
Analysis of the Development of Lacquerware in Chengdu and the
Demand for Cultural and Creative Product Design
Ying Zhang and Jiaxing Wei
*
School of Art and Design, Guilin University of Electronic Technology, Guilin, China
Keywords: Culture and Art, Product Design, Demand Analysis, Big Data.
Abstract: Chengdu lacquerware, as a traditional Sichuan handicraft, is one of the national intangible cultural heritages
with great regional characteristics, and it carries the wisdom of the Sichuan people, and it is our unshirkable
responsibility to pass on and develop these traditional folk handicraft skills. With the rise of the economy, the
consumer philosophy and needs of users have changed, no longer just to meet the functionality of the product,
but to pursue the individuality of the product. Under the economic development trend, User participatory
design is the inclusion of the user in the design, in which all participants have equal status and power.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Historical Development and Aesthetic
Characteristics of Chengdu Lacquerware China is the
"Land of Lacquerware" (Duan, 2022). Dating back to
the ancient Shu period, more than 3,000 years ago, the
art of lacquer was already well developed in Chengdu
during the Warring States period, when it was used
all over China. During the Western Han period, the
lacquer art of Chengdu was supplemented by the
invention of the needle scratching and gold filling
method, and the pile lacquer method of using thick
substances to fill in the patterns. In particular, the top
of the vessel inlaid with metal flowers and leaves, to
agate or glazed beads for the button, the mouth of the
vessel body inlaid with gold and silver buckles and
hoops and other techniques very popular. The
lacquerware produced in Chengdu, Pixian and the
northern part of Guanghan County in Sichuan has
formed its own style and is self-contained. This paper
summarises the development of lacquerware in
Chengdu and the design needs of creative products in
Chengdu, from the development of lacquerware in
Chengdu to the participatory design of actual users
(Niu, 2022).
2 OVERVIEW AND
DEVELOPMENT OF
LACQUERWARE IN
CHENGDU
2.1 Overview of Chengdu Lacquerware
Chengdu lacquerware, also known as "halogen
lacquer", was included in the first batch of the
national intangible cultural heritage list in 2006
(Yang, 2022). Chengdu lacquerware is made from
wood, porcelain, linen and paper, and is repeatedly
painted with natural lacquer and lacquer, then
polished and varnished to create a glorious craft. In
addition to the carving and colouring process, in
recent times Chengdu lacquerware has developed a
variety of techniques, such as concealing, concealing,
depicting and carving, making it a richer and more
diverse product range. Nowadays, there are more than
100 kinds of lacquerware products, including
scholar's houses, jars, plates, tea sets, screens and
boxes, which are sold locally and even at home and
abroad (Huang, 2022).
2.2 The History of Chengdu
Lacquerware
Sichuan is rich in raw lacquer and cinnabar, providing
a wealth of raw materials for the production of
lacquerware in Chengdu (Liu, 2022). The lacquer art
348
Zhang, Y. and Wei, J.
Analysis of the Development of Lacquerware in Chengdu and the Demand for Cultural and Creative Product Design.
DOI: 10.5220/0011736600003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 348-353
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

of Chengdu was one of the earliest lacquer crafts in
China and reached a high level of sophistication
during the ancient Shu civilisation. The earliest
lacquerware found in Chengdu to date is a lacquer cup
with the words "Ba Shu Tu" unearthed from a
Warring States tomb in Xindu. In his "Shudu Fu",
Yang Xiong, a literary scholar of the Western Han
Dynasty, praised Chengdu lacquerware for its
"carvings and buttons, a hundred tricks and a
thousand works". During the Three Kingdoms period
(Du, 2022), the lacquer ware excavated from Zhu
Ran's tomb, a chessboard with children on sticks, also
came from Chengdu; during the Han and Tang
dynasties, Chengdu lacquer ware was known as the
'treasure of Shu'. In recent years, most of the lacquer
artefacts excavated from Han tombs in Changsha
Mawangdui, Jiangling in Hubei and Pingba in
Qingzhen, Guizhou, are clearly marked with the
words 'Shu County' and 'Chengchengcao'.
3 DEMAND ANALYSIS OF
CHENGDU LACQUERWARE
CULTURAL AND CREATIVE
PRODUCT DESIGN FOR USER
PARTICIPATION
3.1 Definition of User Participatory
Design
The concept of Participatory Design, PD, is a modern
approach to design that is user-centred, includes the
user in the design process, respects the user's
background, abilities and ideas, and ensures design
equality while meeting the diverse needs of the user.
Compared to traditional design methods (the
differences are shown in Table 1), this approach is
more flexible and open, allowing the user to
participate in the design process to the greatest extent
possible, so that the user has the best possible
interactive experience. Participatory design is now
being used in a number of research areas.
With the rapid development of social and
economic standards, users' needs for products are not
only functional and practical, but more spiritual in
nature (Chen, 2021). The aim of this study is to open
up the design and production rights to users, allowing
lacquer enthusiasts, designers and the general public
to give full play to their own strengths and
characteristics, and to participate in the design and
production of lacquer products with the assistance of
relevant personnel. This will enhance the user's
participation and experience, thus better promoting
and passing on traditional culture.
3.2 Forms of User Involvement in
Design
User participatory design can be used at all stages of
the design process, and its role varies. Before the
design process begins, it helps the user to choose the
direction of the design and there is no set form or
standard for user participatory design, as there are
different levels, needs and types of participant (Liu,
Kou, 2021). In the process of user participatory
design, users should choose the appropriate form
according to their actual needs. A comparative
analysis of the three forms is shown in Table 2.
Table 1: Differences between traditional and user-involved design methods.
Design features
Traditional design
methods
Participatory design
methods
User power Choice Right to choose, create, design
Inclusivity None Inclusivity (no goal)
Main output Product Experience
Value Objective Low production costs Creative needs
Key claims Fast, mass production Open, independent creation
Technical advantages Low
cost
,Short
p
roduction cycle, high
efficiency High output
,originality and diversity
Difficulties in shaping and
decoration
Determined by the designer
Determined by the user's
design ability
Analysis of the Development of Lacquerware in Chengdu and the Demand for Cultural and Creative Product Design
349
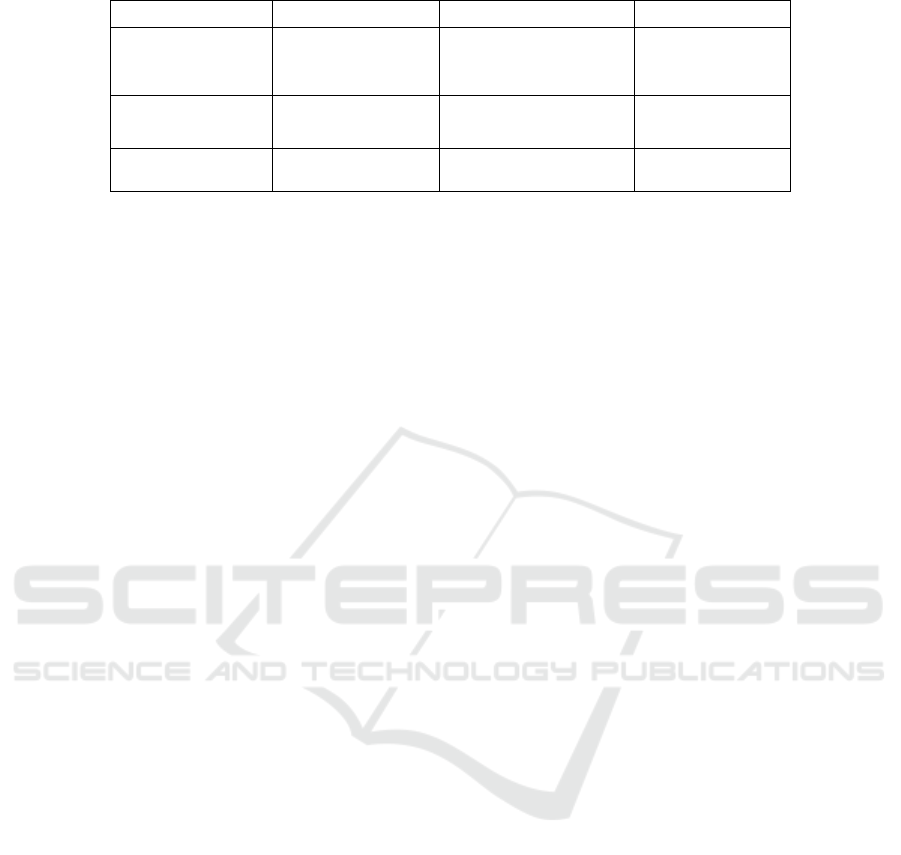
Table 2: Forms of user involvement in design.
Format Features Strengths Difficulties
One to One
Only 1 user can
communicate directly
with the designer
Higher operability and
user motivation Better
and more efficient
User thinking is
limited
Group style 6-8, in small groups
Design more in line with
demand
Users vary from
one user to another
Online Open Everyone More convenient
Conduct
Interaction
3.3 User involvement in the Design
Process
User involvement design starts from user analysis, by
analysing the user's physiology, behaviour and
psychology to establish the user'sneeds, such as
interaction needs, self-fulfilment needs, usage needs
and cultural needs.
Then, we analyse the data of user needs, design
and develop product shapes and decorative elements
to meet the needs of users, and allow users to fully
develop their creativity through user participation in
design.
Through user participation in the design process,
users can give full play to their own creativity and
finally complete the design and production of the
product. The user participation design process is
illustrated.
Step 1: User analysis.
Step 2: Requirements acquisition.
Step 3: User needs analysis.
Step 4: Design element development and user
involvement.
Step 5: Design realisation.
3.4 r Demand Acquisition for Chengdu
Lacquerware Cultural and
Creative Products
Today, the number of different types of cultural and
creative product designs is increasing, and the
demand for cultural experiences is growing, with both
users and designers expecting the product to enhance
the spiritual experience through cultural implantation.
By accurately tapping into information about user
needs, translating them into specific elements of
product design, and presenting external factors such
as the shape, ornamentation and colour of the product
in the design of Chengdu lacquerware cultural and
creative products, the transformation between user
needs and the characteristic elements of the product
is further completed. User needs are categorised in
order to better understand the needs of the target
users. The first step in acquiring user needs for
Chengdu lacquerware cultural and creative products
is to identify the target user group and clarify who the
product is designed for. In determining the target
users, this can be done by analysing the background
information of the user’s identity and through
questionnaires to locate them (Liu, 2021). The user
portrait is a way of standardising the target user group
through questionnaires and user interviews to better
capture the target users and their real needs, to ensure
that the product development process does not deviate
from the user needs, and to use the Kano model user
needs taxonomy to analyse the target user’s needs
preferences and measure the user’s satisfaction with
a certain attribute of the product (Huang, 2021). The
Kano model was used to analyse the preferences of
the target users and to measure their satisfaction with
a particular attribute of the product. This helped the
designers to accurately position the style, function
and shape of the Chengdu lacquerware product
design.
4 EXTRACTING AND
RECONSTRUCTING
ELEMENTS OF CHENGDU
LACQUERWARE PRODUCT
DESIGN FOR USER
PARTICIPATION
As one of the pearls of intangible cultural heritage,
Chengdu lacquerware is of great artistic value in
terms of its production techniques and aesthetic
characteristics. This chapter first analyses the
characteristics of the appearance, decorative elements
and compositional forms of Chengdu lacquerware,
analyses the data collected on ancient and existing
products of Chengdu lacquerware, combines the
regional cultural characteristics of Chengdu
lacquerware and other factors, and constructs an
analysis chart of Chengdu lacquerware cultural and
creative product design. Based on user needs and
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
350
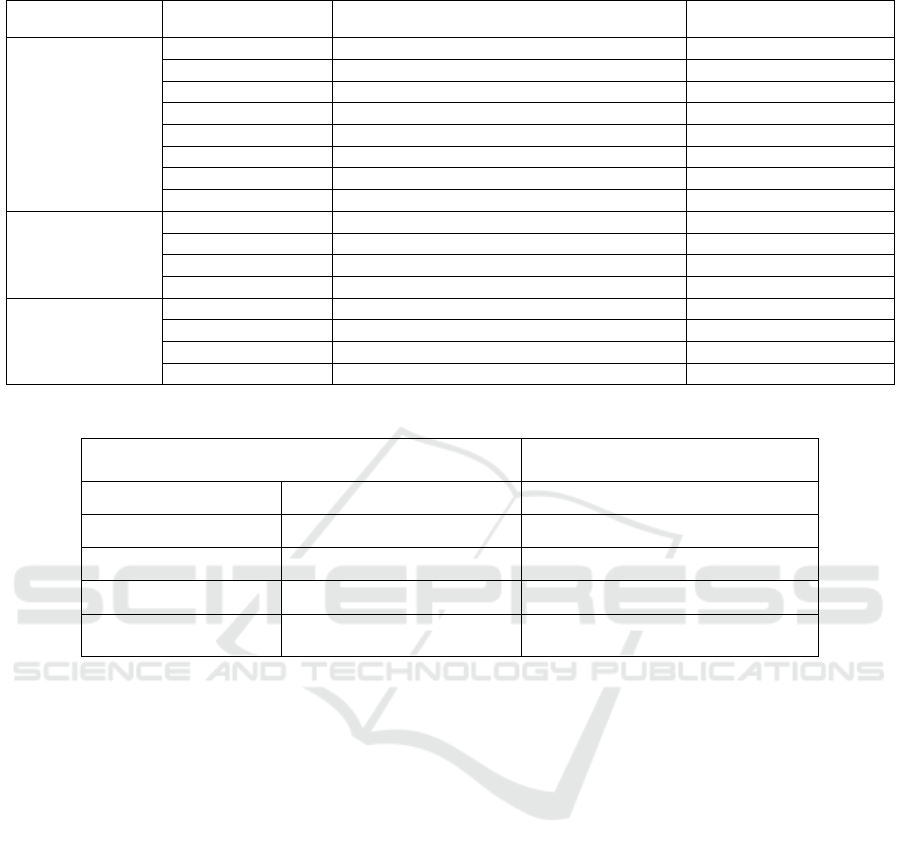
Table 3: Analysis of the stylistic features of Chengdu lacquerware.
Type of object Name of object Stylistic features Use/function
Catering
Lac
q
uer cu
p
s One- and two-eared cu
p
s Holdin
g
wine
Lacquer bottle Cylindrical Holding wine
Lacquered plate Roun
d
Serving foo
d
Lacquer Goblet Cylindrical To hold wine or wate
r
Lac
q
uered tri
p
o
d
The base is threele
gg
edrounded, Servin
g
foo
d
Lac
q
uered box various sha
p
es, Containin
g
ob
j
ects
lac
q
uer
p
ot Dee
p
bell
y
, Servin
g
foo
d
Lacquer pot Square, round or flat jug For wine or wate
r
Grooming
Lacquered trousseau single, square,round,oval, crescent cessories and and foo
d
Lacquered wash Round with widemouth Washlet
Lac
q
uered table
p
aneled le
g
s Place settin
g
s
Lac
q
uered case
g
rated le
g
s Place settin
g
s
Etiquette
Lacquer gui wide mouth and rounded bell
y
Food/giftware
Lacquer bells francium Two types of lacque
r
ritual vessels
lacquered tripo
d
with a rounded base and a flat or rounded foot Ritual vessel
lac
q
uered horse carved from a sin
g
le
p
iece of woo
d
Burial Ob
j
ect
Table 4: Characterisation of the decorative elements of Chengdu lacquerware.
Decorative element categories/themes
Characteristics of decorative
elements
Plant motifs Leaf veins, curly grasses, etc. Embellishment
Animal prints Fish, butterfly, sheep, etc. Exaggerated shapes
Natural landscape motifs Clouds, water ripples,etc. Variety of shapes
Geometric patterns
Dots, straight lines,etc.
Richly layered
Inscriptions "Shu County", "Shi Fu", etc.
Words or symbols conveying
information about an artifact
perceptual imagery, the elements of the Chengdu
lacquerware creative product design are identified.
Using shape grammar, the elements of the Chengdu
lacquerware product were extracted and deformed to
produce a preliminary design solution.
4.1 Characterisation of Chengdu
Lacquerware
4.1.1 Analysis of Exterior Styling Features
There is a wide range of lacquerware in Chengdu,
mainly in the form of everyday objects and
ceremonial objects, and the specific features are
shown in Table 3.
4.1.2 Characterisation of The Decorative
Elements
The decorative elements not only enhance the
overall artistic effect of lacquerware, but are also an
important element of the art of lacquerware (5)
Participation in the production experience.
decoration. The specific characteristics of the
decorative elements on Chengdu lacquerware are
shown in Table 4.
4.1.3 Analysis of The Characteristics of The
Composition Form
The formal characteristics of the composition of
Chengdu lacquer ware are categorised by the type of
object to which they belong, as shown in Table 5.
4.2 User Involvement in The Design
Process
The design of the Chengdu lacquerware product for
user participation is divided into five parts:
(1) Identifying design elements.
(2) Reconstruction of design elements.
(3) Generate design solutions.
(4) Design solution evaluation.
(5) Participation in the production experience.
Analysis of the Development of Lacquerware in Chengdu and the Demand for Cultural and Creative Product Design
351
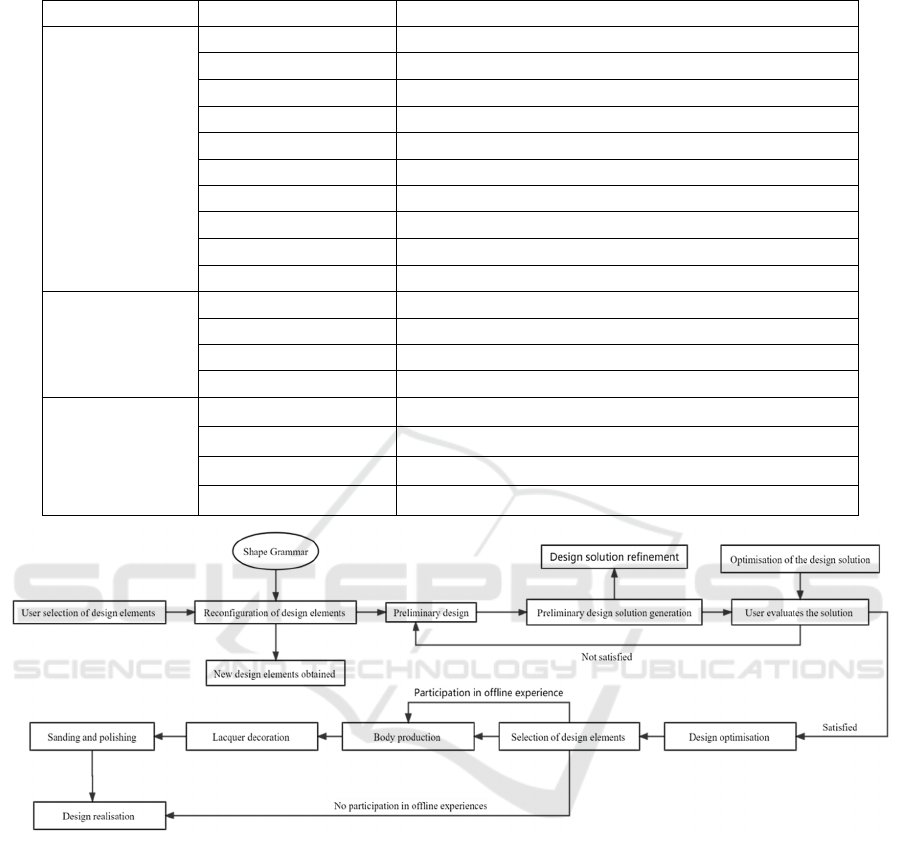
Table 5: Characterisation of the composition of lacquerware forms in Chengdu.
Type Name of the object Composition
Catering
Lacquer cups Smooth one piece
Lacquer bottle Smooth, concave and convex pattern in one piece
Lacquered plate Smooth one piece
Lacquer Goblet Smooth one piece
Lacquered tripod Smooth, concave and convex pattern in one piece
Lacquered box Smooth one piece
lacquer pot Smooth one piece
Lacquer pot Smooth, concave and convex pattern in one piece
Lacquer cups Smooth one piece
Lacquer bottle Smooth one piece
Grooming
Lacquered trousseau Smooth one piece
Lacquered wash Smooth one piece
Lacquered table Smooth and dimpled in one piece
Lacquered case Smooth and dimpled in one piece
Etiquette
Lacquer gui Smooth, concave and convex pattern in one piece
Lacquer bells Smooth, concave and convex pattern in one piece
lacquered tripod Smooth, concave and convex pattern in one piece
lacquered horse Smooth, concave and convex pattern in one piece
Figure 1: User involvement in the design process.
5 SUMMARY AND OUTLOOK
This study adopted a mapping approach to extract
design elements from ancient and existing samples of
Chengdu lacquerware products and reconstructed
them. The workload was relatively high. Therefore, it
is important to consider how to extract design
elements from a large number of samples, develop
more shapes and patterns, and improve design
efficiency. This study used questionnaires and user
interviews in the process of obtaining the actual needs
of users. Due to the number of questions involved in
the questionnaires, some of the respondents may find
it tedious and ultimately the data obtained may not be
accurate enough. In this regard, there is a need to
further enhance the participatory experience of the
respondents in the future research process. Finally, as
this study is based on user participation in the design
of Chengdu lacquerware products, the study is still a
bit unconventional in terms of the form, materials and
techniques of the products themselves, and needs to
be further strengthened and deepened in future
research.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
352

REFERENCES
Chen, N. W. A brief analysis of Han Dynasty lacquerware
excavated in Anhui [J]. Chinese lacquer, 2021,
40(04):1-10. doi:10.19334/j.cnki.issn.1000-7067.2021.
04.001.
Duan Meiling, Zuo Hongwei. Research on the artistic
characteristics and heritage protection of Dafang
lacquerware in Guizhou[J]. Tian Gong, 2022(06):44-46.
Du Xinyi, Zhou Yi. Exploring the application of Yi leather
lacquer painting patterns in leather products[J]. Leather
Science and Engineering,2022,32(01):92-97. DOI:10.
19677/j.issn.1004-7964.2022.01.017.
Huang Qing Sui. The pattern of Tibetan lacquerware[J].
Ethnic Art, 2022(01):82-84+81. DOI:10.16564/j.cnki.
1003-2568.2022.01.001.
Huang Jin. The decorative art of lacquerware craft in
Yangzhou during the Ming and Qing dynasties[J].
Collection and investment,2021,12(12):41-43. DOI:10.
19897/ j.cnki.scytz.2021.12.013.
Liu WC. How to play with lacquer collection [J]. Money
Weekly,2022(01):70-71.
Liu Hanlu, Kou Yan. A study of Jiangxi lacquerware in the
Wei and Jin dynasties[J]. Chinese lacquer, 2021,
40(04):11-17+21. DOI: 10.19334/j.cnki.issn.1000-7067.
2021.04.002.
Liu Xinchan. Creative sustainable development of NRM
from the perspective of IP - taking Fuzhou lacquerware
as an example [J]. Yanhuang Geography, 2021(12):39-
41
Niu Peihong. Exploring the design of Fuzhou lacquerware
products [J]. DOI: 10.16129/j.cnki.mysds.2022.
01.038.
Yang Yiting, Xu He. Feasibility study on incorporating
biodiversity into China's planning environmental
impact assessment[J]. Environmental Impact
Assessment, 2022,44 (01):33-37+41. DOI:10.14068/
j.ceia.2022.01.006.
Analysis of the Development of Lacquerware in Chengdu and the Demand for Cultural and Creative Product Design
353
