
Prediction of Patent Number of "Specialized, Refinement,
Differential and Innovation" Little Giant Enterprises in Jiangsu
Province based on GM (1.1) Mode
Fushun Bai, Yunqian Lv, Keying Chen, Wenxin Fan, Xingcheng Wen and Donghui Wang
*
Ningbo University of Finance and Economics, Ningbo, China
*328793803@qq.com
Keywords: Small Giant Enterprise, Little Giant Enterprise, Jiangsu Province, Gray GM (1.1) Model, Patent Number.
Abstract: The number of patents is an important index to measure the technological innovation ability of an enterprise.
If the most accurate as possible predictions can be made about the number of corporate patents in the region,
It has a positive significance for the future economic development and policy formulation of the region, This
paper uses the gray GM (1.1) model to predict the patent number of listed companies in the "specialization,
refinement, characteristics and novelty" Little giant enterprises in Jiangsu Province, Using the 7-year data
from 2013-2020 as raw data for grey predictions, Establish the prediction model of patent number of
"Specialized, Refinement, Differential and Innovation" Little giant enterprises in Jiangsu Province, Model
tests were also performed using residual estimation, And the patent number prediction model of
"Specialized ,Refinement, Differential and Innovation" Little giant enterprises in Jiangsu Province has been
successfully established.
1 INTRODUCTION
Specialized, Refinement, Differential and Innovation
"little giant" enterprises are the leaders among small
and medium-sized enterprises. They are focused on
market segmentation, strong innovation ability, high
market share, grasp the key core technologies,
excellent quality and efficiency of the vanguard
enterprises, with the characteristics of "specialization,
refinement, characteristics and novelty" (Lu, Gao,
2020; Dong, Li, 2021)
0
. By the end of 2021, the
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology had
cultivated 4,762 national Specialized, Refinement,
Differential and Innovation "little giants" enterprises.
This paper predicts the number of listed Little giant
enterprise patents by GM (1.1) model in Jiangsu
Province.
2 GM (1.1) MODEL
CONSTRUCTION
The basic idea of GM (1.1) model is that the original
sequence is generated once. Due to the accumulated
sequence has an exponential growth trend, the
approximate first-order differential equation is used
to establish the model, and finally the modeling
sequence is reduced to complete the prediction of the
development trend of the original sequence (Xiao,
He, 2021).
The original sequence is:
X(0) = {x(0)(1), x(0)(2), … , x(0)(n)}
X(0)Next, add up to generate as follows:
X
(
)
(K) = X
(0)(i),K=1,2,3, ··· n (1)
A sequence with exponential laws is generated as
follows:
X
()
={X
()
(1), X
()
(2), … , X
()
(n)}
Grasp X(1) The sequence is approximately the
solution of the first-order differential equations.
dx
()
dt
+ax
()
= b (2)
A is the development coefficient of the model; b
is the ash action amount
Bai, F., Lv, Y., Chen, K., Fan, W., Wen, X. and Wang, D.
Prediction of Patent Number of "Specialized, Refinement, Differential and Innovation" Little Giant Enterprises in Jiangsu Province based on GM (1.1) Mode.
DOI: 10.5220/0011750600003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 499-502
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
499

A=[a,b]
Parameters, using the least squares
method to obtain A as:
A=(B
B)
B
Y (3)
In formula:
B=
⎝
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎛
−
1
2
[X
(1) + X
()
(2) 1
−
1
2
[X
(2) + X
()
(3) 1
⋮
−
1
2
[X
(n −1) + X
()
(n) 1
⎠
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎞
Y={X
(2), X
(3) ⋯X
(n)}
The obtained a and b values are inserted into
formula (2) to calculate:
X
(K + 1) = [X
(1) −
b
a
]e
+
b
a
(4)
Prediction function subtracted by formula _ (4):
X
(
)
(
K+1
)
=X
(
)
(
K+1
)
−X
(
)
(
k
)
=
(
1 −e
)
X
(
1
)
−
e
(5)
3 THE DEVELOPMENT STATUS
OF SPECIALIZED,
REFINEMENT, DIFFERENTIAL
AND INNOVATION"LITTLE
GIANT" ENTERPRISES IN
JIANGSU PROVINCE
Since 2011, the Ministry of Industry and Information
Technology first put forward the concept of
specialization, refinement, characteristics and novelty
"little giant" enterprises, the central and local
governments have continuously issued policies to
support specialization, refinement, characteristics and
novelty "little giant" enterprises, phased certification
and listed many batches of national, provincial and
prefecture-level specialization, refinement,
characteristics and novelty "little giant" enterprises.
By the end of 2021, Jiangsu province had cultivated
289 Specialized, Refinement, Differential and
Innovation "little giant" enterprises, ranking the
fourth in China in total.
There are 731 listed companies of Specialized,
Refinement, Differential and Innovation "little
giants" in China, and 73 are listed companies in
Jiangsu province, accounting for about 10% of the
total, ranking the second.
Table 1: Distribution of "Specialized, Refinement,
Differential and Innovation" enterprises.
Province
Quant
it
y
Province
Quant
it
y
Zhejiang
Province
475 Chongqing City 124
Guangdong
Province
433 Shaanxi Province 114
Shandong 369 Shanxi 113
Jiangsu
Province
289
The Guangxi Zhuang
Autonomous Re
g
ion
84
Beijing
Munici
p
alit
y
264 Yunnan Province 61
Shanghai
Munici
p
alit
y
262 Guizhou Province 53
Hunan Province 241 Gansu Province 49
Anhui Province 235
Xinjiang Uygur
Autonomous Re
g
ion
48
Fujian Province 227
Heilongjiang
Province
42
Henan Province 212 Jilin Province 38
Liaoning
Province
212
The Ningxia Hui
Autonomous Re
g
ion
37
Sichuan
Province
212
The Nei Monggol
Autonomous Region
27
Hebei Province 210 Hainan Province 17
Hubei province 177 Qinghai Province 11
Jiangxi
Province
151
Xizang Autonomous
Region
2
Tianjin
Municipalit
y
133
The number of Specialized, Refinement,
Differential and Innovation "Little giant" enterprises
and listed companies in various prefecture-level cities
in Jiangsu Province are shown in the following table.
Table 2: The status quo of Specialized, Refinement,
Differential and Innovation "little giant" enterprises in
Jiangsu Province.
The number
of
enterprises
Number of
listed
companies
Number of
listed
companies/
enterprises
Jiangsu Province 289 73 25.26%
Changzhou City 28 8 28.57%
Huai'an City 12 0 0.00%
Lianyungang City 9 1 11.11%
Nanjing City 45 15 33.33%
Nantong City 27 6 22.22%
Suzhou City 48 21 43.75%
Suqian city 11 1 9.09%
Taizhou City 21 1 4.76%
Wuxi City 32 12 37.50%
Xuzhou Citey 6 3 50.00%
Yancheng 15 4 26.67%
Yangzhou City 23 0 0.00%
Zhenjiang City 12 1 8.33%
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
500
As can be seen from the table, the average listing rate
of specialized "little giant" enterprises in Jiangsu
Province is 25.26%; the listing rate in Suzhou City is
43.75%, ranking the first in Jiangsu Province,
followed by Nanjing City (33.33%).
4 JIANGSU PROVINCE
SPECIALIZED AND SPECIAL
NEW "LITTLE GIANT"
LISTED COMPANY PATENT
NUMBER FORECAST
After collecting the number of 2014-2021 patents of
the specialization, refinement, characteristics and
novelty "little giant" listed companies in Jiangsu
Province, the level ratio table is established according
to the GM (1,1) model;
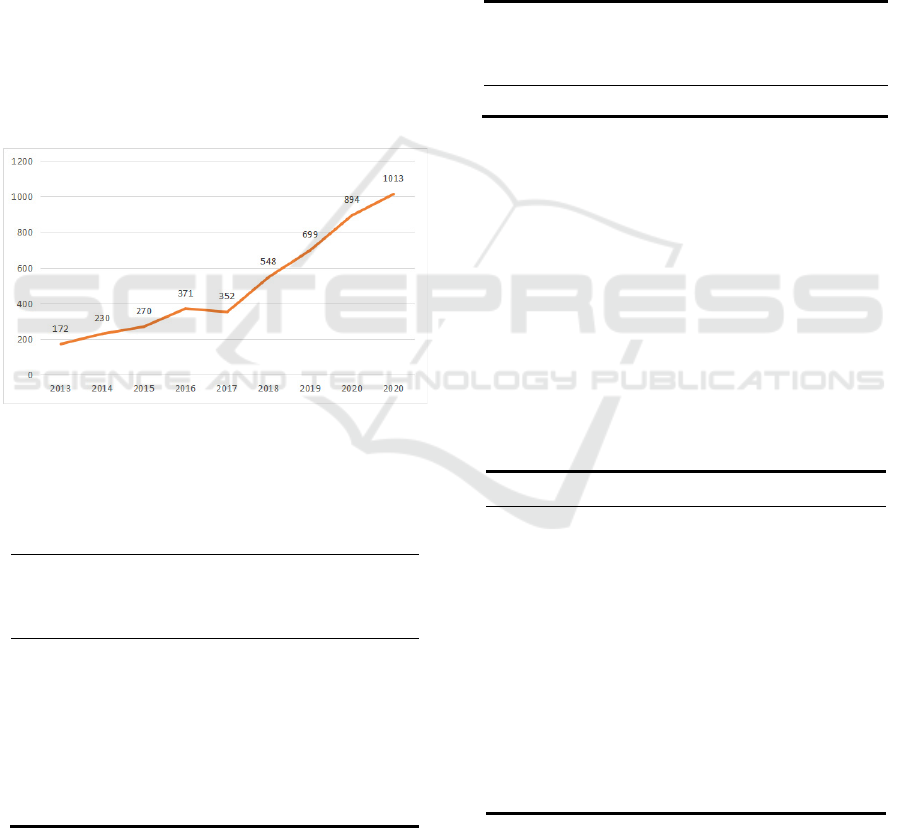
Figure 1: Patent number of "Specialized, Refinement,
Differential and Innovation" listed companies in Jiangsu
Province.
Table 3: GM (1,1) model-level ratio GM (1,1) model-level
ratio table.
order
number
original
value
Tier
ratio
Original value +
translation
conversion shift
value (shift=1013)
Converted
value and
the ratio
2013 172.000 - 1185.000 -
2014 230.000 0.748 1243.000 0.953
2015 270.000 0.852 1283.000 0.969
2016 371.000 0.728 1384.000 0.927
2017 352.000 1.054 1365.000 1.014
2018 548.000 0.642 1561.000 0.874
2019 699.000 0.784 1712.000 0.912
2020 894.000 0.782 1907.000 0.898
2021 1013.000 0.883 2026.000 0.941
As can be seen from the above table,the GM (1,1)
model construction is conducted for the number of
patents, and the level ratio test is first conducted to
judge the suitability and applicability of the data
sequence for the model construction. The level ratio
is the data of the last period / the current period. The
results show that the original data did not pass the
level ratio test,so the translation transformation, that
is,the translation conversion value of 1013.00 is
added to the original value,and the final translation
conversion data level ratio test value is within the
standard range interval [0.819,1.221], which means
that this data is suitable for GM (1,1) model
construction.
Table 4: Results of model construction.
Model building results
developmental
quotient a
The amount
of action in
gray b
The posterior
difference is
compared to
the C value
Small-error
probability
p-value
-0.0767 1037.6652 0.0297 1.000
According to the above table,the development
coefficient a,the gray action amount b,the posterior
ratio C value and the small error probability p-value
are obtained; the posterior difference ratio C value is
0.030 <=0.35,which means that the model accuracy
level is very good. Also,the small error probability p-
value is 1.000 <1.0,meaning that the model accuracy
is very good.
The GM (1,1) model is used to predict the specific
number of patents of listed companies in Jiangsu
Province in the next five years after 2021,as shown
below.
Table 5: Prediction results.
order number original value predicted value
2013 172.000 172.000
2014 230.000 159.912
2015 270.000 253.380
2016 371.000 354.295
2017 352.000 463.253
2018 548.000 580.893
2019 699.000 707.907
2020 894.000 845.043
2021 1013.000 993.108
Back phase 1 - 1152.971
Back phase 2 - 1325.573
Back phase 3 - 1511.930
Back phase 4 - 1713.137
Back phase 5 - 1930.379
RMSE=147.643
This paper establishes a patent application
quantity prediction model based on the grey system
theory (Ma, Song, 2021)
0
According to the forecast
Prediction of Patent Number of "Specialized, Refinement, Differential and Innovation" Little Giant Enterprises in Jiangsu Province based on
GM (1.1) Mode
501

results,the total number of patents in Jiangsu province
in the next five years shows an upward trend. Based
on the forecast results of GM (1.1) model,the number
of patents of 73 listed "Specialized, Refinement,
Differential and Innovation" enterprises in Jiangsu
Province will increase from 2022 to 2027 from 993 to
2027, an increase of 1.94 times in 5 years, with an
average annual increase of 187.
5 CONCLUSION
"Specialized, Refinement, Differential and
Innovation" enterprises have strong scientific and
technological innovation ability From the perspective
of Jiangsu Province, the patent number of
"specialized, Specialized, Refinement, Differential
and Innovation" enterprises currently shows
exponential growth and has extremely strong
development potential. In the context of the national
strong transformation of scientific and technological
achievements, the government needs to create a better
business environment for "Specialized, Refinement,
Differential and Innovation" enterprises to further
achieve high-quality development.
REFERENCES
Dong Zhiyong, Li Chengming. "Specialized, Refinement,
Differential and Innovation" development trend and
path selection of high quality small and medium-sized
enterprises [J]. Reform, 2021 (10): 1-11.
Lu Minfeng, Gao Xuyang.—— is based on the perspective
of cultivating "Specialized, Refinement, Differential
and Innovation" small and medium-sized enterprises [J
/ OL]. Xinjiang Social Science: 1-18 [2022-07-10].
Ma Yuanxin, Song Yan. Application of the grey GM (1,1)
model in patent claim quantity prediction [J]. Journal of
Changchun Normal University, 2021,40 (08): 43-47.
Xiao Jinshan, He Tao. Railway freight volume prediction
based on an improved grey GM (1.1) model [J]. Journal
of Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2021,40 (03): 40-45.
Zhu Nan. Analysis of the transformation path of scientific
and technological achievements of specialized and
specialized new enterprises [J]. Technology think tank,
2022 (07)
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
502
