
Research on the Construction Path of China's Smart Government
Affairs with the Background of "Internet +"
Runshi Zhang
Harbin University of Commerce, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
Keywords:
Digital Government, Intelligent Government Affairs, Government Service, Informatization.
Abstract: With the rapid development of network information technology, the construction of China's digital
government has been promoted, and the level of social informatization has been increasing. The emergence
of smart government affairs is an inevitable requirement to promote the modernization of the national
governance system and governance capacity, and also reflects the continuous optimization and upgrading of
the level of government services reengineering with the government's strong support for the construction of
digital informatization infrastructure. The construction and development of smart government has been the
common concern of governments all over the world, but to China, as a country in the forefront of exploring
digital government construction in the world, there are still many problems that need to be solved. This
paper empirically analyzes the current level of government construction in China, and proposes several
construction paths based on this.
1 INTRODUCTION
In order to meet the global development trend and
better adapt to the needs of China's economic and
social development in the new era, since the 18th
Party Congress, the State Council has put forward
the general plan of "Internet + government affairs
services", requiring the integration of government
affairs services with new technologies such as big
data, Internet, cloud computing, Internet of Things
and blockchain, in order to improve the overall
efficiency of China's government affairs services.
efficiency and cooperation level, and promote the
modernization of the national governance system
and governance capacity. General Secretary Xi
Jinping pointed out in his speech at the 2016
Symposium on Network Security and
Informatization that "we should speed up the
promotion of e-government, encourage government
departments at all levels to break down information
barriers, improve service efficiency, let people run
fewer legs and information run more, and solve the
problem of difficult, slow and complicated work."
After years of development, China's e-government
construction has begun to bear fruit, the level of
interaction between the government and citizens has
also improved significantly. Currently, the number
of Chinese Internet users is nearly one billion, and
mobile payment and digital currency are developing
rapidly. The Internet has become closely related to
our lives and permeates every aspect of our daily
lives. At the same time, the development of 5G
technology-related products such as chip devices
and smartphones in China is also becoming
increasingly sophisticated. 5G technology has also
contributed greatly to the medical field during the
epidemic, and the significant increase in the level of
informationization and digitization of the whole
society has forced the government to provide higher
quality government affairs services.
2 THE BACKGROUND AND
CONNOTATION OF THE
EMERGENCE OF SMART
GOVERNMENT AFFAIRS
2.1 Background of The Emergence of
Smart Government Affairs
The government attaches importance to the
Zhang, R.
Research on the Construction Path of China’s Smart Government Affairs with the Background of "Internet +".
DOI: 10.5220/0011739700003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 445-452
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
445

construction of smart government and supports the
integration of information digital technology
applications in government affairs services with the
fundamental purpose of improving the quality and
efficiency of public services. The Fourth Plenary
Session of the 19th CPC Central Committee
proposed, "Establishing sound institutional rules for
the use of the Internet, big data, artificial
intelligence and other technological means for
administrative management." In 2020, General
Secretary Xi Jinping, while chairing a meeting of the
Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the
CPC Central Committee, emphasized the need to
"accelerate progress in the construction of new
infrastructure such as 5G networks and data
centers." As of June 2021, China has a total of
961,000 5G base stations, of which 190,000 were
newly built in the first six months; the number of 5G
connections has reached nearly 370 million
households, accounting for 80% of the world, and
the infrastructure coverage is a necessary
prerequisite and foundation for the development of
digital construction across the country.
2.2 The Connotation of Smart
Government Affairs
Like smart cities, smart government has the
characteristics of a Chinese imported term. In
English, there is no academic concept with exactly
the same meaning. Similar concepts include Smart
government, Smart government affairs,
u-Goverment, and government3.0. Although these
concepts are expressed in different forms, their
connotations and extensions are extremely similar
(Zhou 2021). This paper defines smart government
as follows: Smart government is based on
e-government, using big data, cloud computing,
Internet of Things, mobile Internet and other
technologies to realize public services from
all-powerful to service-oriented through data
sharing, overall collaboration, and intelligent
management, etc. Therefore, smart government is an
inevitable product of e-government development to
an advanced stage. At the same time, smart
government affairs has the characteristics of
customization, wisdom and big data.
2.2.1 Customization
With the application and development of the Internet
of Things, big data, cloud computing and other
emerging technologies, the "publicness" of public
services is gradually disappearing, and people's
personalized demand for public services is getting
higher and higher, and more targeted and diversified
government affairs services will become
mainstream. This requires the government to
broaden its communication channels, improve the
response speed of government affairs services, and
make government affairs services more flexible and
diversified to meet the increasingly complex needs
of the public.
2.2.2 Intelligent
Relying on big data technology, smart government
obtains data that can meet people's needs from a
large amount of data and provides personalized and
customized services with the characteristics of
wisdom; by integrating and analyzing data, it greatly
improves the intelligence of services; it rebuilds and
upgrades the process of government affairs services
and governs the management elements of
government affairs services to achieve wise
governance.
2.2.3 Big Data
Smart government affairs is a new product in the
context of big data, is its core element. Without big
data, smart government becomes water without
source and wood without foundation. Through
access to big data as well as analysis of big data
based on intelligent decision-making, in order to
achieve the precision, scientific and democratization
of government affairs services. Therefore, the
construction of smart government affairs must be
built on the basis of big data.
3 THE EVALUATION INDEX
SYSTEM OF SMART
GOVERNMENT AFFAIRS
CONSTRUCTION
This paper establishes a smart government affairs
evaluation index system from three aspects, namely,
the government's own construction, infrastructure
construction, and government-citizen interaction
system, which contains three first-level indicators
and eleven second-level indicators.
In the evaluation index system of smart
government construction, A
i
(i=1,2,3) is used to
denote the three -level indicators of the
government's own construction, infrastructure
construction and government-citizen interaction
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
446
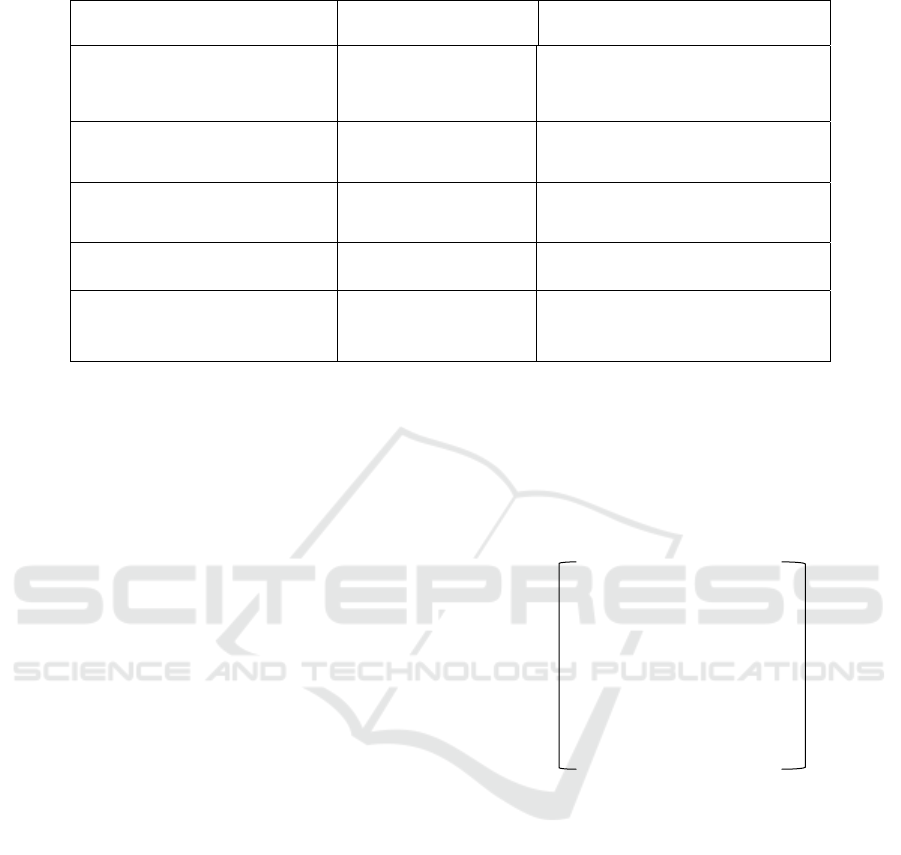
Table 1: Evaluation index system of smart government affairs.
Government Self-construction
(A1)
Infrastructure
Construction (A2)
Government-Civilian Interaction
System (A3)
Number of government website
information disclosure (A11)
Proportion of fixed
broadband users (A21)
Number of administrative
reconsideration events (A31)
Business Transactions (A12)
Wireless Coverage
(A22)
Number of Administrative Litigation
Incidents (A32)
Number of staff (A13)
Rate of smartphone
ownership (A23)
Number of reported complaint
incidents (A33)
Degree of specialization of
Information Disclosure Staff (A14)
Degree of specialization of
Information Disclosure Staff (A14)
Number of trainees (A15)
system, respectively. A
1j
(j=1,2,3,4,5) is used to
denote the number of information disclosure on
government websites, business processing, the
number of staff, the professionalism of information
disclosure staff and the number of people receiving
training in the first level of government
construction; A
2j
(j = 1,2,3) is used to denote the
proportion of fixed broadband users, wireless
coverage and smartphone ownership in the second
level of infrastructure construction, respectively. A
3j
(j= 1,2,3) denotes the number of administrative
reconsideration, lawsuits and complaints in the third
level of government-citizen interaction system,
respectively.
4 GEEWM MODEL
GEEWM model is a combined model of gray
evaluation and entropy weight method (Dong 2015,
Yang 2015). The gray system theory was proposed
by Professor Deng Julong (Deng 1998), which is a
better solution to the problem of incomplete
information and unclear relationship by limited data.
4.1 Determination of The Rating
Result Matrix of The First-Level
Indicators
Firstly, the evaluation matrix was constructed based
on the gray correlation coefficients of the
second-level indicators of the evaluated cities,
secondly, the weights of each second-level indicator
under the ith first-level indicator were calculated,
then the entropy weight method was used to
determine the weights of each second-level
indicator, and finally the evaluation result matrix of
the first-level indicators was written using the
entropy weights and the evaluation matrix.
1.Matrix Ai denotes the standardized data matrix
of the i-th level of indicators in the smart
government evaluation index system.
𝑎
𝑎
𝑎
… 𝑎
A
i
= 𝑎
𝑎
𝑎
… 𝑎
𝑎
𝑎
𝑎
… 𝑎
⋮ ⋮ ⋮ … ⋮
𝑎
𝑎
𝑎
… 𝑎
where𝑎
denotes the standardized data of the jth
secondary indicator under the ith primary indicator
of the tth evaluated city.
2.Calculate the gray correlation coefficients of
the second-level indicators under the ith level index
to construct the judgment matrix. Using the gray
correlation analysis method to analyze the degree of
correlation between indicators, we can analyze the
optimal set of indicators by 𝐴
with 𝐴
( 𝑎
𝑎
𝑎
… 𝑎
), the homogeneity or
heterogeneity of the development trend (where𝐴
as the reference data,𝐴
as the reference data, as the
comparison data), to measure the consistency of the
trend between factors. According to the formula of
gray correlation coefficient, the correlation
coefficient between the jth indicator of the tth
evaluated city and the jth indicator of the reference
indicator set can be obtained as:
Research on the Construction Path of China’s Smart Government Affairs with the Background of "Internet +"
447
𝐻
= (min
𝑎
−𝑎
+ ρ 𝐦𝐚𝐱
𝒌
𝑎
−
𝑎
)/( 𝑎
−𝑎
+ 𝝆𝐦𝐚𝐱𝑎
−𝑎
)
The formula ρ is called the resolution factor, and
in general ρ = 0.5.
3. Determine the weights of each second-level
indicator under the ith first-level indicator. The
entropy weight method is used to determine the
weights of each second-level indicator. The entropy
weight of each second-level index is expressed by𝑒
to denote the entropy weight of each second-level
index, and its formula is: 𝑒
=(
∑
𝑌
ln 𝑌
)/ ln 𝑡,
Among them 𝑌
= 𝑎
/
∑
𝑎
, 𝑌
=0,
lim
→
𝑌
ln 𝑌
=0.
Determine the entropy weights of the
second-level indicators under the first-level
indicators of ground i. The formula is.
𝑊
=(1−𝑒
)/
∑
(
1 −𝑒
)
4.Determine the evaluation result of the ith level
indicator, whose formula is:
𝑅
=
(
𝑊
)
𝑇𝐵
Among them𝑊
= (𝑊
𝑊
𝑊
L 𝑊
)
4.2 The Determination of The Weight
of First-Level Indicators
1. Let the evaluation matrix of the -level indicators
in the performance evaluation system of smart
government be represented by R. The evaluation
matrix of the first-level indicators is composed of
the evaluation result matrix of the second-level
indicators under this first-level indicator, which is
expressed as R=(R
1
R
2
R
3
R
4
R
5
)
T
.
2.The judging matrix C of the performance
evaluation system of smart government construction
can be calculated from the formula.
3.Calculate the entropy weight of the first-level
index by the formula, and calculate the entropy
weight of the first-level index by the formula.
4.Let the result matrix of the performance
evaluation system of smart government construction
be F, and its formula is:
F=W
T
C
5 EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS
5.1 Data Collection
Based on the data provided by the government
information disclosure reports of Guangzhou,
Wuhan, Shanghai, Chengdu, Hangzhou and
Nanjing, China City Statistical Yearbook and the
city's Smart Government Portal, the raw data
collected are shown in Table 2.
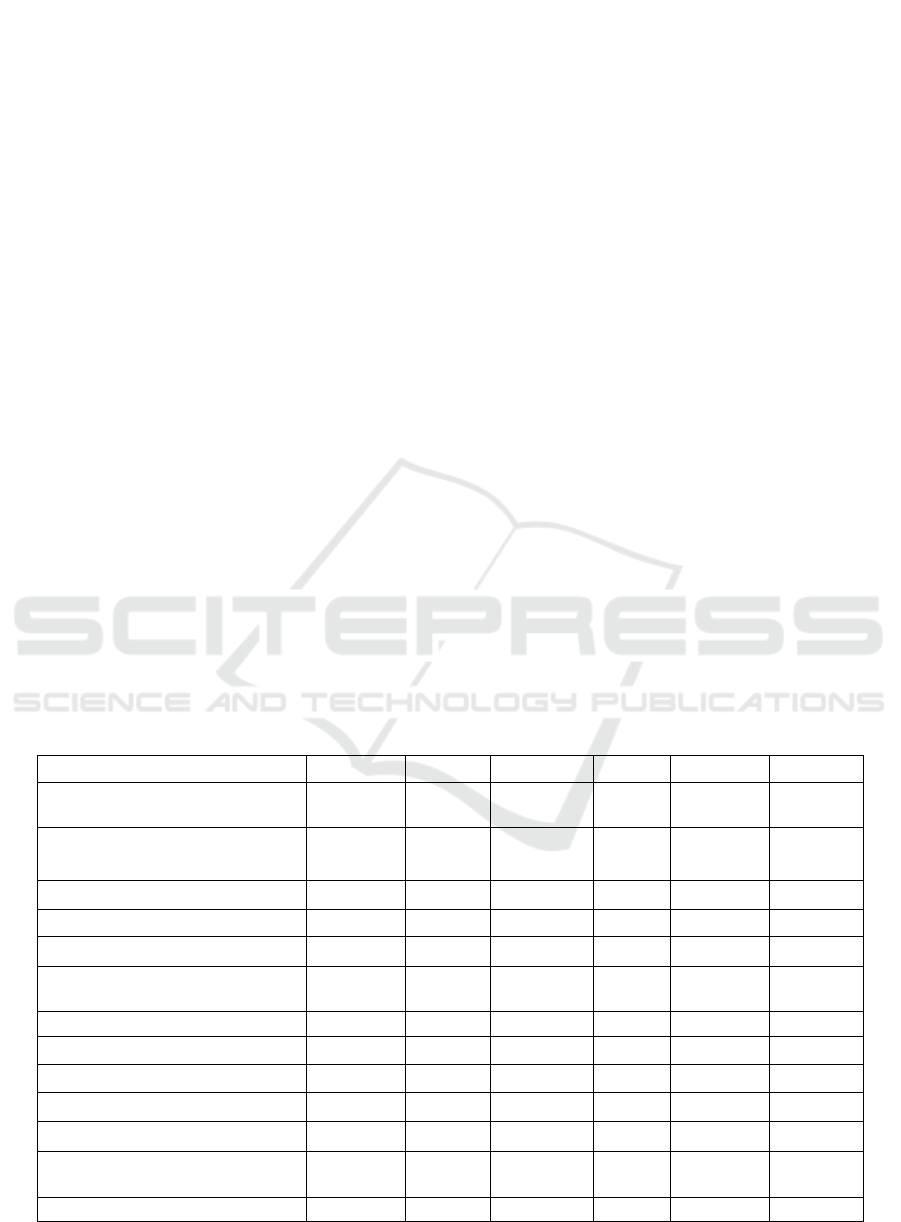
Table 2: Data of each city.
Guangzhou Wuhan Shanghai Chengdu Hangzhou Nanjing
Number of mobile phones per 100
p
ersons
(p
er 100
p
ersons
)
270.94 301.7 234.63 292.08 344.48 539.54
Fixed Broadband Subscriber Ratio
(
Households/ 100
p
ersons
)
42.96 43.16 37.46 42.77 62.23 109.84
Wireless network coverage (%) 2.95 2.12 4.58 2.33 4.43 2.84
Staff
p
rofessional
(
non-
p
rofessional
)
4
(
60
)
42
(
685
)
1
(
34
)
5
(
19
)
32
(
309
)
0
(
5
)
Number of trainees
(p
erson-time
)
155 3670 80 600 2029 50
The number of government website
information disclosure 1108 175247 7266 371523 79185 1009
Total number of inquiries 22340 1352 3117 3009 2940 2000
Online replies 202 97 354 407 495 79
Number of complaints 0 22 0 20 59 0
Re
p
l
y
to the number of com
p
laints 0 12 0 2 57 0
Number of portal websites 1 1 1 1 1 1
Total number of letters submitted
online 180 1352 10 6709 12009 5
Number of letters answered online 51 1168 1 765 120 0
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
448

5.2 Model Solving
5.2.1 The Evaluation Result Matrix of
First-Level Indicators
1.The first level indicator of the smart government
performance evaluation system, "the government's
own construction", is represented by A
1
, which is
based on the data obtained after standardized
processing:
0.000267196 0.016887351 0.016887351
1 0.210993377 0
0.327968037 1 0.115753452 0.131988925
0.011566667 0
A
1
= 0.081717452 1 0.041551247 0.026315789
0.465373961 0
0.253333333 0.232992701 0.111764706
1 0.292527508 0
0.029005525 1 0.008287293 0.151933702
0.546685088 0
This indicator is a positive indicator, so
according to the method of selecting the optimal
indicator, we can know the optimal set of indicators
for the first-level indicator "government
self-building"𝐴
= (1 1 1 1 1)
T
.
2.Calculate the correlation coefficients of the
second-level indicators under the first-level indicator
"government self-building". In the calculation
process, the optimal set of indicators𝐴
is the
reference data,𝐴
= (𝑎
𝑎
𝑎
𝑎
𝑎
)
T
. The
gray correlation coefficients among the factors are
calculated by Equation (3).𝐻
Using the calculated
gray correlation coefficients, we can obtain the
judgment matrix B
1
in order.
0.333392721 0.485559572 0.337128808 1
0.387895602 0.333333333
0.426609526 1 0.361207323 0.365494117
0.335923678 0.333333333
B
1
=
0.352539063 1 0.342830009 0.339285714
0.483266399 0.333333333
0.401069519 0.394630718 0.360169492
1 0.451886517 0.333333333
0.339906103 1 0.335185185
0.370901639 0.524485656 0.333333333
3.Calculate the weights of the secondary
indicators under the first-level indicator
"government self-building", resulting in.
W
=(0.22491,0.203807,0.226611,0.123863,0.22
081)T
4.Calculate the evaluation result matrix of the
first-level indicator "government self-building", and
get.
𝑅
= (0.366551, 0.809315,0.345753, 0.582047,
0.437002,0.33333).
Similarly, according to the method of calculating
the first-level indicator "governmental construction",
the evaluation result matrix of the first-level
indicator "infrastructure construction" can be
calculated as:
𝑅
= (0.375308,0.358234,0.510538,0.360248,
0.555983,0.844275)
The evaluation result matrix of the first-level
indicator "government-citizen interaction system" is
calculated as:
𝑅
= (1,0.68261,1,0.83826,0.333333,1).
5.2.2 Calculate the Weight of First-Level
Indicators
1.The evaluation matrix of first-level indicators in
the performance evaluation system of smart
government construction is represented by R, which
is composed of the evaluation result matrix of each
first-level indicator:
0.366551 0.809315
0.345753 0.582047
0.437002 0.333333
R=(R
1
, R
2
, R
3
)
T
=
0.375308 0.358234
0.510538 0.360248
0.555983 0.844275
1 0.68261
1 0.83826
0.333333 1
According to the calculation results of the
evaluation matrix of the smart government affairs
construction performance evaluation system, the
optimal index set of the smart government affairs
performance evaluation system is selected as:
𝑅
=(0.809315,0.844275, 1)
T
2.The judgment matrix of the performance
evaluation system of smart government construction
is calculated as:
0.429499 1 0.41829 0.594601
0.47238 0.411871
C=
0.415472 0.406815 0.499698 0.407817
0.536299 1
1 0.512251 1 0.6733 0.333333
1
Research on the Construction Path of China’s Smart Government Affairs with the Background of "Internet +"
449

3.Calculate the entropy weights W of the smart
government performance evaluation system:
W=(0.352308 0.328894 0.318798)
T
5.2.3 The Evaluation Results of Smart
Government Affairs Construction
The final performance evaluation matrix F of smart
government construction for the six cities
Guangzhou, Wuhan, Shanghai, Chengdu, Hangzhou
and Nanjing is calculated.
F=(0.606761 0.649411 0.630513 0.558258
0.449052 0.792798)
In summary, it can be seen that the above six
cities in the order of high to low level of
construction of smart government affairs: Nanjing,
Wuhan, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Chengdu, Hangzhou.
5.3 Results Analysis
According to the results of the evaluation of the
performance of smart government construction can
be seen in Nanjing smart government construction
effect is the best, followed by Guangzhou, Shanghai
in these six cities in the disadvantage.
1.The weight matrix of the smart government
affairs performance evaluation system shows that
the government's own construction is the largest
proportion of the current smart government affairs
performance evaluation system. In this aspect of the
government's own construction, Wuhan is the best
among the six cities, followed by Chengdu, and
Guangzhou, Shanghai, and Nanjing are not very
different in this aspect. Therefore, Guangzhou,
Shanghai and Nanjing can make efforts by
increasing the number of information disclosure on
government websites, strengthening the online
government office, increasing the number of
government websites and strengthening the training
of government staff.
2.In terms of infrastructure construction,
Shanghai and Hangzhou are better built, while
Wuhan and Chengdu are at a disadvantage among
the six cities, so Wuhan and Chengdu can make
efforts in fixed broadband usage, wireless network
coverage and smartphone ownership, and vigorously
improve the level of urban smart government
construction.
3.In terms of the interaction system between the
government and the public, Guangzhou, Shanghai
and Nanjing are better built, and the citizens are
more satisfied with the government, but relatively
speaking, Hangzhou is less invested in this area.
From the perspective of indicators, the
government's own construction of this indicator in
the performance evaluation system of the
construction of smart government affairs services
accounted for a larger proportion, Shanghai in the
infrastructure and the construction of the
government-citizen interaction system are relatively
good, but because of the lack of the government's
own construction, so the overall situation of the
construction of smart government affairs services in
the six cities in the lower level. It can be seen that
the construction of smart government affairs is a
whole, any lack of one aspect may cause the
construction of smart government affairs can not
meet expectations. Although Nanjing is in the
middle level in the construction of government itself
and infrastructure construction, it is in the leading
level of smart government construction among these
six cities because of the balanced development in
these three aspects.
6 THE CONSTRUCTION PATH
OF SMART GOVERNMENT
AFFAIRS
6.1 Improve the Institutional
Mechanism of Government Affairs
Services
The goal of smart government is to improve the
internal structure and process of government
organizations through digital technology, optimize
work content and provide more convenient services.
To improve the government service system and
mechanism, we need to reform the government at all
levels of government, from top to bottom, and
fundamentally adjust the technology application and
business development of the government,
organizations or departments (Wang 2019).
First of all, we should take the "one table
project" as the main grip to promote the business
process integration of government departments. The
so-called "one table project" is to draw on the
experience of South Korea, Singapore and other
countries in the construction of smart government,
combining information from different enterprises
and citizens into one table, and then combining the
data in the table into different services according to
the needs, turning the "information islands" caused
by the original segmentation This will transform the
"information silos" caused by compartmentalization
into a dynamic "data ocean", reconstruct the service
model, improve administrative efficiency, and
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
450

promote the modernization of government
governance capacity.
Second, update and transform the current
government management service concept. To
achieve such a change, on the one hand, the
government should take meeting public demand as
the starting point for designing smart government
service systems and providing more convenient and
accurate government affairs services; on the other
hand, the construction of smart government affairs
services should be tested by the convenience of
public use.
Third, establish a new responsibility and
incentive mechanism. There are three main points:
First, in response to the new background of smart
government, new division of responsibilities for
government departments and their staff should be
added to supplement and improve the existing
functions. Second, to change the existing
performance-oriented phenomenon of smart
government, provincial governments should set up
evaluation criteria based on the development goals
of local government, and promote the construction
of smart government by establishing a performance
evaluation mechanism that integrates construction,
evaluation, and improvement. Third, on the basis of
the assessment to establish a corresponding
incentive mechanism, according to the assessment of
the construction of smart government and the
situation to determine the direction, strength and
structure of the investment of funds to stimulate the
enthusiasm of government departments at all levels
to continuously improve their own construction.
6.2 Strengthen The E-Government
Regulatory System and
Information Security Construction
The Internet is not a place outside the law. At
present, the Chinese government is lagging behind
in the laws and regulations related to data sharing
and business collaboration, and there is an urgent
need to build a legal protection system suitable for
the construction of smart government in China. In
the context of "management and service", we should
improve the legal system and system of smart
government from three aspects.
First, we should pay close attention to the trend
of information security of smart government affairs,
combine the practical application of China's smart
government affairs, clarify the concept of
information security of government, establish the
corresponding principles of protecting information
security of smart government affairs, and start the
legislative work to clarify the protection object,
protection scope, protection mode, emergency
measures, relief ways and accountability mechanism
of information security. Joint universities, research
institutes and other research institutions to establish
a legal framework for information security of smart
government affairs services, including pre, during
and post response strategies.
Secondly, promote the revision of relevant laws,
change the focus to the direction of information
security management of smart government affairs
services establish the concept of whole process
management of government information, the whole
process of leaving traces, electronic signature
authorization, etc., and modify or repeal the original
corresponding provisions. For the collection of
government information, the scope of archiving,
authority, duration, destruction, etc. should be
redefined and standardized, and on this basis, fully
assess the risk of information security and clarify the
emergency measures for adverse consequences. By
clarifying the basis of punishment, penalty standards
and other contents, the implementation of
information protection should be strengthened in
order to guarantee the absolute security of
government information to the maximum extent.
Third, improve the legal system and rule of law
the information security prevention and control. The
legal status of information security should be
improved, and the introduction of administrative
regulations on information security should be
accelerated. In addition, the legal gaps of
information security of government affairs, such as
the emerging concept of information security of
smart government affairs affairs, constitutive
elements, regulatory procedures and conditions,
legal responsibilities and penalties, etc. should be
supplemented and improved. Finally, the
construction path of "current law revision + future
special chapter legislation" will be formed to
promote the establishment of information security
legal system in a gradual and hierarchical manner
and realize the rule of law of information security
(Gai 2021, Niu 2021).
6.3 Pay Attention to The Introduction
and Training of Digital Talents
Whether it is developing 5G technology or building
a digital nation, excellent digital talent is the basic
guarantee for its continuity. Digital talent is the
foundation for building smart cities and digital
government. Cultivating digital talents is a
systematic process:
Research on the Construction Path of China’s Smart Government Affairs with the Background of "Internet +"
451

First, the government should fully utilize service
outsourcing and resident service models to alleviate
the shortage of information technology talent teams,
while cooperating with high-tech enterprises to
provide basic operation and maintenance services in
the form of outsourcing, and outsourcing services
and materials in different combinations with the
actual demand as the starting point.
Second, establish a new mode of joint learning
and exchange, break the barriers of human resources
flow between regions, industries and departments,
share top experts' ideas on the basis of saving money
and reasonable coordination, and promote the
training of talents in the fields of big data, cloud
computing, Internet of Things and artificial
intelligence through training innovation.
Thirdly, we employ supernumerary personnel
and teams in the fields of operation and
maintenance, customer service, and application
development to enrich the work force and give them
corresponding treatment and remuneration.
Continuously grow the team of external personnel
according to the stage needs, and cooperate well
with institutional personnel to bring out the
maximum strength. Fourthly, we should cooperate
with universities, attach importance to the
development of communication technology,
information engineering and other related disciplines
in the "double first-class" universities and provide
financial support, take advantage of the local
universities and encourage special research through
the "excellent talent program"; support engineering
colleges and universities to set up Support
engineering colleges and universities to set up
related majors, systematically train and reserve
technical talents, and lay the foundation for sending
high-quality talents to the society in the future;
through government departments, higher vocational
colleges and universities will join hands with
high-tech enterprises to carry out practical training
and internship, and continuously train vocational
and technical talents.
7 CONCLUSIONS
Smart government reform in the "Internet +" era is
about improving people's wellbeing and
modernizing China's governance system and
capacity, and should receive timely attention and
progress. Starting from the innovation of
information technology to drive government
governance, this paper sorts out the basic
background, connotation, construction significance
and development trend of smart government,
investigates the main problems existing in smart
government, and puts forward the optimization path
of smart government. However, the analysis of the
existing problems and optimization path of the
current reform needs to be further integrated and
optimized from the perspective of public
administration and other disciplines. All in all, smart
government service reform in the Internet era still
needs to be optimized and promoted, and will
become an important strategic highland of public
governance reform.
REFERENCES
Dong, H.Y. & Yang, X.Y. (2015). Research on logistics
capacity of Agricultural products based on Entropy
weight grey correlation Method: A Case study of
Shanxi Province [J]. Price Monthly,
Deng, J.L. (1998). Basic Method of Grey System [M].
Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and
Technology Press.
Gai, H.W. & Niu. C.W. (2021). Journal of Liaoning
Administrative College, 50-54.
Wang, C.M. (2019). Openness and Integration: Smart
Government Construction in the Vision of Governance
Capacity Modernization [J]. Leadership Science,
15-18.
Zhou, X. (2021). On the Interactive relationship between
"smart government" and "digital Government" [J].
China Management Informatization,162-164.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
452
