
Digital Transformation of Smart Industries and Transformation of
Smart City Governance Models in the Context of Internet Technology
and Digital Economy
Han Zhu
School of Finance, Taxation and Public Administration, Shanghai Lixin University of Accounting and Finance,
Shanghai, China
Keywords: Internet Technology, Digital Economy, Smart Industry, Smart Cities, Digital Transformation.
Abstract: New digital technologies are profoundly influencing the process of industrial transformation and urban gov-
ernance, as well as proposing new models and paradigms for smart city governance. How to digitally trans-
form smart industries and govern smart cities in the context of Internet digitalization is an important issue to
promote the modernization of national governance system and governance capacity. Based on the concepts
and theoretical foundations related to the digital economy and Internet technology, this study is based on the
vision of the digital industry transforming the governance system, deeply grasping the impact of the Internet,
blockchain, big data and other technologies on the governance of smart cities and examining the laws of
digital transformation of smart industries and the models of urban governance respectively. The study aims
to grasp the logic and evolutionary laws of smart city governance and provide research directions and ideas
for subsequent institutional research.
1 INTRODUCTION
As a spatial structure where different factors and re-
sources and economic activities are highly concen-
trated (Yi, 2019), cities play an important role in the
economic and social development of a country. As a
new production factor and strategic asset, data has be-
come a fundamental resource for urban development
(Wang, 2020). With the application and development
of big data, cloud computing and industrial internet,
data technology has been deeply embedded in all as-
pects of urban governance, becoming an important
means and carrier for fine urban management, and
thus smart city governance has come into being. At
the same time, emerging technologies are profoundly
influencing social innovation and the transformation
and development of urban governance. The digital
transformation of smart industries and the transfor-
mation of urban governance arising from the fusion
of data and emerging technologies are major issues in
promoting the development of smart cities. Promot-
ing the modernization of the national governance sys-
tem and governance capacity and strengthening the
construction of smart cities will become important
symbols of the overall deepening of reform, while
strengthening the construction of digital government,
digital cities and digital industries, and enhancing the
digital intelligence of urban public services and social
governance will also become important conditions for
the construction of new cities. In this context, the dig-
ital transformation of smart industries and smart city
governance are integrated and developed (Yao, Zhen,
2022), promoting each other, interdependent and, un-
der certain conditions, mutually constrained. This
study focuses on the digital transformation of smart
industries in the context of smart cities and the char-
acteristics of the model of smart city governance on
this basis, in order to deepen the understanding of
smart industries and smart cities, which has important
theoretical significance and practical value.
2 DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION
OF SMART INDUSTRY
The degree of digital transformation in the smart in-
dustry is characterized by a progression from strong
to weak, in the order of element transformation, struc-
ture transformation, strategy transformation and loca-
tion transformation(Fig.1).
Zhu, H.
Digital Transformation of Smart Industries and Transformation of Smart City Governance Models in the Context of Internet Technology and Digital Economy.
DOI: 10.5220/0011750800003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 503-511
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
503
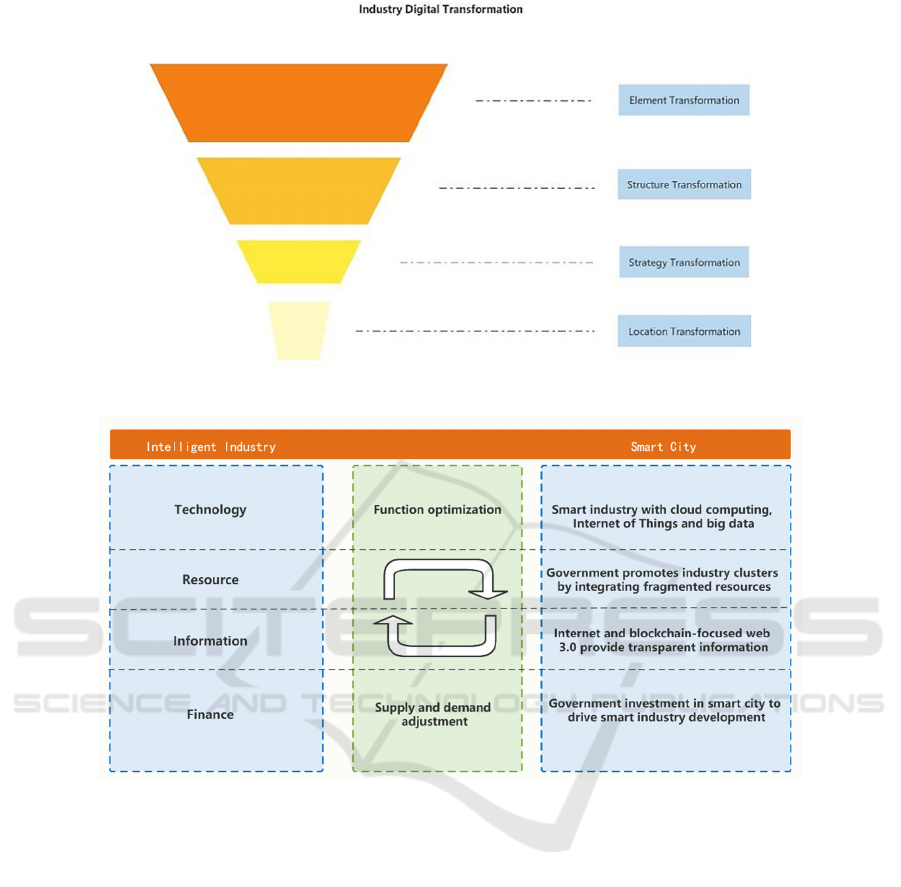
Figure 1: Industry Digital Transformation. [Self-painted].
Figure 2: Integration of smart industries and smart cities. [Self-painted].
2.1 Element Transformation
Smart industry is the basis for the development of
smart cities, while smart cities provide space for the
development of smart industry. However, the inter-
connection and integration of the wisdom industry
and the wisdom city are influenced by many other el-
ements, the main ones being technology, resources,
information and capital, which intermingle and pro-
mote each other to jointly promote the development
process of the wisdom industry and the wisdom city
and facilitate the digital transformation of the wisdom
industry. The development process of smart industry
and smart city is to make full use of these influencing
factors to form a reasonable structure of smart indus-
try and the spatial layout of smart city, and to realize
the integration and progress of smart industry and
smart city(Fig.2).
2.1.1 Technology Elements
The birth of big data technology, artificial intelli-
gence technology, edge computing technology and
blockchain technology has further promoted the de-
velopment of the digital industry while optimizing the
functions of smart cities. since 2010, the smart indus-
try has gradually emerged as a new industry in the
country. Numerous companies have entered the smart
industry, their technologies cover a wide range of
fields, and their mature scientific achievements have
been effectively utilized in the construction of smart
cities. In line with the six dimensions of the digital
industry (Fig.3), many digital and intelligent transfor-
mations and upgrades based on data have emerged.
For example, virtual spaces are gradually shifting
from "visual scenes" to "governance scenes" driven
by technologies such as artificial intelligence and
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
504

Figure 3: Six Dimensions of Digital Industries. [Self-painted].
digital twins (Wang, 2022); RFID identification tech-
nology is already widely used by customs; mobile
IOT technology is helping smart streetlights to be de-
ployed on a large scale on the city's roads; cloud com-
puting technology is being used to provide a wide
range of services. The government cloud based on
cloud computing technology is widely used by gov-
ernment departments; big data technology and artifi-
cial intelligence technology are rapidly promoting the
transformation of data center wisdom; blockchain
technology helps promote the sharing, utilization and
security of information between regions, departments
and enterprises; digital interaction system and gov-
ernment-citizen interaction platform, which are logi-
cally constructed in two-dimensional space such as
digital city and big data, greatly improve the effi-
ciency of government operation. The three-dimen-
sional space with virtual reality and metaverse as the
underlying logic provides a more ideal paradigm for
future government-enterprise collaboration. The cur-
rent application of wisdom industry in a series of mu-
nicipal projects has also gradually created a wisdom
city platform capable of providing wisdom services to
the government, enterprises and citizens, which pro-
vides a broader space for the digital transformation of
industries, including the wisdom upgrading of new
wisdom industries and traditional industries
2.1.2 Resource Elements
Resources mainly include R&D resources and human
resources. R&D resources give rise to human re-
sources, and human resources can make better use of
R&D resources to maximize their effectiveness. In re-
cent years, China has gathered many universities and
new R&D institutions to create national key laborato-
ries, national technology centers and a large number
of enterprises with independent R&D capabilities. By
integrating R&D resources to create a closed loop of
R&D-talent, a virtuous cycle is formed. In terms of
human resources, by actively building a wisdom tal-
ent pool, strengthening the interaction between the
government, enterprises, universities and research in-
stitutions, building an integrated platform for indus-
try-university-research, promoting talent innovation
and exchange, and promoting the integration of wis-
dom industry and wisdom city development talent is
a key element in determining the construction of wis-
dom cities and wisdom industry innovation, and tal-
ent capacity building is indispensable. In the process
of promoting the development of wisdom industry
and wisdom city, there are two main paths to
strengthen the construction of talents. (Xu, Zhang,
Zhang, 2013) One is to gather talents from outside.
Cities need to attract and gather talents by creating a
good physical environment and cultural atmosphere.
To strengthen the introduction of talents, the city has
taken the lead in formulating and continuously opti-
mizing settlement and housing policies for high-level
talents, domestic and foreign university graduates and
foreign talents, so as to provide convenience and pro-
tection for their work and life. To promote the devel-
opment of smart industries, talent policies should fo-
cus on entrepreneurial talent and scarce talent in key
industries and promote the flow of talent to compa-
nies related to smart industries. Secondly, the govern-
ment needs to cultivate talents from within. It needs
to uphold the concept of openness and innovation, en-
courage universities to cultivate talents in line with
industrial trends, and actively guide the community to
jointly cultivate the key talents needed for smart in-
dustries and smart cities.
Digital Transformation of Smart Industries and Transformation of Smart City Governance Models in the Context of Internet Technology and
Digital Economy
505

2.1.3 Information Elements
Information has a high strategic position as an im-
portant resource for innovation and development in
today's society, and some scholars believe that it is the
basis for innovation and competitive advantage, as
the unique ability to disseminate, store, organize, pro-
cess and analyze information becomes a good condi-
tion for constituting a modern think tank. (Peng,
Chen, Li, 2021) The information element has contrib-
uted to the flourishing of think tank construction. In-
formation think tanks serve public policy, and as
think tanks, they have tremendous information sup-
port for the digital industry in both political advice
and academic research and theoretical innovation; in-
formation think tanks allocate human, material and fi-
nancial resources rationally so as to carry out human
resource management, fund management, project
management and results management and other re-
lated work, improve efficiency and shorten the pro-
cess, and can develop and utilize information to the
greatest extent The information think tank plays the
functions of planning, organizing, implementing and
controlling, effectively integrating the research re-
sources of the think tank, making full use of the ex-
pertise and research capabilities of the intellectual
subjects, forming an efficient and high-quality
knowledge production process, producing high-qual-
ity knowledge products, and delivering them to the
government, the public and the international commu-
nity through different ways, channels and media to re-
alize the value of the results The project will also pro-
mote the digital transformation of industries.
2.1.4 Finance Elements
Funding is the material basis for supporting the con-
struction of smart cities and the development of smart
industries. At the early stage of smart city construc-
tion, the government promoted the construction of
smart cities through investment, which in turn led to
the development of smart industries. In recent years,
China has actively promoted the integration of indus-
try, academia and research, which has led to the de-
velopment and growth of the wisdom industry and the
formation of a complete upstream and downstream
industrial chain. In the late stage of smart city devel-
opment, China has made full use of the advantages of
high management efficiency and strong technical in-
novation capacity of institutions and social capital
and the leveraging and amplifying effect of financial
funds to promote the construction of smart cities in
China, relying on the Internet, big data, cloud compu-
ting, block chain, artificial intelligence and other fi-
nancial technologies to vigorously develop Internet
finance and promote the flow of financial capital to
industrial construction and urban governance, thereby
realizing the smart industry The promotion of smart
city construction. At the same time, financial technol-
ogy has greatly reduced the operating costs and ac-
cess threshold of inclusive finance, realized measura-
ble, asset-based and data-based credit systems, and
enabled everyone to participate in urban construction
and industrial development through financial invest-
ment. It has effectively promoted urban infrastructure
construction and economic and industrial develop-
ment in numerous fields such as road transport, new
district development, ecological protection, cultural
tourism, biomedicine, software and information ser-
vices and education and healthcare.
2.2 Structure Transformation
The digital transformation of smart industries is a pro-
cess of integration and development with cities. On
the one hand, the development of smart industries
stimulates demand on the socio-economic side, thus
stimulating the intrinsic vitality of cities; on the other
hand, the improvement of smart city functions will
also provide conditions for the development of smart
industries and enhance competitiveness. In the devel-
opment process of smart industries and smart cities,
the integration and development of smart industries
and smart cities have formed different stages due to
the fundamental change of their leading dynamics
(Fig.4). In recent years, the integration and develop-
ment of China's wisdom industry and wisdom cities
has been deepening and has gone through three devel-
opment stages in chronological order.
2.2.1 Policy-Oriented Stage of the Initial
Transformation
The focus of this stage is on policy support, and the
government needs to formulate relevant policies that
are conducive to the digital transformation of the
smart industry and use high technology to guide the
gradual formation of the prototype of the smart indus-
try, so that a cluster of smart industries can be formed.
In terms of space, some scholars believe that modern
urban space is gradually transforming towards the in-
telligent and digital elements brought about by the
fourth industrial revolution, i.e., more attention is
paid to the technological empowerment of urban
space brought about by digital technology in the pro-
cess of embedding in urban governance. At this stage,
both smart industrial bases and smart urban areas
formed by smart industrial agglomeration show a
clustered distribution, and smart urban areas mainly
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
506

Figure 4: Structural transformation of the digital industry. [Self-painted].
expand around smart industrial bases, forming a one-
dimensional urban space.
2.2.2 The Market-Oriented Phase of
Mid-Term Integration
The focus of this phase is on market expansion. With
the gradual development of the concept of smart cit-
ies, the focus of attention is no longer limited to the
construction of infrastructure, but more on the market
pull effect of the city. Whether the mid-term market
expansion can be completed to lay the foundation for
the later scale development becomes the key to the
successful completion of the digital transformation of
the smart industry at this stage. The construction of
smart cities has led to the development of urban
transport, education and finance, and the develop-
ment of transport, education and finance has created
a favorable environment for the market expansion of
the smart industry, further promoting the digital trans-
formation of the smart industry. Spatially, smart in-
dustry bases and smart city areas began to show a
point-axis distribution, and smart industries and smart
city areas began to expand along the axis, with adja-
cent areas connecting to form a two-dimensional ur-
ban space.
2.2.3 The Later Stages of Integration in the
Competitiveness-Oriented Phase
This stage focuses on the creation of competitiveness,
which is the ability of a city to attract, compete for,
own and transform resources, occupy and control
markets and its ability to create value and provide
welfare for its residents in comparison with other cit-
ies in the development process. (Ni, 2001) The im-
provement of a city's competitiveness is mainly
achieved through urban industries. The returns and
influence of urban industries determine, to a certain
extent, the city's ability to create value and reflect its
competitiveness. In the advanced stage of digital
transformation of wisdom industry is to expand the
competitiveness of the city in the region by improving
the level of wisdom industry, so as to obtain more re-
sources to promote the digital transformation of wis-
dom industry and the development of wisdom indus-
try and wisdom city. Spatially, smart industry bases
and smart city areas show a net-like and face-like dis-
tribution, with closer links between smart industry ba-
ses, forming smart industry clusters and neighboring
smart city areas gradually forming three-dimensional
urban spaces.
2.3 Strategy Transformation
2.3.1 Investment-Driven
This type takes deepening the supply-side structural
reform as the main line, strengthens top-level design
and overall coordination ability, and promotes the
digital transformation and development of smart in-
dustries and the improvement of urban functions
through project investment and construction to build
a smart city. On the one hand, it promotes the devel-
opment of wisdom industry through key projects, ex-
tends the industrial chain and improves the wisdom
industry ecology. Focus on the development of core
wisdom industry, through the injection of funds and
technological innovation, focus on the development
of software and information services industry, medi-
cine and health, artificial intelligence, new energy ve-
hicles, integrated circuits, smart grid, rail transporta-
tion, intelligent manufacturing equipment eight key
industries, to build a "goose array" of industrial clus-
ters; continue to promote industrial complementary
chain to strengthen the chain Stabilize the chain, fo-
cus on building iconic major industrial projects start-
ing from industrial demand, and cultivate a number of
core enterprises that can drive the integration and per-
Digital Transformation of Smart Industries and Transformation of Smart City Governance Models in the Context of Internet Technology and
Digital Economy
507

fection of the industrial chain and create a new intel-
ligent industrial ecology. On the other hand, through
investment and construction to improve the city's wis-
dom city function, strengthen the city's important car-
rier support. Coordinated planning of industrial struc-
ture and urban spatial layout, project access as a grasp
of efforts to build a new carrier of urban wisdom in-
dustry with outstanding benefits of industrial cluster-
ing, through investment to promote the digital trans-
formation of wisdom industry.
2.3.2 Consumption-Driven
This type aims to promote the digital transformation
and development of smart industries by consumption,
focusing on demand-side structural reform and man-
agement, expanding domestic demand for urban con-
sumption, improving the urban consumption environ-
ment and enhancing the quality of consumption,
forming a positive interaction between the supply and
demand sides. On the one hand, it relies on new smart
industries and the smart transformation of traditional
industries to create new consumption growth points,
promote economic development and optimize the
functions of smart cities. Vigorously develop new
smart industries, promote digital consumption, and
support the development of online industries such as
the layout of telecommuting, online education, tele-
medicine and online entertainment; guide the wisdom
of traditional industries, and guide commercial enter-
prises to implement digital transformation. On the
other hand, through the construction of a multi-level,
integrated development of the smart city consumption
carrier platform, to stimulate consumption enthusi-
asm, ensure consumer safety, promote economic de-
velopment, and pull the transformation and upgrading
of industrial wisdom. Expanding the spatial axis of
consumption in the smart city, by building a brand
publishing platform, establishing brand advantages,
promoting the development of fashion characteristic
industries and the improvement of business service
systems, and pulling the digital transformation of
smart industries through consumption.
2.3.3 Innovation-Driven
The type takes reform and innovation as the funda-
mental driving force, highlighting the core position of
innovation drive in the process of digital transfor-
mation and development of the "wisdom industry. On
the one hand, in order to promote the development of
the smart industry, it focuses on differentiated support
and diversified cultivation of innovation subjects, es-
tablishes a full-cycle and full-factor innovation sup-
port system oriented by market demand, and pro-
motes the integration and development of the innova-
tion and industrial chains. We will implement actions
to improve the quality and efficiency of new R&D in-
stitutions, promote the exchange and cooperation of
various innovation subjects, guide the flow of various
innovation elements to the industrial end through
government policies, and form a market-oriented
model for the integration and development of indus-
try-university-research; cultivate a matrix of science
and innovation enterprises in a gradual manner, pro-
vide differentiated policy support and management
according to the scale and development stage of the
enterprises, and deepen the implementation of the
plan to introduce high-level overseas talents and pro-
jects to effectively improve the programmed will also
deepen the implementation of the scheme for the in-
troduction of high-level overseas talents and projects,
so as to enhance the innovative and entrepreneurial
capabilities of talents. On the other hand, we will op-
timize the carrier function of the smart city by con-
structing a multi-level and three-dimensional innova-
tion space, promote the development of smart city
construction in the direction of marketisation, special-
ization and refinement, and enhance the scale effect,
agglomeration effect and comprehensive effect of the
smart industry. Promote the high-quality develop-
ment of high-tech parks, enhance the level of co-ordi-
nation and coordination management of high-tech
zones, create market-oriented, differentiated and dis-
tinctive high-tech parks through the integration of in-
novative resources and the coordinated layout of in-
dustries, enhance the overall economic benefits and
development quality of parks, and promote the digital
transformation of smart industries through innova-
tion-driven.
2.4 Location Transformation
2.4.1 Digital Transformation of Smart
Industries in the Old City
In the early stages of digital construction in the old
city, there was a lack of guidance on the concept of
smart city construction, and the digital construction
of various departments was uneven, with poor links
between departments, forming "information islands",
which greatly reduced work efficiency and caused a
waste of resources. In order to solve the above prob-
lems, we need to co-ordinate the wisdom construction
of the old city and the digital transformation of tradi-
tional industries, and on the basis of the existing in-
formation construction and industrial transformation,
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
508

we should redesign the top level and build a central-
ized government data platform to interconnect the
isolated information systems of various departments,
so as to realize the interconnection and sharing of in-
formation between departments. At the same time, as
the economic and cultural center of the city, the old
city has many influential regional shopping districts
that gather the best quality consumer markets, attract
consumers from across the city and contribute the
most to the city's commercial output. However, with
the rise of the O2O model, the low-cost, high-effi-
ciency and zero-inventory online retail industry be-
gan to emerge (Wei, zhen, Xi, Wang, 2013), the tra-
ditional circulation order and marketing model of
commercial production and sales were broken, the
traditional commercial space structure of the city
faced impact, and the government began to explore
and practice in the face of the new situation. In recent
years, in order to accelerate the construction of smart
cities, China has implemented infrastructure renova-
tion and upgrading and data resource sharing and
opening projects based on in-depth investigation and
research in cooperation with smart city construction
units, focusing on "data + governance" and "data
+ decision-making". In addition, the project will be
managed in the whole process of project creation, im-
plementation, acceptance and application of wisdom
projects, so as to achieve the coordination of wisdom
projects. At the same time, it will guide the coopera-
tion between the Internet-based online industry and
the offline shopping areas of traditional cities, jointly
create new scenes, new experiences and new market-
ing, and data-driven online and offline operations in
the whole area to create a new intelligent consump-
tion model, lead the consumption trend and promote
the digital transformation of the wisdom industry in
the old city.
2.4.2 Digital Transformation of Smart
Industries in the New City
Compared to the old city, the new city has a relatively
weak industrial base, lacks leading industries, and
originally had a low overall industrial level, weak
consumption and weak markets. The digital transfor-
mation of the wisdom industry in the new city should
give priority to top-level design and planning from
the wisdom city aspect, co-ordinate the construction
of a wisdom city service platform, provide better and
more convenient services for enterprises, and create a
good environment for the development of the wisdom
industry. The new city should strengthen new wisdom
industry landmarks, seize development opportunities,
vigorously develop new wisdom industry systems,
focus on complementing and strengthening chains,
creating new development platforms, developing new
application scenarios, strengthening support for ma-
jor projects, forming new growth points with explo-
sive and leading power, deepening the integration of
industry and city, and promoting the digital transfor-
mation of wisdom industry and the rapid development
of wisdom cities.
3 A PARADIGM SHIFT IN
URBAN GOVERNANCE
With the rapid development of intelligent technolo-
gies such as cloud computing, the Internet of Things
and big data, the smart industry is not only at the fore-
front of modern industrial development, but also lead-
ing the development of human-centered smart city
construction and new urbanization. The injection of
smart industries provides the impetus for the develop-
ment of the city's economy, and the economic devel-
opment drives the infrastructure construction of smart
cities, improves the functions of smart cities, opti-
mizes the quality and layout of urban space, which in
turn creates the flow and concentration of population
and capital, increases the supply of labor, talent and
capital for smart cities, and will also drive the demand
for the economic, social, political, cultural and eco-
logical functions of cities. The new demand and the
existing foundation of smart city construction will in
turn provide the impetus and guarantee for a new
round of upgrading of the smart industry, thus form-
ing a virtuous cycle of integration and development
of the smart industry and the smart city. In this new
era, as a result of the digital transformation of the
smart industry, the governance model of the city has
also changed from traditional governance to a new
type of governance. Some scholars believe that the
governance of a new type of city involves the com-
prehensive role of multidimensional factors such as
values, institutions and technologies. (Yi, 2022) In
the context of the development foundation and differ-
ent stages of the integration of smart industry and
smart city and the digital transformation of smart in-
dustry, according to the four core elements of value,
politics, market and tools, this paper classifies urban
governance models into four types, which are the in-
novative governance model with multi-sectoral col-
laboration, the innovative governance model with the
participation of subdivided multi-dimensional sub-
jects, the innovative governance model with a human-
centered approach and the smart city The scientific
assessment model of governance (Fig.5).
Digital Transformation of Smart Industries and Transformation of Smart City Governance Models in the Context of Internet Technology and
Digital Economy
509
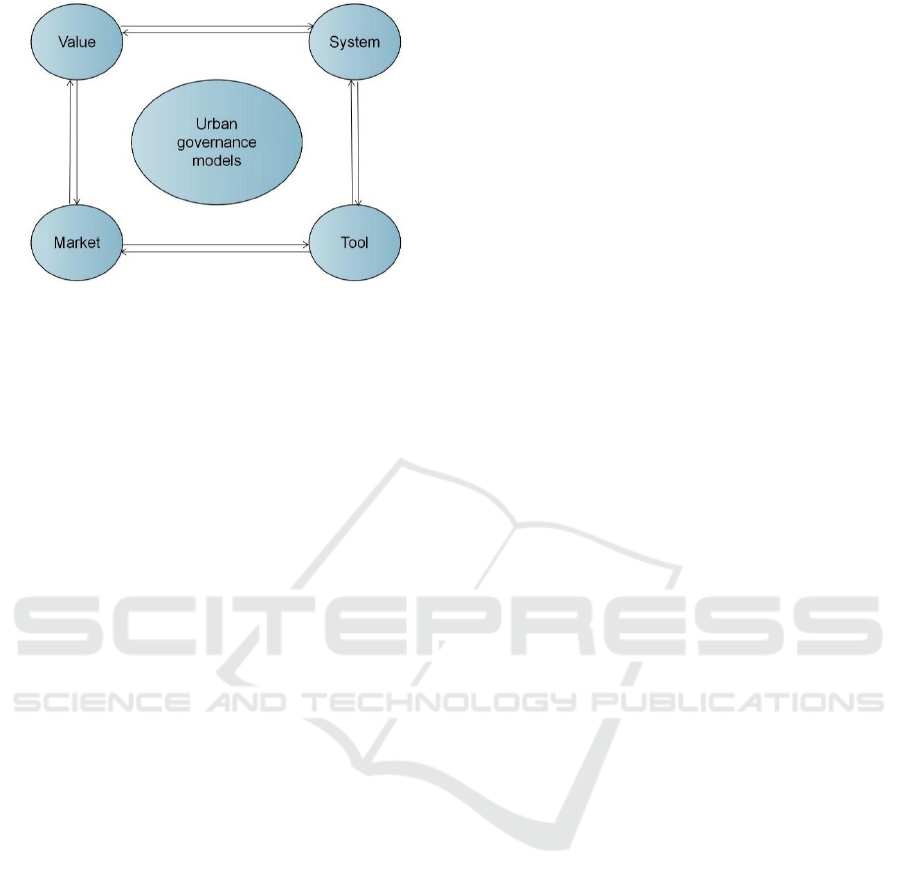
Figure 5: Four elements of the urban governance model.
[Self-painted].
3.1 Value: An Innovative Governance
Model with Multi-Sectoral Synergy
In the context of a smart city, the subjects of urban
governance include government departments, enter-
prises, the public and social groups, etc., but it is the
government departments that play the leading role, so
it is necessary to innovate the governance model,
build an integrated, refined and visualized public in-
formation platform governance model, compose a
public information system with spatial data, image
data and monitoring videos of the governance tasks
of each department, and construct a multi-depart-
mental collaborative After acquiring information and
data from the platform, the decision makers of smart
city governance can conduct comprehensive analysis,
unified scheduling and formulate measures. The col-
laborating departments can also exchange infor-
mation and data in real time in the wisdom infor-
mation platform, share resources and dovetail with
each other to jointly manage problems, forming a pat-
tern of multi-departmental collaborative governance.
3.2 Market: An Innovative Governance
Model that Breaks down the
Participation of Multiple Actors
In the context of smart cities, the governance of cities
must be jointly participated by multiple subjects in or-
der to achieve better governance results. The govern-
ment should organically unify and coordinate multi-
ple subjects to participate in urban governance to-
gether. Government departments should fine-tune the
decomposition of the work involved in the govern-
ance subjects and refine the work tasks and spatial
units of the subjects, so that the two can be effectively
dovetailed and the "invisible hand" of the market can
be used to reduce the waste of human, material and
financial resources, so that the governance tasks can
be completed in a very short period of time and the
efficiency of urban governance can be improved.
3.3 System: An Innovative Model of
People-Centered Governance
In the context of smart cities, the starting point of ur-
ban governance is to serve the public and improve
their standard of living and quality of life. Therefore,
an innovative people-oriented governance model
should be established to involve more public partici-
pation. Publicity and participation are important fea-
tures of smart cities, and all aspects of smart city gov-
ernance should be open to the public, with improved
public participation mechanisms and group efforts.
The smart information platform should facilitate pub-
lic participation in different time periods and spatial
areas with the help of tools such as cloud computing,
big data and the Internet of Things, opening up chan-
nels for reflection and improving governance effec-
tiveness. (People's Daily, 2020)
3.4 Tool: A Scientific Assessment
Model for Smart City Governance
In the context of smart cities, the government should
adopt a scientific assessment model to evaluate
whether the governance of the city is in place and
whether the results are satisfactory. In the assessment,
multiple methods should be used to make the assess-
ment conclusions as authentic, objective and scien-
tific as possible. The government should go deep into
the governance scene and directly participate in the
governance of the smart city; or use the interview
method and questionnaire method to assess the effec-
tiveness of the governance of the smart city, the
method chosen must be scientific and effective, and
can well control the real situation. If problems are
identified in the process of smart city governance, rel-
evant government departments, enterprises or social
organizations should be instructed to rectify them in
order to achieve better governance results.
4 CONCLUSION
Driven by smart technology, the digital transfor-
mation of smart industry and the integration of smart
industry-driven smart cities are important ways of ur-
ban development in the new era. Taking the digital
transformation of smart industries as an entry point,
this paper summarizes the specific types of digital
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
510

transformation of smart industries in China in recent
years and their influencing elements, and analyses in
depth their intrinsic logic and influencing mecha-
nisms. On the basis of a structured analysis of the de-
velopment of multiple integration, it summarizes the
four major modes of urban governance and their mul-
tiple integration development characteristics that
have been demonstrated in smart cities influenced by
the development of smart industries. In this new era,
it is necessary to integrate the multiple elements in-
volved in the development of smart industries and
smart cities, to give full play to and balance the power
of the government and the market, and to realize the
digital transformation of smart industries and the ef-
ficient integration of smart industries and cities, so as
to promote the overall improvement of the level of
industrial development, the effectiveness of urban
governance and the quality of social and economic
development.
REFERENCES
Chengzhi Yi. The Inner Logic and Optimization of Govern-
ment Response Mechanisms for Urban Residents' En-
vironmental Demands - An Analytical Framework
Based on Holistic Governance[J]. Nanjing Social Sci-
ence,2019(08):64-70+120
Chengzhi Yi. The Governance Logic of People’s Cities: An
Embedded Analysis Based on Values, Institutions and
Tools[J]. Nanjing Social Science, 2022(07):61-70.
Chong Yao, Feng Zhen, The Multiple Integration and De-
velopment Mechanism of Smart Industry and Smart
City - Nanjing City as an Example[J]. Nanjing Social
Science, 2022(06):59-67.
Chunhui Wang. Basic Strategies for Accelerating the Cul-
tivation of Data Factor Markets[J]. China Telecom In-
dustry,2020(05):42-45.
Pengfei Ni. Analytical Paradigm and Conceptual Frame-
work of Urban Competitiveness in China[J]. Dynamics
of Economics, 2001(06):14-18.
Proposal of the Central Committee of the Communist Party
of China on Formulating the Fourteenth Five-Year Plan
for National Economic and Social Development and the
Visionary Goals for 2035[N]. People's Daily, 2020-11-
04(001).
Qingrui Xu, Suping Zhang, Jun Zhang. Talent Strategy and
the Construction of Smart City[J]. Journal of Xi'an Uni-
versity of Electronic Science and Technology (Social
Science Edition), 2013,23(02):1-6.
Yinwei Wang. The Logic of Digital Transformation of
Government Governance In Shaping Urban
Space[J].Urban Development Research,
2022,29(06):85-91.
Zhouhong Peng, Fei Chen, Gang Li. Elements of Infor-
mation Capability and Construction Path of New Think
Tanks[J]. Think Tank Theory and Prac-
tice,2021,6(03):1-9.
Zongcai Wei, Feng zhen, Guangliang Xi, Bo Wang. Glob-
alization, Flexibility, Compounding and Differentia-
tion: A Study on the Evolution of Urban Functions in
the Information Age[J]. Economic Geography,
2013,33(06):48-52.
Digital Transformation of Smart Industries and Transformation of Smart City Governance Models in the Context of Internet Technology and
Digital Economy
511
