
Research on Human Resource Competency Model of Logistics
Enterprises Based on Temporal Ontology
Xiaoyan Chen
School of Business Administration, Wuhan Business University, Wuhan, China
Keywords: Temporal Ontology, Logistics Enterprises, Human Resources, Competence.
Abstract: Research on Human Resource Competency Model of logistics enterprises based on temporal ontology, a
general temporal ontology model is constructed, and a temporal data representation method of human
resources based on temporal ontology is proposed and applied to the prediction process. The temporal data
representation method can show the time information in the data more carefully, and combined with SWRL
rules, the accuracy of reasoning results is higher.
1 INTRODUCTION
Logistics enterprises can not improve the overall
modernization level and their competitiveness
overnight. They must take key fields, key
technologies and core talents as the breakthrough.
Talent is one of the basic elements of logistics
enterprises. The competition among enterprises has
gradually evolved from the competition of industrial
technology content and management level to the
competition of enterprise talents. The middle and
senior managers of enterprises are the core employees
of enterprises, which often directly determine the
success or failure of enterprises. The recruitment of
middle and senior managers is the main channel for
enterprises to obtain key talents, which directly
affects the healthy growth and future development of
logistics enterprises. Enterprises often invest a lot of
human and financial resources in the recruitment fair
of middle and senior managers. Therefore, the
success of recruitment is not only related to the
introduction of suitable talents, but also affects the
future development of enterprises, it is also related to
the cost-effectiveness of enterprises. At present,
when recruiting middle and senior managers,
logistics enterprises often judge the personnel
matching degree based on simple job analysis and
combined with the applicant's educational
background, professional knowledge, skill level and
work experience, rather than making recruitment
decisions through comprehensive consideration of
the applicant, and there is no effective evaluation of
the applicant's internal motivation and core
competence, There is no application of competency
model in the recruitment of middle and senior
managers in logistics enterprises (SKILLEN, 2014).
Logistics enterprises are the basic components of
modern logistics industry. It has the characteristics of
many employees, strong market flexibility and wide
distribution, but its development degree does not
occupy an advantage in the competition of logistics
market for a long time, its development speed is slow
and its development level is not high. China's
logistics enterprises have a long way to go in
speeding up their own modernization and
modernization, strengthening exchanges and
cooperation with foreign logistics giants in terms of
talents, technology, management and ideas, focusing
on their main business, improving service level and
strengthening international competitiveness. The
research content of this topic can not only guide the
recruitment practice of logistics enterprises for
middle and senior managers, but also promote the
transformation of the recruitment mode of the whole
industry to a more scientific and perfect direction
(Wang, 2013).
At present, the competition of talents has become
the main aspect of the comprehensive
competitiveness at the national and enterprise levels.
For an enterprise, talents have increasingly become
an important embodiment of its core competitiveness
and an important indicator of the comprehensive
strength and overall level of the enterprise, which
makes the introduction and maintenance of key
talents of the enterprise particularly important. In
particular, logistics enterprises, because they belong
to labor-intensive industries, have large talent
mobility and low attention to talents for a long time,
706
Chen, X.
Research on Human Resource Competency Model of Logistics Enterprises Based on Temporal Ontology.
DOI: 10.5220/0011755900003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 706-711
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

resulting in a serious lack of high-quality all-round
talents in the logistics industry. Therefore, middle and
senior managers in key positions often play a decisive
role in the rise and fall of enterprises. How logistics
enterprises can recruit managers who are consistent
with the enterprise's strategic culture and values, the
highest matching with vacant posts and have the best
performance level in the future, and improve their
competency level and contribution to the
organization to the greatest extent is an urgent
problem for each logistics enterprise. It can make a
scientific prediction of its future performance in
combination with its previous performance. This
leads to the lack of scientificity and practicability of
employment decision-making, which will not only
lead to the rejection of some really suitable
candidates, but also reduce the recruitment efficiency
and accuracy. In view of the shortcomings of the
traditional recruitment model of logistics enterprises,
a new talent recruitment model is needed to guide the
recruitment of middle and senior managers of
logistics enterprises. The competency model provides
an effective method for the recruitment of middle and
senior managers in logistics enterprises. According to
the actual situation of China's logistics enterprises,
combined with the relatively mature competency
model, this paper studies the method of using
competency model in the recruitment of middle and
senior managers in China's logistics enterprises,
studies and summarizes three main competency
models of logistics enterprises, and summarizes the
core competency characteristics that have an
important impact on the performance of middle and
senior managers in logistics enterprises, and establish
a recruitment system accordingly. The recruitment
system of middle and senior managers in logistics
enterprises based on competency model can not only
make logistics enterprises recruit managers with the
best matching degree according to their own strategic
culture, but also improve the competitiveness of
enterprises as a whole. (LEE, 2017)
In the field of management, the earliest research
on competency was carried out by Taylor, the "father
of scientific management". His research on "scientific
management" was called "management competencies
movement" at that time. Taylor's view is that the
management of enterprises can be studied with the
knowledge of physics. As early as 1911, Taylor
observed the practical activities of factory workers.
After long-term research, he found that there was a
big gap between different employees in completing
the same work. The work efficiency and quality of
better performing workers and worse performing
workers are very different. Therefore, he proposed for
the first time to evaluate the daily work of workers
through the application of time and action analysis,
so as to delimit the constituent elements of workers'
competency. On this basis, a more complete and
standardized operation process is constructed, and
finally the purpose of improving workers' work
efficiency is achieved.
2 HUMAN RESOURCE
COMPETENCY MODEL OF
LOGISTICS ENTERPRISES
The research on the competency model of human
resources in logistics enterprises in China began in
1998. An article on competency appeared for the first
time in the Journal of psychology. In the article
"evaluation and quantitative evaluation method of
management cadres in the communication industry",
the job evaluation of managers in the post and
telecommunications industry was applied according
to the targeted competency characteristics. In the late
1990s, Chinese scholars began to conduct theoretical
research on the competency model in order to explore
a competency model that can be used by Chinese
enterprises and help enterprises improve
management efficiency and overall competitiveness
according to the specific situation of China.
In 2003, Professor Wang Chongming and
Professor Chen minke of Zhejiang University
summarized the basic competency characteristics of
middle and senior managers through the practical
application of the "position analysis method based on
Competency Model" and the interview and
investigation of middle and senior managers in more
than a dozen domestic science and technology
enterprises, and pointed out that due to the different
positions and managers, Their competency
characteristics are also different. In addition, by
constructing the competency model of enterprise
managers under China's economic conditions at that
time, Professor Wang Xiaojun proposed eight
dimensions that middle and senior managers should
have competency characteristics. And try to predict
the future performance of managers (PHAN, 2017).
In 2004, Professor Yao Xiang and Professor
Wang Lei of Peking University conducted a
questionnaire survey on the project managers of it R
& D department, summarized the competency
characteristics and internal requirements of IT
enterprise project managers, and discussed how to
apply the competency model to the recruitment and
training of IT enterprise project managers. In 2005,
Research on Human Resource Competency Model of Logistics Enterprises Based on Temporal Ontology
707
professors Zhang De and Wei Jun of Tsinghua
University studied the customer managers of
commercial banks. This paper discusses the
competency model corresponding to the customer
manager of commercial banks, and summarizes six
basic competencies that the customer manager of
commercial banks should have by interviewing
managers of several commercial banks. In 2006,
Professor Wang Chongming and Professor Liu
Xuefang of Zhejiang University studied the
competency model of family enterprise successors,
this paper puts forward the key competency items that
family business successors should have and the
evaluation criteria of whether family business
successors are qualified or not. In the same year, Zhao
Hui, Huang Xiao and Wei Xiaojun studied the
competency of Party and government leading cadres,
basically summarized the professional quality and
competency of Party and government leading cadres
under the current situation in China, and established
the competency model of Party and government
leading cadres. (CHICCO, 2016)
In 2007, Zhao Shuming and Du Juan studied the
competency elements and evaluation criteria of
enterprise managers, put forward the evaluation
theory of the competency of middle and senior
managers, summarized the previous research on
management competency, and laid a foundation for
the future research on manager competency
(MANIU, 2013).
In recent years, domestic researchers' research on
competency model theory has gradually expanded to
all fields and levels, and are committed to the further
development and application of competency model.
Competency model has gradually been used by more
organizations in human resource management
practice. At that time, under the background of the
transformation of enterprise organization and
management mode, the overall professionalization of
managers and the high enthusiasm of management
theory research, western countries have made rapid
progress and great achievements in the research of
competency and competency model, and their
theoretical achievements have been fully applied in
the practice of enterprise human resource
management. The research on competency and
competency model in China began under the
background of the comprehensive reform of state-
owned enterprises in the process of economic system
transformation, mainly through the introduction and
reference of foreign theoretical achievements and
research. Some progress has been made in the
exploration of the application of relevant theories to
practice, but there is still a big gap compared with
foreign countries, A systematic and comprehensive
theoretical system has not yet been formed.
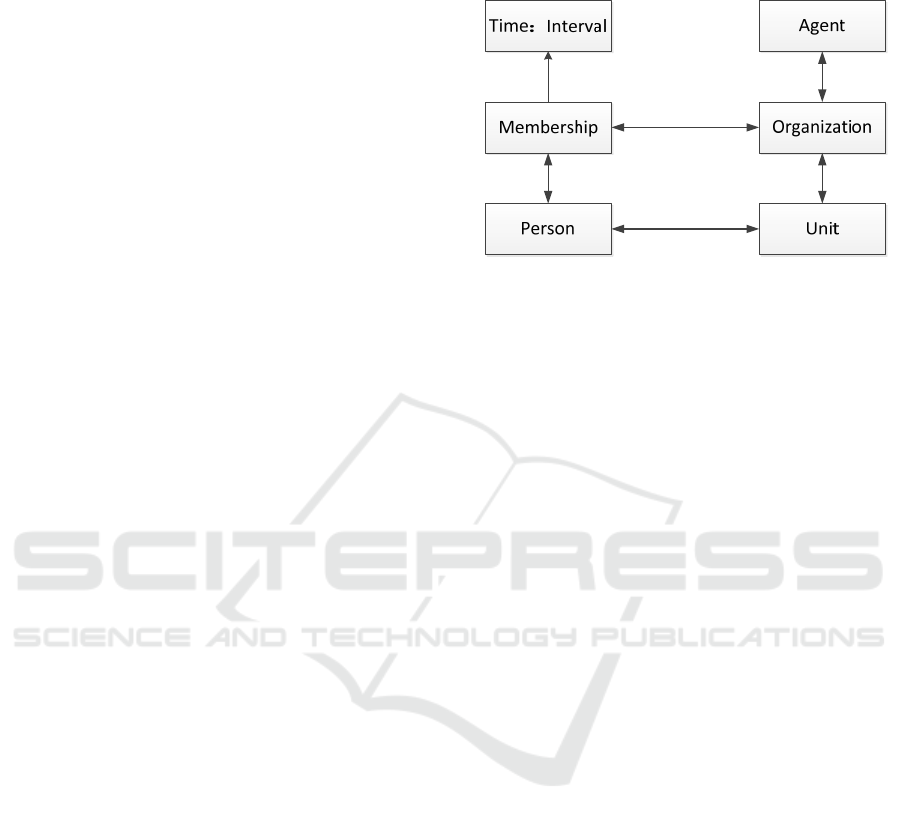
Figure 1: Improved organizational ontology structure.
3 CONSTRUCTION OF HUMAN
RESOURCE COMPETENCY
MODEL OF LOGISTICS
ENTERPRISES BASED ON
TEMPORAL ONTOLOGY
In terms of content, employee data mainly has two
time types:
(1) Effective time: refers to the time when an
event or object occurs or exists in reality. If an
employee starts in 2017 and leaves in 2018, the data
about the employee is only valid between 2017 and
2018.
(2) Transaction time: refers to the time when an
event or object is recorded, updated, or deleted in the
data.
In addition, employee data also has other time
characteristics, including absolute / relative, concave
convex, multi granularity, periodicity, etc.
3.1 Absoluteness/ Relativity of Time
The absoluteness of time refers to the time expressed
in numbers. For example, the employee's entry time
is "September 18, 2018". Relativity means that there
is no precise time expression. If employees who are
employed before 2018 are selected, the relative time
is before 2018.
3.2 Concavity and Convexity of Time
It refers to the continuity and discreteness of time.
From the perspective of salary, the annual salary of
employees will change every year, so the salary
change is continuous. From the perspective of
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
708
professional title, there is no obvious law of
professional title promotion, and the time is
uncertain. Only when the promotion conditions are
met can there be promotion qualification. In addition,
employees may be promoted once or twice during
their tenure, or even not. Therefore, the promotion of
employees' professional titles is discrete.
3.3 Multi Granularity of Time
The length of time indicated by the data is different.
The time cycle of human resources includes short-
term, medium-term and long-term. The
corresponding time granularity can be divided into
day, month and year.
3.4 Periodicity of Time
It refers to the regular fluctuation of the time
represented by the data. For example, a large number
of employees flow in enterprises every June.
From the comprehensive analysis of the content
and temporal characteristics of employee data,
combined with the time ontology modeling meta
language, based on BFO (basic formal ontology) and
owl time, supported by time relationship and centered
on time formal expression, expand relevant classes
and attributes, and establish human resources
temporal ontology including time attributes and
constraints. It represents the dynamic change process
of things and highlights the tensity in the change
process.
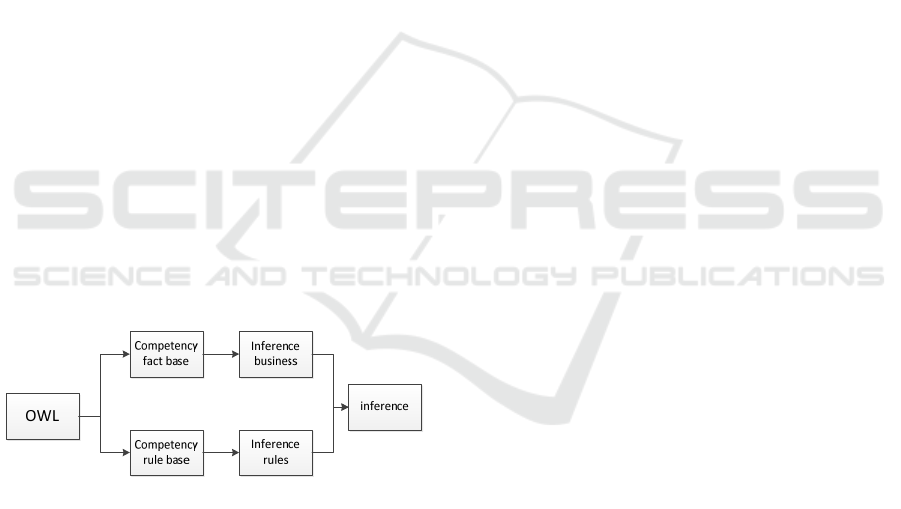
Figure 2: Framework of reasoning mechanism based on
competency rules.
BFO is an upper ontology, in which the concepts
are given the meaning of human resources field: BFO
is used to represent the concept and relationship of
salary and professional title change process. BFO
divides all entities into two categories: continuous
and current. Subclass of continuous class: generically
dependent continuous class is a collection affected by
influencing factors in the change process, such as
employee salary, professional title; Independent
continuous is a collection of influencing factors, such
as performance. Subclass of current: process class
represents the change process, such as salary change,
professional title change, etc; The temporary region
class represents the start / end time (zero -
dimensional temporary region) and duration (one -
dimensional temporary region) of the change process.
Although BFO allows users to establish different
domain ontologies with similar understanding
methods and the same concepts, so that these
ontologies can be compatible, BFO only provides the
relationship between overall concepts and lacks the
specific time relationship between entities.
Therefore, owl time is used as a supplement to the
time relationship between entities. The core of owl
time is the Allen interval relationship. Allen interval
relationships represent 13 relationships between time
intervals, namely before, after, meets, met by,
overlaps, overlapped by, starts, started by, during,
contains, equals, finishes, finished by. However, Owl
- time cannot represent the periodicity of time. In
addition to the relationship between intervals, there
are two types of relationships: the relationship
between time points and time intervals, and the
relationship between time points. For time point and
time interval, there are three relationships: point
before interval, point after interval and point between
intervals, which are represented by time: before, time:
after and time: inside attributes respectively; There
are three relationships between time points: before,
after and equal, which are represented by time:
before, time: after and time: equal attributes
respectively. The supplementary time: equal attribute
indicates the equality relationship between time
points. When two ontologies are integrated, the
problem of heterogeneity between ontologies needs
to be solved. If heterogeneous types are synonyms, a
mapping relationship is directly established between
them. According to the literature, the synonym of
zero - dimensional temporary region in BFO is time
point, and the synonym of one - dimensional
temporary region is time interval. The instant and
interval in owltime represent the time point and time
interval respectively. So map BFO: Zero -
dimensionaltemporal region to time: instant; Map
BFO: one - dimensionaltemporalregion to time:
interval. The change process needs time description,
so BFO: process and time: temporalentity are mapped
through the attribute BFO: occupi -
estemporalregion.
Use SWRL to express the tensity in the rules, and
explain the salary rise rules and professional title
promotion rules. The rules are formulated according
to the employee manual of the Internet company.
(1) Salary increase rules: salary increase is made
according to working years, performance, length of
Research on Human Resource Competency Model of Logistics Enterprises Based on Temporal Ontology
709

service, professional title promotion and other
factors.
(2) Professional title promotion rules:
professional title promotion is formulated according
to the time of obtaining professional title,
employment time, certificate, thesis and other factors.
The promotion of professional titles is regarded as a
dynamic event, which simplifies the representation
process when indicating re-election. It does not need
to match whether the annual professional titles meet
the conditions, but only depends on the length of
service. If there is a professional title promotion
during the period, corresponding examples will be
added in BFO to simplify the complexity of
reasoning. The temporal ontology model and SWRL
rules are reasoned by reasoning engine. The temporal
ontology instances and SWRL rules in the ontology
knowledge base are transferred to drools through
swrldrools tab, and then the drools inference engine
is started to infer to obtain new knowledge. Finally,
the new knowledge is transferred back to the owl
original ontology as the instance or instance attribute
of the original ontology.
The constructed human resources temporal
ontology is used to represent temporal data, that is,
ontology instantiation. Taking the employee salary
change part as an example, the temporal ontology of
human resources is explained as follows: for
example, the salary change of employee No. 10006
from 2017 to 2018 is shown in Figure 5. Every time
the salary changes, an instance of BFO: process is
generated. The instance consists of three parts: (1) the
time of change (temporary region). This part
describes the time specifically, including year,
month, day, duration and time relationship. If the
employee's salary remains stable after this change
and will not change until the current time, add the
time: hasend attribute (2) Independent continuous
salary is expressed in BFO: salary (3) The influencing
factors of the change include paper, promotion, work
year, tenure, performance, etc. these factors affect the
salary change of the next year.
The construction of SWRL rules combines the
concepts in temporal ontology, complements the
missing relationship in temporal ontology, and makes
up for the lack of reasoning ability of temporal
ontology. For example, rule 3: worked for W1 - W2
years, worked as senior engineer for at least y years
and m months, and the salary increased by s yuan.
The working years are calculated according to the
employment time. Swrlb: greaterthan is used to limit
the working years, i.e
workYear (? pers - on,? w) ^
swrlb:greaterThan ( w2 ,? w) ^
swrlb: greaterThanOrEqual (? w, w1 );
The title is senior engineer, using
bfo:participatesInAt-SomeTime(? person,? q)
^
bfo:hasOccurrentPart (? q,? stage ) ^
title (? Stage ("senior engineer") means;
BFO: occupies - temporalregion (?)? stage,?
interval) ^ time: hasTemporalDuration(? interval,?
dur)^time:years(? dur,? y) ^
time:months(? dur,? m) ^swrlb:greaterThan(?
y,y) ^
4 CONCLUSION
In this paper, a general temporal ontology model is
constructed, and a temporal data representation
method of human resources based on temporal
ontology is proposed and applied to the prediction
process. The temporal data representation method can
show the time information in the data more carefully,
and combined with SWRL rules, the accuracy of
reasoning results is higher. Since only continuous
time intervals are considered in the construction of
temporal ontology model, we can consider expanding
temporal ontology in the next step, so that the
temporal ontology model can represent time intervals
with gaps; the temporal data representation method
proposed in this paper can be considered for temporal
data modeling in other fields.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
"The Application of Competenty Model in
Recruitment of Middle-Senior Managers in Logistics
Enterprises"(Project No.2021CSLKT3-093) of the
scientific research plan of China Society of Logisticts
Annual Research in 2021
REFERENCES
Chicco D, Masseroli M. Ontology-based prediction and
prioritization of gene functional annotations[J].
IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology
and Bioinformatics,2016,13(2):248-260.
Lee C I, HSIA T C, HSU H C, et al. Ontology – based
tourism recommendation system [C] / / International
conference on industrial engineering and applications.
Nagoya, Japan: IEEE,2017:376-379.
Maniu I, Maniu G. A human resource ontology for
recruitment process [J]. Review of General
Management, 2013, 10(2):12-18.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
710

Phan N, DOU Dejing, WANG Hao, et al. Ontology-based
deep learning for human behavior prediction with
explanations in health social networks [J]. Information
Sciences, 2017, 384: 298-313.
Skillen K L, Chen Liming, NUGENT C D, et al.
Ontological user modeling and semantic rule-based
reasoning forpersonalisation of help-ondemand
services in pervasive environments[J]. Future
Generation Computer Systems,2014,34:97-109.
Wang Xiaohuan, WONG T N, FAN Zhiping. Ontology
based supply chain decision support for steel
manufacturersin China [J]. Expert Systems with
Applications, 2013, 40(18):7519-7533.
Research on Human Resource Competency Model of Logistics Enterprises Based on Temporal Ontology
711
