
Introduction of a Modern Management Model of Energy-saving
Technologies at Enterprises
R. H. Bekmurzayeva
1a
, R. K. Ashuralieva
2b
and G. U. Magomedbekov
3c
1
Chechen State University named after A.A. Kadyrov, Russia, Grozny
2
Dagestan State Technical University, Makhachkala, Russia
3
Dagestan State University, Makhachkala, Russia
Keywords: Energy saving, energy efficiency, digital economy, energy sector, global economy, technology.
Abstract: The article examines global trends in the energy sector in the information society. 4 stages of the formation
of the concept of energy saving as a global trend in the historical concept are highlighted. The architectonics
of the formation of models of energy development of the 4th investment cycle is defined as the interrelation
of two models of the development of energy-efficient technologies "Energy Efficiency +" and "New
Paradigm". The directions of implementation of these models as ensuring sustainable socio-economic
development at all hierarchical levels of the economy are determined: consumers, enterprises, countries, the
whole world. The drivers of the development of the "Energy Efficiency +" technology are: the dominance of
centralized energy; the development of trigeneration; the development of dispersed generation; economically
sound innovations; the development of smart energy models in individual clusters (Smart Grid). The
definition of the energy efficiency criterion is proposed based on the Best-in-Class methodology and an
attributive approach in order to realize the potential.
1 INTRODUCTION
The introduction of new engineering and design
solutions in energy supply systems, which provide for
the integrated use of renewable energy sources, will
solve an important economic and scientific and
technical problem of reducing the consumption of
traditional fuel and energy resources for domestic
enterprises. This corresponds to the Energy Strategy
of Russia for the period up to 2035 (Order ..., 2020)
and other legislative documents. However, a complex
of issues related to the definition of the domestic
specifics of the introduction of a modern model of
energy-saving technologies among economic agents
requires in-depth analysis and methodological
clarification. It is becoming increasingly difficult for
energy companies to determine which set of
communication tools is effective for creating long-
term relationships in the market and achieving
optimal influence on the consumer.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5936-7235
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4281-1608
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2238-505X
It should be noted that recently there has been an
increasing interest among scientists and practitioners
in the existing problems of the development of the
energy sector, as evidenced by the appearance of
numerous publications. In modern conditions, the
problem of rational use of energy resources is
becoming increasingly important at all hierarchical
levels: consumers; enterprises; countries; the whole
world.
The need to introduce the concept of energy
conservation as a factor of social development is
considered in the literature from different angles:
saving natural resources (Mady, 2020),
environmental pollution (Di Somma, 2015),
competitiveness of individual companies (Griffiths,
2015), industries and states (Lieder, 2018), the
welfare of society (MacElroy, 2016), Energy security
(Zolotukhin, 2017). Despite numerous studies and the
practical significance of the results obtained, it should
be noted that such issues remain insufficiently
studied: global trends of the fourth investment cycle
Bekmurzayeva, R., Ashuralieva, R. and Magomedbekov, G.
Introduction of a Modern Management Model of Energy-saving Technologies at Enterprises.
DOI: 10.5220/0011554600003524
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Methods, Models, Technologies for Sustainable Development (MMTGE 2022) - Agroclimatic Projects and Carbon Neutrality, pages
57-61
ISBN: 978-989-758-608-8
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
57

in the energy sector; formation of energy
development models; conditions for building an
energy-efficient society as conditions for sustainable
development of the national economy, etc.
The purpose of the article is to study the
introduction of a modern management model of
energy-saving technologies at enterprises in an
information society.
The methodological and theoretical basis of this
work is the methods of analogy, expert evaluation,
comparison, research of domestic and foreign authors
in the field of modern management model of energy-
saving technologies at enterprises.
2 MANUSCRIPT PREPARATION
The balanced development of the economy, the
environment and society is at the heart of the problem
field of sustainable development. "Solving this
problem requires thoughtful actions that must be
carried out taking into account the interrelationship of
environmental, economic and social aspects"
(Bekmurzaev, 2021). If we consider the stages of the
formation of the concept of energy saving as a global
trend in the historical concept, we can distinguish four
stages.
Stage 1. The invention of accounting devices for
monitoring the volume of consumption of resources,
in particular energy. In developed countries, this falls
in the second half of the XIX century. The
introduction of scientific and technological
achievements in the activities of industrial enterprises
(in particular, steam-based technologies), as the latest
round of the industrial revolution, led to the need to
reduce production costs in order to maximize profits.
Stage 2. The first half of the XX century. The
creation of industrial giants, the active development
of transport and telecommunications networks has led
to a significant increase in the energy intensity of
products. The era of energy and industry of this
historical period can be divided into 2 stages: Fordism
and post-Fordism. Henry Ford is mainly credited with
the development of a modern mass production
system, as a result of the creation of a conveyor. Mass
production has significantly increased the energy
consumption of industrial enterprises.
Stage 3. The second half of the XX century. The
first global crisis in the energy sector in the 70s of the
XX century led to the "oil war", which has been
constantly happening for more than 30 years. The
United States began to create an alliance of oil-
importing countries like the "Anti-OPEC". In
December 1974, a conference was held in
Washington, at which the "International Energy
Agency" (IEA) was created. Formally, the IEA was
formed in order to determine joint actions by
participants in the event of a new energy crisis, as
well as to coordinate plans for better long-term
provision of energy sources (Tetreault, 1981).
The economy needed new cheap types of energy
– the emergence of nuclear power allowed to
significantly reduce energy costs, but raised the issue
of energy security to a new level. This issue is
particularly acute after the tragedy at the Chernobyl
Nuclear Power Plant in 1986. This was the second
shock in the sphere of the use of the atom, when the
problem of the survival of humanity as a whole arises.
The emergence of the last, 4th stage, was
additionally influenced by many other factors, but,
first of all, these are factors of global economic
transformations: the emergence of the Internet, the
achievements of industry 4.0, increased labor
migration, the expansion of the activities of
multinational companies, etc. In the global energy
sector, a new 4th investment cycle is being launched
these days, in which, according to the International
Energy Agency, such global trends will operate (Fig.
1).
Figure 1: Global trends of the 4th investment cycle in the
energy sector (Safe...).
Today, a new energy civilization is being formed
in the leading countries, the main features of which
are: energy efficiency; intelligent energy systems built
according to the Smart Grid concept; decentralization
of energy; new energy sources, etc. The development
of energy of the 4th investment cycle is implemented
within the framework of such models (Fig. 2).
new centers of
attraction for
investments are
being formed with a
lower "entry
threshold" than in
traditional energy
integration of new technological solutions,
new consumers and new suppliers
technological
progress forms
new solutions in
the energy sector
more and
more efficient,
cheaper
Global trends
gas market
restructuring: mobile,
competitive, with
developed distribution
restructuring of
business
processes
a
fundamental
change in
the nature of
demand and
the status of
energy
consumers
in the
market
MMTGE 2022 - I International Conference "Methods, models, technologies for sustainable development: agroclimatic projects and carbon
neutrality", Kadyrov Chechen State University Chechen Republic, Grozny, st. Sher
58
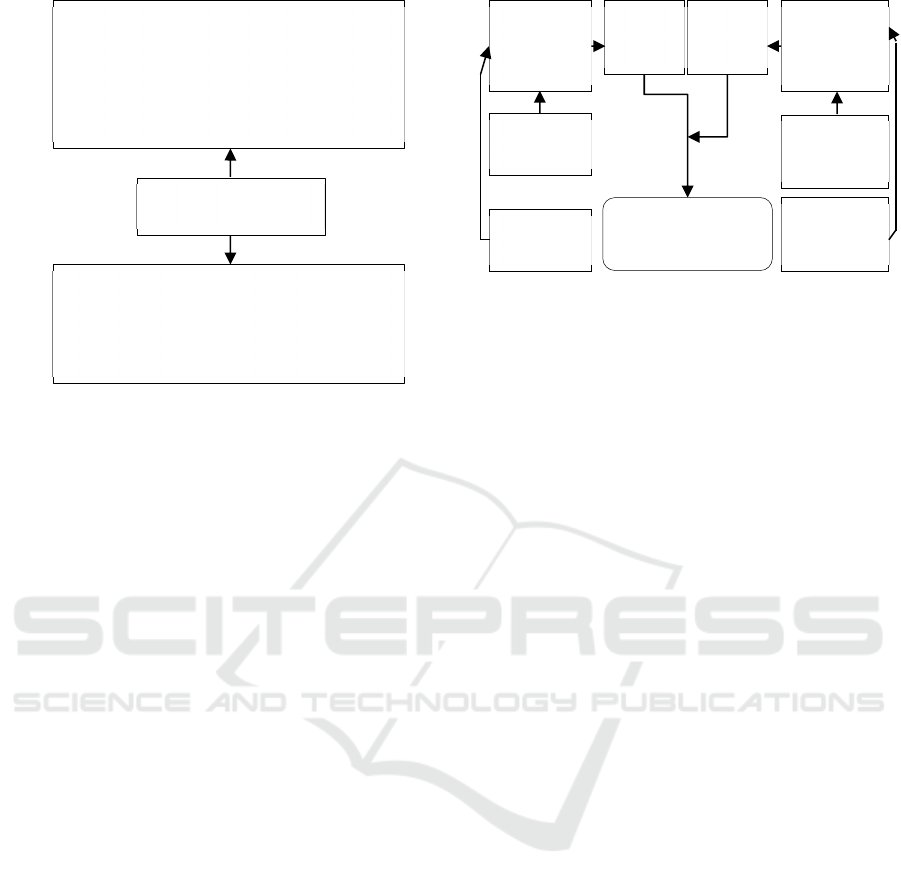
Figure 2: Architectonics of the formation of energy
development models of the 4th investment cycle (Azzuni,
2018).
The components of the activation of the "Energy
Efficiency+" development model in the medium term
are: the dominance of centralized energy; the
development of trigeneration; the development of
dispersed generation; economically sound
innovations; the development of smart energy models
in individual clusters (Smart Grid). There is no doubt
that the sustainable socio-economic development of
any country largely depends on the growth of energy
efficiency of the national economy.
Based on the conducted content analysis
regarding the definition of existing approaches to the
definition of the terms "energy saving" and "energy
efficiency", within the framework of this study, the
following definition of the term "energy saving is a
set of actions aimed at obtaining progressive results
regarding the rational and efficient use of energy
resources in order to save energy, reduce energy costs
and losses associated with the reduction of the
negative impact on the environment, the achievement
of a beneficial socio-economic effect" is proposed.
"Progressive results" means focusing on the
samples (countries, companies) with the highest
energy efficiency. This is possible by comparing
these indicators with estimates of the best and
advanced technologies (Best-in-Class) in the study
area based on determining the distance between the
studied result and the efficiency limit. Thus, it is
possible to determine energy efficiency categories
based on the Best-in-Class methodology in order to
realize the potential (Fig. 3).
Figure 3: Determination of the energy efficiency criterion
based on the Best-in-Class methodology in order to realize
the potential.
AB as a set of energy efficiency criteria is the
general set of world criteria (A) and national criteria
(B): AB = AΔB. At the same time, it should be noted
that in order to ensure the competitiveness of national
enterprises in world markets based on the energy
saving factor, national criteria should approach the
world ones: the covariant functor displays the
function f: B→A.
Each block of the subset A and B is a Boolean of
local exponents: 2
A
, respectively = {A1, A2}; 2
B
=
{B1, B2}. A subset of the second type under the
assumption of induction 2
A
or 2
B
, a subset of the first
type defines a subset of this type obtained from some
single subset of the second type by adding the element
a0, hence: 2A = A1 ᴗ A2 and A1 ᴖ A2 = ⊕. Each of
the minimums are the minimum criteria for energy
efficiency. So, if we define the criteria of
technological equipment as a technological basis for
ensuring the energy efficiency of an enterprise, we
can thus characterize this minimum. A1 "Theoretical
minimum" is the specific energy consumption
required to perform certain work or transform
materials in accordance with the laws of electro– and
thermodynamics; A2 "Practical minimum" is the best
in world practice indicators of specific energy
consumption when using commercially technologies
with a certain efficiency. Decomposition analysis can
be used to study the influence of factors affecting the
energy intensity of GDP (Table 1). This method is
recommended to be applied by the International
Energy Agency in the practical activities of
enterprises (Energy..., 2016).
The considered decomposition analysis is used for
a more detailed analysis of energy efficiency and
requires additional input data. In order to overcome
this disadvantage of the considered methodology, it is
necessary to determine the aggregated energy
efficiency, consisting of individual indicators: energy
the "Energy Efficiency+" model
1) development of nuclear energy, renewable energy sources;
2) launch of second wave energy efficiency programs (online
consumption management);
3) Carbon capture and sequestration technologies (Carbon
capture and sequestration - CCS)
4) increase in the fuel and energy balance of renewable
energy
the "New Paradigm" model
1) Smart Grid in the "active networks" version;
2) market liberalization in the field of generation, dispersed
generation
3) restructuring of cities (Smart City)
4) the market of energy capacities and the entry of a "buyer -
seller" into it
Energy development of the
4th investment cycle
В2
the best
national
indicators
А
World
criteria
А1
theoretical
minimum
АВ
energy efficiency
criteria
А2
practical
minimum
А3
average
international
indicators
В3
averaged best
national
indicators
В1
poor national
indicators
А
National
criteria
Introduction of a Modern Management Model of Energy-saving Technologies at Enterprises
59

intensity, electrical capacity and fuel capacity of
GDP.
The indicator of the energy intensity of GDP
reflects the trends in the development of the economy
at the macro level from the standpoint of energy
consumption with the definition of the appropriate
type of economic activity: intensive (energy-saving)
or extensive (energy-consuming). Energy-efficient
societies can successfully solve the problem of
efficient provision of energy resources for the
purpose of socio-economic development of the
country. At the same time, appropriate measures are
used in the state regulatory policy in order to increase
the influence of energy factors of stimulants on the
vector of social development based on the
optimization of energy costs.
Table 1: A logical-structural model of the influence of
factors leading to changes in the volume of final energy
consumption.
Factors
Economic secto
r
Industry Househol
d
Transpor
t
Activity
added value of
the total output
of goods
population
size
passenger
traffic or
cargo
volume
Structure
the share of
output of
various types of
products
number of
square
meters per
person
passenger
traffic or
cargo
volume for
transport
Performance
the amount of energy used per unit of activity in
each of the sectors of final energy consumption
In the XXI century, it is possible to solve the
problem of increasing the efficient use of energy
resources only by introducing the latest energy-
efficient technologies and equipment that meet the
appropriate stage of scientific and technological
progress. Unfortunately, in our country, only some
sectors of the economy are gradually switching to the
principles of Industry 4.0. At the same time,
developed countries began to discuss the specifics of
the entry of national economies already to Industry
5.0. Today, business efforts should be focused on
innovative development, especially in the field of
overcoming technical and technological
backwardness.
Energy efficiency is characterized by constant
changes that entail an increase in its level due to
economic, environmental and social components,
ensuring harmonious development at the micro, meso
and macro levels of any system. Increasing energy
efficiency ensures the achievement of energy
independence of the state and business entities, which
is defined as the use of fuel and energy resources
simultaneously with energy-saving production
technologies in order to meet the energy needs of
various entities in different spheres of functioning
without outside interference. At the same time, it is
advisable to cooperate at all levels: national, private,
public. Effective development of the domestic
economy requires public awareness that energy
efficiency is not just a condition for sustainable
development, but an indicator of the self-sufficiency
of the state, a marker of its readiness to be at the
forefront of innovative development, to attract
modern innovative technologies that will ensure
economic and energy independence.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Of all technically possible measures to ensure energy
efficiency, only some are economically feasible and
economically attractive for a certain period of time.
In order to determine the best way to achieve savings
as a result of investments in energy efficiency
projects, it is important to separate economically
sound and financially attractive projects. The
difference between economically sound investments
and economically attractive investments can be
explained by different discount rates between public
and private investments, the indirect impact of energy
savings and the impact of external factors.
When analyzing the transformation of scientific
approaches to determining the content of energy
saving and energy efficiency in enterprises, certain
features of development are highlighted. It is
necessary to consider in more detail the issue of the
development of the energy platform as a basis for
enterprise management based on the concept of
energy conservation. At the same time, it is necessary
to take into account the trends of the current stage of
development of an energy-efficient society,
especially the concept of Smart Grid.
REFERENCES
A safe Europe in the world. European Security Strategy.
https://www.consilium.europa.eu/media/30825/qc7809
568ruc.pdf.
MMTGE 2022 - I International Conference "Methods, models, technologies for sustainable development: agroclimatic projects and carbon
neutrality", Kadyrov Chechen State University Chechen Republic, Grozny, st. Sher
60

Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated
09.06.2020 No. 1523-r "Energy Strategy of the Russian
Federation until 2035", 2020. Ministry of Energy of the
Russian Federation,
https://minenergo.gov.ru/node/1026.
Azzuni, A., Breyer, C., 2018. Definitions and dimensions
of energy security. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews:
Energy and Environment. 7 (1), e268.
Bekmurzaev, I. D., Dadaev, Ya. E., 2021. Implementation
of Green, blue and circular economy concepts within
the sustainable development goals. Applied science and
engineering. 2442(1).
Di Somma, M., Yan, B., Bianco, N., Graditi, G., Luh, P.B.,
2015. Operation optimization of a distributed energy
system considering energy costs and exergy efficiency.
Energy Conversion and Management. 103. pp. 739-
751.
Energy efficiency indicators. Highlights, 2016. Statistical
report. International Energy Agency. p. 154.
Griffiths, T. L., Lieder, F., Goodman, N. D., 2015. Rational
use of cognitive resources: Levels of analysis between
the computational and the algorithmic. Topics in
cognitive science. 7(2). pp. 217-229.
Lieder, F., Griffiths, T. L., Huys, Q. J., Goodman, N. D.,
2016. The anchoring bias reflects rational use of
cognitive resources. Psychonomic bulletin & review. 25
(1). pp. 322-349.
MacElroy, J. D., 2016. Closing the carbon cycle through
rational use of carbon-based fuels. Ambio. 45 (1). pp. 5-
14.
Mady, C. E., Pinto, C. R., M.., 2020. Application of the
Second Law of Thermodynamics in Brazilian
Residential Appliances towards a Rational Use of
Energy. Entropy. 22 (6). p. 616.
Tetreault, M. A., 1981. Organization of Arab Petroleum
Exporting Countries: history, policies, and prospects.
https://www.proquest.com/openview/7992aabbcac3ee
807d5389a631fcca63/1?pq-
origsite=gscholar&cbl=1821138.
Zolotukhin, V. M., Gogolin, V. A., Yazevich, M. Y., 2017.
Environmental management: the ideology of natural
resource rational use. IOP Conference Series: Earth
and Environmental Science. 50(1). pp. 12-27.
Introduction of a Modern Management Model of Energy-saving Technologies at Enterprises
61
