
Research on Industrial Transformation Path of Jiangsu Province
under Digital Economy
Qi Wang
Harbin University of Commerce Department of Economics Harbin, Heilongjiang Province, China
Keywords: Digital Economy, Industrial Transformation, Development Path.
Abstract:
The status of industrial structure not only reflects the quality of regional economic development, but also is
an important basis for future regional economic growth. At present, digital economy has become a new
development pattern of global economy. With the power of digitalization to guide the transformation and
upgrading of related industries, and promote the integration and penetration of information technology and
the real economy. On the one hand, this can accelerate the transformation of traditional industries to digital,
and on the other hand, it can develop new forms of digital economy and form new drivers of economic growth.
This paper analyzes the present situation of industrial structure in Jiangsu Province, explores the development
path of industrial digitalization in Jiangsu Province, and promotes regional economic development.
1 INTRODUCTION
Industrial level is an important factor of economic
growth, which determines the quality and level of
economic development. Industrial structure is an
important factor affecting economic growth. The
transformation and adjustment of industrial structure
are of great significance in the development of
national economy. Jiangsu province is one of the
major economic provinces in China. Since the reform
and opening up, the economy of Jiangsu Province has
developed rapidly. In 2020, the province's GDP
reached 10.3 trillion yuan, ranking second only to
Guangdong among 31 provinces, municipalities and
autonomous regions in China. Facing the
contradictions of industrial structure, such as
uncoordinated industrial structure, excess production
capacity, weak independent innovation ability,
inadequate control of core technology, and the
conflict between economic development and
resources and environment, Jiangsu province has
gradually lost the advantages of traditional elements
after 40 years of rapid growth. The evolution of
industrial structure from primary to senior is in urgent
need. (Chen, 2017)
At present, digital economy, as an emerging
economic form, has attracted wide attention from all
walks of life and has great research value. This paper
mainly focus on digital economic role in regional
industry development problems, first by Jiangsu
province bureau of statistics released the correlative
data statistics yearbook 2020, Jiangsu province, by
analyzing the digital economy under the current status
and existing problems of the industrial structure of
Jiangsu province to explore the path of digital
economy's influence on the transformation and
upgrading of industry of Jiangsu province, and the
development direction of key industries.
2 THE INTERNAL MECHANISM
OF DIGITAL ECONOMY
PROMOTING INDUSTRIAL
STRUCTURE UPGRADING
The internal logic of world industrial structure
upgrading shows that technological progress is the
internal driving force of industrial structure
upgrading, and every technological progress will
bring about the transformation of economic
paradigm. Under the new economic paradigm,
emerging technology industries tend to surpass the
traditional industries and gradually become the
leading industry in the industrial system, and promote
the transformation and upgrading of traditional
industries through the effects of industry association
and technology diffusion, so as to upgrade the
240
Wang, Q.
Research on Industrial Transformation Path of Jiangsu Province under Digital Economy.
DOI: 10.5220/0011734000003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 240-245
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

industrial structure to a higher level. In the era of
industrial economy, the optimal combination of
production factors such as land, labor and materials
promotes the iteration and upgrading of industrial
structure. With the appearance of the law of
diminishing marginal return, the growth capacity of
the traditional factors of production has been
increasingly weak, and the bottleneck constraints
have become increasingly prominent. The digital
economy created by the new generation of
information technology takes data as the most
important factor of production. The characteristics of
high efficiency, cleanliness, low cost, reproducibility
and mass acquisition of data overcome the inherent
defects of traditional factors of production, and has a
"high multiplier" effect. Although the cost of fixed
assets in the early stage is high for the construction of
digital infrastructure and the investment of intangible
assets, once successful, the marginal use cost is low
or even infinitely tends to zero. This not only breaks
the trap of diminishing marginal return in the era of
industrial economy, but also promotes the continuous
improvement of value creation ability.
Digital economy can also promote the upgrading
of industrial structure through continuous innovation.
In the digital economy era, we can make full use of
all kinds of existing resources through product
innovation and business model innovation to
empower traditional industries, create space for value
increment, and realize the transformation and
upgrading of traditional industrial structure. For
example, in the financial industry, big data and
artificial intelligence technology has been applied to
risk control departments, which has greatly improved
the risk control ability, and the financial system
protection system is also gradually improved. The
intelligence of digital technology can continuously
innovate and learn. It can help human beings to
complete the work that may not be completed for a
long time, shorten the time of industrial upgrading,
and improve the efficiency of industrial upgrading.
More and more intelligent products create excess
profits for producers. After traditional commodities
are endowed with digital technology content, their
added value and derivative value also increase.
Therefore, digital economy is a green, innovative,
sustainable and high-quality economic paradigm, and
a new driving force that can lead the upgrading of
industrial structure.
3 CURRENT SITUATION OF
INDUSTRIAL STRUCTURE IN
JIANGSU PROVINCE UNDER
DIGITAL ECONOMY
3.1
Current Situation of Industrial
Structure of Jiangsu Province
3.1.1 Three Industrial Output Value
Structure Analysis
According to the data of Jiangsu Statistical Yearbook,
we can calculate the proportion of the three major
industries in the total output value of Jiangsu
Province from 2001 to 2019. Figure 1 shows the
specific data.
From Figure 1, we can see that the industrial
layout of Jiangsu Province has gradually changed
from the "two, three, one" structure to the "three, two,
one" structure. The proportion of primary industry
decreased year by year, from 11.6 percent in 2001 to
4.3 percent in 2019. Before 2015, the secondary
industry occupied the largest proportion and was the
main force driving the economy of Jiangsu Province.
Since 2005, the proportion of the secondary industry
began to decline gradually. The proportion of the
tertiary industry has increased significantly. By 2019,
the proportion of the tertiary industry in Jiangsu
Province has exceeded 50% of the total output value,
and the tertiary industry has gradually become the
main part of the industry, which is in line with the
general law of industrial structure evolution. (Jiangsu
Bureau of Statistics, 2020).
Figure 1: Proportion of Output Value of Three Industries in Jiangsu from 2001 to 2019 (%).
Research on Industrial Transformation Path of Jiangsu Province under Digital Economy
241
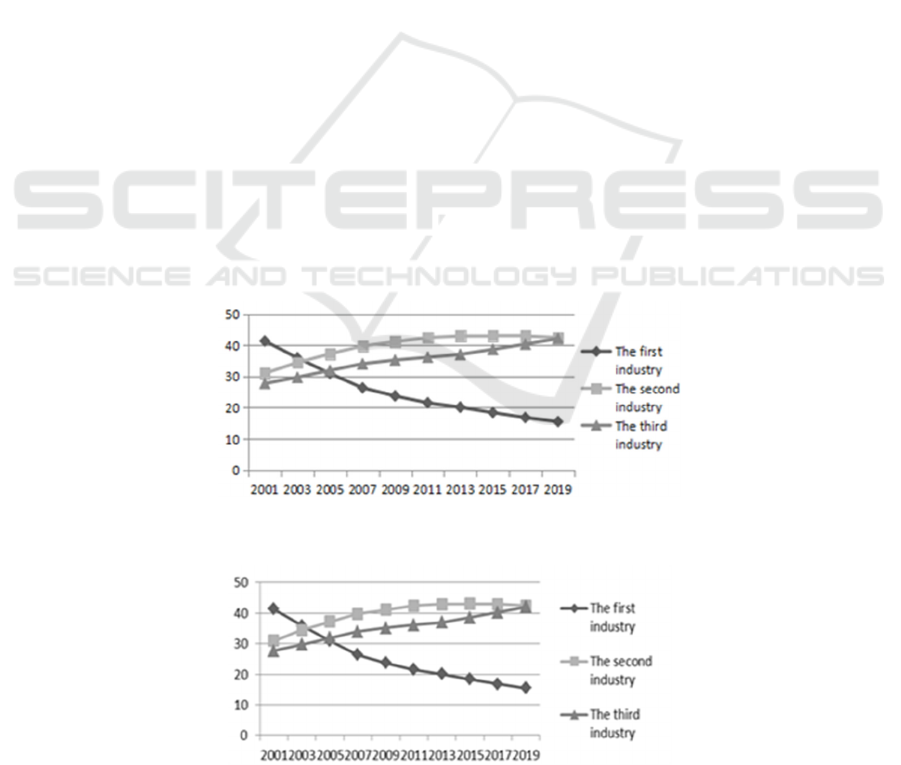
3.1.2 Analysis of The Employment Structure
of Three Industries
In the analysis and comparison of the industrial
structure, the analysis of the employment structure of
the three industries is the focus of the research,
because the employment structure is a basic indicator
reflecting the change of the industrial structure.
From Figure 2, we can see that, from 2001 to
2019, the employment structure of the three industries
in Jiangsu Province has undergone significant
changes. The proportion of the employed population
in the primary industry has continued to decline, from
41.3 percent in 2001 to 15.5 percent in 2019.
Compared with 2001, the proportion of the employed
population in the secondary industry has increased
significantly, from 31% to 42.4%. The proportion of
the employed population in the tertiary industry also
shows an obvious upward trend, rising from 27.7% in
2001 to 42.1% in 2019. Moreover, the gap between
the number of employed population in the secondary
industry and the number of employed population in
the tertiary industry is also narrowing. By 2019, the
gap between the proportion of the two is only 0.3%.
Thus, a large number of labor force transfer from
primary industry to the second and third industry,
with the change of employment structure in
accordance with the laws of Clark, namely along with
the development of the economy, raising the level of
national income, labor force transfer from primary
industry to secondary industry, the first but with the
further development of economy, labor force
transferring to the tertiary industry. (Jiangsu Bureau
of Statistics, 2020)
3.1.3 Analysis of Employment Structure of
Three Industries
In the analysis and comparison of industrial structure,
the analysis of employment structure of three
industries is the focus of research, because
employment structure is a basic index reflecting the
change of industrial structure According to Figure 3,
we can see that from 2001 to 2019, the employment
structure of the three industries in Jiangsu Province
has undergone significant changes. The proportion of
employed people in the primary industry has been
declining, from 41.3 percent in 2001 to 15.5 percent
in 2019. Compared with 2001, the proportion of the
employed population in the secondary industry has
increased significantly, from 31% to 42.4%. The
proportion of employed population in the tertiary
industry also showed an obvious upward trend, rising
from 27.7% in 2001 to 42.1% in 2019, and the gap
between the number of employed population in the
secondary industry and the number of employed
population in the tertiary industry was also
narrowing, until 2019, the gap between the two was
only 0.3%. (Jiangsu Bureau of Statistics, 2020) Thus,
a large number of labor force transfer from primary
industry to the second and third industry, with the
change of employment structure in accordance with
Figure 2: Proportion of Employed Population in Three Industries in Jiangsu from 2001 to 2019 (%).
Figure 3: Proportion of Employed population in three Industries in Jiangsu Province from 2001 to 2019 (%).
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
242

with the laws of Clark, namely along with the
development of the economy, raising the level of
national income, labor force transfer from primary
industry to secondary industry, the first but with the
further development of economy, labor force
transferring to the tertiary industry.
3.1.4 Deviation Degree Analysis of
Industrial Structure
When analyzing the industrial structure of a region,
the coordination degree among industries and the
effective utilization degree of resources should also
be considered. It is a measure of the coupling degree
of input structure and output structure. In terms of this
coupling, researchers generally use the degree of
structural deviation to measure the rationalization of
industrial structure. Its computation formula is:
|*|E
1
=
=
n
i
i
i
L
Y
L
Y
(1)
Where E represents the degree of structural
deviation, “Y” represents output value, L represents
employment, “i” represents the industry i, and N
represents the number of industrial sectors,
L
Y
i
i
L
*
Y
is the deviation degree of the industrial
structure of the industry i. The deviation degree of a
certain industry is positive, indicating that the
proportion of the output value of the industry is
greater than the proportion of the number of
employed people. The stronger the ability to absorb
labor, the tendency of labor transfer is there;
otherwise, there may be a trend of labor transfer out
of the industry. The larger the structure deviation
degree E value is, the more the economy deviates
from the equilibrium state and the more unreasonable
the industrial structure is. See the table1below for
specific data.
From Table 1, we can see that the deviation degree
of industrial structure in Jiangsu Province presents a
downward trend, dropping from 1.71 in 2001 to 0.99
in 2019, indicating that the industrial structure of
Jiangsu Province is evolving toward rationalization.
Specifically, the deviation degrees of the primary
industry structure are all negative, and the absolute
value is always at a high level, with an average value
of -0.72, indicating that the proportion of employed
people in the primary industry is far greater than the
proportion of output value, and there is a phenomenon
of labor surplus, low labor output efficiency, and the
labor force needs to be transferred to the secondary
and tertiary industries. (Jiangsu Bureau of Statistics,
2020) The deviation degree of the secondary industry
structure is positive, and presents a gradually
decreasing trend, and finally reaches 0.05. The
coordination degree of the industrial structure and the
employment structure is continuously improving. The
deviation degree of the tertiary industry structure has
always been positive, while the deviation degree of
the tertiary industry structure has always been
positive and generally at a low level. It has been rising
steadily since 2007, indicating that with the increase
in the proportion of the output value of the tertiary
industry, the labor force has been flowing from the
primary and secondary industries to the tertiary
industry.
Table 1: Deviation degree of industrial structure in Jiangsu from 2001 to 2019.
Year
The first
industry
The second
industry
The third
industry
Degree of
structural
deviation
2001 -0.72 0.67 0.32 1.71
2003 -0.74 0.58 0.22 1.54
2005 -0.74 0.52 0.11 1.37
2007 -0.73 0.41 0.09 1.23
2009 -0.73 0.32 0.12 1.16
2011 -0.71 0.22 0.17 1.10
2013 -0.71 0.14 0.22 1.07
2015 -0.70 0.09 0.23 1.02
2017 -0.72 0.06 0.23 1.02
2019 -0.72 0.05 0.22 0.99
Research on Industrial Transformation Path of Jiangsu Province under Digital Economy
243

3.2 The Development of Digital
Economy Among Provinces
Data from the White Paper on The Development of
China's Digital Economy (2020) shows that the
digital economy in China's provinces has maintained
a sustained growth trend in recent years, and
provinces with higher levels of economic
development have also developed rapidly. As one of
the major economic provinces in China, Jiangsu
province's digital economy development level is at
the forefront of the country in terms of total amount,
proportion and growth rate. (Li, 2020)
From 2012 to 2016, in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei,
Yangtze River Delta and Pearl River Delta economic
circles including Jiangsu Province, each province has
formed agglomeration effect of scientific research
and information technology resources, as well as
prosperous tertiary industry and active consumption
network, the development level of digital economy
ranks in the forefront, higher than the national
average. (Li, 2021)
4 THE DEVELOPMENT PATH OF
INDUSTRIAL
TRANSFORMATION AND
UPGRADING IN JIANGSU
PROVINCE UNDER DIGITAL
ECONOMY
4.1 To Strengthen The Digital
Transformation of Traditional
Industry
Digital industry focused on using digital technology
to upgrade traditional industries, through digital
technology and information supply two main forms
of the traditional three key sectors such as agriculture,
manufacturing, services in the industry to upgrade,
among them, from the production mode, management
mode and circulation mode transformation
agriculture, forming the countryside, it is also a
practice of rural revitalization strategy, An important
way to achieve targeted poverty alleviation; from the
intelligent production, network collaboration, value-
added services and other aspects to realize intelligent
manufacturing, promote the emergence of "new
manufacturing"; comprehensively improve the
service level of finance, retail, logistics, education
and other industries in terms of service mode and
service content, so as to realize the intelligence and
digitalization of agriculture and manufacturing
industry and the digitalization and diversification of
service industry.
4.2 To Promote The Development of
New Formats
In traditional manufacturing, especially in Jiangsu
province has certain advantages of machinery,
electronics, clothing and other industries on the basis
of research and development, production operation,
marketing, maintenance, promotion of new
technology such as network collaborative design,
virtual simulation, through the Internet platform for
integrated production and marketing resource, such
as the application of "Internet +" supply chain
management mode, to promote the system of
horizontal integration between enterprises, We will
create a new form of manufacturing driven by digital
technology.
4.3 Develop Service-Oriented
Manufacturing
On the one hand, it establishes the data collection,
analysis and manufacturing execution system,
records the relevant data of intelligent products and
users throughout the whole process, scientifically
controls the entire supply chain and production line,
and establishes the data resource catalog, opens the
relevant data resources in an orderly manner, so as to
improve the labor productivity of all staff and the
CNC rate of equipment of key enterprises. On the
other hand, C2B new business model is applied to
deepen the application of digital technology in value-
added services such as quality diagnosis and remote
fault maintenance, and promote the transformation of
manufacturing enterprises to full life cycle
management, providing system solutions and
information value-added services.
4.4 Develop Smart Services
With network platform development support
services, with new technology and data as a driving
force, on the basis of credit system, promoting new
finance, retail, logistics, digital and wisdom, and
wisdom to areas such as education reform, and
orderly development of financial service of science
and technology, so as to promote the rapid
development of digital economy and industry
integration, the third industry, because of the huge
kinetic energy release. Fully integrating the existing
subsystems of various departments, such as digital
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
244

urban management, urban planning, medical and
health care, transportation and water conservancy,
government services, public services and other
information subsystems, can realize the multi-
direction communication of information equipment,
information resources and information systems
across departments, and build a smart city of
"intelligence, information and network".
4.5 Increase The Digital Talent
Support
We will make overall plans for the development of
digital industries, predict the demand for industrial
talents, and accelerate the cultivation of digital talents
in key industries and fields. We will establish a sound
vocational education system and strengthen digital
economy vocational training to meet the needs of
talents. Establish regional digital economy excellent
talent pool, build digital talent exchange information
platform, open up excellent talent return information
channel; encourage enterprises and the government to
fund the exclusion of some digital economy high-tech
talents to study abroad. Increase research funding for
digital talents, cultivate "mass entrepreneurship and
innovation" talents of digital economy, and promote
the continuous growth of outstanding talents from all
sides.
5 CONCLUSION
Through sorting out and analyzing the present
situation of industrial structure and digital
development of Jiangsu province, the following
conclusions are drawn :(1) in terms of industrial
structure, the industrial layout of Jiangsu province has
gradually changed from the "second, third and first"
structure to the "third," "second and first" structure,
and the tertiary industry has gradually become the
main industry; (2) in terms of employment structure,
with the development of economy, the employment
population of the primary industry in Jiangsu
province gradually transfers to the secondary and
tertiary industries, which conforms to the Clark law;
(3) the deviation degree of industrial structure in
Jiangsu province shows a downward trend, and the
industrial structure is rationalizing. However, the
primary industry still has surplus labor force, labor
output efficiency is low. Therefore, under the
background of the rapid development of digital
economy, we can promote the upgrading of industrial
structure and production type in Jiangsu province by
means of Internet and digital technology, so as to
realize sustained, healthy and rapid economic
development.
REFERENCES
Chen,X. and Hu,X.(2017) Research on the status quo and
countermeasures of industrial structure transformation
and upgrading in Jiangsu province. J. Journal of Jiangsu
university of science and technology., 23(05):17-20.
Jiangsu Bureau of Statistics. (2020) Jiangsu Statistical
Yearbook.China Statistics Press,Beijing.
Li,X. and Wu,J. (2020) Digital economy drives regional
differences in industrial structure transformation and
upgrading. J. International Economic Cooperation.,
(04):81-91.
Li, Q. (2021)The status quo and transformation path of
Hebei's industrial structure under digital economy. J.
Journal of Shijiazhuang vocational and technical
college., 33(01):35-39.
Research on Industrial Transformation Path of Jiangsu Province under Digital Economy
245
