
Modern Trends in the Development of Environmentally-oriented
Innovative Processes in Construction
Ismail Shakhgiraev
1a
, Salambek Aliyev
2b
and Naida Gasanova
3c
1
Chechen State University, Grozny named after A.A. Kadyrova, Grozny, Russian Federation
2
Grozny State Oil Technical University Named After Academician M.D. Millionshchikov, Grozny, Russian Federation
3
Dagestan State Technical University, Makhachkala, Russian Federation
Keywords: Ecologization of the economy, environmental audit, secondary raw materials, recycling, technology,
construction.
Abstract: The article discusses the main stages of the selection of innovative production technologies that are adapted
to the environmental and economic constraints in force in accordance with national and international
regulations on the state of the environment, and also take into account the social component as one of the
components of sustainable development. An algorithm for the step-by-step selection and evaluation of optimal
solutions is presented in compliance with environmental, economic and social imperatives based on the
principles of sustainable development. The ways of transition of the construction industry to a new conceptual
development framework are proposed, within which the priority is the cascade involvement of natural
resources in the production process and minimizing the volume of residual products. Analyzed and proposed
promising areas of application of information and environmentally-oriented technologies for predicting the
life cycle of an object with the possibility of its increase.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since the 70s of the last century, mankind has realized
that information about the state of the environment,
coordination of efforts to collect, store and process
and analyze it are a necessity for further existence. In
1970, under the auspices of the UN, the Stockholm
Conference on Environmental Protection was held,
where the Environmental Program (UNEP) was
adopted. It developed the basic concept of monitoring
and assessment of the state of the environment, as
well as common terminology (Agenda…). Since
then, economic entities can be legally liable for
environmental damage. This led to significant
additional financial losses that enterprises began to
experience. Financial and fiscal instruments caused a
shift in business philosophy towards compliance with
environmental legislation in their activities.
Outwardly, such measures are very reminiscent of a
financial audit. Therefore, the environmental review
procedure is called environmental audit (State…).
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6644-9519
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6644-9519
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3179-4889
The first companies to develop and implement
their own environmental review programs were US
Steel, Allied Chemical, and Occidental Petroleum.
Industrially developed countries were initially leaders
in environmental auditing. The environmental audit
procedure is used to resolve conflicts between carrier
companies and national environmental authorities.
The most common is a specialized environmental
audit on accounting for production waste, etc. It
should be noted that a modern environmental audit is
not only a check of the state of an enterprise for
compliance with the requirements of environmental
legislation, but also the basis for developing a set of
measures to prevent its possible violations (
Directive…). Thus, environmental audit is
transformed from an ordinary administrative tool for
monitoring compliance with the law into an economic
and legal tool for stimulating the environmental
activities of an enterprise.
Another type of non-state environmental audit can
be considered voluntary rating certification in the
Shakhgiraev, I., Aliyev, S. and Gasanova, N.
Modern Trends in the Development of Environmentally-oriented Innovative Processes in Construction.
DOI: 10.5220/0011568200003524
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Methods, Models, Technologies for Sustainable Development (MMTGE 2022) - Agroclimatic Projects and Carbon Neutrality, pages
183-188
ISBN: 978-989-758-608-8
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
183

manufacturing industry. Modern world standards on
the regulation of environmental parameters of the
architectural and construction industry concern
mainly the environmental, energy and economic
efficiency of the so-called "green buildings" (green
building) and are developed as systems. The best
known of these are BREEAM (building
environmental performance assessment method) and
LEED (leadership in energy and environmental
design) (Maliene, 2010). Today, more than 50
international agreements are in force abroad, which
directly relate to the issues of environmental
monitoring and auditing the state of enterprises and
adjacent territories. Special working groups have
been created, whose task is to develop
recommendations and action plans on environmental
monitoring for the countries of the world.
Environmental international policy is based on the
task of preventing the generation of waste, promoting
reuse, recycling and processing of waste into
biologically safe substances. The priority goal is to
turn waste into resources and reduce their generation.
Domestic legislation in this area, despite a fairly
developed regulatory framework, does not fully
comply with such requirements. So, the
implementation of these requirements is associated
with significant changes and additions in the legal
field. First of all, our country faces the necessity of
transition to a new conceptual basis of economic
development. Most sectors of the national economy,
which are resource-intensive due to direct
dependence on the raw material base, are built on a
linear model of the economy. The linear model
assumes an increase in resource costs in direct
proportion to production volumes, which contradicts
the problem of preserving valuable natural resources.
In contrast to the linear model of the circular
economy, it is focused on the continuous or cascade
turnover of technical and biological materials during
production and minimizing the volume of residual
products. This approach coincides with the biosphere-
compatible economic orientation and environmental
imperatives (Dedicoat, 2016).
The purpose of this work is to develop a
mechanism for managing the construction complex,
which ensures the transition of the construction
industry to a new conceptual development
framework, within which the priority is the cascade
involvement of natural resources in the production
process and minimizing the volume of residual
products. The mechanisms of greening the economy
and their success will depend on the correlation of
specific programs in each sector of the national
economy. The strategy of modernization of the
construction industry, as one of the resource-
intensive, is one of the serious problems of the
modern economy.
The methodological basis of the study is the
regulatory legal acts regulating the investment and
construction sphere, statistical data, methodological
developments and other literature on the study of the
innovative construction complex and ecological
construction.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
In Russia, the main component of the environmental
assessment system is an environmental review, which
is organized and carried out by the Federal Service for
Supervision of Natural Resources. “Environmental
expertise in our country is the establishment of
compliance of documents and (or) documentation
substantiating the economic and other activities
planned in connection with the implementation of the
object of environmental expertise, with
environmental requirements established by technical
regulations and legislation in the field of
environmental protection, in order to prevent negative
impact such activities on the environment”
(Federal…). Directive 2008/98/EC of 2008 on waste
introduced measures to protect the environment and
human health by preventing or reducing the negative
impacts of production and waste management, as well
as reducing the overall consequences of the use of
resources and increasing the efficiency of such use.
This document is based on the ambitious goal of
moving closer to the “recycling society”. It prioritizes
recycling measures, encourages separate collection of
waste and reuse of products. The directive sets out the
criteria for classifying waste as a by-product and the
procedures by which the status of waste ends, when
the waste is no longer considered waste, but a
potential resource. Advantages are given to
technologies based on energy resources from
renewable sources and secondary raw materials. But
such a condition is a limitation not only in the use of
primary environmental resources (as a cause), but
also in economic development (as a consequence).
The concept of limitedness in relation to the natural
environment has several vectors: limitedness of the
main natural resources and energy sources necessary
to continue the process of development and economic
growth; limitation of the main components of the
environment, characterizing its qualitative
parameters, assessment of the state, which is derived,
on the one hand, from the amount of emitted
pollution, on the other hand, from the ability of
MMTGE 2022 - I International Conference "Methods, models, technologies for sustainable development: agroclimatic projects and carbon
neutrality", Kadyrov Chechen State University Chechen Republic, Grozny, st. Sher
184

various ecosystems to self-regulate; limitation in the
socio-economic dimension, which is associated with
the demand (demand) for a clean environment, that is,
the limitation in meeting the needs of a psychological,
aesthetic recreational nature by various elements of
the natural environment; limited functions of
terrestrial ecological systems as the natural capital of
the planet.
All over the world, the ecological concept of the
development of the construction industry, called
"Green Building", is becoming more widespread.
Ecological construction is aimed at solving the issues
of the qualitative component of construction through
the use of environmental technologies in the
planning, design, construction, operation and disposal
of buildings. The use of such technologies allows
minimizing the harmful effects of the construction
industry on the environment and humans. Thanks to
the use of "green" technologies, the reduction of
atmospheric and water pollution, the conservation of
natural resources, and the improvement of comfort
and safety of indoor premises are achieved.
The tool for the examination of a construction project
for compliance with the presence of "green"
technologies in it, determining its level of quality, is
the Certification System for "green" buildings
(Sukhinina, 2013). “The idea of sustainable
development has evolved significantly from the
principle of “greening” the economy, that is, from the
relationship between man and nature, to the principle
of a stable economy without increasing the capacity
to use irreplaceable natural resources” (Shakhgiraev,
2019). The main problem at the microeconomic level,
where environmental and economic problems are
localized, is the need to make a difficult choice
between economically exalted and biosphere-
compatible technical progress. Not every new
production technology that is beneficial in terms of
labor and capital productivity is environmentally
sound. This means that the technology must be
assessed against an environmental standard, in terms
of emitted pollution and/or in terms of the use of
original natural resources. Thus, the choice that
enterprises make in connection with the greening of
new technologies and products will depend not only
on economic factors (economic calculation), but also
on mandatory legal regulation and environmental
expertise - especially in the case of productive
innovations - on knowledge and environmental
awareness of consumers and the economic benefits
they produce.
That is, the assessment of a new technology by a
business entity is to determine the balance between
choice and limitations. It is difficult to make a choice
in favor of a cost-effective technology that would
meet environmental standards and could be
implemented in a certain region, based on material,
technical and human resources, without a
qualitatively new methodology and tools for
environmental and economic analysis. Figure 1
shows the allocation of a biosphere-compatible
production technology, taking into account the
limitations of the environmental and economic
aspects of development.
Figure 1: The choice of innovative technology under
environmental and economic constraints.
The complexity of the choice is also
predetermined by the multi-vector nature of
environmental policy, that is, a kind of excess of goals
that, in conditions of limited financial, material and
labor resources, cannot be simultaneously
implemented. Therefore, it is necessary to evaluate a
promising technology according to such a cumulative
indicator that takes into account environmental and
economic constraints, the financial possibilities of the
present and is capable of transformation over time in
accordance with changes in the legal and
technological environment. The sequence of selection
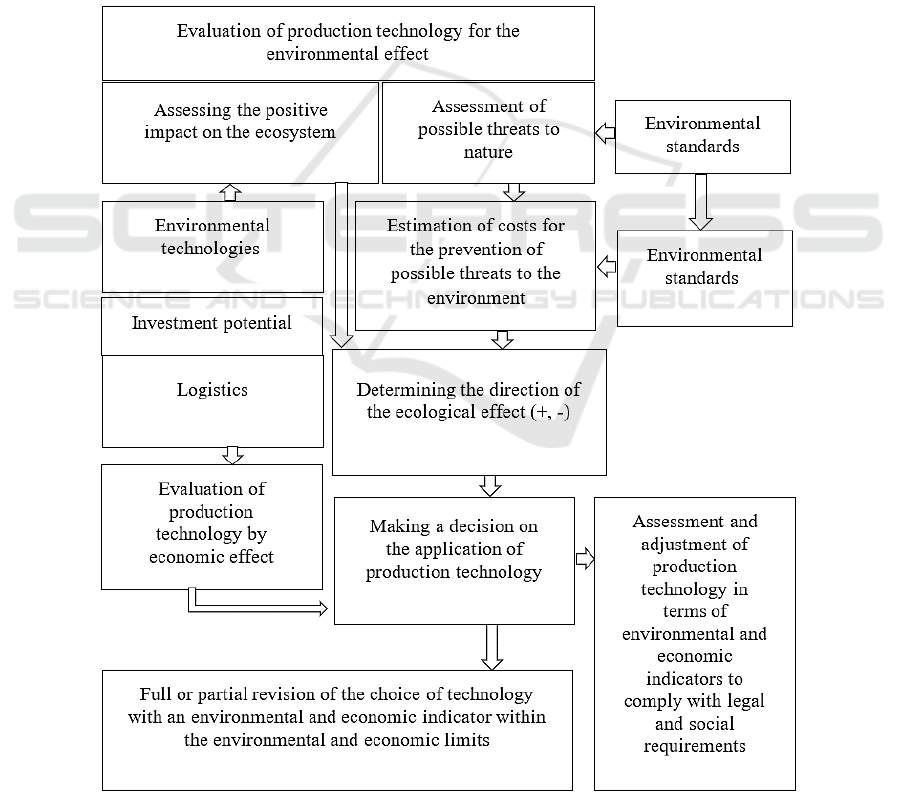
and evaluation of rational production technology is
shown in Figure 2.
The algorithm can be adapted to any industry with
the addition of specific blocks of restrictions and
variable blocks that characterize the features and
stages of the choice of technological solutions. The
base of environmental technologies for the
construction industry should be formed according to
the fundamental principle of world standards in the
field of waste management, namely, reducing the
amount of waste that is sent to the final disposal. To
do this, all technologies related specifically to
construction (design of buildings and structures,
production of building materials, semi-finished
products, structures and products) should be aimed at
Environmental
restrictions
Economic
restrictions
Design stage
Production analysis of
the project
Human resources
assessment
environmental
technology
Financial
opportunities
(investments);
Logistics;
Effective
economic
technologies.
environmental
standards;
Environmental
technologies;
Environmental
assessment.
Modern Trends in the Development of Environmentally-oriented Innovative Processes in Construction
185
applying a clear waste management hierarchy. The
priority is the principle of preventing the formation of
construction waste, minimizing (or no) recycling.
Despite the fact that the contribution of human
capital to the dynamics of economic indicators is
increasing every year, the growth in the use of
primary natural resources continues to grow. It should
be taken into account that the depletion of mineral
reserves and the degradation of the environment that
accompanies the extraction of raw materials reduces
public welfare, i.e. statistically, these processes
should reduce the rate of economic growth. This
circumstance makes us take a different look at the
recycling of materials, since the recycling of
resources can be considered as a new, largely hidden
source of economic growth without negative
consequences for the environment.
It is believed that recycling can significantly
reduce the use of natural resources. The launch in
2018 of the Circular Economy Initiative in Germany,
one of the pioneering activities in this area, included
discussions in the scientific community about the
potential of recycling for the country's economy, as
well as the development of a roadmap for political
action, as important tasks. Calculations showed that
recycling, service life extension and energy efficiency
will reduce the consumption of primary raw materials
by 68% by 2050. It is expected that the accelerated
development of the recycling market and green
technologies will make a significant contribution to
this process. The Circular Economy Roadmap for
Germany 2021 notes that only about 13% of the
resources consumed in the country are currently
derived
from recycled materials (taking into account
Figure 2: Algorithm for selecting and evaluating rational technology within the scope of environmental and economic
restrictions.
MMTGE 2022 - I International Conference "Methods, models, technologies for sustainable development: agroclimatic projects and carbon
neutrality", Kadyrov Chechen State University Chechen Republic, Grozny, st. Sher
186

intermediate consumption, this figure increases to
18%) (Kadner, 2021), in general In the European
Union, 11.9% of the raw materials and materials used
in 2019 were obtained by recycling waste
(Sustainable…).
The process of reuse of waste for the same
purpose after their processing - recycling of building
materials and structures - is one of the areas of
greening building technologies. Today in our country
there is no single cost estimate for a project using
recycled construction waste, and the lack of a
regulatory framework does not contribute to the mass
dissemination of environmental solutions. It should
also be noted that the cost of processing secondary
raw materials is too high, primarily due to the lack of
proper initial sorting; secondly, there is no effective
system of control and punishment for non-
compliance with environmental standards; thirdly,
the collective socio-ecological consciousness of the
community, aimed at maintaining non-material
values, has not been formed. The way to overcome it
is the centralized introduction of a system of
mandatory processing of construction waste and its
recycling, the subordination of design technological
and economic solutions to environmental restrictions
and the principle of balanced nature management;
technological re-equipment of construction
production under environmental control by the state.
At the same time, IT technologies should be more
widely introduced into the process of the entire life
cycle of an object - from the stage of conceptual
development, design through the stages of
construction and operation to dismantling. This
makes it possible to implement many aspects of
environmental and economic development, namely:
timely assessment of the state of a construction object
in order to ensure a warranty and post-warranty
period of operation to extend the life cycle; designing
the timing and scope of modernization,
reconstruction, disposal of a construction site to
predict the production capacities of construction and
processing enterprises; introduction of new concepts
in the approach to the design of buildings and
structures that would take into account changes in the
functional feasibility of objects in the real estate
market - the concept of functional transformation.
3 CONCLUSIONS
Domestic legislation requires revision in order to
harmonize the conceptual apparatus, in particular, the
provision of definitions for the concepts of "separate
collection", "prevention of education", "reuse", "best
available technologies".
But for the effective implementation of world
standards, it is not enough just to harmonize the legal
aspects. For the construction industry, it would be
appropriate to stimulate processing production,
recycling, the introduction of new design concepts
aimed at increasing the life cycle of an object by
universalizing primary architectural and design
solutions based on the biosphere compatibility
paradigm. In this regard, it requires the development
and adjustment of building codes that would regulate
the boundaries of the use of construction scrap as a
structural material. This would lead to the expansion
of the use of recycling and products from secondary
raw materials without the introduction of fiscal
mechanisms for environmental audit. Technology is
a necessary factor for economic development and
growth. There is no doubt that new technologies
provide an advantage in economic development. But
in the context of environmental restrictions imposed
on economic growth, it would be wrong not to take
into account the social component of sustainable
development. Ecologization of the economy is
accompanied by a shift in the center of economic
analysis from costs and intermediate results to the
final results of economic activity and further to
predicted development trends in accordance with the
principles of social responsibility. Therefore, the
achievement of balanced socio-ecological and
economic solutions should be based on a change in
the ecological and economic orientation of the
structure of human needs and standards of well-being
in the direction of rejecting the dictates of supply and
artificially stimulating secondary needs.
REFERENCES
Directive No. 2008/98/EC on waste and the repeal of a
number of Directives. Ministry of Energy and
Environmental Protection.
https://web.archive.org/web/20170925181621/.http://n
arodirossii.ru/?p=15667.
Dedicoat, K., 2016. Circular economy: what it means, how
to get there. pp. 52-68.
State of play with extended producer responsibility,
opportunities and challenges, 2014. Global
Environment Forum, pp. 58-64.
Agenda for the 21st century. United Nations Conference on
Environment and Development. Rio de Janeiro, 1992.
Sukhinina, E. A., 2013. Basic provisions and comparison of
international environmental standards in the
construction industry. Bulletin of the Saratov state.
tech. university. 1(73). pp. 209-215.
Modern Trends in the Development of Environmentally-oriented Innovative Processes in Construction
187

Federal Law No. 174-FZ of November 23, 1995 (as
amended on July 2, 2021) “On Environmental
Expertise”. Electronic fund of legal and normative-
technical documents.
https://docs.cntd.ru/document/9014668.
Shakhgiraev, I. U., 2019. Green structures in the concept of
sustainable development of modern cities. Regional
building complex: investment practice and
implementation of PPP: materials of the All-Russian
scientific and practical conference. p. 376-383.
Kadner, S., Kobus, J., Hansen, E., 2021. Circular Economy
Initiative Deutschland: Circular Economy Roadmap
for Germany. Munich/London: acatech/SYSTEMIQ. p.
104.
Maliene, V., Deveikis, S., Kirsten, L., Malys, N., 2010.
Commercial Leisure Property Valuation. International
Journal of Strategic Property Management. 14(1). pp.
35-48.
Sustainable development in the European Union:
Monitoring report on progress towards the SDGs in an
EU context, 2021. Eurostat. p. 412.
MMTGE 2022 - I International Conference "Methods, models, technologies for sustainable development: agroclimatic projects and carbon
neutrality", Kadyrov Chechen State University Chechen Republic, Grozny, st. Sher
188
