
Systematic Method of Targeting the Strategic Innovation Research
System in Transport
Nikolai Vnukovsky
a
, Svetlana Rachek
b
, Olga Selina
c
,
Ekaterina Konysheva
d
and Yana Khomenko
e
Ural State University of Railway Transport, Yekaterinburg, Russian Federation
Keywords: Systematic method of goal setting, the system of research, the transport industry, strategic innovative activity
in transport, goal tree, decomposition, technological approach, resource approach, role approach, conceptual
models, structural-functional, information-digital models, cluster-analysis, knowledge system in transport.
Abstract: The article considers one of the innovative directions - the research system of strategic innovation activity in
transport based on a systematic target setting method. The package of conceptual, algorithmic, structural,
functional, informational and criterial models of the research system of strategic innovation activity in
transport is presented, which allowed creating a knowledge system for managers to make reasonable
management decisions based on intellectual-computer support. In order to create a system of research on the
model scientific research methodology, a working slogan, satisfying the principles of measurability,
modifiability and continuity of the transport industry, has been developed. To achieve the goal, a tree of
objectives was built, which, when decomposed only by the technological approach, yielded more than 600
financial and economic objectives. On the basis of resource and role-based approaches, lists of strategic
innovation research system functions were compiled, subjected to cluster analysis, and conceptual modelling
of the research system of the transport industry was carried out. Based on the scientific study of strategic
innovation research system formed the structure of the research system of strategic innovation activities by
introducing the intellectual block of innovation in the form of a knowledge system in transport.
1 INTRODUCTION
"Sustainable development is about meeting the needs
of the present generation without compromising the
ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
This principle should become the central guiding
principle of the United Nations for all governments
and ministries, private companies, organisations and
enterprises" (Łuczak and Just, 2021; Shcheglov,
2018).
In this regard, the sustainable development of an
industrial enterprise is based on the following
concepts:
– the need for innovation for the functioning of
the production business processes (Cheng, et
al., 2020);
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2732-7163
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6450-4641
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5930-2175
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1963-3866
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5399-9423
– constraints in the development of innovative
technologies of the enterprise to meet the
demand on commodity markets.
In this case, the following must necessarily
change: to increase the number of innovative products
and technologies; to increase the efficiency of
innovative technologies and the management quality.
Such changes help to maintain the growth of demand
satisfaction for the production process and the needs
on the commodity markets.
Today, economic theories set limits in the form of
(Pasinetti, 2021):
– marginal costs;
– marginal profit;
– Supply and demand equilibrium, which do not
allow for a lack of innovation.
260
Vnukovsky, N., Rachek, S., Selina, O., Konysheva, E. and Khomenko, Y.
Systematic Method of Targeting the Strategic Innovation Research System in Transport.
DOI: 10.5220/0011582600003527
In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific and Practical Conference on Transport: Logistics, Construction, Maintenance, Management (TLC2M 2022), pages 260-265
ISBN: 978-989-758-606-4
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

Therefore, any technological development
(innovation) should be evaluated in terms of its
contribution to the enhancement of sustainable
economic development (Shabalov, et al., 2021; Mok
and Kan, 2013). In addition, investment in innovation
on the principles of sustainable economic
development allows the industrial enterprise to create
a system of long-term and sustainable profit through
the efficient use of all resources.
From the point of view of innovation development
in the processes of the Russian economy
modernization, an important direction is to create
such an innovation environment, so that the existing
knowledge, technology, innovation development,
scientific research could be turned into a final product
demanded by the economy in the shortest possible
time, to create a priority for the mass implementation
of innovation in all spheres of activity (Guo and Shi,
2021; Morgan, et al., 2021).
The most pressing issue in the development of
scientific innovation areas can be identified as
strategic innovation activity, which is sufficiently
well disclosed in the literature, but the research tools
and systems of strategic innovation activity (SIRS)
themselves are underdeveloped. Therefore, this
article applies a systematic method of targeting SIRS,
on the basis of which modelling was carried out,
conceptual, algorithmic, structural-functional,
informational and criterial models of SIRS were
developed (Jin Ko, et al., 2021; Vnukovsky, 1999).
The whole package of these models will make it
possible to form intellectual-computer support in the
future and, ultimately, to create a knowledge system
for managers to make competent and well-founded
management decisions.
2 METHODS
Based on the literature review, the lists and
characteristics of stakeholder satisfaction slogans
were generated in relation to the development of a
research system for the economic, information and
management aspects of strategic innovation
activities. The primary list of 44 keywords has been
evaluated dichotomously (0 or 1) according to their
importance for the main actors of innovation and
investment. From the primary list of slogans, a
working slogan for Strategic Innovation Research
System (SIRS) (Boso, et al., 2012; Brozovic, 2018;
Wales, 2015) was formulated.
The creation of a socially demanded competitive
investment and innovation enterprise, relevant to the
contemporary transitional economy, with high
guarantees of economic security and a special
research system (SIRS), which provides qualitative
functioning and timely reform of the enterprise taking
into account the appearance of innovative
technologies which satisfy the principles of
measurability, modularity and continuity (Covin and
Wales, 2018; Gupta, et al., 2019; Ho, et al., 2016; Li,
et al., 2008).
The global goal of SIRS is to develop a demanded
SIRS that provides information on the quality
functioning and timely reform of the innovative
enterprise.
A technological approach has been chosen to
identify local goals.
Level I local targets:
1. Fixing the quality of SIRS input streams.
2. Fixing the quality of SIRS regulations.
3. Fixing the quality of the SIRS implementation
tools.
4. Fixing the quality of the SIRS output streams.
5. Fixing the quality of the innovation process
technology.
Local Level II objectives:
1.1 Fixing the quality of SIRS customer quality
information.
1.2 Fixing the quality of information about
innovation capital.
1.3 Fixing the quality of SIRS input information.
2.1 Fixing the quality of regulations by type of ID.
2.2 Fixing the quality of standards by areas of IA
application.
3.1 Fixing the quality of innovation resources
(IR).
3.2 Fixing the quality of innovation tools (IT) of
RS.
4.1 Fixing the quality of SIRS clients on outputs.
4.2 Fixing the quality of innovation capital at
output.
4.3 Fixing the quality of output information.
5.1 Fixing the quality of innovative technological
processes (ITP) by stages.
5.2 Fixing the quality of ITP by management
levels.
5.3 Capturing the quality of ITP by professional
levels.
Decomposition according to the technological
approach alone resulted in more than 600 specific
financial and economic tasks.
In order to obtain a list of functions from the list
of tasks, a method for distinguishing two components
was used - a routine one, based on precedents and
oriented on computer databases, and a creative one,
designed for the user's intellect. The creative
component - innovation analysis is organised with the
Systematic Method of Targeting the Strategic Innovation Research System in Transport
261

help of a smart cueing system (SCS), SIRS, which
helps to find a way to solve the problem.
More than 80 SIRS functions are derived,
presented according to groups: quality of innovation
processes, breadth of innovation services, technology
of innovation processes, customer classification and
documentation.
The resource-based approach additionally
considers the current state of the innovation
enterprise, the quality of innovation processes and
their results, and the information-intellectual nature
of the enterprise's innovation activities.
In the role-based approach, lists of main and
subject support roles of IA were formed, to which
subject-system and information-computer aspects of
the problem were attributed. The obtained role
structure of innovative enterprise allowed to make an
additional list of functions for the roles of the head
and main innovation manager, which in terms of
breadth of coverage of IA issues satisfy the
requirement of the list completeness as much as
possible.
Based on these approaches, various SIRS lists of
functions were compiled and subjected to a cluster
analysis. To describe the properties of the functions,
the main types of SIRS support, its resource and
technology components were considered, and the
object orientation was taken into account. The object
orientation was expressed by the IA specificity, the
resource component by knowledge-intensiveness,
and the technological component by the quality of
processability. A dichotomous way of quantifying the
properties of SIRS functions was used. Cluster
analysis takes into account the principle of function
synthesis and the need to combine specific and non-
specific functions in SIRS. The complete structure of
the functions has three main levels: routine,
knowledge-intensive and specific highly intelligent
multimedia.
For each selected function, a list of requirements
was generated for implementation in SIRS, in terms
of generating the information to be collected for each
IA profile and presenting the diagnostic opinion
dynamically, for example, for each type of security
(ordinary shares, preference shares, debentures,
convertible bonds and other securities). The dynamic
nature for all types of investment activities is adjusted
with inflation projections for each calculation period,
and risks are considered and assessed at all stages of
IA development.
According to the typology of technological
systems of strategic innovation research, the main
stages, methods and models used, as well as the
corresponding tool support for technological schemes
of innovation research are grouped.
As the next step in the systematic method of goal-
setting, SIRS modelling was carried out. Conceptual,
algorithmic, functional-structural, criteria and
information models of SIRS have been developed.
The general concept of SIRS consists in
modelling SIRS by implementing the cycle:
management, identification, interoperability,
optimization of the lower IA levels on the basis of
subsystems: computing and information
environment, the SIRS object and interface means,
functionally interconnected by human investment
activities aimed at improving the quality of SIRS
processes and results.
The base-level concept of SIRS is to model SIRS
through distributed management of the downstream
implementation - management, identification,
interoperability and optimisation of the lower levels
of the LED through sub-systems-based dialogue
points.
Hierarchical computing facility, LED object and
modular interfacing facilities, functionally linked by
the activities of SIRS users and maintenance
personnel, aimed at determining the stability of the
current situation, selecting and applying adaptive
bifurcation mechanisms of development, evolution of
the self-organising SIRS system, improving the
efficiency and quality of innovation processes and
SIRS results, automating research on technological
investment processes and implementing active
learning methods in order to improve the SIRS
science and technology base and create a modern
industry of innovation activities.
The base-level concept of prospective SIRS
consists in modelling and synthesis of SIA through
centralized management of top-down cycle -
management, identification, compatibility and
optimization of lower levels of SIA according to the
requests of system users based on subsystems with
programmable architecture: computing environment,
SIA object and intelligent interface tools, functionally
united by user activities as well as system integration,
formalization, structuring, modelling, optimization,
on the one hand, and intellectualization
The architecture of the main subsystems of SIRS
is constructed as a programmable structure in the
form of a set of properties and characteristics that
define the relationships between the blocks of the
system. The architecture of the computing
environment is programmable in order to align it with
the nature of the SIA task at hand. The
programmability of the SIA object structure allows to
solve the task of synthesis, i.e., creation of the SIA
TLC2M 2022 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC AND PRACTICAL CONFERENCE TLC2M TRANSPORT: LOGISTICS,
CONSTRUCTION, MAINTENANCE, MANAGEMENT
262

object based on the known model. The SIA object
structure programmability can be considered as one
of the ways to control the SIA object.
Programmability of interface architecture provides
functional flexibility of subsystems during their
interaction with SIA and computational environment.
The general concept of the computing
environment within SIRS consists in the
implementation of receiving, transmitting, processing
and storing information about SIA, SIRS and its
subsystems by managing it through a human-machine
dialogue, based on software and hardware, aimed at
automating the acquisition of information about
strategic innovation activities to improve the
efficiency and quality of research tools.
The base-level concept of computing environment
at the present stage within SIRS consists in realization
of reception, transfer, processing and storage of data
and knowledge about SIRS and its subsystems by its
management by means of human-machine dialogue,
based on software-hardware, aimed at automatization
of obtaining new knowledge about SIA to increase
the efficiency of experimentation tools and creation
of modern IA industry.
The general concept of interface tools within the
framework of SIRS is to provide information
interaction between the computational environment
and the SIA object by organizing impact on the SIA
object and recording its response to impact on the
basis of experimental hardware, aimed at increasing
the efficiency of primary information acquisition for
the purpose of end-to-end automation in the IA field.
The base-level concept of modern interfacing
means within the framework of SIRS consists in
providing information interaction between modern
computing environment and SIA object by means of
adaptive stabilization of control parameters of IA
object and registration of integral responses of SIA
object on the basis of modern hardware and software,
aimed at increasing informativeness of SIA research
with the purpose of end-to-end automation and digital
transformation under the influence of SIRS.
The general concept of human innovation activity
in SIRS consists in heuristic search for solutions by
implementing informal operational research of SIRS
and its subsystems, aimed at efficient operation,
maintenance, service and upgrading of the system to
ensure the life cycle of SIRS.
Human investment activities in SIRS are closely
intertwined with human activities in general. The
feedback of this activity model is presented in the
form of an activity law for this development stage:
Y = F (X1, X2, X3, X4, X5, X6; R ), (1)
where Х1-Х6 are the factors for the existence of
activities: by scope, focus, product, scope, dynamics
of innovation processes;
R is a relationship matrix between these factors.
In most detail, the algorithms of the block
responsible for the work of the decision maker - user
of the innovation manager, financial analyst and
designer (systems engineer) with the knowledge
system in the operation of SIRS were investigated.
The algorithms of SIA situation assessment with
sustainability analysis and economic risk
management of innovation activities are also
presented.
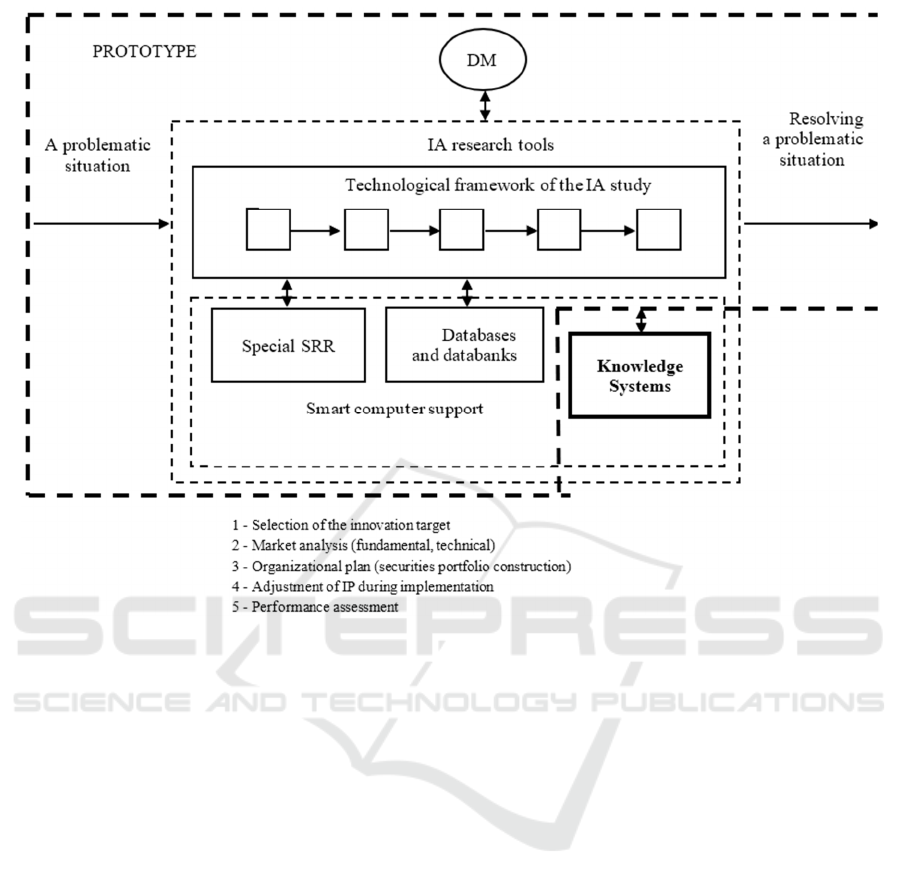
Thus, based on the conducted scientific research
of strategic innovation research system, the structure
of SIRS can be formed and presented in the form of
the following scheme (Figure 1).
3 RESULTS
The following results have been obtained from the
conducted scientific research:
– Methodological, system-informational
prerequisites for the development of models of
economic, information-innovation and
management processes of strategic investment-
innovation activity have been obtained to
create a research system of strategic
investment-innovation activity.
– The investment and innovation activities of
modern enterprises have been analysed and
modelled taking into account the uncertainties
and venture factors of transforming economy
as a prototype of technology for the study of
investment and innovation activities.
– The following models of strategic investment
activity research have been developed:
conceptual (general, basic-level, modification-
level), systemic (tuple-level).
– The structure of the strategic investment-
innovation activity research system is formed
taking into account the introduction of a new
innovation block for the knowledge system
research system.
– System-based requirements for the
technological scheme of strategic investment
and innovation activity research through the
methodological chain "slogans (the most
significant factors) - problem - problem - global
goal - local goals - objectives" are formulated.
Systematic Method of Targeting the Strategic Innovation Research System in Transport
263
4 CONCLUSIONS
The importance and value of this work lies in the fact
that it provides a methodology for scientific research
in any field of activity both for enterprises and
organizations, and for the development and
improvement of business processes, as well as
competitiveness of developing companies and
corporations. Further development and
modernization of the proposed research system is
planned to apply it in practice, taking into account the
research of uncertainties in a changing environment
based on the assessment of quality criteria for the
management of strategic investment and innovation
activities of modern facilities.
REFERENCES
Boso, N., Cadogan, J. W., Story, V. M., 2012.
Entrepreneurial orientation and market orientation as
drivers of product innovation success: A study of
exporters from a developing economy. International
Small Business Journal 31(1), 57–81.
Brozovic, D., 2018. Strategic flexibility: A review of the
literature. International Journal of Management
Reviews 20(1), 3–31.
Cheng, Z., Tan, Z., Guo, Z., Yang, J., Wang, Q., 2020.
Recent progress in sustainable and energy-efficient
technologies for sinter production in the iron and steel
industry. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews
131, 110034.
Covin, J. G., Wales, W. J., 2018. Crafting high-impact
entrepreneurial orientation research: Some suggested
guidelines. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice
43(1), 3–18.
Guo, T., Shi, Z., 2021. Systematic Analysis on the
Environment of Innovative Small and Medium
Enterprises. Physics Procedia 24, Part B, 1214-1220.
Gupta, V. K., Atav, G., Dutta, D. K., 2019. Market
orientation research: A qualitative synthesis and future
research agenda. Review of Managerial Science 13(4),
649–670.
Ho, J., Plewa, C., Lu, V. N., 2016. Examining strategic
orientation complementarity using multiple regression
analysis and fuzzy set QCA. Journal of Business
Research 69(6), 2199–2205.
Figure 1: SIRS structure.
TLC2M 2022 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC AND PRACTICAL CONFERENCE TLC2M TRANSPORT: LOGISTICS,
CONSTRUCTION, MAINTENANCE, MANAGEMENT
264

Jin Ko, Y., O'Neill, H., Xie, X., 2021. Strategic intent as a
contingency of the relationship between external
knowledge and firm innovation. Technovation Volume
104, 102260.
Li, Y., Liu, Y., Duan, Y., Li, M., 2008. Entrepreneurial
orientation, strategic flexibilities and indigenous firm
innovation in transitional China. International Journal
of Technology Management 41, 223–246.
Łuczak, А., Just, M., 2021. Sustainable development of
territorial units: MCDM approach with optimal tail
selection. Ecological Modelling 457, 109674, 0304-
3800.
Mok, K. H., Kan, Y., 2013. Promoting entrepreneurship and
innovation in China: Enhancing research and
transforming university curriculum. Frontiers of
Education in China 8(2), 173–197.
Morgan, T., Obal, M., Jewell, R. D., 2021. Strategic change
and innovation reputation: Opening up the innovation
process. Journal of Business Research 132, 249-259.
Pasinetti, L. L., 2021. Economic theory and institutions.
Structural Change and Economic Dynamics 56, 438-
442.
Shcheglov, E. V., 2018. Priority industrial policy
instruments for sustainable economic development of
Perm Krai's industrial enterprises. Financial Economics
8, 532-536.
Shabalov, M. Yu., Zhukovskiy, Yu. L., Starshaia, V. V.,
2021. The influence of technological changes in energy
efficiency on the infrastructure deterioration in the
energy sector. Energy Reports 7, 2664-2680.
Vnukovsky, N. I., 1999. Structural and functional models
of SIRS. Intellectual information technologies in
managerial activity: Proceedings of II International
scientific-practical seminar. Ekaterinburg: Publishing
house of IPK UGTU, p. 24-28.
Wales, W. J., 2015. Entrepreneurial orientation: A review
and synthesis of promising research directions.
International Small Business Journal 34(1), 3–15.
Systematic Method of Targeting the Strategic Innovation Research System in Transport
265
