
Sustainable Development of the Metallurgical Industry based on the
Development of Waste-free Technologies and an Environmentally
Oriented Economy
Ilya Igumenov Maximovich
1
, Galina Pavlovna Gagarinskaya
2,3
,
Alexander Vladimirovich Gagarinsky
4
, Alexander Alexandrovich Khorovennikov
5
and Danila Alexandrovich Nekorysnov
1
1
Samara State University, Samara, Russia
2
Moscow State University of Technologies and Management Named After K.G. Razumovsky (PKU), Moscow, Russia
3
Volga Cossack Institute of Management and Food Technologies, Dimitrovgrad, Russia
4
Moscow State Pedagogical University Samara Branch, Samara, Russia
5
Samara State Transport University, Samara, Russia
Keywords: Environmentally-oriented economy, labor productivity, innovation, lean manufacturing, green economy.
Abstract: The article presents innovations in the organization of labor activity and personnel management of an
industrial enterprise. The topic of lean and eco-friendly production has been actively analyzed. The
unrestrained uncontrolled growth of the market economy leads to an increase in consumption and production
of goods, natural resources used for this, to an increase in harmful emissions and production waste into the
biosphere (environment). Humanity has come to an increasingly acute contradiction between its growing
needs and the inability of the biosphere to provide them with resources without collapsing. Aluminum is
called a material for the "green economy".
1 INTRODUCTION
The problem of studying the sustainability of the
development of the economy of the metallurgical
sector of industry is becoming increasingly important
today. This is due to the fact that one of the most
important problems in the organization's activities is
the insufficiently effective use of working time by
staff. The relevance of the study of this problem is
determined by the peculiarities of modern reality,
when the internal environment of the organization
becomes more complex, and the external
environment requires the organization to constantly
search for improving work efficiency.The working
time of most employees of modern organizations is
condensed to the limit, the working day is not
standardized, and yet it is often not possible to
complete all the planned tasks by the specified
deadline, and the results of the activity itself do not
always satisfy the management. Therefore, the
problem of managing the rationalization of the use of
working time by personnel as society develops,
increasing the dynamism of changes, increasing the
"information component" in the final product,
becomes a significant factor in the effectiveness of
the organization.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The methodological basis of the research consists of
general scientific dialectical, systemic and situational
approaches, laws of logic, typology, basic provisions
of economic theory and entrepreneurship theory, as
well as methods of economic and mathematical
modeling, economic analysis and synthesis, empirical
generalization, etc.
The empirical basis of the study was the official
information of the Federal State Statistics Service, the
Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian
Federation, the Ministry of Energy of the Russian
Federation, open sources of petrochemical companies
and their divisions (Rosneft Oil Company, Gazprom
Neft, Sibur Holding, etc.), published materials and the
results of research by domestic and foreign scientists,
and also, the primary information of economic
research carried out with the direct participation of
the author for fourteen years (2008-2021)
300
Maximovich, I., Gagarinskaya, G., Gagarinsky, A., Khorovennikov, A. and Nekorysnov, D.
Sustainable Development of the Metallurgical Industry based on the Development of Waste-free Technologies and an Environmentally Oriented Economy.
DOI: 10.5220/0011570800003524
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Methods, Models, Technologies for Sustainable Development (MMTGE 2022) - Agroclimatic Projects and Carbon Neutrality, pages
300-305
ISBN: 978-989-758-608-8
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

(Chapman,2003; Das, 2004; Marler, 2010; Stone,
2009).
In the development of industry, along with large-
scale investment projects, the following characteristic
stages can be distinguished: over the past 15-20 years
- the development and expansion of the application of
the concept of lean manufacturing; over the past 10
years, the addition to the "lean" environmental
agenda; in recent years and months, the transition to
the concept of sustainable development, including the
above and the social sphere.
The concept of lean manufacturing was developed
by Toyota, which was actively perceived and
developed by a large number of companies around the
world. With its adaptations and features, with
different names, this system of continuous
improvements, involving as many employees as
possible, has become an integral part of the
production and overall business activities of all
modern successful metallurgical companies. This
experience is reflected in a large number of book
publications, articles, studies and essays (Marler,
2010; Schmidt).
The unrestrained uncontrolled growth of the
market economy leads to an increase in consumption
and production of goods, natural resources used for
this, to an increase in harmful emissions and
production waste into the biosphere (environment).
Humanity has come to an increasingly acute
contradiction between its growing needs and the
inability of the biosphere to provide them with
resources without collapsing.
Awareness of this problem led to the idea and
strategy of sustainable development of global
civilization, states, regions, industrial companies and
enterprises.
Locally, in a number of regions of agglomerations
and single-industry towns, there is a significant
excess of emissions over absorption. The Federal
project "Clean Air" has set a goal to reduce harmful
emissions by 20% in 12 major industrial centers by
2024. In his annual message, the President proposed
to expand such quotas to all cities where the problem
of air quality is acute, and there are more than 40 of
them in the country (Das, 2004; Sapunova, 2018).
In general, over the next 30 years, i.e. by 2050, the
task has been set to ensure in the Russian Federation
a better net result on the difference between emissions
and absorption of greenhouse gases than neutral in the
European Union. This goal is quite achievable with
an active policy of decarbonization of industry and
the economy, with a significant potential for the
absorption of greenhouse gases.
Responsible industrial corporations and
companies, including metallurgical ones, create and
implement their development strategies and programs
that provide for a significant reduction in energy
consumption and harmful emissions in the regions
and places of their production locations.
Among the metallurgical companies, the
production of aluminum and metal products from
aluminum alloys is interesting. Aluminum is called a
material for the "green economy". Firstly, it is
produced in the Russian Federation mainly using
renewable sources of electricity (HPP). Secondly, the
waste from this during production or during disposal
(at the end of the life cycle of the final products) is
fully involved in production cycles. Thirdly, the use
of aluminum and its alloys due to their unique
properties provides a low mass of structures,
sufficient strength, high corrosion and cryogenic
resistance, etc., brings an improvement in the
technical characteristics of products and benefits in
their operation, both economic and environmental.
The figure 1 shows the areas of application of
aluminum.
Figure 1: Areas of aluminum consumption by industry (%).
The priorities of the aluminum industry in
developed countries include the expansion of the use
of aluminum in various consumer industries and the
development of production of products with high
added value. Russian aluminum production
enterprises have been merged into RUSAL
Corporation. At the end of last year, they produced
3.75 million tons of aluminum. The corporation
positions itself as a manufacturer of products with a
low carbon footprint, which is less than 4 tons of
CO2
Sustainable Development of the Metallurgical Industry based on the Development of Waste-free Technologies and an Environmentally
Oriented Economy
301

per ton of metal. Mainly due to the fact that the energy
of hydroelectric power plants (HPPs) is used in the
production of aluminum. The global average is 12
tons of СО
2
. In China, the largest producer of
aluminum, where coal plants form the basis of
energy, the carbon footprint reaches up to 18 tons per
ton of metal (Strohmeier, 2007; Tzafrir, 2005).
RUSAL has registered its own brand of "low-
carbon" aluminum Allow, including for its more
successful promotion with the "green brand" on the
world market. RUSAL plans to develop its
advantages, has begun a large-scale modernization of
its four largest plants in Krasnoyarsk, Bratsk,
Shelekhov (near Irkutsk) and Novokuznetsk. This
project will require 380 billion rubles and is designed
for 2022-2027. RUSAL expects that by updating
production and switching from the traditional
electrolysis technology used worldwide to the
prebaked anode electrolysis technology, it will make
its aluminum production even more productive,
environmentally friendly and economical.
Along with aluminum producers (RUSAL, etc.),
manufacturers of metal products made of aluminum
alloys (tapes, sheets, profiles, pipes, rods, stampings)
adopt and implement their strategies and programs for
the transition to "green technologies" and "green
metal products" together with increased productivity.
So, for example, Arconic Corporation (Arconic),
which includes the company Arconic SMZ JSC
(hereinafter SMZ - Samara Metallurgical Plant), due
to the "greening" of their technologies, significantly
improved environmental indicators for 2020 -
according to the corporation, greenhouse gas
emissions were reduced at plants around the world (-
14%), consumption energy (-12%) and water (-8%);
SMZ reduced the consumption of electricity (-6%),
gas (-7%) and water (-13%) (Sarukhanyan, 2016)
(Sarukhanyan, 2016;GOST R ISO 14001-2016).
In 2020, SMZ once again confirmed compliance
with the requirements of the international
environmental standard ISO 14001, and also received
professional recognition from the international
organization ASI (Aluminum Stewardship Initiative),
which develops and promotes standards for
responsible management of aluminum production
and marketing. In the annual regional competition of
the Samara region "Eco-leader – 2020", SMZ took
first place in the nomination "Industrial Giant".
Constant investments help the plant to comply with
advanced technologies and environmental standards:
since 2005, USD 0.5 billion have been allocated for
the modernization of the SMZ, including for the
improvement of environmental protection and
industrial safety systems – more than USD 40 million.
A multi-year program for the conservation of the
biodiversity of the Samara region, which is supported
by the Arconic Foundation, contributes to the
protection of the ecological well-being of the Samara
region. Over 5 years, the Fund has allocated USD 235
thousand for the implementation of environmental
projects in the Samarskaya Luka National Park and
the Zhiguli State Reserve (Amrutha, 2020; Zakharov,
2019).
Arconic and SMZ aluminum metal products can
be attributed to the leaders in environmental
friendliness – to "green semi-finished products".
Their use in subsequent technological conversion
industries (packaging, mechanical engineering,
construction, etc.), producing the final "green
products", carries not only an improvement in the
technical characteristics of products and economic
benefits, but also positive environmental effects.
3 RESEARCH RESULTS
An example of a "green metal product" of SMZ is an
aluminum tape for beverage cans. Aluminum can is a
leader in recycling and environmental friendliness.
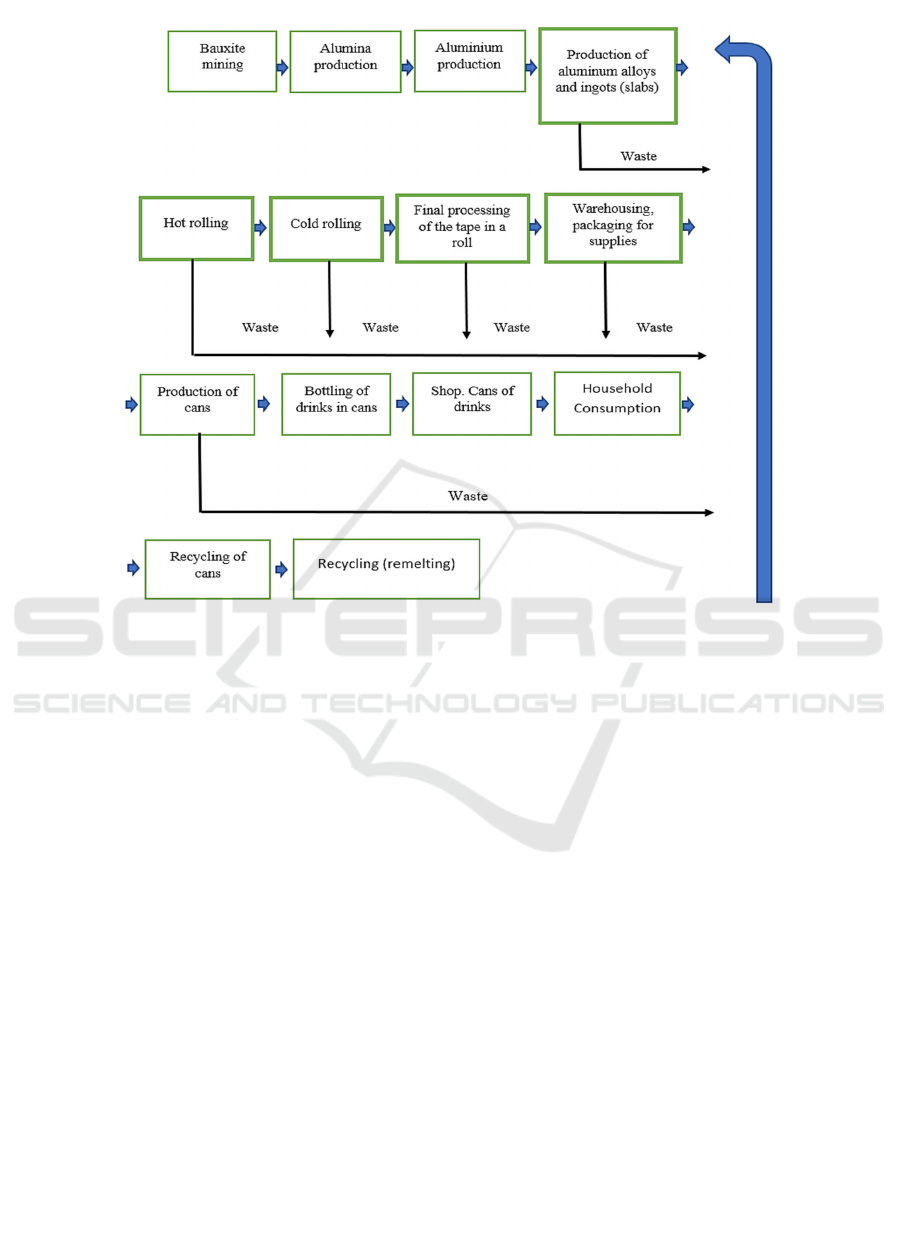
The figure 2 shows the scheme of production and
recycling of aluminum, tin tape and cans. From 4 tons
of bauxite, 2 tons of alumina are obtained, of which 1
ton of aluminum. Further along the production cycle
and recycling, all waste (there is a permanent program
to reduce them) and recycled cans are fully involved
in production. Treatment and recycling of one
aluminum can (0.5 liters – 14 grams) instead of
producing an appropriate amount of primary
aluminum by electrolysis, prevents the release of 100
grams of
CO2
. In Russia, there are factories for the
production of aluminum cans with a total output of
several billion pieces per year. Aluminum alloys, due
to their advantages, are increasingly used in transport
engineering. Arconic Corporation is actively working
in this direction. Along with the supply of metal
products for the aircraft industry, Arconic, together
with manufacturers of ground transport equipment,
participates in the creation of new types and models
of machines using aluminum parts and structures. The
corporation's enterprises master and supply the new
types and sizes of metal products necessary for this.
For example, Ford uses an all-aluminum body made
of Arconic sheets and profiles in the manufacture of
the F-150 SUV pickup truck. SMZ initiates and
participates in a number of projects for the use of its
products in special road and rail transport. Examples
of such machines are railway hoppers – for the
transportation of bulk products, tankers for the
MMTGE 2022 - I International Conference "Methods, models, technologies for sustainable development: agroclimatic projects and carbon
neutrality", Kadyrov Chechen State University Chechen Republic, Grozny, st. Sher
302
transportation of fuel, aggressive acids and cryogenic
liquid products, etc. The bodies and tanks for them
are made of aluminum metal products with special
properties. Compared with steel analogues, the load
capacity increases, energy costs and
CO2
emissions
decrease, corrosion resistance and service life
increase, intrinsic safety is guaranteed (important
when transporting fuel), etc (Teo, 2001; Ryazantsev,
2020).
The social sphere is the sphere of human capital,
its condition and development: employees of the
company and the surrounding community. For
employees, these are, first of all, conditions for safe
and comfortable work, conditions of remuneration
and social package, conditions for training and
development, conditions for equality and fairness, for
involvement in improvements in all spheres and
business processes. For the community, this is the
company's activity to improve the ecology and socio-
cultural environment, to improve the professional
level and vocational guidance of young people in
places (locations) of activity, etc. Attention is also
paid to the younger generation – through career
guidance programs at school, robotics classes, etc.
The corporation and the plant cooperate with
universities and colleges in the locations of the main
required specialties. Meetings are held with
applicants and students.
Labor productivity is one of the most important
means (factors) and methods of sustainable
development and is the subject of modern research in
the field of economic and social sciences. Systematic
work to stimulate its growth is carried out through
specialized centers of competence and labor
productivity growth created in a number of countries
(an overview of which is given in our article). At the
same time, recent research papers often emphasize
the importance of social growth factors along with
technical ones. Attention is paid to the introduction of
lean manufacturing practices and organizational
culture modernization programs (Sapunov, 2021;
Simionescu, 2020).
There are various metrics to measure
performance. Their choice for specific research is
determined by the policy vector, as well as the
availability of data. The coefficient used to evaluate
labor productivity allows you to evaluate the
efficiency of using resources for the production of
goods and services. In this case, both total
employment and the total number of hours worked
can be considered as indicators of resource
utilization.
Figure 2: Aluminum production and recycling of aluminum tape and cans.
Sustainable Development of the Metallurgical Industry based on the Development of Waste-free Technologies and an Environmentally
Oriented Economy
303

One of the most widely used approaches at the
country level is the measurement of labor
productivity as gross domestic product (GDP) per
hour of work. Productivity that takes into account
working hours is more indicative in terms of
reflecting labor costs than productivity that takes into
account the number of employees (OECD, 2019). If
you rely on the number of employees, the study will
miss the impact of the development of part-time and
overtime work (Das, 2004; Ryazanov, 2021).
The disadvantage of using the number of hours
worked in the denominator of the formula is the
complexity of obtaining statistical data and their
reliability. Even in developed countries, working
hours are most often recorded in terms of the number
of hours paid, rather than the actual hours worked.
Accordingly, such non-working hours as paid annual
leave, sick leave, maternity leave, parental leave, etc.
are not adjusted. There is a common situation when
statistics are collected only for certain categories of
workers (only for employees) or for certain categories
of enterprises (belonging to key sectors of the
economy or having a sufficiently large size) (ILO,
2015). For underdeveloped countries, these problems
are getting worse.
The models that allow the country to achieve a
high level of labor productivity are:
1) low cost of the final product with a large
volume of production and a low percentage of
employees (typical for Arab countries
specializing in oil production);
2) production of expensive products with a high
(or at least average) percentage of the
employed population (typical for the United
States and most Western European countries);
3) production of expensive products with a low
percentage of the employed population.
Labor productivity in a broad sense includes the
productivity of materialized labor (characterized by
the profitability of capital investments) and the
productivity of human labor (characterized by the
volume of production). When forming the policy of
labor productivity management, special attention is
paid to the technical side of the issue - the purchase
of new equipment, the introduction of resource-
saving technologies, modernization of production
lines, etc. All this requires additional costs, as it is
associated with investment activities. In a resource-
constrained environment, more and more companies
decide to activate their internal reserves and develop
measures aimed at increasing labor productivity
through the proper organization of the workspace,
business processes and the introduction of lean
manufacturing technologies.
The main provisions of the scientific organization
of labor are:
− improvement of labor specialization,
− improvement of workplace organization,
− improvement of working methods,
− optimization of the labor force rating,
− staff training (Krivov, 2016).
One of the modern forms of labor specialization is
outsourcing of non-core functions, standard and mass
operations using similar algorithms for different
enterprises. The obvious advantages of outsourcing
are the absence of the need for investments in
specialized equipment and training of qualified
employees, the guarantee of uninterrupted operation,
the possibility of applying the best practices and
experience, as well as the ease of control "by results".
At the SMZ, for example, vehicles used to deliver
products to customers have been outsourced.
Within the framework of personnel management
at a new level of automation, such tools for improving
the efficiency of employees' working hours as
timekeeping and photographing working hours, as
well as standardization of operations, have become
widespread.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The methods used to assess the level of labor
productivity often do not reflect the real picture. This
makes it difficult not only to conduct international
comparisons, but also to assess changes in dynamics.
Analysis of some existing methods and
performance management policies has shown that
they can be divided into two groups. The first is
focused on the use of reserves, optimization of
existing business processes, production, logistics, etc.
The second involves additional investments and is
aimed at introducing modern technologies. The latter
will be effective only if all the processes at the
enterprise are sufficiently developed and fixed, and
the organizational culture corresponds to the goals
and objectives of the company (Bikmukhametova,
2019).
Building a policy of labor productivity
management, most countries rely on small and
medium-sized businesses, form effective consulting
and methodological support for enterprises
participating in the program, and create regional and
industrial support centers.
The question of whether labor productivity is a
source of structural changes or, conversely, arises as
a result of economic restructuring remains debatable.
MMTGE 2022 - I International Conference "Methods, models, technologies for sustainable development: agroclimatic projects and carbon
neutrality", Kadyrov Chechen State University Chechen Republic, Grozny, st. Sher
304

A number of economists note in their works that the
problem of labor productivity management is not so
relevant and does not require special attention, it is
necessary to focus on managing domestic demand
and developing tools to stimulate it. In our opinion,
labor productivity management is the most important
condition for ensuring sustainable socio-economic
development. In the conditions of the demographic
trap, the growth of labor productivity will ensure a
decent level and quality of life of the population, the
restructuring of the economy to a new regime. At the
same time, labor productivity should be understood in
a broad sense, when not only technical growth factors
play an important role, but also the transformation of
social and organizational components, the
involvement of all employees in a continuous process
of improvement. Only an integrated approach can
ensure the achievement of growth targets and the
stability of the economic system.
REFERENCES
Chapman, D. S., Webster, J., 2003. The use of technology
in the processes of recruitment and selection of
candidates for work. International Journal of Selection
and Evaluation. 11. pp. 113-120.
Das, T. K., Teng, B. S., 2004. The risk-based view of trust:
a conceptual framework. J. Bus. Psychol. 19(1). pp. 85-
116.
Marler, J. H., Fisher, S. L., 2010. An evidence-based review
of e-HRM and strategic human resource management.
Stone, D. L., Lukaszewski, K., 2009. An extended model of
factors influencing the adoption and effectiveness of
electronic human resource management system.
Human Resources Management Review. 19. pp. 134-
143.
Strohmeier, S., 2007. E-HRM research: overview and
implications. Review of Human Resource Management.
17. pp. 19-37.
Teo, T. S. H., Soon, L. G., Fedric, S. A., 2001.
Implementation and impact of Human Resources
Information Systems (HRIS). Research and Practice in
the field of human resources. Management. 9. pp. 101-
117.
Tzafrir, S., 2005. The relationship between trust, HRM
practices and firm performance. Int. J. Hum. Resour.
Manag. 16(9). pp. 1600-1622.
Schmidt, A. V., The Development of Human Capital on the
Basis of Wage Efficiency. Sochi Journal of Economy,
pp. 300-307.
Schmidt, A. V. Forms of the organization's contribution to
the development of human capital, Research,
systematization, cooperation, development, analysis of
socio-economic systems in the field of management
economics: proceedings of the III All-Russian School-
Symposium of Young Scientists. pp. 236-240.
Ryazantsev, S. V., Arkhangelsky, V. N., Vorobyova, O. D.,
2020. Demographic development of Russia: trends,
forecasts, measures. National Demographic Report -
M.: LLC "United Edition", p. 156.
Sapunov, А. V., Sapunova, T. A., Bagyan, G. A., 2021.
Analysis of the current demographic situation in the
russian federation. Journal of Natural and
Humanitarian Studies. 33(1). pp. 187-189.
Sapunova, T. A., Gordeychik Yu. A., 2018. Problems of the
demographic crisis in Russia. Vector of Economy.
5(23). p. 22.
Sarukhanyan, L. A., 2016. Problems of the institution of
marriage in the Russian Federation. International
Journal of Applied and Fundamental Research. 11-4.
pp. 775-777.
Shchelakova, V. A., Negreeva V. V., Salmanov A. B.,
2019. Assessment of the demographic situation to
ensure the national security of Russia. Scientific journal
of National Research University ITMO. The series
"Economics and Environmental Management". 3. pp.
77-81.
Simionescu, M., Krivokora, E., Fursov, V., Astakhova, E.,
2020. Problems of development of the labor potential
of the regions of the russian federation, taking into
account their differentiation. Terra Economicus. 16(4).
pp. 95-101.
Ryazanov, V., 2021. The crisis is not childish. Expert. 17.
Amrutha, V. N., Geetha, S. N., 2020. A systematic review
on green human resource manage-ment: Implications
for social sustainability. Journal of Cleaner
Production. 247. pp. 119-131.
Bikmukhametova, I. S., Alyoshkina, O. V., 2019.
Definition of the category "corporate social
responsibility". Electronic scientific journal "Vector of
Economics". 12.
Zakharov, D. K., Kashtanova, E. V., 2019. Introduction of
professional standards in the personnel management
system of the organization. Personnel and intellectual
resources management in Russia. 8(6). pp. 34-37.
GOST R ISO 14001-2016. National Standard of the
Russian Federation "Environmental management
systems. Requirements and application guide"
https://docs.cntd.ru/document/1200134681.
Sustainable Development of the Metallurgical Industry based on the Development of Waste-free Technologies and an Environmentally
Oriented Economy
305
