
Modern Model of Food-service Management in Railway Transport
Roza Timakova
1,2
and Evgeniya Samoylova
2
1
Ural State University of Railway Transport, Yekaterinburg, Russian Federation
2
Ural State University of Economics, Yekaterinburg, Russian Federation
Keywords: food service, RW-catering, passenger service, railway transport, service, catering.
Abstract: In the competitive environment of the transport industry, the issues of providing passenger service in railway
transport have become conceptual importance. The change in the trajectory of the tourism and hospitality
sector development aimed at the domestic tourist market and the reduction in air traffic at this stage due to
objective reasons allows Russian Railways to strengthen its position. The developed food service management
model based on the proposed innovative solutions of a product, marketing, process, and organizational nature
is a potential resource project for the formation of a customer-oriented service. As a niche product service, an
improved branded concept of the RW food is proposed as a result of the building new service standards, the
use of innovative production technologies, the digitization of customer services and business processes, and
the improvement of the quality of service, which will contribute to the promotion of a complex product in
railway transport—passenger transportation, and growth of the economic efficiency of the Russian Railways.
1 INTRODUCTION
The sustainability of the transport system is primarily
determined by the volume of freight and passenger
traffic and the quality of transport services.
According to MGI, the total value of infrastructure
assets for the development of infrastructure should be
70% of GDP; in the Russian Federation, their total
value has reached 61%. According to the
Comprehensive Plan for the Modernization and
Expansion of the Main Infrastructure for the period
up to 2024, about 40% of the investments will be
directed to infrastructure, including transport
(Markova, 2021), which will ensure the intensive
development of the transport system and its customer
focus.
Currently, effective business strategies are
focused on customer service and, accordingly, on
effective service technologies. Unlike other modes of
transport (air and bus ones), the duration of travel by
rail transport is significant, which determines the
direction in the service strategy. According to
(Misaeva, 2021), the increasing popularity and
accessibility of railway tourism for residents of
various regions of Russia and the revival of railway
tourism as a new business area as a result of the
technology of using direct cars in passenger tourist
trains are one of the possible measures to accelerate
the restoration of pre-crisis traffic volumes.
Consolidation and creation of interorganizational
relations of public authorities, regional structures, the
Russian Railways, tour operators, and other
enterprises operating in the hospitality industry,
contributes to the promotion of mutually beneficial
areas of this activity: from sharing resources
(managerial, informational, material, labour,
financial) to improving work efficiency, building up
the investment potential of territories in the context of
pandenomics and pronounced positive dynamics of
the overall and the average degree of satisfaction
(Timakova, 2021).
The study of the technological features of the
organization of servicing passengers traveling by rail,
including for tourism purposes, shows the need to
consolidate structural units at the Russian Railways to
create a single service product. The product line
offered by the Russian Railways for its passengers
includes a standard set: ticket sales, including the cost
of bed linen, transportation, accommodation,
catering; sale of printed and souvenir products and
sanitary and hygienic supplies. However, in a
competitive environment, a new quality of services,
in particular catering services, is being formed, in
order to increase profitability and to improve the
efficiency of the enterprise. Against the backdrop of
the established mentality of passengers: meals on
trains are expensive, it is more reliable to take food
with you or to buy at stations along the way of the
train, there is a need for food and experiences, in
108
Timakova, R. and Samoylova, E.
Modern Model of Food-service Management in Railway Transport.
DOI: 10.5220/0011579800003527
In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific and Practical Conference on Transport: Logistics, Construction, Maintenance, Management (TLC2M 2022), pages 108-113
ISBN: 978-989-758-606-4
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

accordance with the expectations of customers of
different target groups. It is known that at present, a
sustainable consumer behavior model of the
population is also projected through gastronomic
preferences. Thus, according to (Rogach, 2020), more
than 55% of the surveyed foreign respondents note
that they always purchase tours based on online
reviews containing photos of beautiful meals. At the
same time, 31% of respondents confirm that they also
always take pictures of their food in a restaurant or a
cafe and 15% of respondents post such photos on
social networks. It is the positive reviews about the
food service that often become the basis for choosing
a tour for 30% of respondents and always—for 17%.
People are attracted to objects/events/things that
allow them to demonstrate their desired image, while
generating positive impressions and increasing the
rating of enterprises captured in such a context.
The Russian Railways provide guaranteed
(standard prepaid) meals—it is included in the ticket
price and additional meals—depending on the type of
carriages. Additional meals are presented as a full
board basis or half board basis, to choose from
(breakfast, lunch, or dinner) and with a choice from
the menu. Along with this, certain prerequisites that
make it possible to strengthen the service component
in the implementation of the “RW food” (RW
nutrition), the so-called meals on transport (the
authors introduce a new term by analogy with in-
flight meals on air transport) against the backdrop of
the COVID-19 pandemic and sanctions measures to
limit international air traffic with the Russian
Federation, for parallel global trends have arisen:
development of domestic tourism due to the existing
steady growth in the number of citizens of the Russian
Federation to local travel within the country and an
increase in the passenger flow of such tourists, which
predetermines the purpose of the study as the
development of a modern model of food service
management in railway transport based on the
existing resource potential of the Russian Railways in
the implementation of the RW food.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The sources for the study were publicly available
official information resources, including the Russian
Railways website, and research literature. During the
study, basic terminology has been used, in accordance
with GOST R 51006-96 “Transport Services. Terms
and Definitions” and the state standard GOST R
51004-96 “Transport Services. Passenger
Transportation. Nomenclature of Quality Indicators»;
general scientific research methods based on content
analysis, using the deconstruction method, an
analytical approach and system synthesis, followed
by interpretation of the research results, have been
used.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Achievement of performance indicators set by the
Russian Railways is determined by an integrated
approach to increasing passenger turnover as a result
of carrying more passengers and improving the
customer service. According to the information
shown in Figure 1, it can be seen that over the past
decade, the largest passenger turnover was in 2012—
114.0 billion Pkm, followed by a downward trend due
to various reasons—increased competition from air
carriers, active development of outbound tourism,
non-competitive railway transport service, etc.
In 2020, the main factor that significantly affected
all areas of activity, including the transport industry,
was the COVID-19 pandemic (Umanets, 2021).
Under these conditions, the passenger turnover has
reached a drop depth of 48.2 billion Pkm, which
amounted to 51.5% of the pre-pandemic level in
Figure 1: Passenger turnover through the network of the Russian Railways.
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021
Passengerturnover,
billion pass-km
Years
Modern Model of Food-service Management in Railway Transport
109
2019. However, in 2021, with the change in the travel
trajectory of the country's population and the dynamic
development of domestic tourism, the passenger
traffic through the Russian Railways network has
reached 103.4 billion Pkm, including long-distance
passenger traffic amounted to 72.0% of the total
turnover against 68.5% in 2020 and 74.3% in 2019.
In short-term forecasting, indicators can improve due
to geopolitical changes due to the growth of domestic
tourism and the active movement of the country's
population between regions. In order to consolidate
the position of rail transportation and to increase the
competitiveness of the Russian Railways, it is
necessary to strengthen the customer focus of service
departments, including food service, which, in our
opinion, can also be due to the efficiency of
activities—other activities currently bring profit to
the holding, unlike passenger transportation.
The corporate strategy of the Russian Railways
has been built, in accordance with the main objectives
of the predictive socioeconomic development of the
Russian Federation until 2030 and the Transport
Strategy of the Russian Federation for the period up
to 2030. The target business model for the balanced
development of the Russian Railways holding is
shown as the following blocks: transportation and
logistics ones, passenger transportation and service,
infrastructure, international engineering, and
transport construction, and a social one. The
Passenger Transportation business block as the center
of responsibility for providing customer-oriented
passenger service includes areas for improving the
product offer, digitizing customer services and
business processes, improving the quality of service,
and achieving economic efficiency.
Strategic planning of a public catering complex as
a result of the development of an integrated
management model is an effective way to assess the
development of the company (Timakova, 2021) and
it is adaptively applicable when planning the RW
catering concept in the food service model at the
Russian Railways.
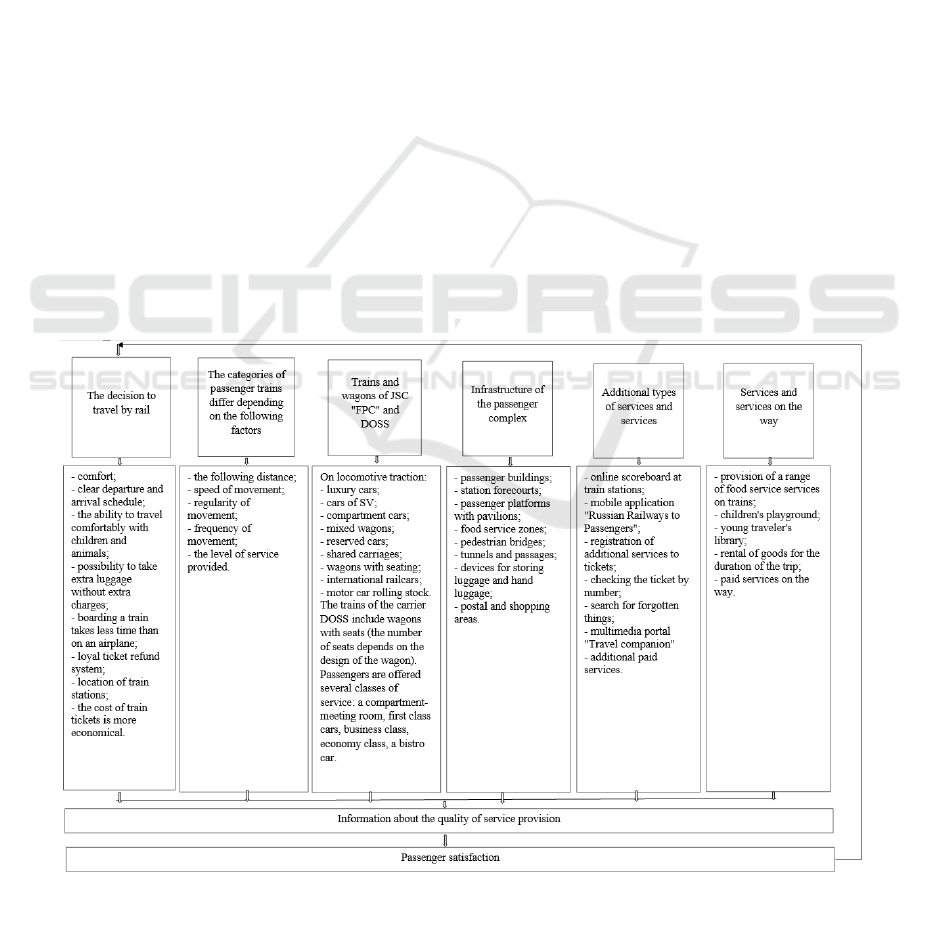
The business process for achieving the quality of
service in the passenger transportation is shown in
Figure 2.
Under these conditions, for the introduction of
innovations, in accordance with the requirements of
GOST R 56261-2014 “Innovation Management.
Innovations”, it is necessary, according to (Makarova,
2021), to use micro- and macromodels that allow
comparing situations “as it is” and “what to do” in
order to predict the consequences. On average,
domestic enterprises spend 1-2% of their budget on
innovations.
Table 1 shows the main types of innovations that
are proposed to be introduced as a part of the
Figure 2: Block diagram of creating the quality of transport services of the quality management subsystem in the passenger
transportation of the Russian Railways.
TLC2M 2022 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC AND PRACTICAL CONFERENCE TLC2M TRANSPORT: LOGISTICS,
CONSTRUCTION, MAINTENANCE, MANAGEMENT
110

improvement of the “food service” at the Russian
Railways.
At the same time, according to the typology, the
food service model refers to an innovative
(competitive) strategy, which increases the
competitiveness of railway transport, contributing to
an increase in passenger traffic and the development
of domestic tourism, including railway tourism.
Considering tourism as a potential resource for the
quantitative growth of a passenger traffic, it is
necessary to pay attention to the possibilities of niche
tourism products and to expand the tourist flow
through the transition from the traditional model of
the tourism product range to the strategic one, from
extensive to intensive development. It is well known
that the issues of expanding the range when selling a
tourist product are especially relevant for Russia,
where the main flow of tourists is directed to two key
destinations—St. Petersburg and Moscow
(Preobrazhensky, 2021).
In most foreign countries, on-train catering
companies in the world are owned by the carriers
themselves.
At the same time, the transfer of a part of non-core
functionality to outsourcing companies under the
customer experience management in railway
transport, when assessing the perception and
impressions of a consumer from traveling by rail, can
improve the quality of passenger service and reduce
the service product cost (Gulyaeva, 2021).
In the Russian Railways, ready-made meals are
produced by the Unified Catering Network (UCN)
enterprise (Arpicom Management Company), which,
according to a contract with the Federal Passenger
Company (FPC), JSC, provides catering services for
passengers of luxury cars on a number of long
distance trains.
On April 15, 2021, the Russian Railways have
launched a test stage of the “Concept for the Provision
of Catering Services” on long-distance trains of FPC,
JSC. Special bistro cars, which are supplied with
sterile containers with ready meals, appear as a part
of the new concept.
When forming an RW food, it is conceptually
important to take into account the existing positive
experience in creating an information system for
ordering in-flight catering, which, according to
(Pavlyukovich, 2021), will automatically change the
number of servings and the range of products in
orders depending on the change in the route of a
Table 1: Characteristics of different innovation types.
Types Characteristic
Technological
Gradual
Product
New products (RW food, additional food—assortment, packaging, new partners—
outsourcing)
New application of products (guaranteed food)
Vending machines with snacks and hot drinks
Modern mobile snack bar
Night menu, brunches, continental breakfasts
Family full board, group meals
Radical
Process
Delivery technology (RW food workshop, logistics, delivery centers, catering)
Unified system of product quality standards for outsourcing catering companies
Unified system for auditing the quality of products and services
Software (intelligent automation)
Lean manufacturing (management concept aimed at minimizing losses)
Offer of soft drinks
Non-technological
Gradual
Organization
al
Creation and implementation of workflow, systematization of the enterprise
(corporate code, regulations)
Operational management system (implementation of operational software, food
service standards, service, appearance)
Organization of the work of the kitchen and the trading area (regulations, regulatory
documentation, reci
p
e & cookin
g
p
rocess flow card, HACCP,
p
roduction control
)
Marketing
Promotion, valuation, communications (RW food market research, price positioning,
communication strategy, cash flow forecast)
Social
Accessible environment
Social tourism for senior citizens
Patriotic education
Modern Model of Food-service Management in Railway Transport
111

board, the change in the composition of the crew, and
the number of passengers.
An interesting solution in the form of edible
dishes for environmentally friendly passenger service
is proposed for in-flight passenger service
(Kolpinskaya, 2021), which can also be successfully
used in the RW food.
Among all modes of transport, it is railway
transport that is distinguished by comfort, a variety of
accommodation conditions, the ability to provide
passengers and travelers-tourists with a range of
services (transport, food, accommodation, leisure
activities). The cars have increased comfort; they are
equipped with air conditioners or climate control
systems, comfortable seats, panoramic windows,
shower cabins. Informativeness while traveling by
rail is higher than by bus (Kosareva, 2021).
At the same time, the issues of providing
passenger service are currently becoming important
due to the expected growth in passenger traffic
against the backdrop of geopolitical changes, a
certain reduction in air travel, where the main
ideology was to reduce travel time. Passenger
satisfaction in railway transport shall be determined
primarily by the comfort of travel and the level of
development of service technologies.
In order to improve the customer service and to
organize feedback from passengers, the Russian
Railways operate a number of client servers: a virtual
reception desk, a hotline, customer support centers in
the Telegram and Viber messengers, and the Russian
Railways to Passengers mobile app. The information
obtained shall be confirmed by the results of
marketing research (Chocholac, 2018), where the
analyzed criteria were ticket prices, the convenience
of transportation, the customer service, and the train
staff’s behavior during the trip, the cleanliness of the
car interiors, the frequency of proposed connections,
and the offer of refreshing drinks during the trip.
Tutu.ru, the Analytical Center for the Trips and
Travel Service, is joining in to study the opinions of
passengers. For the period from mid-2016 to the
present, more than 475 thousand responses have been
collected, which makes it possible to form an
assessment of the service quality, the results of which
are available to all visitors when searching for a
railway ticket on the website.
According to the results of a 2020 study
(Kasymova, 2020), using Google forms, it was found
that 53.8% of respondents do not use catering services
on the train; 23.1% of them visited the restaurant car;
15.4% purchased products sold by the conductor;
7.7% chose meals included in the ticket price.
According to (Hwang, 2021), consumers who
choose an individual, rather than a fixed menu, and an
individual way of eating meals, rather than in groups,
have a higher level of perception of the functional
value of meals and satisfaction, which is taken into
account when creating a food service management
model.
An important component of the proposed food
service management model is the direction to reduce
waste in the production and sale of the RW food (as a
result of the implementation of the lean production
concept), the reasons for which can be an
unreasonable number of food orders when booking, a
late refusal of a prepaid order by passengers, order
changes, quality, temperature of the meals, etc.,
which is consistent with the opinions of a number of
authors (Gao, 2021; Gladysz, 2020).
The most important problems of food service and
organization of the RW food include: non-
standardized menu of regional catering shops
throughout the entire route of the railway train, high
cost of raw materials, design features of railway
transport (restriction on the location of food sets)
(Zyukina, 2020). The modern food service
management model should be based on service
standards.
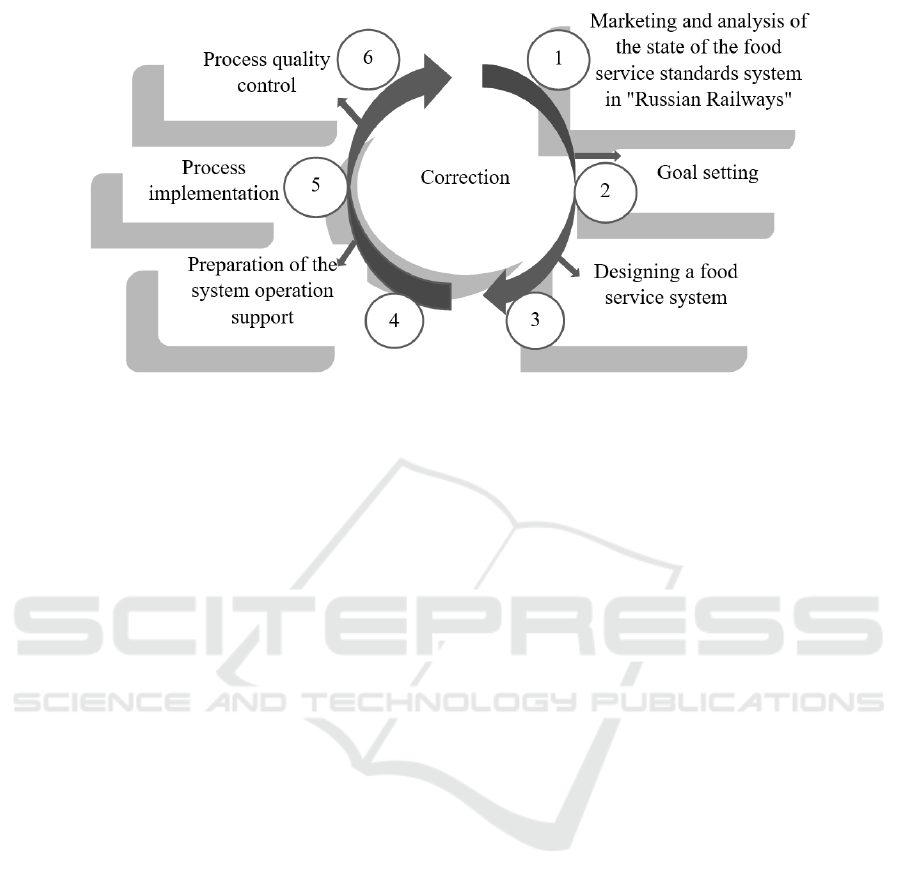
The proposed business model for food service
management includes the following elements:
marketing and analysis of the food service standards
system state at the Russian Railways, goal setting,
designing the food service system, preparing to
ensure the system operation, implementing the
process, monitoring the quality of the process at
Figure 3.
In the process of implementing the food service
model, the basic principles of ВУК (Russian:
Всеобщее управление качеством), or TQM
(English: Total Quality Management) should be
taken into account. With this approach, the consumer
assessment process can include an assessment of the
quality of not only the results obtained, but also the
internal (production) processes of the transport
company, as well as the quality of service by
personnel (Lavrov, 2018).
In our opinion, the proposed food service model
based on formalized features will increase the
profitability of this direction in railway transport.
4 CONCLUSION
Against the backdrop of the transport market
saturation with services for the transportation of
passengers and increased competition in the current
TLC2M 2022 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC AND PRACTICAL CONFERENCE TLC2M TRANSPORT: LOGISTICS,
CONSTRUCTION, MAINTENANCE, MANAGEMENT
112
conditions of limited air traffic and, accordingly, an
increase in passenger traffic in rail transport,
including through the active development of domestic
tourism, the issues of service efficiency in organizing
the RW food are of particular importance. In order to
improve customer service, various innovative
solutions are proposed aimed at creating an integrated
approach to the provision of services (management,
marketing, production, service standards), the use of
outsourcing and catering services, the introduction of
the concept of “lean production” in the provision of
food services, the organization of an innovative RW
food models and development of adaptive service for
different categories of passengers. The developed
business model of food service management based on
a set of technological and non-technological
innovations will make it possible to create a client-
oriented model for managing railway transport
services.
REFERENCES
Markova, E. S., Voronin, N. V., 2021. Innovation
Economics and Law 2 (17), pp. 9-18.
Misaeva, E. V., 2021. Economics and Business: Theory and
Practice 4-2 (74), pp. 26-29.
Timakova, R. T., Ergunova, O. T., Lebedev, A. V.,
Ilyukhina, Yu. V., 2021. Bulletin of St. Petersburg State
University of Economics (UNECON) 6 (132), pp. 62-
68.
Rogach, O. V., Frolova, E. V., Shcherbachenko, P. S., 2020.
Revista Inclusiones 7, 20.
Umanets, V. V., 2021. Economics of Railways 3, pp. 60-66.
Timakova, R. T., Ergunova, O. T., 2021. II International
Conference on Economic and Social Trends for
Sustainability of Modern Society – (ICEST-II 2021)
116:229, pp. 2037-2045.
Makarova, I. V., Shubenkova, K. A., Mavrin, V. G., Boyko,
A. D., 2021. Computer Research and Modeling 13(2),
pp. 381-394.
Preobrazhensky, A. B., Garkushina, N. A., 2021. Service
Plus 15(3), pp. 29-42.
Gulyaeva, O. A., 2021. Proceedings of the II International
Scientific and Practical Conference, pp. 26-29.
Pavlyukovich, D. S., Panfilov, I. A., Kosheleva, A. A.,
Sopov E. A., 2021. Prospects of Science 8 (143), pp.
33-36.
Kolpinskaya, A. A., Gazhur, A. A., 2021. Modern
Innovative Technologies in Economics, Science,
Education, pp. 248-254.
Kosareva, N. V., Adashova, T. A., 2021. Bulletin of the
Altai Academy of Economics and Law 2, pp. 61-65.
Chocholac, J., Trpisovsky, M., Kudlackova, N., 2018.
Transport Means, pp. 246-251.
Kasymova,
D. M., Yashkova, N. V., Rastegin, D. B.,
Bulganina, S. V., Lebedeva, T. E., 2020. Moscow
Economic Journal 9, 53.
Hwang, J., Kim, S., Lee, Y-K., 2021. International Journal
of Hospitality Management 93: 102750.
Gao, S., Bao, J. L., Li, R., Liu, X. J., Wu, C. F., 2021.
Sustainable Production and Consumption 26, pp. 78-
88.
Gladysz, B., Buczacki, A., Haskins, C., 2020.
RESOURCES-BASEL 9(12):144.
Zyukina, S. L., 2020. Technical and Technological
Problems of Service 3 (53), pp. 26-30.
Lavrov, I. M., 2018. ETAP: Economic Theory, Analysis,
Practice 5, pp. 135-142.
Figure 3: Business model of food service management.
Modern Model of Food-service Management in Railway Transport
113
