
International Research Progress on Traffic Accident Based on
Bibliometric Analysis Method
Jie Zhang, Yu Zhang, Hao Wang and Yuanyuan Yu
Research Institute of Highway, Ministry of Transport, Beijing, 100088, China
Keywords:
Traffic Accident Analysis, Bibliometric Analysis Method, Visualization, VOS Viewer, Severity.
Abstract: It is important to research on the characteristics, distribution rules, and mechanisms of traffic accidents,
which are carried out to explore the deep-seated causes of accidents. Based on bibliometric analysis method,
this paper conducts a quantitative analysis of 8125 papers in the field of traffic accident research from the
past five years. It is concluded that the most important document source in the current traffic accident field
is Accident analysis and prevention, the most important research countries are the United States and China,
and the most important research institutions are Tsinghua University and Tongji University. The main
research hotspots are traffic accident severity analysis, statistical analysis of traffic accidents, short-term
prediction of traffic accidents, prediction of traffic accident severity, and analysis of the impact of dynamic
factors such as weather on accidents. It has certain reference significance for domestic scholars to intuitively
understand the topics that have not been fully researched in our country and the gap between existing
research and foreign frontier fields through comparison.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to “The Global Status Report on Road
Safety 2018” issued by the World Health
Organization (World Health Organization, 2018),
road traffic crashes now represent the eighth leading
cause of death globally and road traffic injury is
now the leading cause of death for children and
young adults aged 5–29 years. Deaths from road
traffic crashes have increased to 1.35 million a year.
That’s nearly 3 700 people dying on the world’s
roads every day. Tens of millions of people are
injured or disabled by traffic accidents every year.
The property losses, medical expenses and
emergency expenses caused by traffic accidents are
huge, and they also bring huge trauma to the family
and society.
The occurrence of traffic accidents is the result
of a combination of factors such as people, vehicles,
roads, environment, and management. Through
research on the characteristics, distribution rules,
and mechanisms of traffic accidents, the deep-seated
causes of accidents are explored in order to provide
technical support for the prevention of traffic
accidents. In recent years, domestic and foreign
scholars have carried out a series of studies on
traffic accidents and achieved a series of results.
Domestic and foreign scholars analyse the impact of
human factors on traffic accidents from the
perspective of dangerous driving behaviours such as
distracted driving, aggressive driving, fatigue
driving, and drunk driving (Zhang, 2020; Klauer,
2014; Abegaz, 2014; Almahasneh, 2014), analyse
the impact of vehicle factors on traffic accidents
from the perspective of vehicle safety technical
performance such as active and safety of vehicles,
protection of vulnerable road users and vehicle
occupants, body collision compatibility (Kahane,
2015; Li, 2016; Badea-Romero, 2013), analyse the
impact of road factors on traffic accidents from the
perspective of road alignment, road safety facilities
and lighting facilities (Wong, 2007; Ma, 2010;
Yang, 2017).
At present, there are more and more researches
on road traffic accidents, but most of them focus on
certain aspects of road traffic accidents such as
dangerous driving behaviour, vehicle compatibility
design, road alignment optimization, etc. Existing
research results lack analysis from macro
perspectives such as road traffic accident research
trends, cutting-edge technologies, and research
hotspots. Based on the document co-occurrence
network analysis and visualization tool VOS viewer
Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, H. and Yu, Y.
International Research Progress on Traffic Accident based on Bibliometric Analysis Method.
DOI: 10.5220/0011701400003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 5-10
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
5

software, this paper conducts a quantitative analysis
of 8125 papers in the field of traffic accident
research from 2016 to 2020. Through the source of
the document, the main research country, the main
research institution, the author of the paper,
quantitative analysis of key words and cited papers
in the paper, the most important sources of literature
in the current traffic accident field, the most
important research countries, research institutions
and scholars, as well as the research trends, research
frontiers and research hotspots in the field of traffic
accidents are summarized.
2 BIBLIOMETRIC ANALYSIS
METHOD
Bibliometrics refers to the cross-science of using
mathematical and statistical methods to
quantitatively analyse all knowledge carriers. It is a
comprehensive knowledge system integrating
mathematics, statistics, and philology, focusing on
quantification. The measurement objects are mainly:
the amount of documents (various publications,
especially journal articles and citations), the number
of authors (individuals, collectives or groups), the
number of words (various document identifications,
most of which are thesaurus), document
measurement. The most essential feature of learning
is that its output must be "quantity".
2.1 Data Sources
The data source of this study is the core database in
Web of Science (WOS). In the database, through
entering "traffic accident" in the keyword part and
"2016-2020" in the age part, a total of 8125 related
documents are retrieved. The retrieval information is
stored in 17 files in a group of 500 pieces, and the
file format is ".txt" file.
2.2 Analysis Tools and Methods
VOS viewer (VOS viewer Manual, 2020) is a
software tool used to create maps based on network
data and to visualize and browse these maps. The
functions of VOS viewer can be summarized as
follows.
Create a map based on network data. You can
create a map based on an already available network,
or you can build the network first. VOS viewer can
be used to build a network of scientific publications,
scientific journals, researchers, research
organizations, countries, keywords or terms. Items
in these networks can be connected by co-authors,
simultaneous occurrences, citations, bibliographic
coupling or citation links.
Visualize and explore the map. VOS viewer
provides three kinds of map visualization: network
visualization, coverage visualization and density
visualization. The zoom and scroll functions allow
you to browse the map in detail, which is essential
for handling large maps containing thousands of
items. The "Create Map" wizard in VOS viewer can
be used to create a new map. There are multiple
ways to create a new map.
3 ANALYSIS AND
VISUALIZATION OF
CO-OCCURRENCE NETWORK
OF TRAFFIC ACCIDENT
LITERATURE
3.1 Literature Sources
According to the number of documents from each
source not less than ten papers, the top ten document
sources selected are shown in the following table.
According to the search results listed in Table 1,
the top ten document sources with the highest total
link strength have a total of 975 articles, accounting
for 12% of the total number of documents retrieved.
Among them, Accident analysis and prevention is
the journal that publishes the largest number of
papers in the field of traffic accidents. There are 333
articles in total, accounting for 4.10% of the total
number of retrieved documents. The number of
citations and total link strength of articles are much
higher than other journals. The second to tenth
places are Transportation research part-f-traffic
psychology and behaviour, Traffic injury
prevention, International journal of environmental
research and public health, Analytic methods in
accident research, Sustainability, Safety science,
Journal of safety research, Plos one, Journal of
advanced transportation.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
6

Table 1: Literature sources.
Serial
number
Source
Number of
articles
Cited
times
Total connection
strength
1 Accident analysis and prevention 333 2723 683
2 Transportation research part-F: traffic psychology and behavior 139 661 201
3 Traffic injury prevention 144 550 176
4 International
j
ournal of environmental research and
p
ublic health 57 292 141
5 Analytic methods in accident research 18 675 136
6 Sustainability 56 85 120
7 Safety science 66 509 116
8 Journal of safety research 40 246 105
9 Plos one 74 319 103
10 Journal of advanced transportation 48 129 91
3.2 Research Countries
According to the number of published papers in
each country not less than five papers, and the
number of citations not less than five papers, the
information of the top ten countries selected is
shown in the figure below.
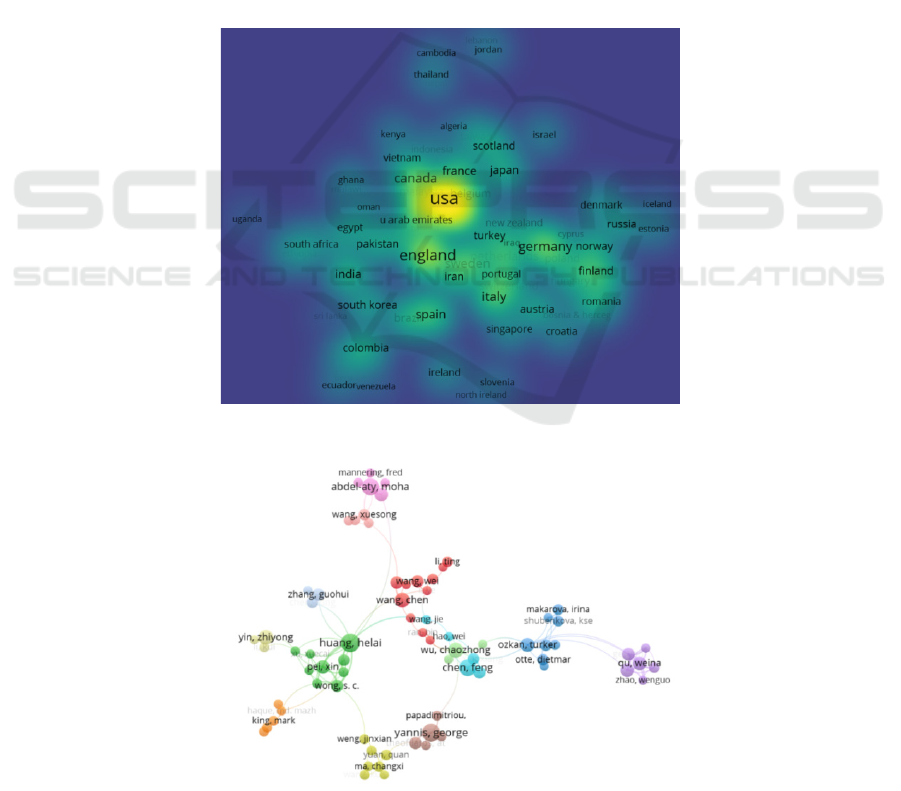
According to the search results listed in Figure 1,
the top ten countries with the highest total link
strength have a total of 4376 articles, accounting for
53.86% of the total number of documents retrieved.
Among them, China is the country with the largest
number of published papers, with a total of 1514
articles, accounting for 18.63% of the total number
of retrieved documents, and the United States has a
total of 971 papers, accounting for 11.95% of the
total number of retrieved documents, but the number
of citations and total links of Chinese articles both
are lower than the United States, which is about
90% and 80% of the United States respectively. The
above data indicates that the quality of Chinese
articles needs to be further improved. The third to
tenth places are the United Kingdom, Australia,
Germany, Sweden, Canada, Italy, Spain, and the
Netherlands. These countries are all economically
developed countries that have higher requirements
for traffic safety and more funding.
3.3 Research Organizations
According to the fact that each organization has
published no less than nine papers, and the number
of citations no less than four papers, the selected top
ten organization information is shown in the
following table.
Table 2: Research organizations.
Serial number Or
g
anization Number of articles Cited times Total connection stren
g
th
1 tsinghua univ 74 414 76
2 tongji univ 84 546 63
3 shahid beheshti univ med sci 53 108 57
4 univ tehran med sci 37 124 51
5 cent s univ 34 385 47
6 southeast univ 67 256 40
7 wuhan univ technol 74 148 39
8 beijing jiaotong univ 60 156 34
9 univ hong kong 21 221 33
10 changan univ 70 199 31
International Research Progress on Traffic Accident based on Bibliometric Analysis Method
7
According to the search results listed in Table 2,
the top ten research institutions with the highest
total link strength have a total of 574 articles,
accounting for 7.06% of the total number of
documents retrieved. Among them, Tongji
University is the university with the largest number
of published papers, with a total of 84 articles,
accounting for 1.03% of the total number of
retrieved documents, and Tsinghua University has
74 papers, accounting for 0.91% of the total number
of retrieved documents, but the total link strength of
Tsinghua University’s papers is higher than Tongji
University. The third to tenth places are Shahid
Behshidi Medical University, Tehran Medical
University, Central South University, Southeast
University, Wuhan University of Technology,
Beijing Jiaotong University, Hong Kong University
and Chang' an University.
3.4 Research Authors
According to each author's publication of no less
than five papers and no less than three citations, the
information of the top ten authors is selected, and
the co-author network among prolific authors is
shown below.
According to the search results listed in Figure 2,
the top ten authors with the highest total link
strength have a total of 114 articles, accounting for
1.40% of the total number of documents retrieved.
Among them, Huang Helai of Central South
University is the author with the largest number of
papers published in the field of traffic accidents in
the past five years. There are 21 articles in total,
accounting for 0.26% of the total number of
retrieved documents. The number of citations and
total connection strength of the article are much
higher than other authors.
Figure 1: Density maps of major research countries.
Figure 2: Co-author network among prolific authors.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
8
3.5
Key Words
According to the number of occurrences of each key
word not less than twenty times, the top twenty key
word information is filtered out, and the
visualization view of keyword coverage in the field
of traffic accidents is shown in the following table.
The visualized view of the coverage of keywords
in the field of traffic accidents is shown in the figure
below.
Figure 3: Key word coverage visualization view.
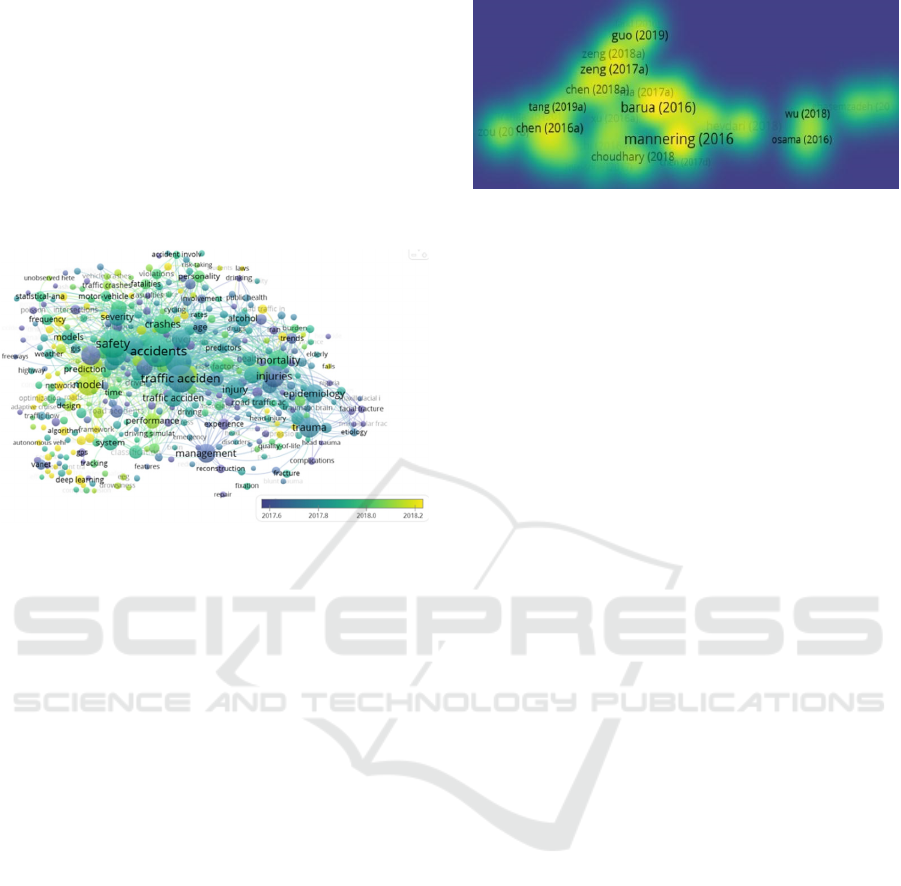
According to the search results listed in Figure 3,
the top twenty key words with the highest total
connection strength are accidents, risk, safety, traffic
accidents, injuries, mortality, crashes, drivers,
model, road safety, impact, trauma, injury,
epidemiology, behavior, severity, injury severity,
traffic safety, age, alcohol. Indicating that the main
research direction of traffic accidents is the severity
of the accident, the main research objects are
drivers’ driving behavior, age, blood alcohol
content, etc. The main indicators for judging the
severity of the accident are injury rate, fatality rate,
etc.
3.6
Cited Literature
According to the number of citations of each article
not less than ten times, the top fifty literature
information is screened out. The density map of the
citations in the field of traffic accidents is shown in
the following table.
The density map of citations in the field of traffic
accidents is shown in the figure below.
Figure 4: Citation density map.
Among the top fifty cited papers, they mainly focus
on the following seven research directions:
• Analysis of the severity of injuries to
drivers, occupants, and cyclists in traffic accidents.
• Statistical analysis of traffic accident data.
• Short-term prediction of traffic accidents.
• Prediction of the severity of traffic accident
damage.
• Analysis of intersection accidents.
• Analysis of the causes of accidents such as
fog and rain.
• Analysis of the impact of dynamic factors
and vehicle speed on the accident.
4 CONCLUSION
Based on the document co-occurrence network
analysis and visualization tool VOS viewer software,
this paper conducts a quantitative analysis of 8125
papers in the field of traffic accident research from
2016 to 2020. Through the source of the document,
the main research country, the main research
institution, the author of the paper, quantitative
analysis of key words and cited papers in the paper,
it is concluded that the most important document
source in the current traffic accident field is
Accident analysis and prevention, the most
important research countries are the United States
and China, and the most important research
institutions are Tsinghua University and Tongji
University. The main research hotspots are traffic
accident severity analysis, statistical analysis of
traffic accidents, short-term prediction of traffic
accidents, prediction of traffic accident severity, and
analysis of the impact of dynamic factors such as
weather on accidents. The research results of this
article provide domestic scholars with an intuitive
understanding of the topics that have not been fully
studied in my country and existing the gap between
research and foreign frontier fields has certain
reference significance.
International Research Progress on Traffic Accident based on Bibliometric Analysis Method
9

ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work is supported by National Key R&D
Program of China (Grant No. 2019YFE0108000).
REFERENCES
Abegaz, T., Berhane, Y., Worku, A., Assrat, A., Assefa,
A.. Effects of excessive speeding and falling asleep
while driving on crash injury severity in Ethiopia: a
generalized ordered logit model analysis. 2014. Accid.
Anal. Prev. 71, 15–21.
Almahasneh, H., Chooi, W.-T., Kamel, N., Malik, A.S.,
Deep in thought while driving: an EEG study on
drivers’ cognitive distraction. Transp. Res. Part. F:
Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2014. 26, 218–226.
Badea-Romero, A., Javier Páez, F., Furones, A., Barrios,
J.M., de-Miguel, J. L.. Assessing the benefit of the
brake assist system for pedestrian injury mitigation
through real-world accident investigations. Saf. Sci.
2013. 53, 193–201.
Kahane C J. Lives saved by vehicle safety technologies
and associated Federal Motor Vehicle Safety
Standards,1960 to 2012, DOT HS 812 069.
Washington, DC: National Highway Traffic Safety
Administration, 2015.
Klauer, G S., Guo, Simons-Morton, G B., Ouimet, C M.,
Lee, E S., Dingus. Distracted driving and risk of road
crashes among novice and experienced drivers. The
New England journal of medicine, 2014, 370(1): 54-
59.
Li Yibing, Sun Yueting, Xu Chengliang. Developing
trends of automotive safety technology: An analysis
based on traffic accident data. J Automotive Safety
and Energy, 2016, Vol. 7 No. 3.
Ma Ming. Research of Urban Road Crash Analysis based
on Multivariate Statistical Techniques. Wuhan
University of Technology. 2010.
VOS viewer Manual. Nees Jan van Eck and Ludo
Waltman. 2020.
World Health Organization, The Global Status Report on
Road Safety 2018, Geneva: World Health
Organization, 2018.
Wong, S.C., Sze, N.N., Li, Y.C. Contributory Factors to
Traffic Crashes at Signalized Intersections in Hong
Kong. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2007,
39(6):1107-1113.
Zhang Xuxin, Wang Xuesong, Ma Yong, Ma Qingbian.
International research progress on driving behavior
and driving risk. China J. Highw. Transp, 2020, Vol.33
No.6.
Yang Ting. Analysis of the influence of road alignment
factors on traffic safety. Chang'an University, 2017.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
10
