
Comparison of Precipitation from Different Meteorological Stations:
A Case Study
Yansong Xiao
1
, Yahua Liao
2
, Lijuan Li
1
, Jianlin Hou
1
, Sijun Li
1
, Zhipeng Tan
1
, Rujing Deng
1
,
Zhihong He
1
, Hongguang Li
1
and Bin He
1,*
1
Chenzhou Tobacco Company of Hunan Province, 423000, Chenzhou, Hunan, China
2
Hunan Provincial Tobacco Company, 410004, Changsha, Hunan, China
Keywords: Different Site, Regression Model, Time Scales, Relationship.
Abstract: Precipitation (P) can affect the growth, yield and quality of tobacco. This study compares P from the field
automatic meteorological station (FMS) and national meteorological station (NMS) which are installed in
different sites in Guiyang County, Chenzhou City of south Hunan Province on different time scales (whole
year, tobacco-growing season and different tobacco-growing stages). The results show that P, P differences
(ΔP), and day numbers of P difference (ΔP < 0 mm, = 0 mm, and > 0 mm) between FMS and NMS are
different at different sites and different time scales. The range of ΔP between FMS and NMS are from 20.4 to
339.1 mm with the absolute error from 4.6% to 48.4%, and day number is 0 - 133 d for ΔP < 0 mm, 7 - 191 d
for ΔP = 0 mm and 8 - 158 d for ΔP > 0 mm; In most cases the quadratic regression model could describe well
the correlation in P between NMS and FMS on different time scales, but the accuracy of the regression model
varies with different sites and different time scales. Therefore, it is necessary to determine climate zones firstly
for a tobacco-planting region and then FMS should be installed for each zone to obtain the real zonal P data
for meeting the requirements of fine meteorological services and revealing more accurately the relationship
between climate and the growth, yield and quality of tobacco.
1 INTRODUCTION
Many studies in China have shown that precipitation
(P) can directly affect the growth, yield and quality of
tobacco (Xu and Wang, 2016; Liu, 2017 and 2020; Xu
et al., 2019; Ji et al., 2021). Usually 0.8 - 1 kg of water
is needed to produce 1 kg of tobacco leaves, and the
suitable precipitation is 500 - 600 mm in the whole
tobacco-growing season, among of which, 100 - 120
mm, 230 - 280 mm and 150 -180 mm in the rooting,
flourishing and maturing stages of tobacco,
respectively (Liu, 2017).
P is dependent on the spatial location and can be
influenced by many factors, such as latitude,
longitude, altitude, vegetation and so on. But in China
there is usually only one national meteorological
station (NMS) in a county and in most cases, it is not
in the tobacco-planting region, thus, P of NMS can’t
reflect the real P of a tobacco-planting region, P
predicted by the model based on the data of NMS may
lead to the mis-decision and result in the adverse
effects for the planting of high-quality tobacco.
In recent years the field automatic
meteorological stations (FMS) have been installed in
some tobacco-growing regions in China (Li et al.,
2015a and 2015b; Liu, 2020; Shi and Liu, 2016), and
have supported the determination of transplanting
time of tobacco (Li et al., 2019)
and the effects of
climate parameters on quality formation of tobacco
(Zha et al., 2014; Gao, 2021). However, usually the
data of P have to be used from the nearest NMS for a
tobacco-planting region without NMS, and also P data
of multi years (for example, 20 years or more) from
NMS nearest the tobacco-planting region have to be
used to establish the predicting model of P because
many FMS have not been setup for a long time in
China. However, some studies found there are
differences in the data of climate parameters (for
examples, temperature, relative humidity and
atmospheric pressure) between NMS and FMS even
in the same small region (Chen et al., 2018 and 2019;
Yu et al., 2021), however, no comparison so far is
reported between P between FMS and NMS.
Chenzhou City, as the most typical region of
Nanling Hill Ecological Zone of tobacco with the
76
Xiao, Y., Liao, Y., Li, L., Hou, J., Li, S., Tan, Z., Deng, R., He, Z., Li, H. and He, B.
Comparison of Precipitation from Different Meteorological Stations: A Case Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0011596400003430
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Agricultural and Biological Sciences (ABS 2022), pages 76-82
ISBN: 978-989-758-607-1; ISSN: 2795-5893
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

aroma style of burnt-pure sweet in China (Luo et al.,
2019), is the largest tobacco-planting region in Hunan
province, accounting for about 1/3 (2.67 × 10
4
hm
2
) of
the total tobacco-planting area in Hunan (Luo et al.,
2017). Some studies were conducted on P in tobacco-
growing regions in Chenzhou and showed that,
according to the suitable values of P for the high-
quality tobacco, P was unfavorable in rooting stage but
suitable in flourishing and maturing stages of tobacco-
growing (Rong, 2013), excessive P in early growing
stage was a main factor inducing the occurrence of
unfavorable “high temperature forced early-maturity”
(Kuang, 2009), P changed irregularly on the scales of
year, tobacco-growing season, and in the rooting and
flourishing stages of tobacco-growing (Kong et al.,
2020). However, the climatic data used in the above
studies are either from NMS (Chen et al. 2015; Rong,
2013; Kuang, 2009; Kong et al., 2020) or from FMS
(Gu et al, 2020; Wang, 2017), so far there is no report
on P comparison between FMS and NMS, and the
differences in P from different meteorological stations
possibly can lead to the misjudgments about the
relationship between P and tobacco. So here we
propose the following two hypotheses: 1) P data
recorded in the national metrological station (NMS) in
a county (usually there is only one NMS in a county in
China) is different from that recorded in the
metrological station (FMS) installed in the tobacco-
planting region, which is mainly due to the difference
in the spatial sites, also to the differences in terrain,
land use type and so on, so P data of NMS can’t be
directly used to establish the model for predicting P in
the tobacco-planting region, for it would lead to mis-
decisions and the adverse effects on tobacco planting.
2) there is a certain correlation and comparability
between precipitation data of NMS and FMS, this
correlation is dependent on the location and time, and
could be used to modify the model based on P data of
NMS in order to improve further the prediction
accuracy of P in the tobacco-planting region. We hope
that the results of our study can prove further that FMS
should be installed in tobacco-planting region in
revealing more accurately the relationship between P
and tobacco-planting, and meet the requirements of
fine meteorological services in the tobacco-planting
region.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Information of Study Region
Chenzhou City is located in the southeast of Hunan
province of south-central China, between 112˚13' to
114˚14' in east longitude and 24˚53' to 26˚50' in north
latitude with a total area of 1.94×10
4
km
2
, which
belongs to subtropical monsoon humid climate with
annual mean temperature of 15.4-18.3°C, cumulative
sunshine hours of 1510.3-1764.3 hrs, precipitation of
1320.3-1654.7 mm and frost-free season of 235-296
d (Rong, 2013). The altitude of Chenzhou City ranges
from 70 to 2061 m, and the landform is complex with
mountains and hills accounting for about 3/4 of the
total area. The main soil types are red soil, yellow-red
soil and paddy soil (Hunan Agriculture Department,
1989), and the total area of cultivated land is
30.96×10
4
hm
2
with the areas of 25.94×10
4
hm
2
of
paddy fields (Chenzhou Municipal Bureau of Statistic,
2018). Tobacco is mainly cultivated in paddy fields
under the rotation of tobacco and late rice.
2.2 Sources, Processing and Analysis of
Climate Parameters
The original daily cumulative P are from the NMS in
Guiyang County (GY, No. 57973) and from FMS
(Temperature and Humidity Recorder 179-TH,
Beijing Dingxuan Shengshi Technology Co., Ltd.) in
Fangyuan Town (FY) and Aoquan Town (AQ), two
important tobacco-planting regions in GY installed in
October 2019.
Three-time scales are used in our study, which
include the whole year (from January 1 to December
31), tobacco-growing season (from March 10 to July
20) and different tobacco-growing stages (the rooting
stage from March 10 to April 20; the flourishing stage
from April 21 to May 31, and maturing stage from
June 1 to July 20).
Microsoft Excel 2016 and IBM Statistics SPSS
22.0 software are used for data processing and
analysis. The abnormal data are eliminated according
to the mothed of mean ± 3×S.D. The significant
difference and correlation are indicated by p<0.05 or
p<0.01.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Comparison of P between FMS and
NMS on Different Time Scales
The statistical information of P of FMS and NMS at
different time scales is presented in Table 1 From
Table 1 it can be seen that P, absolute error (AE) and
relative error (RE) of P between FMS and NMS are
different at different time scales, the range of P
difference between FMS and NMS are from 20.4 to
Comparison of Precipitation from Different Meteorological Stations: A Case Study
77

339.1 mm with the absolute error from 4.6% to 48.4%.
At the scale of year, in 2020, P of FY and AQ was
154.6 mm (10.5%) and 149.8 mm (10.2%) higher than
GY, respectively. However, in 2021, P of FY and AQ
was 339.1 mm (20.7%) and 142.4 mm (8.4%) lower
than GY, respectively. At the scale of tobacco-
growing season, in 2020, P of FY and AQ was 75.7
mm (10.0%) and 35.2 mm (4.6%) higher than GY,
respectively. However, in 2021, P of FY was 67.5 mm
(8.4%) lower than GY, while P of AQ was 139.6 mm
(17.4%) higher than GY. At rooting and flourishing
stages in 2020 and 2021, P of FY and AQ was 117.1
mm (30.2%), 61.0 mm (15.7%) and 20.4 mm (11.8%),
76.4 mm (44.3%) higher than GY in 2020; 26.0 mm
(14.0%), 49.1 mm (26.5%) and 18.9 mm (4.6%), 16.7
mm(4.1%) higher than GY in 2021; while at maturing
stage, in 2020, P of FY and AQ was 67.4 mm (36.7%)
and 74.9 mm (40.8) lower than GY, respectively;
However, in 2021, P of FY was 106.8 mm (48.4%)
lower than GY, while P of AQ was 46.5 mm (21.1%)
higher than GY. The statistical information of day
numbers of P difference (ΔP < 0 mm, = 0 mm, and >
0 mm) between FMS and NMS at different time
scales is presented in Table 2. From Table 2 it can be
seen that the day numbers of ΔP are different at
different time scales, day number is 0-133 d for ΔP <
0 mm, 7-191 d for ΔP = 0 mm, 8-158 d for ΔP > 0 mm.
At the scale of year, there are 27.0%-36.3%, 40.7%-
49.3% and 23.0% of days in 2020-2021 in FY with P
lower than, equal to and higher than in GY,
respectively; 4.4%-29.8%, 41.3%-52.3% and 28.9%-
43.3% of days in 2020-2021 in AQ with P lower than,
equal to and higher than in GY, respectively. At the
scale of tobacco-growing season, there are 27.8%-
33.1%, 39.1%-42.9% and 27.8%-29.3% of days in
2020-2021 in FY with P lower than, equal to and
higher than in GY, respectively; 0-33.1%, 42.1%-
43.6 % and 24.8%-56.4% of days in 2020-2021 in AQ
with P lower than, equal to and higher than in GY,
respectively. In rooting stage, there are 40.5%, 21.4%-
40.5% and 19.0%-38.1% of days in 2020-2021 in FY
with P lower than, equal to and higher than in GY,
respectively; 0-57.1%, 16.7%-50.0% and 26.2%-50.0
% of days in 2020-2021 in AQ with P lower than,
equal to and higher than in GY, respectively. In
flourishing stage, there are 0-31.7%, 29.3%-39.0%
and 29.3%-70.7% of days in 2020-2021 in FY with P
lower than, equal to and higher than in GY,
respectively; 0-31.7%, 26.8%-36.6% and 31.7%-73.2
% of days in 2020-2021 in AQ with P lower than,
equal to and higher than in GY, respectively. In
maturing stage, there are 14.0%-18.0%, 56.0%-64.0%
and 22.0%-26.0% of days in 2020-2021 in FY with P
lower than, equal to and higher than in GY,
respectively; 0-14.0%, 54.0%-60.0% and 26.00%-
46.0% of days in 2020-2021 in AQ with P lower than,
equal to and higher than in GY, respectively.
Table 1: Comparison of P on different time scales.
Scale Year
GY FY AQ
P (mm)
P
(mm)
AE (mm) RE (%)
P
(mm)
AE
(mm)
RE
(%)
Whole year 2020 (n=366) 1466.8 1621.4 154.6 10.5
1616.
6
149.8 10.2
2021 (n=365) 1636.0 1296.9 -339.1 -20.7
1493.
6
-142.4 -8.7
Tobacco-growing
season
2020 (n=133) 757.3 833.0 75.7 10.0 792.5 35.2 4.6
2021
(
n=133
)
803.6 736.1 -67.5 -8.4 943.2 139.6 17.4
Rootin
g
sta
g
e 2020
(
n=42
)
388.2 505.3 117.1 30.2 449.2 61.0 15.7
2021
(
n=42
)
172.4 192.8 20.4 11.8 248.8 76.4 44.3
Flourishing stage 2020 (n=41) 185.4 211.4 26.0 14.0 234.5 49.1 26.5
2021 (n=41) 410.7 429.6 18.9 4.6 427.4 16.7 4.1
Maturin
g
sta
g
e 2020
(
n=50
)
183.7 116.3 -67.4 -36.7 108.8 -74.9 -40.8
2021
(
n=50
)
220.5 113.7 -106.8 -48.4 267.0 46.5 21.1
Notes: AE = FY or AQ - GY, RE(%) = (FY or AQ - GY)×100/GY.
ABS 2022 - The International Conference on Agricultural and Biological Sciences
78

Table 2: Day numbers of different P values at different time scales.
Time scale
Site Period
ΔP (℃)
Total (days)
< 00> 0
Da
y
%Da
y
%Da
y
%
Year FY 2020 133 36.3 149 40.7 84 23.0 366
2021 101 27.7 180 49.3 84 23.0 365
AQ 2020 109 29.8 151 41.3 106 28.9 366
2021 16 4.4 191 52.3 158 43.3 365
Tobacco season FY 2020 37 27.8 57 42.9 39 29.3 133
2021 44 33.1 52 39.1 37 27.8 133
AQ 2020 44 33.1 56 42.1 33 24.8 133
2021 0 0 58 43.6 75 56.4 133
Growing stage FY 2020 Rooting 17 40.5 9 21.4 16 38.1 42
Flourishing 13 31.7 16 39.0 12 29.3 41
Maturin
g
7 14.0 32 64.0 11 22.0 50
2021 Rooting 17 40.5 17 40.5 8 19.0 42
Flourishing 0 0 12 29.3 29 70.7 41
Maturing 9 18.0 28 56.0 13 26.0 50
AQ 2020 Rooting 24 57.1 7 16.7 11 26.2 42
Flourishing 13 31.7 15 36.6 13 31.7 41
Maturin
g
7 14.0 30 60.0 13 26.0 50
2021 Rooting 0 0 21 50.0 21 50.0 42
Flourishing 0 0 11 26.8 30 73.2 41
Maturing 0 0 27 54.0 23 46.0 50
Notes: P = GY-FY or GY-AQ.
3.2 Regression Models of P between
NMS and FMS at Different Time
Scales
SPSS software were used to decide the optimal
regression model of P between FMS and NMS based
on the comparison of the accuracies of all kinds of
models listed in SPSS, although there are obvious
differences in P between FMS and NS, Table 3 shows
in most cases the quadratic regression model could
describe well the correlation in P between FMS and
NMS on different time scales except in FY at the
scale of tobacco-growing season, in rooting stage in
2020 and maturing stage in 2021, and in flourishing
stage in AQ in 2020. It also can be seen from Table 3
that, p are 0.000 except in AQ in flourishing and
maturing stages in 2020 (p=0.081 and 0.016) and in
maturing stage in 2021 (p=0.190). R
2
is 0.298-0.733
with a mean of 0.511 in FY and AQ at the scale of
year, 0.323-0.732 with a mean of 0.518 in FY and AQ
at the scale of tobacco-growing season, and 0.068-
0.819 with a mean of 0.542 at the scales of the
different tobacco-growing stages.
4 DISCUSSION
It is well-known that P are different in different sites
even in small space, our study also not only found the
differences in P between FMS and NMS, but also
found the difference in P between FMS in FY and in
AQ. Generally, P is increased with the decreases of
latitude and the increase of altitude and vegetation
coverage, but it actually is still very difficult or
impossible to give a clear quantitative explanation for
the difference in P in the three sites of our study even
there are the information available of longitude,
latitude, altitude, topography, land use type and
vegetation coverage of the three sites listed in Table
4. For examples, the latitude from north to south is
25°55′36″ for FMS in AQ, 25°44′58″ for NMS in GY,
and 25°40′49″ for FMS in FY, the altitude from high
to low is GY (329,1 m), FY (320.4 m) and AQ (250.0
m), which are not consistent with P, which from high
to low is FY (1621.4 mm), AQ (1616.6 mm) and GY
(1466,8 mm) in 2020, GY (1636.1 mm), AQ (1493,6
mm) and FY (1296.9 mm).
Comparison of Precipitation from Different Meteorological Stations: A Case Study
79
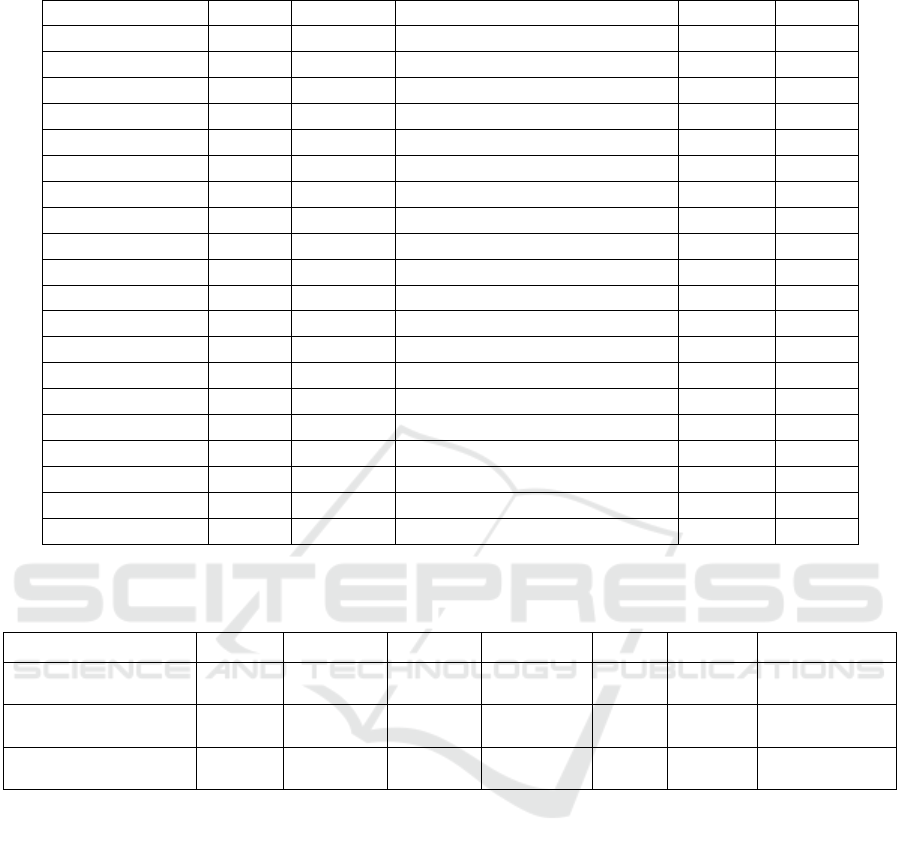
Table 3: Regression models of P between NMS and FMS at different time scales.
Time scale Site Year Regression model R
2
p
Year FY 2020
y = -0.004x
2
+ 1.125x + 0.296 0.733 0.000
2021
y = -0.003x
2
+ 0.787x + 0.440 0.593 0.000
AQ 2020
y = -0.016x
2
+ 1.314x + 0.732 0.419 0.000
2021
y = 0.003 x
2
+ 0.213x - 0.440 0.298 0.000
Tobacco season FY 2020 y = 1.039x + 0.345 0.732
0.000
2021 y = -0.004 x
2
+ 0.929x + 0.774 0.641
0.000
AQ 2020 y = -0.012 x
2
+ 1.094x + 1.639 0.323
0.000
2021 y = -0.011 x
2
+ 1.180x + 2.145 0.375
0.000
Rooting stage FY 2020 y = 1.201x + 0.931 0.788
0.000
2021 y = 0.007x
2
+ 0.648x + 1.378 0.748
0.000
AQ 2020 y = -0.020x
2
+ 1.719x + 0.694 0.708
0.000
2021 y = -0.016x
2
+ 1.566x + 0.828 0.568
0.000
Flourishing stage FY 2020 y = 0.024x
2
+ 1.668x – 0.147 0.753
0.000
2021 y = -0.009x
2
+ 1.328x + 0.560 0.819
0.000
AQ 2020 y = 0.451x + 3.679 0.076 0.081
2021 y = -0.011x
2
+ 1.353x + 1.254 0.743
0.000
Maturing stage FY 2020 y = 0.009x
2
+ 0.280x + 0.434 0.775
0.000
2021 y = 0.410x + 0.465 0.302
0.000
AQ 2020 y = -0.019x
2
+ 0.817x + 0.987 0.162
0.016
2021 y = -0.011x
2
+ 0.785x + 3.465 0.068 0.190
Notes: in regression model, y and x are the data of climate parameters from the field and national stations, respectively.
Table 4: Information of FMS and NMS in Guiyang County (GY) of Chenzhou City.
Meteorological Station Site Longitude Latitude Altitude (m) Terrain Land use Period of P data
FMS FY 112°40′0″ 25°40′49″ 320.4 plain Farmland
2020.1.1-
2021.12.31
FMS AQ 112°34′36″ 25°55′36″ 250.0 Plain Farmland
2020.1.1-
2021.12.31
NMS (No. 57973) GY 112°43'29" 25°44'58" 329.1 hill Forest
2020.1.1-
2021.12.31
Notes: FY and AQ are the main tobacco-growing towns of GY.
Meanwhile, we think the stability and reliability of P
data of NMS data is better than that of FMS, which is
based on the facts that we have found that in other
tobacco-planting regions, FMS occasionally does not
work well, thus affect the accurate acquisition of P data.
Anyhow, we believe that as long as FMS is under normal
operation in the tobacco field, the obtained precipitation
data are reliable and acceptable.
Compared with the suitable P at tobacco-growing
season and at different tobacco-growing stages,
according to Table 5, the suitability of P for tobacco-
planting are similar (all are excessive) in GY, FY and
AQ in tobacco-growing season and in rooting stage in
2020 and 2021, in flourishing stage in 2021, in the
maturing stage (all are insufficient) in 2021, while it is
different in flourishing stage in 2020 and maturing stage
in 2021, in which P is insufficient in GY and FY, but
suitable in AQ in 2020, while P is excessive in GY
and AQ and insufficient in FY in 2021, which
means that sometimes the differences in P from
different meteorological stations possibly can lead
to the misjudgments about the relationship
between P and tobacco, it is necessary to obtain the
real data of P for a specific site when analyze the
relation between P and the growth, yield and
quality of tobacco.
The previous studies on comparison between
FMS and NMS mainly focused on the differences
in temperature, relative humidity and atmospheric
pressure (Chen et al., 2018 and 2019, Yu et al.,
2021), so far, there is no report on P difference
between FMS and NMS, which may be due to
more complex influential factors (mainly include
site, terrain, vegetation, hydrological condition,
ABS 2022 - The International Conference on Agricultural and Biological Sciences
80

and human activities) or high spatial variation of P. Our
study compares (Table 6) the accuracy in predicting P at
FY and AQ stations in the same period by using the
models of whole year, tobacco-growing season and
different tobacco-growing stages between FMS and
NMS. It can be seen from Table 6 that tobacco growing
season model is more accurate than whole year model in
predicting P in tobacco-growing season and in maturing
stage in FY and AQ in 2020 and 2021. But the optimal
model is different in predicting P in rooting and
flourishing stages, for examples, in rooting stage,
tobacco-growing season model is more accurate
for FY in 2020 and AQ in 2021, while rooting
model is more accurate for FY in 2021 and AQ in
2020; In flourishing stage, tobacco-growing
season model is more accurate for FY in 2020 and
2021, while flourishing model is more accurate for
AQ in 2020 and 2021, which mean the site and
time scale must be considered when predicting P
with regression model between NMS and FMS.
Table 5: Suitability assessment of P at different time scales.
Time scale
Suitable
P (mm)
*
Year
GY FY AQ
P (mm) Suitable or no P (mm) Suitable or no P (mm)
Suitable or
no
Tobacco season 500-600 2020 757.3 excessive 833.0 excessive 792.5 excessive
2021 803.6 excessive 736.1 excessive 943.2 excessive
Rooting stage 100-120 2020 388.2 excessive 505.3 excessive 449.2 excessive
2021 172.4 excessive 192.8 excessive 248.8 excessive
Flourishing stage 230-280 2020 185.4 insufficient 211.4 insufficient 234.5 suitable
2021 410.7 excessive 429.6 excessive 427.4 excessive
Maturing stage 150-180 2020 183.7 insufficient 116.3 insufficient 108.8 insufficient
2021 220.5 excessive 113.7 insufficient 267.0 excessive
Notes: Data of suitable P are from Liu 2017.
Table 6: Accuracy of regression models of P between NMS and FMS at different time scales.
Time scale Model
FY AQ
2020 2021 2020 2021
ME RSME ME RSME ME RSME ME RSME
Tobacco-growing season Year 0.18 1.94 -1.23 4.15 -0.62 6.93 -5.28 10.54
Season 0.58 0.79 -0.27 2.89 -0.22 6.73 2.43 2.61
Rooting stage Year -0.31 3.37 0.78 2.47 1.61 7.18 4.53 9.48
Season 0.81 1.12 0.11 1.47 1.63 7.41 2.45 2.52
Rooting 3.49 5.17 0.34 1.45 1.25 5.29 1.14 2.53
Flourishing stage Year 0.42 0.52 2.84 6.15 1.10 10.01 -7.71 12.26
Season 0.54 0.67 -1.38 4.23 -0.54 9.22 2.78 2.81
Flourishing 6.42 15.92 11.24 21.16 0.53 7.67 1.51 2.65
Maturing stage Year 0.41 0.50 -0.38 3.12 0.6 1.47 -3.9 9.83
Season 0.44 0.50 0.30 2.39 1.23 2.19 2.13 2.45
Maturing -0.83 3.10 -0.88 5.09 -0.38 5.02 -0.37 12.84
5 CONCLUSION
Our study shows that there are obvious differences in
P between FMS and NMS in different locations and
at different time scales even in the same tobacco-
planting county. Although P is significantly
correlated between NMS and FMS in most cases, and
the regression models could be used in predicting P
from the data of NMS for a tobacco-growing region
without FMS, however, the accuracy of the
regression model varies with different sites and
different time scales, therefore, it is necessary to
Comparison of Precipitation from Different Meteorological Stations: A Case Study
81

determine climate zones firstly for a tobacco-planting
region, and then FMS should be installed for each
zone to obtain the real P data of the zone to meet the
requirements of fine meteorological services and to
reveal more accurately the relationship between
climate and tobacco in the tobacco-growing region.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was supported by the Project of Chenzhou
Company of Hunan Tobacco Company (No. 2019-
45). We would like to express thanks to those who
helped in soil sampling and analysis.
REFERENCES
Chen, D., Chen, Y. Y., Zhang, L. and Nie, J. X. (2018).
National observation stations and automatic weather
stations in vineyard area at the east foot of Helan
mountain: Comparative analysis of the minimum
temperature. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,
34(30): 110-117.
Chen, D., Li, N., Gao, Y. Y., Dai, M. J. and Hou, X. X.
(2019). Temperature comparison analysis between
Wuzhong city national basic weather station and Litong
District regional automatic station from 2015 to 2017
and its correction. Modern Agricultural Science and
Technology, (5): 185-187.
Chen, Y., Zhou, Q. M., Yang, H. Q., Yang, H. W. and Li,
H. G. (2015). Analysis of the climate characteristics
during field growth period of tobacco in producing
areas of the typical strong flavor type tobacco leaves in
Xiangnan. Chinese Tobacco Science, (36): 56-62.
Chenzhou Municipal Bureau of Statistics, (2018).
Chenzhou Statistics Yearbook, Chenzhou, China.
Gao, Z. Z. (2021). Study on climatic indexes of upper six
flue-cured tobacco leaves in central Henan province.
Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China.
Gu, M. M., Wang, Z. T., Ni, X. C., Zhang, C., Zhang, J. Y.,
Luo, W. J., Chen, W. C., Han, X. B., Zhang, S. G. and
Zhu, D. H. (2020). Ecological mechanism of heat-
forced maturity of flue-cured tobacco in southern
Hunan Province. Tobacco Science & Technology,
53(5): 26-32.
Hunan Agriculture Department 1989. Hunan Soils. China
Agriculture Press, Beijing, China.
Ji, S. H., Zhao, X. B., Wang, C. C., Zhan, R. F. and Lu, P.
(2021): Correlation between main climatic component
of tobacco leaf in Baoshan tobacco-growing area.
Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 49(6): 134-139.
Kong, X. Z., Li, D. C., Li, W. J., Li, H. G. and Xiao, Y. S.
(2020). Study on climate changes for flue-cured
tobacco growth in Chenzhou city of Hunan province.
Agricultural Sciences. (11): 487-499.
Kuang, C. F. (2009): Climatic characteristics and suitability
assessment on tobacco-growing in Chenzhou of Hunan.
Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, (17):
284-285.
Li, L. Y., Xu, Y. M. and Wang, S. S. (2015a). Advance in
effects of climatic factors on aroma components of
flue-cured tobacco. Chinese Tobacco Science, 36(1):
107-113.
Li, B., Zheng, F. W., Qing, X. T., Xiao, J., Xu, L. Q. and
Huang, Q. C. (2019). Different tobacco planting units
in Xiangxi Autonomous Prefecture: Estimate of climate
characteristic values. Chinese Agricultural Science
Bulletin. 35(18): 67-71.
Li, Z. H., Zhang, Y. G. and Li, J. Y. (2015b): Ecological
mechanisms for the formation of the fragrance style of
flue-cured tobacco. Science Press, Beijing, China.
Liu, G. S. (2017). Tobacco culture. China Agriculture
Press, Beijing, China.
Liu, G. S. (2020). Theory and practice of strong-aroma
style flue-cured tobacco in China. Science Press,
Beijing, China.
Luo, D. S., Wang, B. and Qiao, X. Y. (2019). Explanation
of national regionalization of leaves style of flue-cured
tobacco. Acta Tabacaria Sinica, 25(4): 1-9.
Luo, J. Q., Xiao, Y. S., Zhong, Q., Yu, J. L. and He, B.
(2017): Production status and development
countermeasures of highly flavored type tobacco leaves
in Chenzhou.
Hunan Agricultural Sciences, (8): 116-
118.
Rong, K. D. (2013): Analysis of climatic resources and
weather service on tobacco production in Chenzhou.
Tillage and Cultivation, (6): 59-60.
Shi, H. Z. and Liu, G. S. (2016): Ecological basis for
formation of strong-aroma style flue-cured tobacco.
Science Press, Beijing, China.
Wang, Z. T. (2017). The monitoring of "heat-forced
maturity" index in Xiangnan and the response of heat
and irradiance stress on photosynthetic physiology in
tobacco. Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou,
China.
Xu, Y. M., Song, W. J. and Wang, C. D. (2019).
Characteristics of tobacco quality and style of typical
producing areas of high-quality and specific flue-cured
tobacco in China. Science Press, Beijing, China.
Xu, Y. M. and Wang, C. D. (2016). Ecological conditions
of typical producing areas of high-quality and specific
flue-cured tobacco in China. Science Press, Beijing,
China.
Yu, F., Hou, S. S., Gu, X. P., Gu, S. H. and Zuo, J. (2021).
Correlation between microclimate in Kiwi fruit orchard
and temperature and humidity in national
meteorological station in Shuicheng county. Guizhou
Agricultural Sciences, 49(6): 120-127.
Zha, H. B., Fu, X. T., Li, X. Y., Huang, W., Tao, Y. P.,
Zhao, F., Ni, X., Lu, W. L., Xiao, J. F., Gao, S. B.,
Chen, S., Wang, W. B., Yang, J. and Zhang, Y., (2014).
Classification of tobacco field microclimate types and
its correlation with chemical composition of tobacco
leaves in Zhaotong. Chinese Tobacco Science, 35(2):
88-93.
ABS 2022 - The International Conference on Agricultural and Biological Sciences
82
