that awnings and
coverings in the form of technical fabrics require the
creation of a strong support contour with tension and
anchor devices for the stability of the structure against
strong winds and sometimes snow loads. When
studying such coatings from soft shells, it is
noteworthy that steel posts, solid or prefabricated
arches, guy wires and anchors, apparently, are much
44
Nakhaev, M. and Salamanova, M.
Electrostatic Fiber-reinforced Concrete: New Opportunities in Construction.
DOI: 10.5220/0011554300003524
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Methods, Models, Technologies for Sustainable Development (MMTGE 2022) - Agroclimatic Projects and Carbon Neutrality, pages
44-47
ISBN: 978-989-758-608-8
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
larger in weight and cost than the technical fabrics for
tent covering themselves. Despite the often complex
technology of cutting technical fabric and its sewing
or welding (Patent RU 2622571, 2017).
Most of the coatings of large long-term structures
are built from rigid materials - from reinforced
concrete and precast concrete, and sometimes sheet
metal is used for membrane coatings. These materials
have long been widely used in construction practice
(Ledenev, 2016; SP 52-117-2008, 2008). The use of
prefabricated reinforced concrete slabs or metal
membrane coatings requires a well-equipped and
capital-intensive production base for its
implementation.
Technical solutions are known, based on the use
of mesh or fabric materials in the form of a shell, for
fixing the spatial shape of which the impregnation of
the shell material with a fixing composition is used.
For this purpose, curing compounds based on epoxy
resins, acrylic compositions and other compositions
of polymeric substances are used. For example, in
order to fix the shape of the shell impregnated with a
hardening composition, the contour elements of the
shell are made in the form of a sleeve from the shell
material, impregnated or filled with a hardening
composition (A.s. 935578 MKL E 04 B, 1982).
The disadvantages of using polymer curing
compositions to fix the shape of the shell are that this
technology is characterized by high labor intensity of
manufacture and insufficient rigidity and strength of
the cured shell contour. Since polymers have strength
indicators and modulus of elasticity many times lower
than those of steel. In addition, work with curing
compositions is strictly limited in time, since the
viscosity of the prepared compositions increases
rapidly over time. Working with curing compounds is
associated with unhealthy epoxy resins, acid
hardeners, plasticizers and solvents, especially during
formulation and curing.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
In Russia, a new type of additive technology has been
proposed - the so-called electrostatic molding of
products and structures from fiber-reinforced
concrete (Kokoev, 1997). The new technology gives
more creative freedom to the architect. It is
appropriate to note here that each new technology
sooner or later finds its niche in the construction
practice. For example, the prominent French
constructivist architect Le Corbusier in the first third
of the 20th century contributed to the widespread use
of concrete and glass in architecture with his projects
(Le Corbusier, 2004; Andrew Ayers, 2004). He is also
known worldwide for his pioneering work on precast
concrete. In 1914, Le Corbusier created and patented
the Dom-Ino House project, which was essential for
his creative biography. In fact, this was the very first
frame-type house project for serial construction. In
this project, he for the first time foresaw (together
with engineer M. Dubois) the great possibilities of
building from large-sized prefabricated reinforced
concrete elements - flights of stairs, floor slabs,
columns, etc.
But back to our topic. It is better to explain the
essence of "electrostatic" fiber-reinforced concrete
with an example. The selected objects are related to
the construction of hip roofs that crown centric
buildings, both in religious and civil buildings.
Coverings in the form of tents are also found in the
construction of cottages, exhibition and trade
pavilions, tourist centers and campsites. The tents can
be with double negative Gaussian curvature and
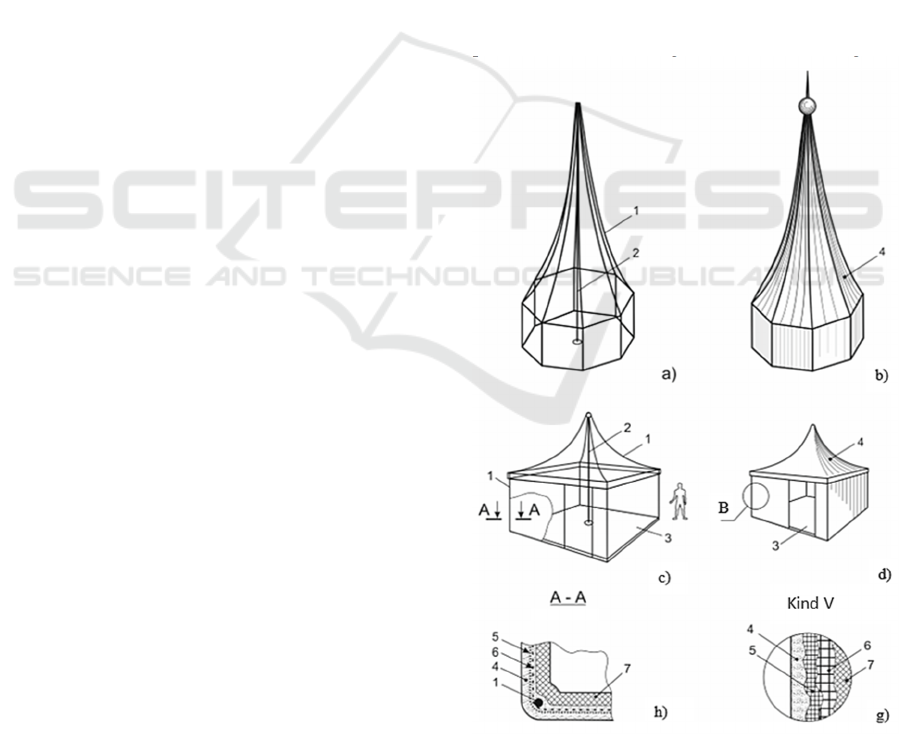
prismatic with zero or negative curvature (see figure).
Figure 1: Electrostatic fiber-reinforced concrete - new
opportunities in construction.
Electrostatic Fiber-reinforced Concrete: New Opportunities in Construction
45

Before moving on to the technology of the
method, it should be noted that the electrostatic
deposition of layers of dry concrete mix on the
shaping frame occurs without impact and noticeable
mechanical impact, in contrast to the coating
technology, for example, with shotcrete. The first
electrostatically deposited dry layer of fiber-
reinforced concrete, after moistening and a short time
delay, significantly increases the strength of the
shaping frame. As the number of layers of concrete
increases, the strength of the frame rapidly increases,
many times ahead of the load from the increase in the
mass of fiber-reinforced concrete.
a) the shaping frame of the prismatic tent, made
of wire reinforcement;
b) a prismatic tent, covered on the outside with
fiber-reinforced concrete, and on the inside
with shotcrete glass fiber-reinforced concrete;
c) pavilion wire frame with prismatic or conical
tent with negative Gaussian curvature; d) a
pavilion covered on the outside with fiber-
reinforced concrete, and on the inside with
shotcrete glass-fiber-reinforced concrete; h)
section A-A; g) view B.
1 - ribs of the shaping frame made of reinforcing
wire, 2 - inventory mast, 3 - base (floor) of the
structure, 4 - layers of concrete deposited by
electrostatic sprayers; 5 - thinned burlap, 6 - welded
or woven mesh, 7 - shotcrete layer of glass fiber
reinforced concrete.
Thus, the shaping frame can be made lightweight.
Therefore, for the manufacture of the framework of
the structure, it is possible to use reinforcing wire,
welded or woven wire mesh, duplicated with a
thinned coarse fabric (sparse burlap) made of jute and
other hydrophilic fibers. This reduces the labor
intensity and metal consumption of manufacturing a
shaping frame for low-rise buildings. In addition, the
method allows the use of a water-cement ratio close
to the theoretical one for a given concrete
composition. The optimal W/C value should provide
savings in cement without reducing the strength of
fiber-reinforced concrete. So, the shaping frame of
the building is made of reinforcing wire, the openings
are closed with steel welded or woven mesh. Outside,
thinned burlap made of jute and other hydrophilic
fibers is attached to the mesh. In this case, the cells in
the wire mesh are desirable from 30 mm in size and
above, and on the burlap the cells in the light should
be in the range of 5-12 mm. In the manufacture of a
shaping frame for a tent with a double negative
curvature, a flexible woven steel mesh is used,
thinned burlap is attached to the mesh from the
outside. Form limited areas of the surface of double
curvature, using the property of a woven mesh and
burlap to change the density of the weft and warp
threads.
The burlap is moistened for electrical
conductivity, the shaping frame is grounded, and
using a manipulator with electrostatic sprayers, the
burlap, together with the underlying mesh, is covered
with a dry concrete mixture containing reinforcing
fibers. The process of coating the shaping frame with
a dry mix is affected by the electrical resistivity of
cement particles and other components of the dry
mix. Of the industries where electrostatic technology
is used, it has been established by practice that the
area of optimal electrical conductivity of particles for
their electrostatic deposition (cement, fine sand, fly
ash, fiberglass, etc.) has a wide range - from 107 to
109 Ohm∙m (Petzold, 1990; Lagarias, 1960).
The settling of the dry concrete mix and the
wetting of the dry concrete mixture with water mist
must be separated by time and/or distance along the
building surface so that the high humidity air does not
reach the electrostatic sprayers. It is better to moisten
the applied layer of dry concrete with a cold fog
generator. Fog generators spray water with droplets
no larger than 50 microns. The cycles of coating with
a dry mixture and moistening with water are repeated
until the required thickness of fiber-reinforced
concrete is obtained. Between cycles, time delays are
made for the fiber-reinforced concrete to gain initial
strength.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
To prepare a dry mix of concrete, hydrophilic quick-
hardening Portland cement with fine mineral
additives and fibers is used. Instead of fine sand,
depending on the requirements for the structure and
its purpose, mineral powders are used - finely ground
waste from stone processing or ash and slag waste, fly
ash from electrostatic precipitators of power plants,
perlite powder, volcanic ash, cement dust from
electrostatic precipitators of cement plants and other
finely dispersed materials of natural and technogenic
origin (Nakhaev, 2015; Salamanova, 2019;
Salamanova, 2018).
For fiber-reinforced concrete, reinforcing fibers
are used - alkali-resistant glass, basalt, carbon
(Polyacrylonitrile; Hong, 2014), etc. The fibers must
first be freed from lubricants and other hydrophobic
substances. This condition provides good wetting
with water with the addition of surface-active
substances (surfactants) of the concrete mixture and
fibers and contributes to the work of capillary forces
MMTGE 2022 - I International Conference "Methods, models, technologies for sustainable development: agroclimatic projects and carbon
neutrality", Kadyrov Chechen State University Chechen Republic, Grozny, st. Sher
46

to compact the layers of fiber-reinforced concrete. If
water-soluble polymers are added to water to improve
the properties of fiber-reinforced concrete, then the
addition of surfactants is often not required, since
many water-soluble polymers themselves have good
surface activity. To increase the strength of some
objects after the strength of the electrostatically
deposited layers of fiber-reinforced concrete, the
structures can be covered with glass fiber reinforced
concrete from the inside using shotcrete.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Using the technology of electrostatic molding of
products and structures made of fiber-reinforced
concrete will give the following technical and
economic effect:
1. Reducing the labor intensity and metal
consumption of manufacturing shaping frames
of products and structures.
2. In the new technology, for the first time, it
became possible to regulate the W / C over a
wide range, regardless of the complexity of the
product shape. Through the use of a water-
cement ratio close to theoretical, savings in
cement should be achieved without loss of
concrete strength.
3. The use of "electrostatic" fiber-reinforced
concrete for the construction of low-rise
buildings in appropriate climatic conditions
will increase the durability of structures, as
well as reduce the cost of their construction.
REFERENCES
Dr. Jacobi, M. H., 1840. Die Galvanoplastik, oder das
verfahren cohӓrentes kupfer in platten oder nach sonst
gegebenen formen, unmittelbar aus kupferauflösungen,
auf galvanischem wege zu produciren. St. Petersburg:
Eggers et Co.
Bazhenov, Yu. M., Komar, A. G., 1984. Technology of
concrete and reinforced concrete products. Stroyizdat,
Moscow.
Dominguez, I., Romero, L., Espinosa, M., Dominguez, M.,
2013. 3D printing of models and prototypes in
architecture and construction. Revista de la
construccion.
Fedorov, V. T., Kokoev, M. N., 2017. Construction 3D
printer and the development of the Far East Hectare.
Bulletin of the department of building sciences RAASN.
2.
Patent RU 2622571. 2017. C2 IPC E04H15/26. The method
of shaping tent tent shells.
Ledenev, V. V., Khudyakov, A. V., 2016. Shell structures
in construction. Theory, design, constructions,
calculation examples. Tambov State University.
Tambov.
SP 52-117-2008, 2008. Reinforced concrete spatial
structures of coatings and ceilings. Part I. Methods of
calculation and design. Section 6.2. Prefabricated
monolithic structures. Moscow.
A.s. 935578 MKL E 04 B 7/10, published 06/15/1982.
Spatial coverage of the building.
Kokoev, M. N., Fedorov, V. T., 1997. Electrostatic molding
of reinforced concrete products. Concrete and
reinforced concrete. 6.
Le Corbusier, 2004. The Modulor: A Harmonious Measure
to the Human Scale, Universally Applicable to
Architecture and Mechanics. Basel & Boston:
Birkhäuser.
Andrew Ayers, 2004. The Architecture of Paris: An
Architectural Guide. Edition Axel Menges.
Stuttgart/London.
Petzold, A., Peshman, G., 1990. Enamel and enamelling.
Metallurgy. Moscow.
Lagarias, J., 1960. Discharges electrodes and electrostatic
precipitators. Journal of the Air Pollution Control
Association. 10(4).
Nakhaev, M. R., Kharchenko, I. Ya., Murtazaev, S. A. Yu.,
2015. OTDV compositions for injection fixing of soils
with a complex filler of various genesis. Ecology and
industry of Russia. 3.
Salamanova, M. Sh., Murtazayev, S-A. Yu., Alaskhanov,
A. Kh. 2019. Development of Multicomponent Binders
Using Fine Powders. Proceedings of the International
Symposium "Engineering and Earth Sciences: Applied
and Fundamental Research" dedicated to the 85th
anniversary of H.I. Ibragimov. Atlantis Highlights in
Material Sciences and Technology (AHMST). 1.
Salamanova, M. Sh., Mintsaev, M. Sh., Murtazaev, S.-A.
Yu., Saidumov, M. S. 2018. Ecological Aspect of the
Usage of Ahy and Slag Waste in the Chechen Republic.
Proceedings of the International Symposium
"Engineering and Earth Sciences: Applied and
Fundamental Research". Part of series: AER. 177.
Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) carbon fiber.
https://dipchel.ru/store/uglerodnoe-volokno/.
Hong, Li, Cheryl Richards, Watson, James, 2014. High-
Performance Glass Fiber Development for Composite
Applications. International Journal of Applied Glass
Science.
Electrostatic Fiber-reinforced Concrete: New Opportunities in Construction
47
