
Monitoring, Forecasting and Strategic Planning as a Means of
Effective Management of the Processes of Training Specialists in a
Transport University
Natalia Valeryevna Kalganova
a
Ural State University of Railway Transport, Ekaterinburg, Russia
Keywords: Monitoring, forecasting, strategic planning, process management, training of specialists, transport university.
Abstract: The article deals with the issues of monitoring, forecasting and strategic planning in a transport university.
The dialectical relationship between these issues and improving the efficiency of the educational process is
analyzed, the role of forecasting, monitoring and strategic planning as important processes and tools in
managing the quality of education at the university is revealed. In his study, the author relied on the works of
domestic scientists, in particular (Morozova, 2003; Erich, 1974; Kochkarov, 2006; Utkina, 1998). Monitoring,
forecasting and planning are important elements of managing all university processes that are a research
process. Thus, forecasting studies strategic problems, achievement of target results, the most likely
consequences of decisions made, and analysis and use of the results developed in the process of monitoring,
forecasting, planning and designing the training of engineering personnel for a certain period from 5 years to
30 years. The revealed information serves to develop options, a scenario for predicting the further
development of a transport university, making managerial decisions, assessing changes and preventing the
occurrence of negative phenomena.
1 INTRODUCTION
The processes of monitoring, forecasting and
planning are important elements of management not
only for each higher education institution, but for the
entire higher education system of the country, which
is confirmed by the governing documents (Consultant
plus, www.consultant.ru; Contour standard,
normativ.kontur.ru; Judicial and regulatory acts of the
Russian Federation, sudact.ru; Official Internet portal
of legal information, publication.pravo.gov.ru). The
fundamentals define the goals, objectives and main
directions of the state policy in the field of strategic
planning, as well as the mechanisms for
implementing this policy, emphasize the relationship
between the achievement of goals by methods of
forecasting, modeling, indicative planning, balance
calculations and information technology to develop a
system for monitoring and controlling strategic
planning processes.
The main purpose of this work is to determine the
most optimal methods of monitoring, forecasting and
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4117-8329
strategic planning based on the principles of a
systematic approach aimed at regularly assessing the
main processes of educational activities and the
prospects for the development of a transport
university, including scientific and pedagogical
personnel, material and technical base and other types
of activities of the university aimed at effective
management of the quality of training specialists for
the transport industry.
2 MONITORING AS A MEANS
OF EFFECTIVE PROCESS
MANAGEMENT IN A
TRANSPORT UNIVERSITY
Monitoring is a constant control, identification and
assessment of the actual state of the education system
and the most important factors that correspond to the
target results of the qualitative and quantitative
characteristics of the transport university processes.
Kalganova, N.
Monitoring, Forecasting and Strategic Planning as a Means of Effective Management of the Processes of Training Specialists in a Transport University.
DOI: 10.5220/0011580900003527
In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific and Practical Conference on Transport: Logistics, Construction, Maintenance, Management (TLC2M 2022), pages 163-169
ISBN: 978-989-758-606-4
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
163

Monitoring is the basis for predicting the
development of the education system and regulating
the quality of education when making long-term plans
and management decisions.
The object of monitoring is the quality of
education in a transport university. In the process of
monitoring studies, deep analytical work is carried
out to identify and process a large amount of
information.
The objects of monitoring can be: the educational
process, the academic progress of students, the
formation and development of the teaching staff, the
strengthening of the material and technical base of
universities.
Depending on the selected object of monitoring,
the goals and objectives associated with the
implementation of monitoring in practice are
determined.
Goals are the determining factors of research: a set
of evaluation criteria and indicators is formed on the
basis of the goal, research methods are selected, a
monitoring procedure is built; analysis and further use
of monitoring information are subordinated to goals.
Monitoring objectives are implemented on the
basis of scientifically based principles:
1. The principle of targeting and purposefulness
of taking into account the specifics of the
activities of the department, faculty,
department, branch, staff in the formation of
monitoring indicators, the information
collected correlates with the goals.
2. The principle of objectivity and the possibility
of documentary confirmation of the quality of
data provided by departments.
3. The principle of completeness and continuity,
data collection is carried out continuously and
is aimed at obtaining complete information
about the observed object for a long time in the
form of a permanent or periodic check,
followed by registration of materials.
4. The principle of transparency, openness and
publicity of events and data during monitoring
involves various measures to inform all users
about the information collected during
monitoring.
5. The feedback principle that allows you to make
adjustments to the controlled process. The
implementation of this principle is to
immediately respond to detected problems and
errors.
6. The principle of scientificity and completeness
of information for statistical processing, the use
of reasonable models and tracking parameters.
When organizing and conducting monitoring
studies, a variety of methods are used as ways to
achieve goals. All monitoring methods used can be
divided into the following groups in Table 1.
Table 1: Classification of monitoring methods.
General
scientific
methods
Scientific and
empirical:
Specially-
theoretical
analysis observations system analysis
synthesis comparisons statistical
anal
y
sis
induction dimension expert
assessments
deduction ex
p
eriment Del
p
hi metho
d
analogy information
and software
data
p
rocessin
g
sociological
research
proof score graphical
metho
d
g
eneralization the surve
y
SWOT anal
y
sis
modelin
g
testin
g
re
g
ulator
y
hypotheses and
their
confirmation
polling method formation of a
forecast
To determine the directions for further
development of a transport university, it is necessary
to use a modern method - organizing and conducting
a SWOT analysis of the university. This is a special
kind of expert method that is used in monitoring for
subsequent forecasting and planning.
This methodology can be used in the study of
processes in higher educational institutions, in which
dynamism, controllability, dependence on internal
and external factors of functioning, cyclical
development are considered and taken into account.
To develop a SWOT analysis, the formed team, based
on the main provisions, principles and methods of
monitoring, generates four aspects of SWOT and,
using them, offers options, scenarios for the process
of forming a university development strategy.
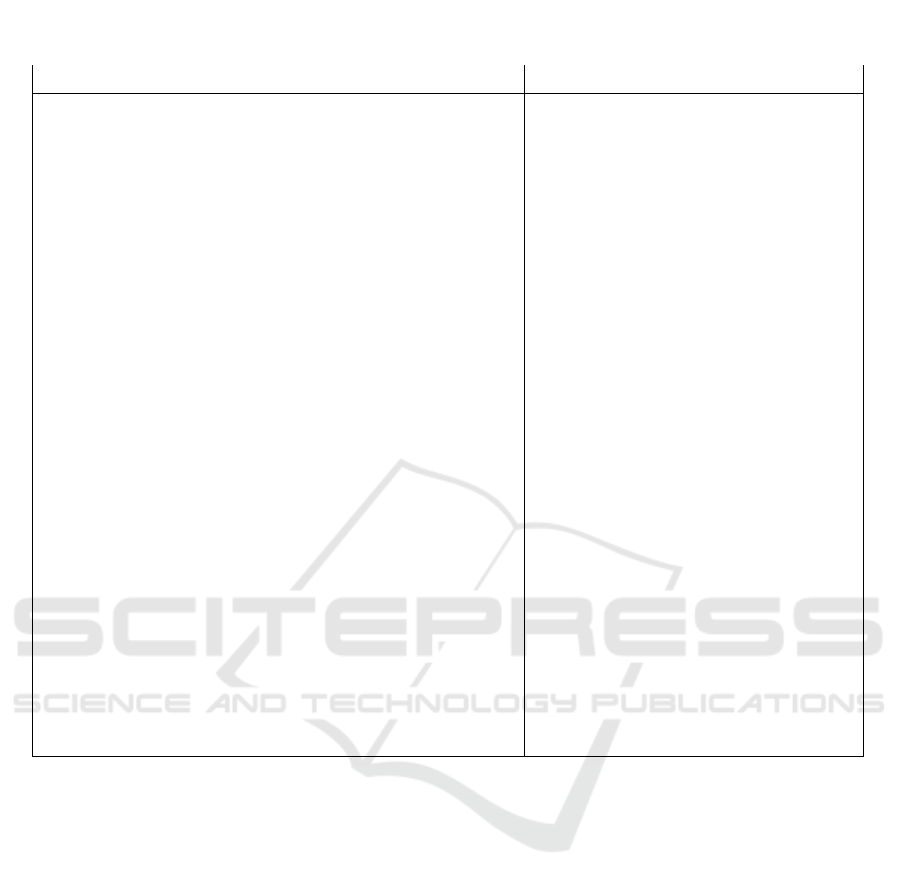
Based on the analysis of one of the transport
universities, conducted by the author, a SWOT
analysis was developed in table 2.
When developing predictive indicators in the
plans and programs for the strategic development of
a transport university, it is necessary to provide for
measures aimed at maximizing the impact of
strengths and opportunities on minimizing
(eliminating) weaknesses and threats, i.e. consider the
logical relationship of the matrix (SO) (WT).
In order to monitor the improvement of the quality
of training of specialists, the development of
professional teaching staff, logistics at the university,
TLC2M 2022 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC AND PRACTICAL CONFERENCE TLC2M TRANSPORT: LOGISTICS,
CONSTRUCTION, MAINTENANCE, MANAGEMENT
164

express diagnostics of the main processes and
program documents of the university can be carried
out.
In order to improve the quality of training of
specialists, it is important to conduct a final diagnosis
of the professional readiness of a graduate, which, in
addition to determining the level of socio-
professional knowledge, skills and abilities, includes
a diagnosis of the degree of development of the
qualities necessary for a future specialist.
3 FORECASTING AS THE MOST
IMPORTANT MANAGEMENT
FUNCTION IN A TRANSPORT
UNIVERSITY
The current pace of scientific and technological
progress requires a scientific approach to forecasting
problems. At the end of the twentieth century, there
was a scientific revolution in the field of forecasting.
The end of the 20th century and the current decade
show how the time frames and scales of progress are
radically changing, which makes it especially
necessary to foresee development prospects. At the
same time, scientific and technological progress
should be immediately reflected in educational
programs, especially in the system of higher
education, in particular in the training of engineering
personnel.
The function of foresight, scientific forecasting
not only for the near future, but also for a more distant
future, is an integral element of the management
process.
The urgent need to solve the problems of scientific
forecasting and strategic planning of the socio-
economic development of universities is caused by
the need to participate in solving these problems not
only government agencies, management
organizations, but also prominent scientists. It is
enough to cite the documents (Judicial and regulatory
acts of the Russian Federation, sudact.ru; Official
Table 2: SWOT analysis of one of the transport universities.
Factors of the internal and external environment influencin
g
the develo
p
ment of the universit
y
Strengths
S
Weak sides W
– high quality of training of specialists
for the transport industry;
– a wide range of transport specialties;
– targeted training of specialists;
– a high level of qualification of the
teaching staff and staff;
– effective management;
– the reputation of the university in the
region;
– distance educational technologies;
- availability of training (acceptable
cost, conditions for admission,
convenient educational process);
– a developed system of career guidance
work of the university;
– organization
international educational cooperation;
– scientific activity of the teaching staff,
a wide range of publications,
preparation and defense of dissertations;
– developed
infrastructure, material and technical
base;
– developed
management system of university
departments;
– high level of publishing activity;
– employment of university graduates.
– lack of budget financing;
– insufficient level of motivation of teaching staff;
– excessive organization of the educational process and educational
and methodological work;
– insufficient
communication with employers;
– low motivation of students;
– lack of a comprehensive offer for the target client;
– template training;
– weak ties with leading Russian universities in terms of attracting
highly qualified teachers;
– absence
material and technical base for scientific research;
– lack of a system of strategic interaction with related companies;
– weak motivation of students, graduate students and teachers for
scientific activity;
– absence centralized management of postgraduate and doctoral
studies;
– association of departments with mixed specialization (there is no
plan for the growth of candidates and doctors of sciences);
– insufficiency of publications in journals included in the list of
Skopus, Web of Science, RUSSIAN SCIENTIFIC CITATION
INDEX;
– skew teaching activities on research;
– participation of teaching staff in grants of various levels;
– a large number of part-time workers among teaching staff;
– a small number of strong technical schools with rich traditions;
– reduction in the number of annual dissertation defenses, incl.
among university staff;
– reduction of the teaching staff from among the young scientists of
the university.
Monitoring, Forecasting and Strategic Planning as a Means of Effective Management of the Processes of Training Specialists in a Transport
University
165
Internet portal of legal information,
publication.pravo.gov.ru; State Duma,
duma.consultant.ru; Morozova, 2003; Erich, 1974;
Kochkarov, 2006; Utkina, 1998), in which, both in
the Decree of the President (Official Internet portal of
legal information, publication.pravo.gov.ru), the
Federal Law (Consultant plus, www.consultant.ru),
and in studies on this topic, the authors (Morozova,
2003; Erich, 1974; Kochkarov, 2006; Utkina, 1998)
give a complete, systematized presentation of
proposals for the development and analysis of
existing experience scientific and technical
forecasting and planning.
The forecasting system is a multi-level structure
based on monitoring results.
Basic principles of forecasting and planning:
– optimality, scientific validity of the planned
solutions in accordance with the selected
criteria;
– balance and proportionality of indicators in
accordance with resource and financial
capabilities;
– allocation of priorities, leading links;
– determination of the time interval («forecast
horizon») for achieving target indicators;
– comparison with similar universities, the
activities of the university and departments;
– continuity, i.e. a combination of long-term and
current plans, continuity, adjustment of
indicators when conditions change;
– substantiation of a backup option (scenario) for
the development of the university, designed to
be implemented in the most unfavorable
conditions.
To determine the directions for further
development of a transport university, it is necessary
to use the methods formulated in the disclosure of the
concept and control functions for subsequent
forecasting and planning.
Table 2: Continued.
Capabilities O Threats T
– formation and dynamism of the list of demanded educational
programs;
– academic mobility at the level of teachers;
– increase in the number of target places with an emphasis on
transport in general and other sectors;
– introduction of a real system for evaluating the effectiveness of
the teaching staff;
– improving the system of remuneration of teachers (including
through additional sources: grants, the federal budget, orders from
large business holdings);
– improving the organization of the educational process (a
combination of traditional and modern forms of education and
types of classes);
– increasing the motivation of students to study;
– equipping classrooms with modern equipment;
– using our own linguistic department to improve the language
competence of teachers and develop international cooperation;
– strengthening communication with employers;
– involvement of representatives of employers in training;
– development of a system of relations between the university and
graduates (lobbying the interests of the university, financing,
moral encouragement, etc.);
– development of programs for the adaptation and retention of
teaching staff, primarily from among young teachers;
– creation of conditions for obtaining a second education and a
second diploma;
– research development
the potential of the teaching staff;
– expansion of the market (expansion of geography) of
educational services both for graduates of educational institutions
and for production workers who wish to undergo retraining,
students of additional education.
– lowering the prestige of the university;
– lack of intrinsic motivation to implement
the strategy;
– liquidation of non-core education that
generates income;
– reduction in the number of defenses of
candidate and especially doctoral
dissertations as a factor in the reduction of
human resources;
– decrease in the number of doctors of
sciences;
– a sudden and sharp decrease in the number
of external part-timers;
– decrease in student enrollment;
– reorientation of transport organizations to
other universities;
– negative state policy in the field of
education for the university;
– decrease in the quality of recruitment of
students (including target ones);
– possible refusal of Russian Railways from
targeted training;
– reduction of budget financing;
– a decrease in demand among the
population for transport specialties, a sharp
reduction in students from among those who
pay the full cost of education;
– closure of a number of specialties.
TLC2M 2022 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC AND PRACTICAL CONFERENCE TLC2M TRANSPORT: LOGISTICS,
CONSTRUCTION, MAINTENANCE, MANAGEMENT
166

In recent years, special methods related to
forecasting have developed especially intensively. In
the monograph (Morozova, 2003), which presents
various (about 100 in total) forecasting methods, as
well as the possibilities and prospects for their use.
Forecasting methods:
1. Intuitive thinking:
– brain attack;
– direct brain attack;
– a method of collecting opinions. Method
«Delphi»;
– The Mendeleev method, which could reveal the
nature and form of interaction between the
elements of the system and their properties, in
particular technologies, before their
identification (invention or refinement), similar
to how the periodic table of chemical elements
was compiled.
2. Exploratory forecasting:
– scenarios;
– iteration;
– historical analogy;
– probabilistic forecasting;
– economic analysis;
– risk assessment;
– statistical models.
3. Normative forecasting:
– resource usage;
– linear programming;
– dynamic programming;
– methods of decision theory;
– System analysis.
4. Methods with feedback:
– integrated information technology systems.
The Delphi long-term forecasting method,
developed by O. Gelmer and his colleagues, has
become widely known abroad. The forecast is carried
out both in the main, priority areas, and in terms of
parameters characterizing the content of the areas:
– in the educational process (indicators of the
quality of training of specialists, digitalization
of all processes in the university, innovative
processes in education, etc.);
– demographic forecasts: the number of
graduates by years of secondary educational
institutions, the plan for entering the university
and graduation;
– dynamics of specialties in the training of
engineering personnel in the region, graduation
plan;
– the dynamics of the teaching staff;
–
scientific sphere (work of graduate and
doctoral students, indicators of dissertation
defenses, grants, number of scientific
laboratories, etc.);
– logistics;
– financial and economic sphere.
A forecast is a set of reasoned assumptions,
expressed in qualitative and quantitative forms,
regarding the future parameters of the educational
system, which is of a probabilistic nature. At the same
time, complex forecasting is considered in different
time periods: as short-term, medium-term and long-
term. One of the conditions for the effectiveness of
the forecasting system is the consistency of forecasts
of different levels of universities of the same profile
of training specialists.
Monitoring, forecasting and planning are
important means of managing university processes,
tools for economic stability and strategic
development of the university. In the case when there
are several ways to implement the plan, scenarios of
possible development are developed.
The forecast horizon is directly related to the
problems of strategic forecasting and designing the
future. Knowing the forecast horizon, one can
estimate what should be measured and how often.
Where, then, are the boundaries of normative
planning? In many cases, they seem to be determined
by the dynamics of the global system of human
society with a deep study of trends.
If long-term normative planning provides for a
new situation in the development of the university,
then it should indicate the time horizon for achieving
these goals. However, this will be an attempt to test
the sufficiency of the university's capabilities to
achieve long-term goals. And if they are not enough,
then forecasting will stimulate the search for new
alternatives, the search for raising funds, and the
mobilization of internal resources.
For forecasting and long-term planning, it is
important to know technologies that affect the main
processes in the educational system, methods of
teaching and mastering knowledge and skills,
assessing the quality of education, and shaping
motivation. A successful forecast should be based on
taking into account all internal and external factors.
4 STRATEGIC PROGRAM AS A
BASIS FOR EFFECTIVE
MANAGEMENT OF
UNIVERSITY DEVELOPMENT
Planning is a hierarchical process of forming
preliminary decisions in the management system that
Monitoring, Forecasting and Strategic Planning as a Means of Effective Management of the Processes of Training Specialists in a Transport
University
167

determines the order with the sequence of individual
events. Depending on the duration of the time
interval, there are short-term, medium-term and long-
term planning. To create a system of regulation of all
processes in the university, it is necessary to develop
a planning and forecasting system and a system of
scientific monitoring;
The system of scientific monitoring, SWOT
analysis, conclusions and indicators based on the
results of the development of forecasting directions
will make it possible to prevent omissions,
weaknesses that can lead to crisis phenomena of a
different nature.
These studies will determine:
– strategic goals of activity and indicators
(indicators) that they intend to achieve, taking
into account the strategy of the Ministry, the
Federal Agency for Railway Transport for the
medium and long term;
– the main tasks through the solution of which
the set strategic goals and the specific areas of
activity corresponding to them are realized;
– intradepartmental and interdepartmental
targeted and other programs, through which the
implementation of certain areas of activity and
the solution of the main tasks are ensured.
Focusing on strategy can help institutions operate
more effectively, make evidence-based decisions,
and set the course for a sustainable future, by
following these guidelines:
– analyze and make decisions regarding the
development of the university, taking into
account the mechanisms that connect all
departments of the university and are
influenced by external factors;
– when developing a strategy, the university
should not be in the role of a passive observer
of external influences, but should develop
measures to manage the external environment
to achieve its own benefit;
– the most important condition for economic
stability and development of the university is
the effective use of finances, savings and cost
reduction.
– redistribution of internal resources, focusing
them on priority areas;
– termination of a non-priority direction that is
not provided with resources, or their
reorientation;
– development of cooperation, partnership, joint
ventures, etc.;
– development of a motivation system for all
university employees;
– constant attention to the dynamic solution of
social problems, such as: raising the living
standards of workers, raising the level of
qualifications, improving the quality of
working life, etc.
Strategy as a field of activity can open up great
opportunities for universities. Taking into account the
experience of a number of universities and theoretical
developments in the field of strategic planning
(Kochkarov, 2006; Utkina, 1998), when formulating
a strategy in Table. 3, the following potentially
important issues should be considered.
The strategy is developed and implemented
through a collective and focused effort. However,
once a strategic program is in place, schools still need
plans to put their strategies into practice. Institutions
must first formulate a strategy and then develop
operational plans to implement the policy provisions
of these statements.
The implementation of plans and projects requires
very significant budget expenditures. It is important
to ensure the sufficiency of these funds for the
implementation of the tasks of the projects, the
effective management of these funds, the possibility
of additional attraction of non-state resources,
provided that the scale is expanded and additional
results are obtained. The allocation of funds for the
implementation of plans and projects must be
justified and carefully calculated.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The article argumentatively shows that monitoring,
forecasting and planning are important elements of
management of all university processes. These
controls represent a research process. So, forecasting
studies strategic problems, the achievement of target
results, the most likely consequences of decisions
taken, as well as the analysis and use of the results of
targets developed in the monitoring process.
Monitoring is a constant monitoring, assessment of
the actual state of the education system, compliance
of the target results with the qualitative and
quantitative characteristics of the development of the
university.
The function of foresight, scientific forecasting is
an integral element of the management process.
An analysis of the experience of a number of
transport universities showed the particular
importance of the strategic planning process, the
formation of preliminary decisions in the
management system. It should be emphasized that
planning is a tool for purposeful management of the
TLC2M 2022 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC AND PRACTICAL CONFERENCE TLC2M TRANSPORT: LOGISTICS,
CONSTRUCTION, MAINTENANCE, MANAGEMENT
168
sustainability and strategic development of
universities, adjustment of approved plans.
REFERENCES
Official site Consultant plus,
http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_
140174/.
Official site Contour standard,
https://normativ.kontur.ru/document?moduleId=1&do
cumentId=332217.
Official site Judicial and regulatory acts of the Russian
Federation, https://sudact.ru/law/postanovlenie-
pravitelstva-rf-ot-05082013-n-662/.
Official website Official Internet portal of legal
information,
http://publication.pravo.gov.ru/Document/View/00012
02111080023.
Official website of the State Duma,
https://duma.consultant.ru/documents/1163340.
Morozova, T. G., Pikulkin A. V., 2003. Forecasting and
planning in market conditions, p. 279.
Erich, J., Gvishiani D. M., 1974. Forecasting scientific and
technological progress, p. 585.
Kochkarov, R. A., 2006. Strategic planning and forecasting.
Bulletin of the Financial Academy, 4, pp. 97-109.
Utkina, E. A., 1998. Strategic planning, p. 440.
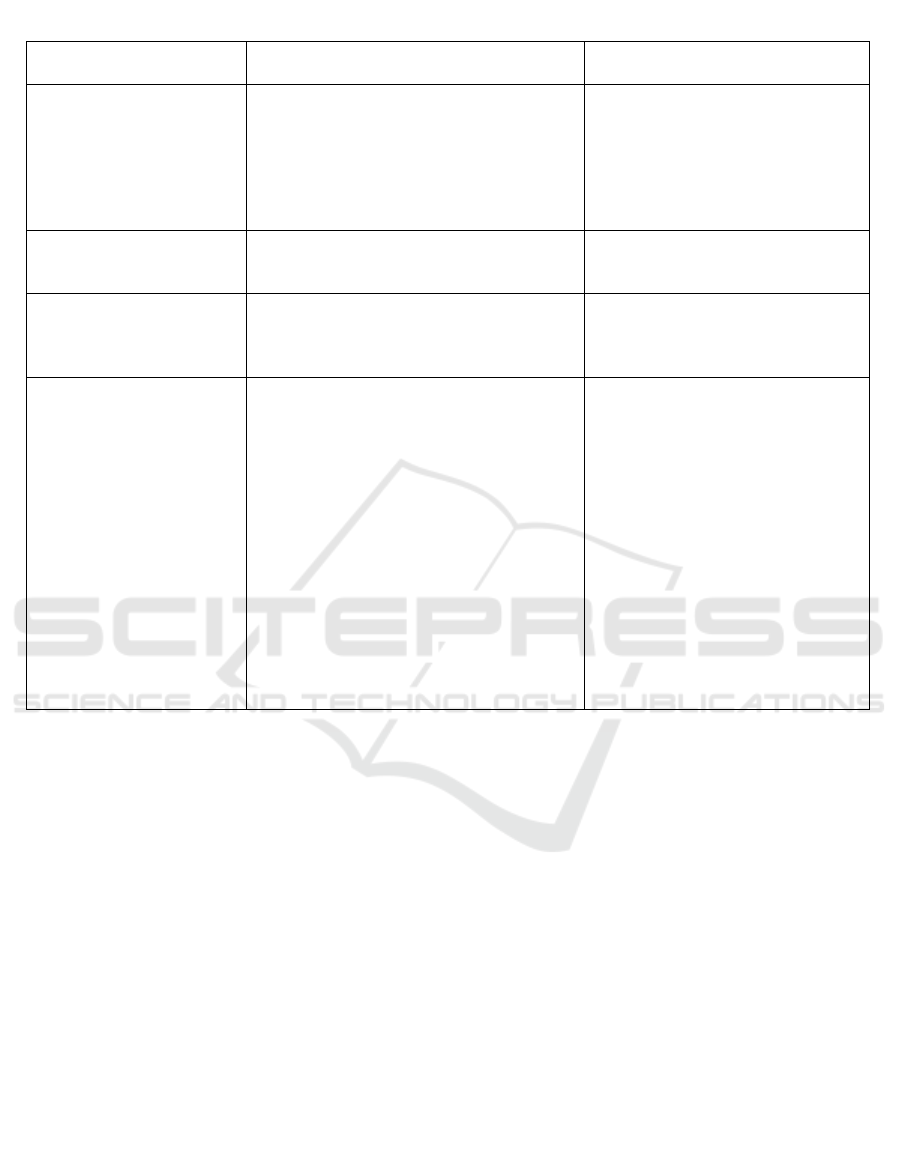
Table 3: Flowchart for the development of the University Strategic Development Program.
Source and guidance
documents (external)
Stages of development Source and guidance documents
(internal)
National Strategy for
Higher Education and
Science.
Railway development
strategy transport in the
Russian Federation and
other documents.
Formulation of strategic goals and
objectives
University charter and other
normative documents
University Ranking Development of strategic goals, objectives
and priorities for the development of the
universit
y
in areas
PEST (STEP), SWOT - analysis
Expert assessment of
competition
Estimated estimates and forecasts for the
implementation of goals, taking into account
various scenarios for the development of the
universit
y
Forecasting methodology.
Estimated data
Order for personnel
training, scientific research,
advanced training, etc.
Certification, licensing,
accreditation programs
financial security.
Estimated investment.
Development of development programs in
the following areas:
– educational activities;
Scientific and innovative activity;
– Development of the human resources
potential of the university;
– International activity;
- Social and cultural activities;
– Development of the publishing and library
complex of the university;
– Management activities;
– Industrial and economic activity.
Infrastructure development;
– informatization of the university complex;
– financial and economic activity;
–
Development of territorial divisions.
Quality control. Conditional
forecast.
Norms, reporting data.
Estimates of expenses and income.
Accounting for options for the
strategic development of the
university.
Monitoring, Forecasting and Strategic Planning as a Means of Effective Management of the Processes of Training Specialists in a Transport
University
169
