
Manufacture of Aluminum-Magnesium Reinforced Metal Matrix
Composite Silicon Carbide with Powder Metallurgy Method
T. Endramawan
1
, A. Sifa
2
, D. Suwandi
1
and E. Riyanto
2
1
Design Manufacturing, Politeknik Negeri Indramayu, Jl. Lohbener Lama no.08, Indramayu, Indonesia
2
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Politeknik Negeri Indramayu, Jl. Lohbener Lama no.08, Indramayu, Indonesia
Keywords: Metal Matrix Composites, Powder Metallurgy, Al-Mg-SiC, Mechanical Properties.
Abstract: Metal matrix composites (Metal Matrix Composites) are a combination of two or more materials with
aluminium metal as the matrix and developed to improve metal properties, strength, high heat stability, and
hardness. Powder metallurgy technique is one of the metal matrix composite manufacturing processes in solid
condition which is still being developed because it is more economical, does not require complicated
equipment. In this study, the manufacture of metal composites with aluminium-magnesium as the matrix and
SiC as reinforcement was carried out using the powder metallurgy method of composition variation (75% Al
: 15% SiC : 10% Mg, 80% Al : 15% SiC : 5% Mg). Then the results of the mixing are compacted at a pressure
of 14 ton-force with a holding time of 4 minutes. After compaction in the form of a specimen, then sintered
at various temperatures (500 °C and 550 °C) for 2 hours. After sintering with a furnance machine, the
specimen is ready to be tested for mechanical properties and microstructure photos. The results of the bending
and hardness test are obtained by increasing the composition of magnesium resulting in the bending strength
and hardness also increasing successively. In mixing Al:SiC:Mg (80%: 15%: 5%) with a temperature of
550°C, the highest bending strength is 50.31 MPa and the highest hardness is 76.21 HV.
1 INTRODUCTION
The results of technology with good quality of course
require processing of technical materials with the
perfect combination so as to create new materials that
have a high level of quality(Pasaribu, 2017). Material
technology composite is one of the smart technology
engineering to get a new material that is much better
than the raw materials used(Ginting, 2009). There are
several composite materials according to the type of
matrix, including metal matrix composites (MMC),
ceramic matrix composites (CMC), and polymer
matrix composites (PMC).
Metal matrix composites have various advantages
over other types of composites. Such as high strength,
high modulus, high toughness and impact property,
low sensitivity to temperature changes or thermal
shock, high surface resistance and low sensitivity to
surface flaws, high electrical conductivity.(Chandra,
2014).
Metal composites that are often used today are
aluminium-based metal matrix composites because
they are one of the most abundant and inexpensive
mineral materials in the world. Al metal as
monolithic, when viewed from the mechanical
properties, such as hardness value (hardness) is very
low. Therefore, Al metal as a monolithic material has
many weaknesses, especially its mechanical strength,
stiffness and coefficient of expansion(Sakti et al.,
2009).
To increase the mechanical value of the metal, it
is necessary to add other elements, one of which is
magnesium. Magnesium has properties such as low
density and light and strong when combined. The
addition of magnesium in certain concentrations can
increase the hardness and bending strength of
aluminum alloys(Shomad & Jordanianshah,
2020).the addition of Mg in aluminum alloys
increases the strength and hardness of aluminum,
increases corrosion resistance and increases
wettability(Supriyatma et al., 2016).
To increase the hardness value of metal
composites, it is necessary to strengthen the metal, by
adding hard materials, such as ceramics. Common
types of ceramic materials used include: Al2O3, SiC,
TiC, and ZrO2. Among these types of ceramics, the
hardest is SiC(Idris et al., 2003).
50
Endramawan, T., Sifa, A., Suwandi, D. and Riyanto, E.
Manufacture of Aluminum-Magnesium Reinforced Metal Matrix Composite Silicon Carbide with Powder Metallurgy Method.
DOI: 10.5220/0011711400003575
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2022), pages 50-55
ISBN: 978-989-758-619-4; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright © 2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

In addition to the matrix and reinforcement,
another important thing is the fabrication technique
used today. Powder metallurgy (powder metallurgy)
has several advantages compared to liquid
metallurgy. The temperature used in powder
metallurgy processes can be lower, that is, below the
melting point of the material. Meanwhile, in liquid
metallurgical engineering, high temperatures are
required to reach the melting point of the component
materials (Ramadhonal, 2010).
(Risky, 2019)examined the effect of the addition
of SiC on the properties of hardness and bending
strength as well as the microstructure of aluminium
composites. The studies varied between SiC (0%, 3%,
5%, 9%). The research proves that there is an increase
in the results of the hardness test and bending test
results for each addition of SiC. This proves that SiC
can increase the strength of metal composites.
(Supriyatma et al 2016) examined the Effect of
Magnesium Addition on Hardness, Impact Strength
and Microstructure of Aluminium Alloy (Al-Si)
Using Lost Foam Casting Method. In this study, there
was an increase in the addition of Mg to Al-Si alloys
based on used car alloy wheels using the lost foam
casting method. The hardness number after the
addition of Mg was 109.70 HRL, and before the
addition of Mg was 99.8 HRL. It was concluded that
the increase was 9.9%.
(Triadi, 2022)examined the effect of sintering
temperature and material composition on the
mechanical characteristics of composites made from
waste aluminium and glass using powder metallurgy
methods. This study found that the specimen with the
highest compressive strength value was found at a
sintering temperature of 590 C and a composition of
90:10, which was 235.59 MPa. While the lowest
strength value is 45.11 MPa at a sintering temperature
of 390 C and a composition of 70 :30. The results of
the hardness test showed that the highest hardness
value was obtained in specimens with a composition
of 90: 10 and a sintering temperature of 590 C,
namely 60 HRF, followed by temperatures of 490 C
and 390 C. The same applies to the composition of
other materials, namely the greatest hardness value is
found at the highest sintering temperature.
1.1 Metal Matrix Composite (MMC)
Metal matrix composite (MMC) comes from a
combination of metal-based materials with ceramics.
MMC can also be called a material consisting of a
matrix in the form of metal and its alloys which is
reinforced by reinforcing materials in the form of
continuous fiber, whiskers, or particulate. The
manufacture of metal matrix composites can be done
by several methods, including powder metallurgy,
diffusion bonding, liquid phase sintering, squeeze
infiltration and stir casting.(Risky, 2019).
The reasons why MMC has been attracting attention
for nearly 30 years:
1. The MMC approach in metallurgical processes is
the only way to produce a wide variety of these
composites. So that the resulting product is very
wide (varied). It is only in this way that we can
combine aluminium, copper, magnesium with the
carbide, oxide or nitride phase. Because the above
material has a solubility to carbon, the nitrogen in
the molten metal is too low.
2. MMC also provides significant changes to the
properties of the material, such as resistance to
high temperatures, does not react to chemicals,
good hardness, and wear resistance.
Metal matrix composites can be made by the
casting method or by the powder metallurgy method.
However, the casting method has a problem, namely
it is difficult to make homogeneous composites,
because the reinforcing particles usually settle or float
due to differences in specific gravity.
1.2 Powder Metallurgy
Powder Metallurgy (Powder Metallurgy) is the
process of forming commercial workpieces from
metal where the metal is in the form of a powder, then
the powder is pressed in a mold and heated below the
melting temperature of the powder to form a
workpiece. So that the metal particles coalesce due to
the mass transport mechanism due to atomic diffusion
between the particle surfaces. Powder metallurgy
methods provide precise control over the composition
and use of mixtures that cannot be fabricated by other
processes. As the size is determined by the mold and
finishing touch.
Basic steps in powder metallurgy
(Demasya, 2018):
1. Powder maker.
2. Mixing.
3. Compaction.
4. Sintering.
Figure 1: Compaction Process(Risky, 2019).
Manufacture of Aluminum-Magnesium Reinforced Metal Matrix Composite Silicon Carbide with Powder Metallurgy Method
51
1.3 Hardness Test
Hardness is the ability of a material to withstand
compressive loads. The hard test mechanism is to
press the indenter to the surface of the test object so
that the geometry of the indentation is obtained. The
type of hard test based on the shape of the indenter is
spherical (for Brinell test), pyramidal (Vickers and
Knoop test), or conical (Rockwell test).
VHN =
,
²
(1)
VHN = Vickers hardness value (HV)
P = amount of load (kgf)
D = average diagonal (mm)
1.4 Bending Test
Bending test is one of the mechanical properties
testing of materials that is carried out on specimens of
materials, both materials to be used as construction or
components that will receive loading. With this load
it will even experience deformation with two
opposing forces acting at the same time(Mahadi ST
& Novri, 2017).
=
..
..²
(2)
Where:
= Bending Stress (MPa)
F = Load (N)
L = Length of span /Support span(mm)
b = Width (mm)
h = Thickness (mm)
2 RESEARCH METHODS
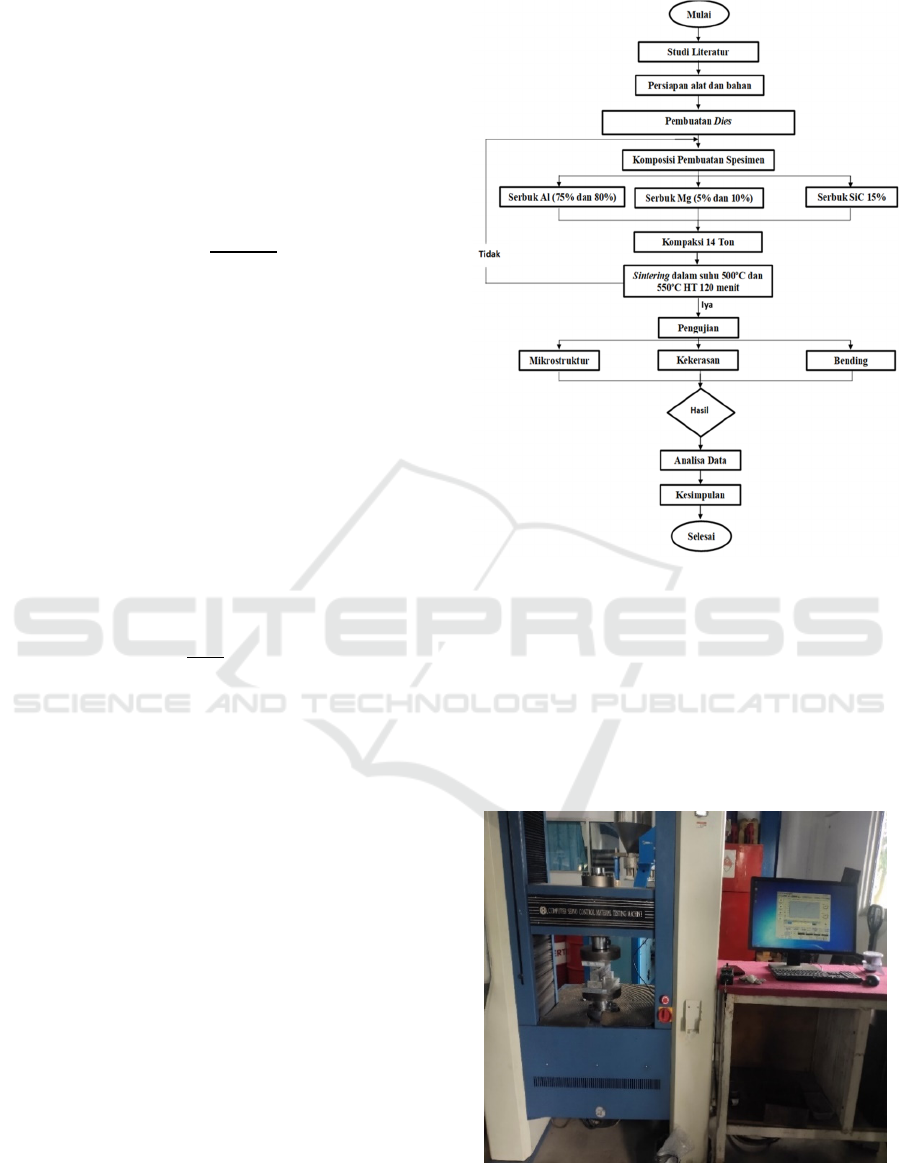
2.1 Research Flowchart
In conducting research, the stages are carried out
referring to the flow chart shown in Figure 2
Figure 2: Research Flow Chart.
2.2 Tool
Details of the equipment used in this study are:
1. Universal Testing Machine
Universal Testing Machinefor the process of
making composites with cold compaction in 14
Tons of compaction that has been dies previously
Figure 3: Universal Testing Machine.
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
52

2. Furnance
Furnance used to carry out heat treatment during the
sintering process with temperatures of 500 C and 550
C on Metal Matrix Composite specimens.
Figure 4: Furnance.
2.3 Ingredient
In this study, the main materials used are aluminium
powder with a content of 85% and magnesium as the
matrix of the metal composite, while the reinforcing
material is silicon carbide.
2.4 Research Procedure
Prepare materials for the manufacture of composites
with a composition (80%Al-5%Mg-15%SiC and
75%Al-10%Mg-15%SiC) then compacted with a
loading of 14 tons and then held for holding time 4
minutes, then The specimen is removed from the
mold for further sintering with a sintering temperature
of 500 C and 550 C.
2.5 Vickers Hardness Test
The hardness test carried out in this study refers to
ASTM E384. The hardness of the SiC-reinforced Al-
Mg composite material was tested using a macro
hardness tester, Innova test brand, with an indenter in
the form of a diamond pyramid with a load of 1 kgf
and indentation time of 30 seconds with 5 tests in one
composite variation.
Figure 5: Vickers Hardness Test Tool.
2.6 Bending Test
The bending test carried out in this study refers to the
ASTM D790, where the shape of the specimen used
is in the form of a plate with sizes, P = 125 mm, l =
12.7 mm and t = 3.2 mm. With the test parameter
compressive speed of 20 m/s and stops at 50%
breaking.
Figure 6: Bending Test.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Hardness Testing
In this study, the hardness test used was a hardness
test using the Vikers method. Hardness testing using
the Vickers method aims to determine the hardness of
a material in the form of material resistance to
pyramid-shaped diamonds with a peak angle of 136
degrees which is emphasized on the surface of the test
material.
In this test the indenter load is 1 kgf with a holding
time of 30 seconds for each hardness test specimen.
The following is the Vickers hardness test process.
Manufacture of Aluminum-Magnesium Reinforced Metal Matrix Composite Silicon Carbide with Powder Metallurgy Method
53
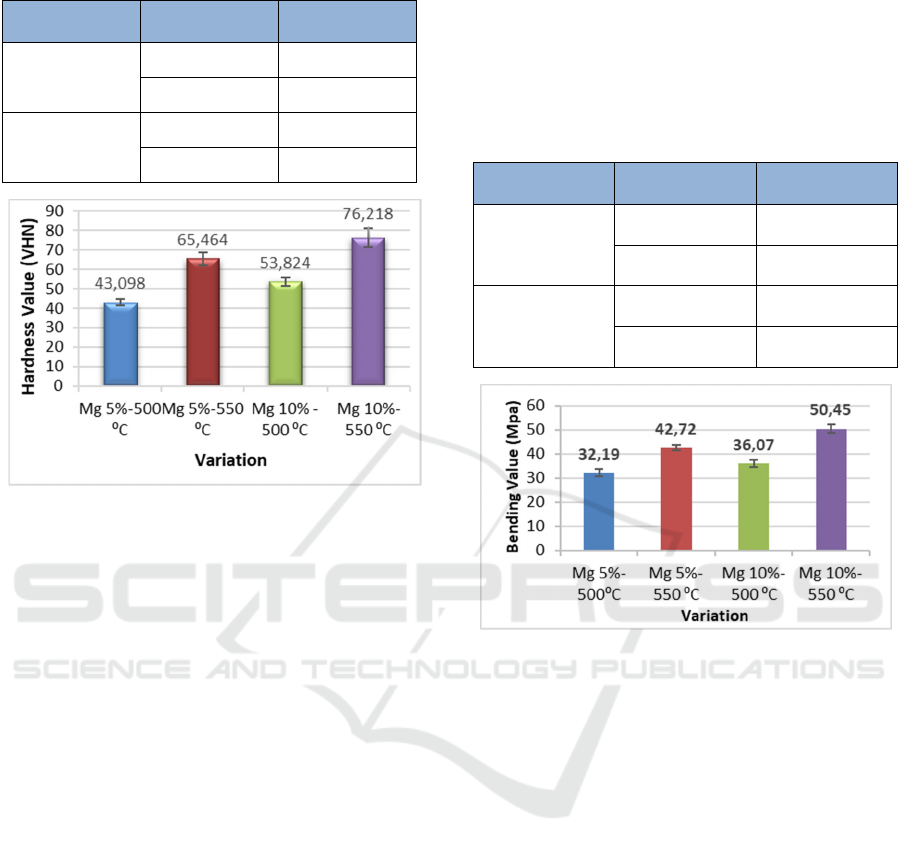
Table 1: Hardness Test Results.
Composition
Variations
Temperature
Variation
Hardness value
(VHN)
Al 75%
SiC 15%
Mg 10%
500
53,824
550
76.218
Al 80%
SiC 15%
Mg 5%
500
43,098
550
65,464
Figure 7: Vickers hardness chart.
The results of the Vickers hardness test show
that with different compositions and sintering
temperatures, we can conclude that the addition of
magnesium and the effect of temperature variations
on the manufacture of Al-Mg metal matrix composite
(MMC) with silicon carbide reinforced with powder
metallurgy method can increase the hardness value
(VHN). This can be seen from the results of the
Vickers Hardness Test on the 5% magnesium
composition in the total mass of the SiC reinforced
Al-Mg specimen at a temperature of 500 C the
average value is 43,098 HV, at the 5% magnesium
composition in the total mass of the Al-Mg reinforced
specimen. SiC at a temperature of 550 C the average
value is 65.464 HV, at a composition of 10%
magnesium in the total mass of SiC-strengthened Al-
Mg specimens at a temperature of 500 C the average
value is 53.824 HV.
The results of this test are similar to the
research(Mahadi ST & Novri, 2017)that the addition
of magnesium can increase the value of hardness and
in research(Triadi, 2022)The higher the sintering
temperature, close to 90% of the melting matrix
temperature, the higher the hardness value.
3.2 Bending Test
In this study, one of the mechanical properties testing
is the bending test carried out to measure how strong
the bending to fracture of a test specimen material is.
In this test, all samples of Metal Matrix Composite
(MMC) standard ASTM D790 with dimensions of
length = 125 mm, width = 12.7 and thickness = 3.2
mm with a compression parameter of 20 m/s and
stops at 50% breaking.
Table 2: Bending Test Results.
Composition
Variations
Temperature
Variation
Bending Value
(Mpa)
Al 75%
SiC 15%
Mg 10%
500
36.07
550
50.45
Al 80%
SiC 15%
Mg 5%
500
32.19
550
42.72
Figure 8: Bending Test Graph.
The results of the bending test show that with
different compositions and sintering temperatures, we
can conclude that the addition of Magnesium and the
effect of temperature variations on the manufacture of
Al-Mg metal matrix composite (MMC) with silicon
carbide reinforced with powder metallurgy method
can increase the value of bending strength. the results
of bending tests on 5% magnesium composition in the
total mass of SiC-reinforced Al-Mg specimens at a
temperature of 500 C the average value is 32.19 Mpa,
at 5% magnesium composition in the total mass of
SiC-reinforced Al-Mg specimens at 550 C the
average value is 42.72 Mpa, at 10% magnesium
composition in the total mass of SiC-strengthened Al-
Mg specimens at 500 C the average value is 36.07
Mpa,at 10% magnesium composition in the total
mass of SiC-strengthened Al-Mg specimens at a
temperature of 550 C the average value is 50.45 Mpa.
The results of the research above are similar to the
research(Triadi, 2022)With the higher the sintering
temperature, the value of the bending compressive
strength increases.
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
54

4 CONCLUSION
The research that has been done can be concluded as
follows:
1. The hardness value of the SiC-reinforced
aluminium-magnesium matrix composite will
increase along with the increase in the addition of
magnesium (Mg) and the increase in the sintering
temperature. The addition of 10% Mg at a
sintering temperature of 550ºC has the highest
hardness of 76.218 HV.
2. The value of the bending strength of the SiC-
reinforced aluminium-magnesium matrix
composite will increase along with the increase in
the addition of magnesium (Mg) and the increase
in the sintering temperature. The addition of 10%
Mg at a sintering temperature of 550ºC has the
highest bending strength of 50.45 Mpa.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author would like to thank the Ministry of
Research and Technology, Indramayu State
Polytechnic and the Department of Mechanical
Engineering, Indramayu State Polytechnic.
REFERENCES
Chandra, B. (2014). effect of heat treatment on the
characteristics of the mechanical properties and
microstructure of metal matrix composites.
Implementation Science, 39(1), 1–24.
Demasya. (2018). The Effect of Variations in the
Composition of Aluminum Powder - Palm Oil Fly Ash
on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure in the
Manufacturing of Aluminum Matrix Composites.
Metal Matrix Composite, 1(3), 82–91.
Ginting, J. (2009). Making Ceramic Reinforced Metal
Matrix Composites (Al/SiCp) And Their
Characterization Through Powder Metallurgy
Methods.
Idris, J., Salim, F., & Suliman, Z. (2003). Study of Wear
and Hardness Properties of Aluminum Matrix
Composites Previous studies have shown that metal
matrix composites have better mechanical properties
than monolithic metals . This can be seen from the
production of aluminum matrix composites. 38, 11–24.
Mahadi ST, M. . and, & Novri, R. (2017). The Effect of
Mixing Variations in Aluminum (Al), Magnesium
(Mg), And Zinc (Zn) Powders on Mechanical
Properties of Metals Using Powder Metallurgical
Methods. 2, 1–8.
Pasaribu, S. (2017). the effect of sintering on the
manufacture of aluminum alloy metal composites.
Application of Embellishment as a Decorative Element
in Modestwear, d(2017), 1–15.
Ramadhonal, S. (2010). Manufacture of Ceramic
Reinforced Metal Matrix Composite ( Al/SiC ) Mixed
with Wood Using Powder Metallurgy Method. 1–87.
Risky, B. (2019). Study of the use of aluminum (Al) powder
mixed with silicon carbide (Sic) for the use of ship
window frames (Scuttle).
Rohani, S. (2021). Effect of SiC and the addition of Mg
volume fraction on the characteristics of the Al6061-
SiC composite. University of Jember Digital
Repository, September 2019, 2019–2022.
Sakti, K., Composites, P., Al, M., Nano, A., Sic, K., Their
Characterization, D., & Repository, USU (2009). The
manufacture of metal al alloy nano ceramic sic
composites and their characterization Thesis.
Shomad, MA, & Jordanianshah, AA (2020). Effect of
Addition of Magnesium Element on Aluminum Alloy
from Used Piston Material. Technoin, 26(1), 75–82.
Supriyatma, I., Triyono, T., & Surojo, E. (2016). Analysis
of the Effect of Addition of Mg to the Aluminum
Remelting Piston Composite Matrix with SiO2
Reinforced on Impact Strength and Microstructure
Using Stir Casting Method. National Seminar on
Machinery and Industry (SNMI X), 14(September),
62–70.
Triadi. (2022). Effect of sintering temperature and material
composition on the mechanical characteristics of
composites made from waste aluminum and glass using
powder metallurgy method Effect of sintering
temperature and material composition on the mechanics
characteristic of. 12(1), 19–28.
Manufacture of Aluminum-Magnesium Reinforced Metal Matrix Composite Silicon Carbide with Powder Metallurgy Method
55
