
Research on the Relationship between Enterprise Internationalization
Level and Performance Based on Multiple Regression and Hausman
Test: Taking Electronic Manufacturing Industry as an Example
Zizheng Wang*
School of Economics, Shandong University, Jinan city, Shandong Province, 250100, China
Keywords: Internationalization of Enterprises, Enterprise Performance, Electronic Manufacturing Enterprises.
Abstract: Since the Belt and Road Initiative has been implemented, China has delivered more and more goods to the
world in the past ten years as the world's largest exporter. Meanwhile, today's China not only needs to export
more goods to foreign countries, but also needs higher quality development. Therefore, in the past decade,
which development phase of China's “going out” enterprises is in? To what extent has the continuous sale of
products in the international market helped the development of enterprises? Based on the sample of some
listed companies in China's electronic manufacturing industry from 2015 to 2019, this paper uses multiple
regression and Hausman test to determine the panel data fixed effect model for regression, so as to analyze
the nonlinear relationship between the degree of internationalization of international enterprises and enterprise
performance. The results show that there is a U-shaped relationship between Chinese electronic
manufacturing enterprises internationalization degree and their performance, that is, they tend to reduce the
benefits of enterprises in the short term and gain higher benefits in the long term. Based on the results, the
paper puts forward some policy suggestions: the state should give some tax incentives to enterprises that want
to operate internationally to resist the initial risks of operation, and at the same time, encourage enterprises to
operate internationally, which has important practical significance for the long-term development of
enterprises.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Research Background
According to the "China's foreign direct investment
communique of 2019" jointly issued by the Ministry
of Commerce, the National Bureau of statistics and
the State Administration of foreign exchange, China's
foreign investment level has maintained the second
level of flow in the last few years. At the same time,
China's foreign investment also has the
characteristics of large coverage, diversified fields
and expanding world influence. In this background,
enterprises as the main force of foreign investment,
their ultimate goal is to expand their international
business and world influence, and ultimately achieve
the effect of improving the overall performance.
Meanwhile, in this context, the country is
constantly implementing the policy of opening up.
Enterprises are encouraged to actively integrate into
the trend of national opening up and world economic
globalization in various ways. For example, Haier
sets up factories overseas, Huawei exports products
directly, Lenovo merges part of the business of IBM,
a well-known foreign enterprise and so on. Many
enterprises are looking for ways that are suitable for
them to expand their business departments in
overseas markets and ultimately maximize the
benefits of enterprises.
In the process of expanding overseas market and
obtaining overseas profits, enterprises will also face
many risks. For example: all kinds of costs necessary
for enterprises to expand overseas business,
differences in cultural systems between domestic and
abroad, suppression of foreign enterprises in order to
maintain their domestic market such as tariffs. At the
same time, enterprises' international business also
needs to bear a lot of opportunity costs, that is, in
order to enhance the funds needed overseas, they
must sacrifice the funds of domestic business. Can
this part of funds that could have been put in China
bring higher performance to enterprises? How will
Wang, Z.
Research on the Relationship Between Enterprise Internationalization Level and Performance Based on Multiple Regression and Hausman Test Taking Electronic Manufacturing Industry as
an Example.
DOI: 10.5220/0011753400003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 627-634
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
627

expanding international business change the
performance in the long run? In this regard, many
domestic and international scholars have made
analyses, their main conclusions are that the degree
of internationalization and enterprise performance
are positively correlated, negatively correlated, U-
shaped relationship, n-shaped relationship and so on.
On this basis, some scholars also explain the
potential reasons for the different results. The
mainstream view is that the effect of enterprise
internationalization level on performance is related to
the maturity of the country's industry and the ability
of technological innovation. For the early scholars
who take the more developed regions as samples
(such as the multinational enterprises in the United
Kingdom and the United States), because the
enterprises in these regions have better maturity and
advanced technology, the improvement of
internationalization will tend to help them obtain
more economic benefits; on the contrary, for the
scholars who take the enterprises of developing
countries as samples in the empirical research,
because these enterprises lack maturity and advanced
technology, they need to adapt to the world
environment, the improvement of inter-
nationalization level will make the enterprises show
a decline trend of enterprise profits at the initial stage.
1.2 Research Significance
From a practical point of view, with the continuous
opening up of China and the gradual maturity and
saturation of the domestic market, many enterprises
want to improve their profits by expanding the
international market, but the fact is that few have
heard that some domestic enterprises have
significantly improved their performance by
occupying a certain share of the international market,
and become influential in the world. Therefore, some
academic empirical analyses can help domestic
enterprises to analyze whether the current
development level of enterprises can support the
enterprise's international strategic behavior, and
analyze the potential risk factors of going to the
international market, so as to help enterprises allocate
idle resources more accurately, provide reference for
the enterprise's strategic objectives, and finally
realize the maximization of enterprise profits; in
addition, analyses can help relevant government
departments analyze how to formulate relevant
policies, let the government know how to support the
enterprises that want to open the international market,
and finally provide practical guidance for the
internationalization strategy of Chinese enterprises.
From a theoretical point of view, many scholars
tend to use the enterprises in developed countries as
samples, which makes some conclusions inconsistent
with the situation of domestic developing enterprises.
Therefore, many different results are obtained, which
are not compatible with the actual situation in China.
This paper takes the electronic manufacturing
enterprises with the highest proportion of overseas
income of China's Listed Companies in 2019 as the
sample to verify the relationship between
internationalization level and enterprise performance,
which can enrich some domestic research samples in
this field and provide valuable reference for future
research.
1.3 Literature Review
Under the background of the gradual rise of
international trade in the 20th century, many scholars
analyze data or create theories to study the
relationship between internationalization degree and
enterprise performance. And most of the early studies
tend to have a positive correlation between enterprise
performance and internationalization level.
Among them, the earliest tended to use large
enterprises in developed countries as samples. The
more representative theoretical research was the
monopoly advantage theory proposed by Hymer in
1971. He believes that enterprises can finally make
greater profits in international operation through the
previously accumulated advantages by accumulating
technical advantages, advanced management mode
and economies of scale (Thomas, 1977). After that,
many scholars further used data for empirical
research. For example, Grant (1987) used the panel
data of large British enterprises from 1971 to 1984 for
regression analysis (Grant, 1987), and Kim (1993)
obtained the data of 125 American enterprises in the
Forbes list from 1982 to 1986 for analysis (Kim,
1993). All of them came to the conclusion that there
is a positive correlation between enterprise
performance and internationalization level. At the
beginning of the 21st century, under the background
of China's accession to the WTO and the expansion
of international trade, Xue Youzhi (2007) also
analyzed the manufacturing enterprises in Jiangsu
Province from 2002 to 2004 in 2007. He also found
that the internationalization of manufacturing
enterprises can significantly promote enterprise
performance (Xue, Zhou, 1990).
With the deepening of research, scholars continue
to come up the idea that there may be a negative
correlation or U-shaped, inverted U-shaped and
horizontal S-shaped between enterprise performance
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
628

and internationalization level. For example, Collins
(1990) made a comparative analysis of 133 of the
world's top 500 enterprises and found that there was
a negative correlation between enterprise
performance and internationalization in developing
countries (Wang, Hu, 2006). Wang Guoshun and Hu
Sha (2006) conducted an empirical study on
manufacturing export-oriented listed enterprises in
Shanghai and Shenzhen, and also came to the
conclusion that enterprise internationalization has a
negative impact on performance (Lu, Beamish,
2001). After that, scholars also continue to realize
that the internationalization level and performance of
enterprises may not be a simple linear relationship,
that is, there can be a threshold. After exceeding this
threshold, there may be a quadratic parabolic
relationship. For example, Lu (2001) and others'
Empirical Research on 164 small and medium-sized
enterprises in Japan from 1986 to 1997 shows that the
internationalization level and performance of
enterprises show a similar U-shaped relationship
(Zhang, Chen, 2017). Domestic scholars Zhang
Xiaotao and Chen Guomei (2017) also draw a
conclusion that the two show a U-shaped relationship
by analyzing the data of 180 Chinese enterprises from
2010 to 2014 (Geringer, Beamish, Dacosta, 1989);
Through the transaction cost theory, many scholars
believe that the increasing transaction scale will lead
to the rising cost, so it presents an inverted U-shape,
and use empirical research to verify this result. For
example, Geringer (1989) conducted an empirical
study on the top 100 large enterprises in the United
States and Europe from 1977 to 1981, and obtained
the conclusion that the internationalization level and
performance of enterprises show an inverted U-
shape.
On the basis of combing the previous domestic
and foreign scholars' existing literature on enterprise
performance and internationalization, it is found that
at different time points, using the data of different
types of enterprises in different countries, the
relationship between enterprise internationalization
level and performance is also different. So the
purpose of this paper is to analyze the interna-
tionalization level and enterprises performance on the
basis of conforming to China's economic environ-
ment conditions, so as to get a convincing conclusion.
2 RESEARCH DESIGN
2.1 Samples and Data Sources
This paper takes the electronic manufacturing
enterprises listed in Shanghai and Shenzhen A-share
market from 2015 to 2019 as the research sample. In
order to ensure the authenticity and reliability of the
research data, the sample is selected in strict
accordance with the following principles: 1) remove
the enterprises that need special treatment due to
abnormal financial data, mainly including St
enterprises. 2) Eliminate the enterprises with missing
data in a certain year. 3) Exclude the enterprises
whose overseas sales revenue accounting for less than
10% of the total sales, that is, the internationalization
level is still at a low level. After selecting, 525
observations of 105 electronic manufacturing
enterprises were obtained. The sample data are
mainly from CSMAR database. Stata12.0 software
was used for data processing.
2.2 Research Hypothesis
According to the theory of first-mover advantage and
the theory of post inferior position proposed by
economist Watson, the first country can accumulate
intangible wealth such as corporate reputation, brand,
culture, and excellent system because of its earlier
occupation of the market, and its economic activities
are also more easily supported by local governments
and have environmental advantages. The resources
also have obvious advantages because they enter the
market first, so the market left to the later entrants is
not large. At this time, there are many barriers to
enterprises in the developing countries when they
enter the international market, such as the lack of
advanced enterprise system and technology, so the
enterprises in the latter developing countries have a
great disadvantage in the early stage of
internationalization because of their high costs
According to the theory of international production
compromise, enterprises must have the advantages of
ownership and internalization in their export
activities. The ownership advantage requires
enterprises to have more advantages in technology or
scale than host enterprises. Internal advantages
require enterprises to have the ability to reduce risks
and obtain information locally. Only after the two
points can be fully met can enterprises choose to
export internationally. According to the research of
many domestic scholars, most of the enterprises in
China are still in the early stage of inter-
nationalization, facing the burden of opening up the
market with high cost. At this time, the investment of
enterprises is generally greater than the profits.
To sum up, this paper predicts that there are many
difficulties in the internationalization of domestic
enterprises at this stage, so the growth of
internationalization tends to cause negative returns to
enterprises in the initial stage. At the same time, it is
Research on the Relationship Between Enterprise Internationalization Level and Performance Based on Multiple Regression and Hausman
Test Taking Electronic Manufacturing Industry as an Example
629

predicted that with the continuous progress of
enterprise internationalization, after gradually
accumulating a certain reputation and forming a
mature enterprise system, the strategic significance
and overall benefits of domestic enterprise
internationalization will gradually highlight.
Therefore, this paper puts forward the following
hypothesis
H0: Internationalization degree and performance
of Chinese Enterprises show a U-shaped relationship.
2.3 Variable Selection and
Measurement
2.3.1 Dependent Variable
In order to accurately measure the profits of
enterprises, domestic and international scholars
widely use financial performance or market
performance. This paper uses the return on assets
(ROA) in financial performance, that is, net profit
after tax / total assets to measure.
2.3.2 Independent Variable
In the empirical analysis of the degree of
internationalization of enterprises, most scholars
measure the degree of internationalization of
enterprises by the proportion of overseas assets,
overseas sales revenue and overseas employees.
Because China's enterprises are still mainly export-
oriented at this stage, the author chooses the
proportion of overseas sales revenue to the total sales
revenue to measure.
2.3.3 Controlled Variable
This paper selects four controlled variables: (1) asset
liability ratio. It is an important index to measure the
performance of an enterprise, which is obtained from
total liabilities / total assets. The enterprises with
higher asset liability ratio will be more cautious in
internationalization, and tend to reduce the risk of
internationalization to reduce the risk of debt. (2)
Enterprise scale. Measured by the natural logarithm
of assets at the end of the year, larger enterprises will
have more strength and need to expand overseas
business and increase their transnational behavior. (3)
Enterprise age. That is, the year of accounting report
minus the year of establishment. Older enterprises
tend to have more experience and survive for a longer
time, which indicates that they have stronger
management ability and more time to implement their
strategies. (4) Research intensity. That is the
proportion of research investment in total operating
revenue. Research is very important for the
development of a country, an industry or an
enterprise. Enterprises with higher research
investment tend to pay more attention to long-term
development and interests, have more ambition for
development, and are more likely to implement
internationalization strategy.
2.4 Research Model
Referring to the literature of domestic scholars, this
paper sets up the regression equation (1):
ROA=β0+β1Fsts+β2Fsts2+β3Debt+β4Size+β5Age+
β6Rd+ai+θit (1)
In the equation, ROA represents enterprise
performance , β0 is a constant term, Fsts is the
degree of internationalization of an enterprise, Fsts2
is a quadratic term to measure the degree of
internationalization of an enterprise, which is used to
test the convexity and convexity of an enterprise,
Debt is the asset liability ratio of an enterprise, Size
represents the scale of the enterprise, age represents
the age of the enterprise, and Rd represents the
Research intensity of the enterprise, ai is a constant
random interference term in time, θit It is a random
interference term that will change with time.
2.5 Multiple Regression and Hausman
Test
Multiple regression refers to using more than two
independent variables to find their relationship with
the dependent variables, and hausman test is a
significance test for the difference between two
estimators of the same parameter in order to obtain
more accurate estimation results.
In this essay, we first use the established multiple
regression model to explore the diversification results
that affect enterprise profits. Then, according to the
random effect and fixed effect of panel data, the two
estimators are obtained and analyzed by Hausman
test.
3 EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS
3.1 Descriptive Analysis
The descriptive statistics of the whole sample data in
2015-2019 are shown in the table below.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
630
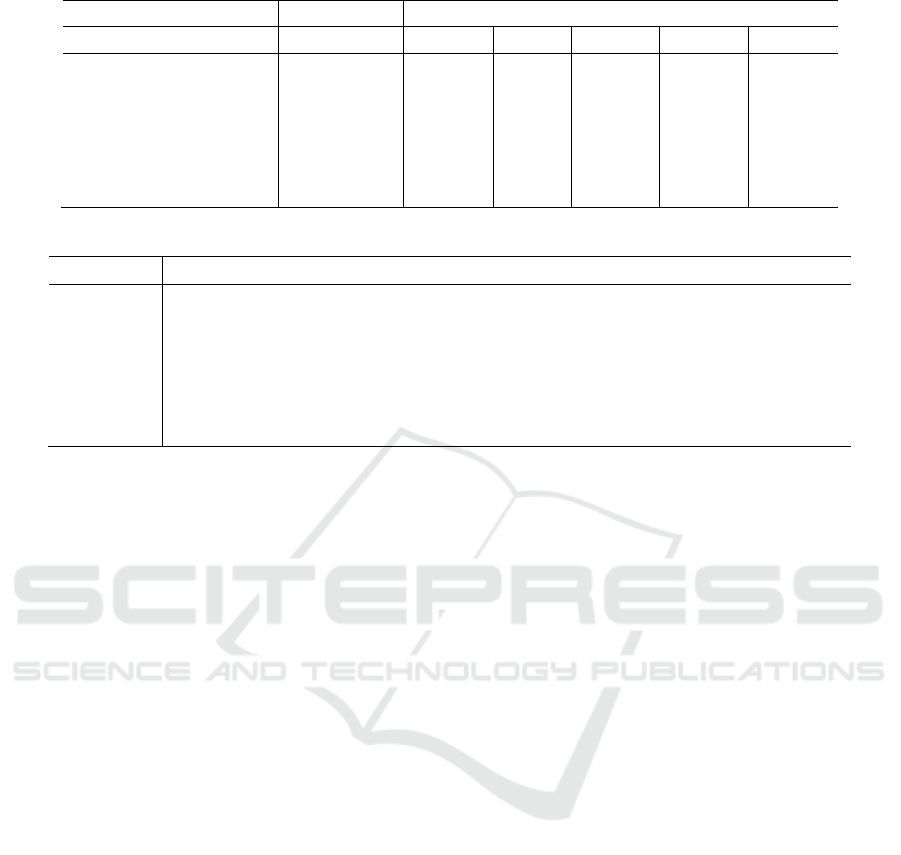
Table 1: Descriptive statistics of whole sample mean.
Variables Sample size Mean
Year 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019
Enterprise performance 105 4.876 5.343 5.354 3.933 3.683
Internationalization level 105 41.918 41.481 40.443 39.995 37.841
Asset liability ratio 105 0.363 0.371 0.391 0.415 0.419
Enterprise size 105 20.316 20.560 20.746 20.841 20.841
Enterprise age 105 15.952 16.952 17.952 18.952 19.952
Research intensity 105 6.728 6.825 6.521 6.846 7.036
Table 2: Correlation among variables.
ROA Fsts Debt Size Age Rd
ROA 1
Fsts -0.0138 1
Debt -0.1614 -0.0679 1
Size 0.1021 0.3915 0.5838 1
Age -0.0389 -0.1308 0.1451 0.1054 1
Rd -0.0277 -0.0307 0.1898 -0.1887 -0.1215 1
As can be seen from the table, from the average
point of view, the average proportion of overseas
sales revenue of the electronic manufacturing
enterprises after selection is very high, about 40%.
And due to the selecting conditions, the lowest is
more than 10%; at the same time, the average survival
age of such enterprises is about 20 years. Combined
with the data, the average life span of group
enterprises in China is 7-8 years, and that of private
enterprises is only 3.7 years, which indicates that the
average life span of international enterprises is longer
than average; the asset liability ratio is about 40%,
which is lower than 63% of the average asset liability
ratio of Chinese enterprises which shows that the
average debt ratio of international enterprises is
relatively low. In addition, the ratio of research
investment to total operating income is about 7%.
From the perspective of trend, the mean value of the
proportion of overseas income decreases year by
year, but the asset liability ratio increases year by
year. It can be preliminarily seen that the
internationalization behavior of enterprises may tend
to let enterprises bear more costs and more liabilities
at the initial stage. Therefore, from the perspective of
internationalization trend, enterprises tend to slowly
reduce the degree of internationalization.
Before using panel data for more detailed
regression analysis, this paper also conducted
correlation test on the main variables, and the results
are shown in the table 2.
The correlation coefficient in the table also
preliminarily verifies the conclusion of descriptive
statistics, that is, there is a negative correlation
between international operation and enterprise
performance. On this basis, in order to ensure the
authenticity of the regression, it is necessary to verify
the relationship between the independent variables.
From the table, except that the correlation coefficient
between asset liability ratio and enterprise size is
higher, which is 0.5638, the absolute value of the
correlation coefficient between each variable is under
0.4. In order to more accurately ensure that there is
no strong correlation between independent variables,
the author further calculated the variance expansion
coefficient (VIF), and obtained that the variance
expansion coefficient is 1.51, which is far less than
10. Therefore, the author verifies that there is no high
correlation between independent variables, and on
this basis, the author carries out the regression
analysis of panel data.
3.2 Regression Results and Analysis
After confirming that there is no strong correlation
between the variables, the author uses stata12.0
software to test the panel data with fixed effect model
and random effect model respectively, in order to
determine the relationship between the electronic
manufacturing enterprises and the degree of
enterprise internationalization. In order to test which
of the two models fits the equation better, this paper
uses Hausman test to select the model. The results are
as follows:
Research on the Relationship Between Enterprise Internationalization Level and Performance Based on Multiple Regression and Hausman
Test Taking Electronic Manufacturing Industry as an Example
631
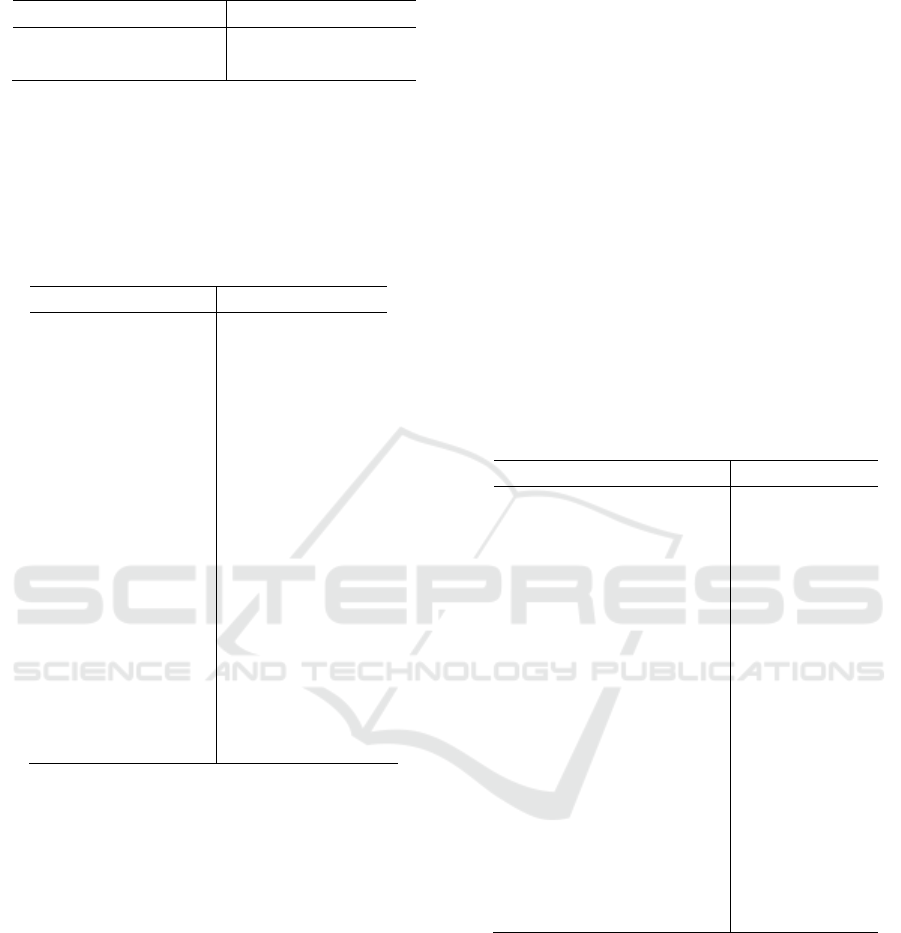
Table 3: Results of Hausman test.
Coef.
Prob 0.0001
Chi-square test value 27.53
SO reject the original hypothesis: random effect is at
the significance level of 1%. Therefore, the fixed
effect model regression was selected. The analysis
results of fixed effect model are shown in the table
below.
Table 4: Influencing factors of enterprise performance
(fixed effect).
Independent variable Coefficient
Fsts -0.384
(-3.49)
Fsts2 0.003
(3.16)
Debt -27,999
(-6.84)
Size 2.63
(2.47)
Age -0.325
(-1.35)
Rd -0.773
(-4.53)
Constant term -18.803
(-1.05)
Sample size 105
R square within group 0.1165
F value
Prob
3.64
0.0000
From the fixed effect model fitting results, except
for the age of the enterprise, each variable is
significant at the 5% significance level, and the F
statistical value of the joint regression is also
significant. The first and second lines of the table
report the first and second order conditions of the
internationalization level on the enterprise
performance. The first-order coefficient is
significantly negative, which means that the
performance of electronic manufacturing enterprises
will decrease by 0.38% when the internationalization
level of electronic manufacturing enterprises
increases by 1%; but at the same time, in the long run,
the quadratic coefficient of enterprises is significantly
positive, which verifies the hypothesis at the
beginning of this paper to a certain extent: the
internationalization level of enterprises and
performance present a U-shaped relationship of first
decreasing and then increasing. At the same time,
according to the preliminary test of quadratic
coefficient in this paper, it is 0.003. According to the
formula, when the internationalization level of
enterprises reaches about 64%, it can reach the lowest
point of U-shape, and turn losses into profits.
3.3 Robustness Check
At present, the main methods of robustness test are:
(1) adjusting the classification of data (such as
adjusting the observation year of panel data); (2)
replace variable with related variable (3) different
measurement methods (such as GMM) are used to
test whether the results are robust. This paper mainly
adopts the second method, by replacing ROA with
ROE, that is, net profit after tax / shareholders' equity,
to measure the enterprise performance, to verify the
robustness of the above results. The results are as
follows:
Table 5: Regression results of robustness test (fixed effect).
Independent variable Coefficient
Fsts -0.766
(-4.19)
Fsts2 0.006
(3.63)
Debt -51.494
(-7.11)
Size 5.278
(2.95)
Age -0.738
(-1.83)
Rd 1.143
(-4.00)
Constant term -42.566
(-1.42)
Sample size 105
R square within group
F value
Prob
0.1158
3.42
0.0000
In the fixed effect model replaced by dependent
variable, except that the coefficient of variables
changed slightly, the sign and significance level of
other variables were consistent with the above.
Therefore, this study is reliable.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
632

4 CONCLUSIONS AND
SUGGESTIONS
4.1 Main Conclusions
In the 43 years since 1978 when China implemented
the "reform and opening up" policy, the state has
constantly put forward various reform policies and
adhered to the principle of continuous opening up and
mutual benefit. On this basis, all industries in our
country continue to absorb foreign advanced
knowledge, while also selling our goods to the world.
And China as a typical late developing economy.
Which stage is the internationalization behavior of
domestic enterprises in now? How does the
increasing overseas sales affect the profits of
enterprises at this stage? All above has become
valuable research topics.
Based on the existing analysis of the relationship
between internationalization degree and
performance, By using multiple regression and
Hausman test, this paper analyzes the
internationalization degree of Chinese electronic
manufacturing enterprises and the evolution of
various important indicators over time, and draws the
conclusion that the internationalization department of
Chinese enterprises at the present stage is not mature
enough. At the same time, in the long run, there is a
U-shaped relationship between internationalization
degree and enterprise performance. Specifically
speaking, in order to open up the international
market, due to the first mover advantages of
enterprises in other developed countries, the barriers
to entry and the immature factors of our own, Chinese
enterprises will face a huge entry cost in the initial
stage of setting up an international department, and
the short-term performance of enterprises will tend to
decrease due to the improvement of the degree of
internationalization. After that, with time elapsing,
after the internationalization behavior of enterprises
has gradually established a certain market reputation,
adapted to the international market habits, and
formed a perfect internationalization system, the
internationalization behavior of enterprises will tend
to bring greater benefits to enterprises.
4.2 Policy Suggestion
The conclusion of this paper has a very important
practical significance for the government, the
enterprises that are implementing the
internationalization strategy and the enterprises that
want to implement the internationalization.
For the government, it should realize that Chinese
enterprises are still in the primary stage of socialism.
At this time, enterprises that want to go abroad will
face great costs. Therefore, if government want to
continue to cultivate some internationally influential
enterprises, it should continue to introduce a series of
reform policies, such as giving some tax incentives to
multinational enterprises and reducing financing
costs. One belt, one road, and other big policies
should be adopted to reduce the pressure of
enterprises in the initial stage of international
operation and improve the survival rate of
enterprises.
For the enterprises that are implementing
internationalization, they should actively deal with all
kinds of problems in the process of
internationalization. From the empirical research,
internationalization behavior can promote the
improvement of enterprise benefit and value in the
long run. With the continuous development of
economic globalization and the continuous saturation
of domestic market in many industries, enterprises
need to expand their competitiveness in order to
continuously achieve profits. The broad international
market brings many challenges as well as
opportunities for development. Enterprises with
international operations should focus on long-term
interests and overcome the difficulties encountered in
the initial stage of internationalization.
For the enterprises that want to enter the
international market, they should first objectively
evaluate the business status and strength of the
enterprises, so as to determine the feasibility of
entering and the strategic objectives of the
enterprises. Because international operation in the
early stage will have a greater negative impact on the
performance of enterprises, and for the enterprise
itself, continuous operation and profit is the first goal.
Therefore, whether they can bear the initial cost of
international operation is the first consideration for
such enterprises. They should not be tempted by the
international market and make a wrong assessment of
their current strength.
REFERENCES
Geringer J M, Beamish P W, Dacosta R C. Diversification
strategy and internationalization: Implications for mne
performance[J]. Strategic Management Journal, 1989,
10(2):109-119.
Grant, Robert M. Multinationality and Performance among
British Manufacturing Companies[J]. Journal of
International Business Studies, 1987, 18(3):79-89.
Kim W C, Burgers H W P. Multinationals\" Diversification
Research on the Relationship Between Enterprise Internationalization Level and Performance Based on Multiple Regression and Hausman
Test Taking Electronic Manufacturing Industry as an Example
633

and the Risk-Return Trade-Off[J]. Strategic
Management Journal, 1993, 14(4):275-286.
Lu J W, Beamish P W. The internationalization and
performance of SMEs[J]. Strategic Management
Journal, 2001, 22(6-7):565-586.
Thomas G. Parry. The International Operations of Nationa
l Firms: A Study of Direct Foreign Investment. Stephe
n Herbert Hymer[J]. 1977, 85(5) : 1096-1098.
Wang Guoshun, Hu Sha. Enterprise internationalization
and business performance: An Empirical Study of
Chinese Manufacturing Listed Companies [J]. Systems
engineering, 2006 (12): 80-83.
Xue Youzhi, Zhou Jie. Product diversification,
internationalization and corporate performance --
Empirical Evidence from Chinese Manufacturing
Listed Companies [J]. Nankai management review,
2007 (03): 79-88Collins, Markham J. A Market
Performance Comparison of U.S. Firms Active in
Domestic, Developed and Developing Countries[J].
Journal of International Business Studies, 1990,
21(2):271-287
Zhang Xiaotao, Chen Guomei. Research on the impact of
internationalization degree and OFDI location
distribution on Enterprise Performance -- Based on the
evidence of China's A-share listed manufacturing
enterprises [J]. International business (Journal of
University of foreign economics and trade), 2017 (02):
72-85.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
634
