
Exploring the Health Information Needs of the Elderly Based on the
Online Health Communities
Yuhan Ma and Qiuli Qin*
School of Economics and Management, Beijing Jiaotong University, China
Keywords: Health Information Needs, Online Health Communities, The Elderly.
Abstract: This paper explored the health information needs of the elderly from two perspectives: information demanders
and information providers. It crawled data from questions and health education sections on the online health
communities. LDA model was applied to cluster the unlabeled questions set and obtain five themes. Then the
dataset of article titles with five categories was used to train the classifiers: CNN-BiLSTM and FastText.
After comparing the matching degree between clustering themes and classification results, this paper put for-
ward some suggestions for caregivers and information providers to assist elderly health management.
1 INTRODUCTION
The aging of the population has become an irreversi-
ble worldwide trend in the 21st century. The United
Nations predicted that the proportion of the elderly
aged over 60 would reach 22% of the global popula-
tion by 2050. The arrival of an aging society would
bring out great pressure on society, family, and med-
ical care (Sun, Shen, 2016). However, the supply of
effective services and resources for older people is se-
riously insufficient and limited. It is necessary to
carry out collaborative aging health management.
In the era of big data, the development trend of
health management is integrated, dynamic, and online
(Tian, Du, 2018). It not only focuses on the treatment
of malignant diseases but also the prevention of a per-
son’s overall health status. The elderly face health
problems such as physical decline and cognitive de-
terioration. They also feel lonely and depressed due
to social isolation or lack of companionship. Some
services for the elderly tried to solve the health man-
agement problem through technology. However, they
failed to gain popularity due to a mismatch between
the older users’ demands and the providers’ ideas
(Jo-
vanović, De Angeli, McNeill, Coventry, 2021).
Therefore, it is essential to collect and understand the
needs of the elderly when intervening in their health
management.
2 RELATED WORK
In the face of demographic changes, some health
needs assessment tools were used for the elderly. Brit-
ish scholars proposed a comprehensive geriatric as-
sessment as a diagnostic tool for physiological, psy-
chological, and social adaptation. Moreover, Euro-
pean scholars developed the Care Dependency Scale
to evaluate the unmet care needs of elderly patients
(Yang, Zhou, Ye, Wang, 2021). Health information
needs reflect the lack of individual health knowledge,
which drives health information behavior (Qian,
Zhou, Zhou, Ren, Li, 2019). Questionnaires and in-
terviews were applied to explore the information
needs and sources of the elderly (Edewor, Ijiekhuam-
hen, Patrick., Emeka, 2016). Another method is
through scoping review to classify the care and sup-
port needs of older people with chronic diseases
(Abdi, Spann, Borilovic, Witte, Hawley, 2019). How-
ever, these traditional methods have some limitations:
researchers need to assist when carrying out question-
naires and interviews due to the understanding ability
of the elderly.
As the Internet has become a channel for the dis-
semination of health information, online health com-
munities provide users with an open platform for in-
formation exchange, question-and-answer consulta-
tion, and social support on health-related issues
(Zhao, 2018). Some of them positively impact on
self-management and daily disease control for pa-
tients (Litchman, Edelman, Donaldson, 2018; Zhang,
512
Ma, Y. and Qin, Q.
Exploring the Health Information Needs of the Elderly Based on the Online Health Communities.
DOI: 10.5220/0011751000003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 512-517
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
Grave, Sklar, Elhadad, 2017). Some researchers used
Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) and binary classi-
fication to divide users into different social support
types (Wu, Hou, Jin, Hu, 2017). With the continuous
development of deep learning technology, long short-
term memory (LSTM) and Convolutional Neural net-
works (CNN) have been applied to recognize entities
in the question and answer texts in the online medical
community
(Liao, Zou, Xi, 2021). However, the plat-
form for elderly users has not received relevant atten-
tion.
Therefore, this paper decided to collect health in-
formation about the elderly from the questions raised
and health education sections of the online health
community. Then it adopted text mining and topic
analysis to explore the elderly health needs from the
perspectives of the information demanders and pro-
viders.
3 EXPERIMENTAL METHODS
The paper applied a python crawler to collect text data
from online health communities. One part came from
information demanders in the questions-raising sec-
tion without labels. LDA model was adopted for topic
identification and clustering. The other part came
from information providers in the health education
section with classification. CNN-BiLSTM and
FastText were used to learn the features and train the
classifiers. By comparing the matching degree of
clustering and classification results, this paper could
comprehensively analyze the health information
needs of the elderly. The whole process of text mining
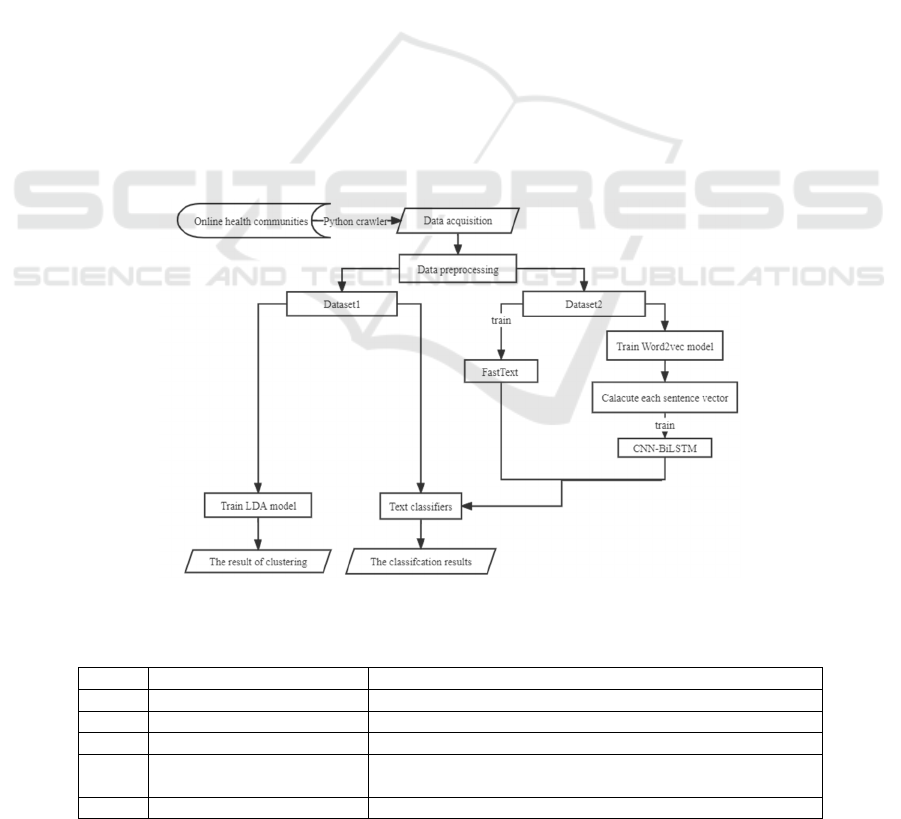
is shown in Figure 1.
3.1 Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
The existing online health communities have two
kinds: one is the social platform with an open medical
module for the discussion of users; the other kind is
the health advice module in the medical website for
various diseases. Table 1 lists the top five domestic
communities in terms of popularity and their func-
tions. After comparing their functions and conven-
ience of operation interface, we selected the 39-health
net as the experimental data.
From the question-raising section of 39-healthy,
1,660 questions associated with physical changes in
older people were stored as ‘Dataset1’, representing
the health information needs of the elderly. The paper
Figure 1: The Processing Flow of Text Mining (Photo credit: Original).
Table 1: Domestic Online Health Community (Table credit: Original).
Website Introduction
1 39-health networ
k
Professional health information
p
ortal
2 Youwenbida net Excellent online health consultation platform
3 Dazhong yangsheng Spread scientific health methods in daily life
4 Xunyiwenyao net
Set up precision medical information inquiry, one-to-one
online consultation, a
pp
ointment re
g
istration
5 Leha health networ
k
A sharing platform to spread the concept of healthy life
Exploring the Health Information Needs of the Elderly Based on the Online Health Communities
513
used the inverted index, TF-IDF model, and cosine
similarity to filter questions with the highest similar-
ity. It selected the proportion of the same keywords,
the rate of difference in sentence length, and the order
of keywords as features. From the health education
section of 39-healthy, five categories of article titles
were stored as ‘Dataset2’, 2,400 pieces respectively,
which are the elderly health care, psychology, dis-
ease, fitness, and diet.
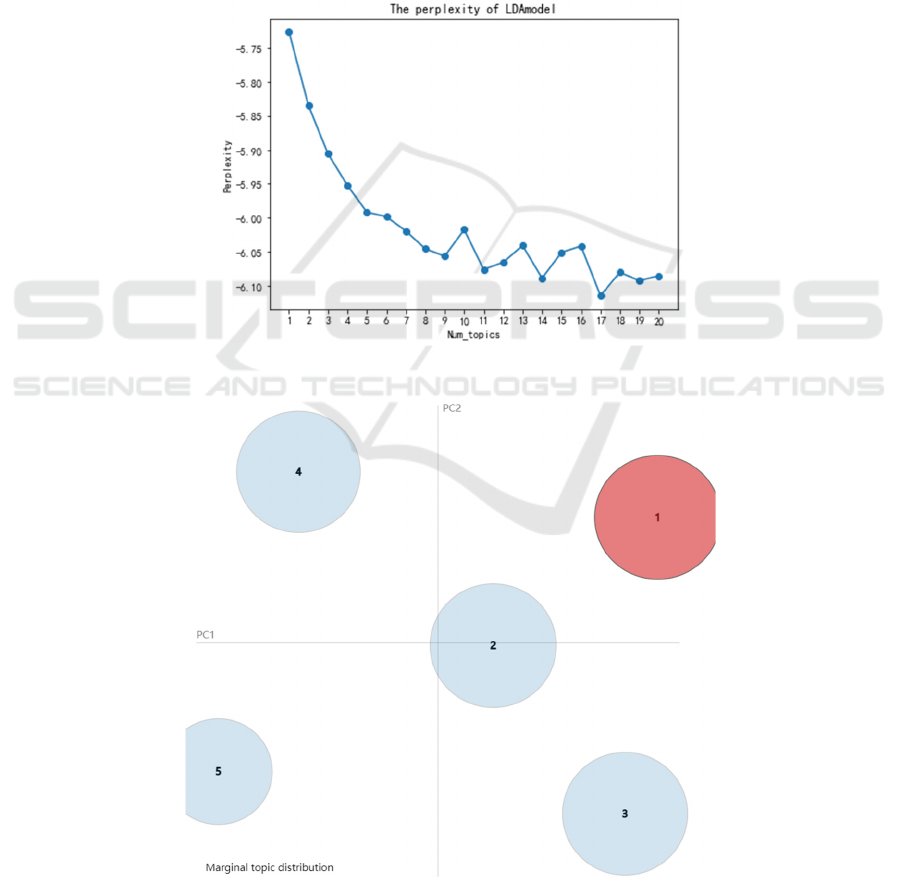
3.2 LDA Model Topic Identification
LDA is an unsupervised Bayesian model to identify
the underlying topic information. It adopts the Bag of
Words approach, treating each document as a word
frequency vector, and transforming textual infor-
mation into digital information. For a training set that
is not manually annotated, the number k specified for
the topic is important. The obvious inflection points
and local minimum values in the perplexity curve in
Figure 2 are taken as references. Five themes were fi-
nally determined based on the principle of non-coin-
cidence of clustering circles in Figure 3.
Figure 2: The Perplexity of LDA (Photo credit: Original).
Figure 3: PyLdavis Visualization of Clustering (Photo credit: Original).
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
514
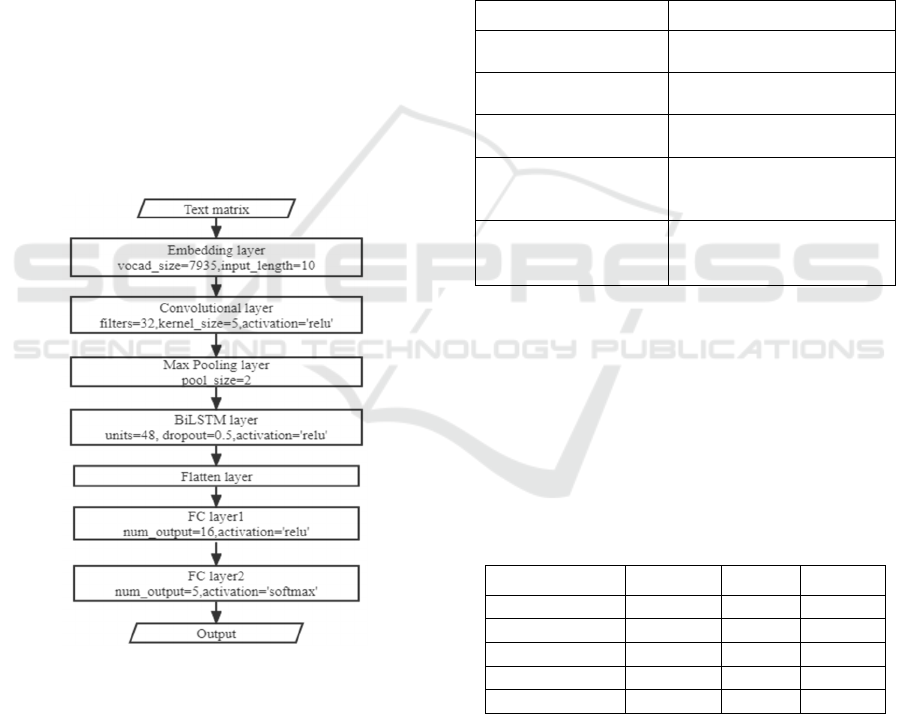
3.3 Construction of Text Classifiers
The paper selected FastText, CNN, and LSTM as
classifiers. FastText can directly train word vectors
and classify text without feature engineering.
Word2Vec can be the input of word embedding based
on the neural network. The parameters setting was as
follows: vector size=100, minimum count=5, win-
dow=5, epochs=5. Since the annotation was aimed
for the whole sentence, rather than a single word, each
sentence vector was calculated and stored. Sentences
less than the max length of them were filled with ze-
ros by the function of pad sequences. The dataset was
divided into a training set and a test set in an 8:2 ratio.
The label of y was converted into a one-hot represen-
tation to prepare for the subsequent input of the neural
network. CNN uses convolutional layers and maxi-
mum pooling or max-overtime pooling layers to ex-
tract higher-level and local features. BiLSTM is suit-
able for dealing with time series and remembering the
connections between words. Combing their ad-
vantages, a hybrid model CNN-BiLSTM was con-
structed as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4: CNN-BiLSTM Model (Photo credit: Original).
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Experimental Results
After the analysis of LDA clustering results and key-
words, Table 2 listed five themes reflecting the health
information needs of the elderly. They paid attention
to the causes and hazards of organ failure, resulting in
chronic diseases. They focused on the changing na-
ture of some diseases with age increasing and the re-
lationship with diet. They worried about symptoms
and prevention of acute onset conditions. Moreover,
they wanted to learn the treatment of osteoporosis,
and humeral head necrosis. They paid attention to the
syndrome caused by heart disease and conditioning
methods. These themes reflected the urgent need for
dietary contraindications and conditioning methods
in the process of declining physical function and re-
sistance of the elderly.
Table 2: Five Themes of Health Information Needs (Table
credit: Original).
Themes Keywords
causes and hazards of or-
g
an failure
cause, chronic, exhaustion,
renal function, eso
p
ha
g
eal
nature of the disease and
diet control
allergic, thrombotic, neurotic,
p
urpura, diet
symptoms and preven-
tion of acute onset
symptom, acute, treatment,
p
revention, h
yp
ertension
treatment of osteoporo-
sis, diabetes, and hu-
meral necrosis
osteoporosis, humerus, necro-
sis, diabetes, treatment
syndromes and condi-
tioning methods of heart
disease
conditioning way, myocardial
infarction, syndromes, atria
After constructing the classifiers, precision, recall,
and F1 were used to evaluate the classification effect
of each category as shown in Table 3. In addition to
health care, CNN-BiLSTM had a good overall effect.
The comprehensive classification accuracy of the
FastText classifier can reach 98%. Therefore, the re-
sults of these two classifiers would be taken into con-
sideration in the subsequent classification.
Table 3: The Classification Evaluation of CNN-BiLSTM
(Table credit: Original).
CNN+BiLSTM Precision Recall F1-score
health care 0.88 0.88 0.88
psychology 0.97 0.96 0.96
disease 0.93 0.89 0.91
fitness 0.93 0.95 0.94
diet 0.9 0.95 0.92
Through the classification results of 'Dataset1' in
Table 4, it can be obtained that psychology and dis-
ease are the most common questions in this dataset,
and the attention to dietary problems is at an average
level. The frequency of the questions about fitness
and health care is very few.
Exploring the Health Information Needs of the Elderly Based on the Online Health Communities
515
Table 4: The Classification Results (Table credit: Original).
Category The amount of data
health care 46
psychology 203
disease 1193
fitness 31
diet 187
However, the results reflected the limitations of
health information demand among older users. Men-
tal health and social support are also influencing fac-
tors, but few of them appeared in the information
need. One reason is that their understanding of health
just stays on the physical health level, neglecting the
issues of mental health and social support. Another
reason is that although the website constantly pub-
lishes educational articles about mental health and di-
etary health care for the elderly, it does not gain the
widespread attention of them.
4.2 Discussion
Nowadays few older people could understand and de-
scribe personal health needs clearly. Moreover, the el-
derly rarely log in to the platforms and expose their
needs because of low trust. As the family members or
caregivers, on the one hand, it is important to make
the elderly aware of their physical condition and help
them adjust their daily habits. On the other hand, it is
necessary to assist them to overcome the digital di-
vide and cultivate information literacy, learning to
achieve self-management and daily maintenance
through the Internet channel.
Combined with the present health demand infor-
mation, information providers could optimize their
health education service, by setting up detailed clas-
sification according to the old users’ needs, making it
convenient for them to find the content of interest.
Medical information service personnel should pub-
lish high-quality, reliable guaranteed health
knowledge, corresponding to potential health infor-
mation needs such as the spirit level and social sup-
port. They should improve the relatively backward
health concept of older users, encouraging them to
seek spiritual comfort and psychological counseling
assistance.
As the traditional pension model in China is
mostly community-based, the elderly put their trust in
the local community. Therefore, information provid-
ers could connect offline communities, contacting the
majority of the elderly for better health education.
Considering the old man's understanding ability, it is
a good choice to visually show the relationship
between disease, diet, exercise, etc. by the knowledge
map.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper analyzed the information needs of the el-
derly in the online community, avoiding the under-
standing bias caused by questionnaires and inter-
views. Not only does it accurately target the needs of
older adults, but it also guides caregivers and health
information providers. Meanwhile, this paper sup-
ports elderly users develop self-diagnosis and care
awareness in the interaction of the internet. As the
basic work of health management for the elderly, this
research has the following contributions: one is
through the text clustering and analysis of online in-
formation to dig out the hidden health needs, avoiding
deviation of questionnaire and interview. As in addi-
tion to the traditional research methods, it inspires the
online information provider to consider the compati-
bility of the elderly demand. Previous studies paid lit-
tle attention to the matching of information demand-
ers and information providers.
Moreover, it can be further expanded from data
diversification and coordinated care. In an aging so-
ciety, it is important to improve older people’s ability
to information search and utilization. Optimizing the
suitability and attractiveness of health websites for
the elderly is a direction of effort.
REFERENCES
Abdi, S., Spann, A., Borilovic, J., Witte, D. L., and Hawley,
M. “Understanding the care and support needs of older
people: a scoping review and categorization using the
WHO international classification of functioning, disa-
bility, and health framework (ICF),” BMC Geriatrics,
19(1), BioMed Central, 2019, pp. 1-15.
Edewor, N., Ijiekhuamhen, O. Patrick., and Emeka,U. P.
“Elderly people and their information needs,” Library
Philosophy and Practice (e-journal), 2016.Bonini, C. P.
1963. Simulation of Information and Decision Systems
in the Firm, Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Jovanović, M., De Angeli, A., McNeill, A., and Coventry,
L. “User requirements for inclusive technology for
older adults,” International Journal of Human-Com-
puter Interaction, 37(20), 2021, pp. 1947-1965.
Liao, K.J., Zou, K.X. and Xi, Y.J. “A text entity recognition
method for online medical community question an-
swering: Based on convolutional neural network and bi-
directional long short-term memory neural network,”
Research on Science and Technology Management,
41(8), 2021, pp. 173-179.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
516

Litchman, M. L., Edelman, L. S., and Donaldson, G. W.
“Effect of diabetes online community engagement on
health indicators: a cross-sectional study,” JMIR diabe-
tes, 3(2), JMIR Publications Inc., Toronto, Canada,
2018, pp. 1-15.
Qian, Y.X., Zhou, H.Y., Zhou, L.Q., Ren, M.L., Li, H. “Re-
search on health Information Demand Mining of elderly
online community users,” Modern Information, 39(6),
2019, pp. 59-69.
Sun, X. Y, and Shen, Y. “Application of health manage-
ment in healthy aging,” Medical information: Medicine
and computer applications, 29(28), 2016.
Tian, M. X, and Du, W. “Research on the current situation,
trend and strategy of health management informatiza-
tion in the era of big data,” Jiangsu Science and Tech-
nology Information, 35(7), 2018, pp. 20-23.
Wu, J., Hou, S.X., Jin, M.M., and Hu, Z. Y. “Research on
text classification and user clustering of online medical
community based on LDA model feature selection,”
Journal of the China Society for Scientific and Tech-
nical Information, 36(11), 2017, pp. 1183-1193.
Yang, L.X., Zhou, S.L., Ye, X.L., and Wang, R. “Research
status and enlightenment of health need assessment
tools for the elderly at home and abroad,” Journal of
Nursing (China), 28(21), 2021, pp. 36-40.
Zhao, D.X. “Review of online health community research
in China,” Library and Information Service, 62(9),
2018, pp. 134-142.
Zhang, S.D., Grave, E., Sklar, E., and Elhadad, N. “Longi-
tudinal Analysis of Discussion Topics in an Online
Breast Cancer Community using Convolutional Neural
Networks,” Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 69,
2017, pp. 1-9.
Exploring the Health Information Needs of the Elderly Based on the Online Health Communities
517
