
Enterprise Credit Risk Management Model Based on Super_SBM
Model
Xiangdong Zhang
College of Arts& Information Engineering Dalian Polytechnic University, Dalian, China
Keywords: Risk Management, Super_SBM Model, Credit Risk.
Abstract: The current risk management model has the problem that the credit risk type is not clear, which leads to the
poor goodness of fit performance of the model the credit risk management model based on SBM model.
Calculate the enterprise exploration factor index, study the correlation degree between the observation
variables, divide the credit risk types, establish the credit system, and use Super_ SBM model obtains index
weight, extracts the importance of risk factors, establishes credit risk management model, and forecasts the
decision-making results of enterprises. Experimental results: the mean goodness of fit of the risk management
model and the other two risk management models is 0.4139, 0.4989, 0.807, proving that the fusion of Super_
SBM model has higher practical value in risk management.
1 INTRODUCTION
Generally speaking, when we discuss the basic
meaning of credit risk, because the economic
meaning of the concept of credit risk is stronger than
that of other angles, we usually study it from the
economic level. However, the definition of the
concept of credit risk has not yet been completely
determined (Oliveira, Mexas, Meirino, et al. 2019).
Credit is an invisible contractual relationship among
the participants in economic activities, which is based
on equality and reciprocity. In the economic activities
of an enterprise, the specific performance may be that
the enterprise obtains money, products or services
with the same physical assets (Kuo, Lin, Chien 2020).
To grasp the definition of enterprise credit risk, we
need to understand the meaning of risk. To
understand risk, we need to pay attention to two
important factors: firstly, risk refers to the situation
that may have bad expectations, and the risk manager
is to prevent and deal with the occurrence of bad
situations, which will bring losses to people the
existence of "risk" means that there are worse than
expected results in all the results (Silva, Fernandes
2019). If the probability of those worse than expected
results is zero, then the risk does not exist, and the
expected good results can always be achieved;
secondly, the probability of the expected result or loss
is not zero, and the probability of occurrence is a
random value. To sum up, risk includes two
important factors: the expected bad loss and the
probability of the expected bad result. Traditionally,
credit risk is the risk that the borrower fails to repay
the debt within the specified period and causes losses
to the lender, so it is also called default risk. With the
continuous maturity of the financial market and the
high attention paid to the credit risk of enterprises,
when the repayment ability of borrowers or
counterparties declines, that is, the credit quality
declines, the price of relevant assets in the market
also decreases, resulting in the loss of credit risk
(Hiebl, Duller, Neubauer 2019, Corrêa, Neto, Souza,
et al. 2019). To define credit risk in a broad sense, we
should first define the credit relationship. Where
there is credit in the relationship between the two,
whether it is on the level of ethics, economy, law or
currency, there is a credit relationship between them.
In a broad sense, credit risk refers to the possible loss
caused by the failure of the other party to perform the
contract (Polly, Stevens, Jordan, et al. 2019). From
the narrow economic perspective, credit risk is
defined as the possible loss to the creditor if the other
party defaults in the expectation of obtaining a series
of income in a fixed period of time. Generally
speaking, a creditor's debt can't be recovered or can't
be recovered in time due to the debtor's breach of
contract, which may bring losses to the creditor. In
short, credit risk refers to the potential loss to the
credit provider when the party accepting the credit
Zhang, X.
Enterprise Credit Risk Management Model Based on Super
S
BMModel.
DOI : 10.5220/0011768200003607
InProceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages813 − 819
ISBN : 978− 989 − 758 − 620 − 0
Copyright
c
2023bySCIT EPRESS˘ScienceandTechnologyPublications, Lda.UnderCClicense(CCBY − NC − ND4.0)
813

refuses or is unable to repay the debt on time and in
full. Enterprise credit generally refers to the credit
relationship between enterprises due to credit sales.
After the credit sales activities, the enterprise will
give the customer the corresponding credit line, that
is, a part of the accounts receivable of the customer
can be paid in the future, which is a financing activity
for the customer (González, Santomil, Herrera 2020,
Johnston, Soileau 2020, Altuntas, Berry-Stlzle,
Cummins 2019). This kind of credit relationship is
based on the premise that the enterprise thinks that
the customer can repay all the money before the due
date. It is a loan relationship guaranteed by the
customer's credit. If the enterprise thinks that the
customer cannot repay the debt when it matures, it
will not grant a credit line. Credit sale is the basis of
accounts receivable and the cause of credit risk. At
present, the academic circles are concerned about
Super_ SBM model, applied to the construction of
enterprise credit risk management model literature is
not very rich, still need to be further explored.
2 ENTERPRISE CREDIT RISK
MANAGEMENT MODEL
BASED ON SUPER_SBM
MODEL
2.1 Calculation of Enterprise
Exploration Factor Index
Exploratory factor is to explore the basic structure of
observation data by studying the internal dependence
of many variables. The basic idea is to find common
factors, and ultimately achieve the purpose of
dimension reduction. Confirmatory factor analysis
(CFA) uses prior information to test whether the
previously collected data work according to the
predetermined structure. First, we need to use
exploratory factors to group financial indicators, then
get preliminary factors after analysis, and then carry
out confirmatory factor research. The growth rate of
total assets is mainly used to reflect the growth degree
of enterprise's operating strength, the expression
formula is as follows:
100%
p
Q
w
=×
(1)
In formula (1),
p
represents the growth of the
total assets of the enterprise in the current year, and
w
represents the total assets at the beginning of the
year. The important basis to judge whether an
enterprise is out of the expansion period is whether
its asset scale is expanded or not. There are two ways
for enterprises to expand assets: one is to expand the
scale of liabilities, the other is to increase the owner's
equity. Companies with single operation and
outstanding main business usually have higher
growth (Huang 2019, Shi, Wang, Wang 2019). This
indicates that the company has a large market demand
for its products and a strong ability to expand its
business. If a company can maintain a growth rate of
more than 30% of its main business income for
several consecutive years, it can basically be
considered as a growth company. The continuous
growth of net profit is the basic feature of a
company's growth, the expression formula is as
follows:
12
100%
rr
E
u
−
=×
(2)
In formula (2),
u
is the net profit of the
enterprise last year, 𝑟
is the net profit of the
enterprise this year, 𝑟
is the net profit of the
previous year. If the increase is large, it indicates that
the company has outstanding business performance
and strong market competitiveness. On the contrary,
if the index is small or negative, then the growth of
the enterprise is very poor. For most production-
oriented enterprises, the growth rate of fixed assets
reflects the expansion of production capacity.
Therefore, when calculating the growth rate of fixed
assets, we should pay attention to the composition of
the increased fixed assets, the expression formula is
as follows:
100%
ab
TT
L
Y
−
=×
(3)
In formula (3),
a
T
represents the net assets at the
end of the period,
b
T
represents the net assets at the
beginning of the period, and
Y
represents the total
fixed assets at the beginning of the period. If most of
the increased parts are under construction, it is
necessary to pay attention to the completion time,
because the completion will have a significant impact
on the current profits. If the growth part has been
completed earlier in this year, then there is no need to
expect a substantial increase in future earnings on the
current basis (Abu-Qarn 2019). It is closely related to
the level of credit risk. The study of solvency can
obtain the ability of an enterprise to deal with risks
and the efficiency of financing. Based on the above
calculation, the steps of obtaining enterprise
exploration factor indicators are completed.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
814

2.2 Classification of Credit Risk Types
From the perspective of sources, credit risk can be
divided into two types: the risk of counterparties and
the risk of issuers. The former is mainly produced in
commercial bank loans and financial derivatives
transactions, while the latter is mainly related to
bonds. In terms of composition, credit risk consists of
two parts. One part is default risk, which refers to the
possibility that one party of the transaction is
unwilling or unable to pay the agreed amount,
resulting in the loss of the other party. In terms of
level, credit risk can be divided into three levels: one
is transaction level, which is related to a single
financial transaction. The second is the level of
counterparties or issuers, which is generated in all
transactions with one counterparties or issuers. The
third is the level of asset portfolio, which is related to
all transactions of market entities, all counterparties
and issuers. The most important step of credit risk
management is to examine the credit of the enterprise.
Enterprises should control credit risk from the source,
require customers to provide business reputation,
financial statements and other information within the
scope of the overall strategic objectives of the
enterprise, strictly review the authenticity and
integrity of the information, and grant corresponding
credit line according to the evaluation results. If it
exceeds the ordinary approval authority, it needs the
approval of the company's higher level management
personnel (Saeidi, Saeidi, Sofian, et al. 2019, Oliveira,
Mexas, Meirino, et al. 2019). Only by establishing a
strict credit system can we minimize the risk from the
source and reduce unnecessary losses for enterprises.
If it is difficult for an enterprise to obtain the
corresponding financial statements and other
information when examining the customer's credit, it
can turn to an independent credit rating agency for
help. In some cases, it can ask the enterprise to
provide property guarantee or third-party guarantee
to ensure the safe recovery of creditor's rights. The
establishment of credit system is an effective way to
reduce the bad debt rate of accounts receivable. On
the one hand, it is strictly controlled from the initial
stage to fully understand the credit risk level of
customers and reduce the credit risk to the lowest
level as far as possible. On the other hand, it increases
mutual trust and mutual understanding with
customers, standardizes the credit relationship
between enterprises and customers, and increases
mutual information, laying a foundation for further
cooperation between enterprises and customers. As a
current asset of an enterprise, the quality of accounts
receivable is related to the authenticity of the
financial situation of the enterprise. The enterprise
shall make an agreement with the debtor that when
the debtor fails to repay the relevant debts on time,
the creditor shall have the right to recover the money
in advance or mortgage the relevant assets with a
third party, so as to ensure the safety of the creditor's
rights. Statistical method is the summary of human-
machine operation and experience (Ojeka, Adegboye,
Adegboye, et al. 2019). The use of modern statistical
methods combined with computer technology can
greatly improve the efficiency of evaluation. With the
development of statistical theory and computer
technology, many new risk assessment methods have
emerged in recent years, such as neural network,
support vector machine and so on. Although they also
have a high correct rate of discrimination, it is
difficult to understand the evaluation process, and the
evaluation results are lack of explanation and
persuasion; other traditional statistical methods, such
as multivariate discriminant analysis, require the
sample distribution to conform to multivariate normal
distribution, which also limits the practical
application. There is no special requirement for the
distribution of sample data, and the result is a
probability value belonging to a certain risk category,
which has a clear meaning and is easy to compare
different evaluation objects. Based on the above
description, complete the credit risk type step.
2.3 Super_ SBM Model to Obtain
Index Weigh
In 2002, tone proposed the DEA efficiency analysis
method based on SBM, that is, when building the
DEA model, we should consider its relaxation
variables, and then study the influence of angle and
radial selection on the input-output relaxation (Huang,
Liu 2020, Zhu, Zhu, Shan 2021). All DMUs are
divided into efficient DMUs and inefficient DMUs to
form Pareto boundary. As a non radial and non angle
data envelopment analysis (DEA), it follows the basic
idea of DEA and envelops the input-output data set
with the most effective technology frontier (An, Wu,
Li, et al. 2019, Lin, Zhu, Han, et al. 2020). Different
from the previous methods, super SBM model puts
the relaxation variables into the objective function to
solve the problem of input and output relaxation.
Super SBM model can be solved directly by software,
without setting production function in advance, and
without considering the problems of index dimension.
This process is the first step in the process of credit
risk management. Enterprises need to conduct a
detailed study on the credit of the opposite party of
credit sales, and also conduct market risk research on
Enterprise Credit Risk Management Model Based on Super
S
BMModel
815
the related industries, because different industries
have different market risks. Some industries are
cyclical and fluctuate with the change of the cycle. If
we do not pay close attention to the change of market
risk, it may cause great credit risk loss to the credit
seller. For example, as a kind of high-quality non
renewable energy, the mining scale of coal industry
will be affected by government policies, and will be
greatly affected by seasonal changes. In contrast, the
higher the solvency, the lower the corresponding
credit risk. If we want to get credit risk income, we
must adopt scientific credit risk management
methods, seriously and comprehensively collect
customers' credit information, and pay close attention
to customers' business dynamics. The characteristic
analysis of enterprise credit risk factors can establish
a special language to describe customer
characteristics, which is commonly used by sales,
marketing, credit and other departments of the
enterprise, so as to strengthen the understanding and
cooperation among various departments. The entropy
weight method is used to determine the index weight
in the index layer, the expression formula is as
follows:
1
c
ij
i
Skdk
=
=−
(4)
In formula (4), 𝑘 is the enterprise credit score
vector,
c
is the standardized value,
d
is the
indicator vector,
i
is the criterion layer, and
j
is
the number of indicators. Enterprises are not
professional evaluation institutions, so in the
selection of characteristic indicators, we should fully
consider the incomplete information collection,
information distortion and other factors, try to make
the technical indicators easier to understand, the
conclusion is relatively accurate and easy to use. Due
to the difficulty and poor accuracy of obtaining credit
information in China, we should focus on qualitative
index analysis, supplemented by quantitative index
analysis.
2.4 Establishing Credit Risk
Management Model
According to the credit management department's
investigation of customers' credit, enterprises identify
and analyze the risk degree of credit sales, formulate
corresponding contract conditions such as collection
method and credit line in combination with their own
control objectives of financial risk, and then track the
financial status and market risk changes of the
enterprise to be granted credit in time before
recovering all funds, so as to ensure the safe recovery
of funds. Perfect credit risk management measures
can effectively reduce the risk of financial loss caused
by credit sales. When a shareholder of a company
borrows a debt, it is equivalent to buying an asset
whose underlying asset is the value of the company's
assets. The principle of the call option whose default
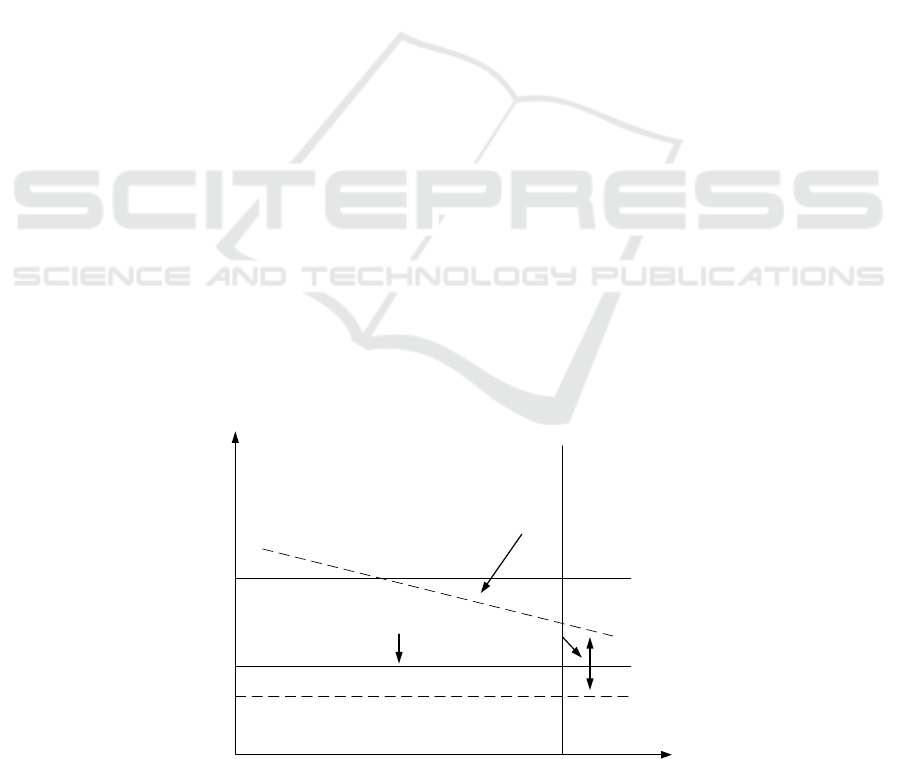
point is the exercise value is shown in Figure 1.
According to Figure 1, to establish a credit risk
management model, we should follow the following
steps: 1. Credit risk identification and evaluation. The
enterprise conducts a detailed investigation and
Research on the financial status, solvency and other
information of customers, further studies and
analyzes the factors that may cause development and
change, analyzes and evaluates with the evaluation
model, and links the evaluation data with the
corresponding authorization mechanism of the
time
Three years
Current
Average value of assets
Asset value
Expected growth
rate of assets
Book value of debt
repayment
Standard
deviation of
asset value
after three
years
Asset value
distribution after
three years
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of enterprise anticipatory breach of contract.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
816

enterprise, so as to give customers the corresponding
credit line. Enterprises revise credit risk management
methods and procedures. (Vij 2019). All members of
the enterprise need to create their own unique credit
culture, which can increase the cohesion of
employees, improve the company's reputation and
market competitiveness. Due to the neglect of the
influence of credit behavior, the credit risk awareness
of Chinese enterprises is generally not high. On the
basis of identifying and measuring enterprise credit
risk, credit risk managers must take appropriate credit
risk control strategies to achieve the goal of credit risk
management. The control before the occurrence of
enterprise credit risk is the control of credit risk in
advance. In modern credit risk management, this kind
of control method is more and more valued and
widely used by people. Before making business
decisions, the credit risk factors inside and outside the
enterprise are analyzed in detail, various risk factors
are estimated comprehensively, and the trend of the
decision results of the enterprise is predicted. It is
assumed that when the asset value of an enterprise is
at a certain value level, the default probability of
credit risk is higher, the default probability of an
enterprise is expressed as:
𝐺 =
√
(5)
In formula (5), 𝑚 is the asset value of the
enterprise, 𝑓 is the critical asset value of credit risk
default, 𝑞 is the standard distribution value, 𝑛 is the
initial asset value of the enterprise, and
z
is the
market risk coefficient. If the possible credit risk
factors are found, preventive corrective measures
should be taken in advance to ensure that the
enterprise's business decisions are always on the right
track, so as to achieve the enterprise goals. To a
certain extent, it can avoid and prevent the mistakes
of control in the event and control after the event.
Credit risk control is also a necessary form of control.
When credit risk problems occur, necessary measures
should be taken in time to control the increase of
losses and reduce losses. Because credit risk may
occur at any time, and the occurrence time of risk
events is extremely short, the credit risk control
requires enterprise decision-makers to have a high
degree of risk perception, and be able to deal with risk
events in time.
3 EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS
3.1 Experiment Content
Firstly, the most significant regression coefficient of
the variable with the largest partial correlation
coefficient was tested to determine whether the
variable entered the regression equation. Then, each
variable in the equation is taken as the last variable
selected into the equation to calculate the index
weight, and the variable with the smallest index
weight is tested to determine whether it remains in the
equation. Repeat this process until no variables are
introduced and no variables can be eliminated. In this
way, the application of stepwise regression method
can introduce and eliminate variables, and the
original eliminated variables may be introduced into
the regression equation later. Because the stepwise
regression method is a general term of a large
category, the selection forward LR method in SPSS
software is mainly selected to test the goodness of fit
of the model under different iterations.
3.2 Experimental Result
In the experiment, the enterprise credit risk
management model based on machine learning and
the enterprise credit risk management model based on
logistic are selected to compare with the designed risk
management model. The goodness of fit of the three
models is tested under different iteration times. The
closer the goodness of fit is to 1, the better the fitting
degree of the regression line to the observed value is.
Table 1: Experimental results of goodness of fit.
Iterations
(
times
)
Enterprise credit risk management
model based on machine learnin
g
Enterprise credit risk management
model based on Lo
g
istic
Risk management
model of desi
g
n
100 0.3016 0.6445 0.7849
200 0.3699 0.7031 0.6638
300 0.2647 0.5432 0.7934
400 0.4458 0.6019 0.8025
500 0.5537 0.3376 0.6974
600 0.6029 0.4116 0.8569
700 0.4631 0.3871 0.7774
800 0.3397 0.4036 0.8639
900 0.6080 0.6003 0.9468
1000 0.6682 0.4319 0.8533
Enterprise Credit Risk Management Model Based on Super
S
BMModel
817

Table 2: Average goodness of fit of. three models.
Number of
experiments (group)
Enterprise credit risk
management model based on
machine learnin
g
Enterprise credit risk
management model based on
Lo
g
istic
Risk management
model of design
1 0.4618 0.5011 0.7984
2 0.4839 0.5026 0.8001
3 0.3364 0.4967 0.8948
4 0.4012 0.5113 0.7866
5 0.3207 0.4837 0.8631
6 0.3489 0.5006 0.6485
7 0.4068 0.4988 0.7933
8 0.4816 0.5022 0.7204
9 0.4553 0.4886 0.8546
10 0.4431 0.5036 0.9102
The experimental results are shown in Table 1.
According to Table 1, the mean goodness of fit of
the three risk management models can be obtained
under different iterations, as shown in Table 2.
It can be seen from Table 2 that the average
goodness of fit of the enterprise credit risk
management model based on machine learning, the
enterprise credit risk management model based on
logistic and the design risk management model are
0.4139, 0.4989 and 0.807 respectively. The average
goodness of fit of the risk management model
designed in the three models is closest to 1, which
proves that the design model has better performance.
4 CONCLUSION
The risk management model designed in this paper
has better performance than the current model, and
enriches the academic literature on enterprise risk
management. At the same time, it broadens the scope
of Super_ SBM model, it provides new feasible ideas
for enterprise risk management. Due to my limited
ability, the article is about Super_ SBM model in
other fields is not comprehensive enough, in the
future, I will continue to work on related research.
REFERENCES
Altuntas M, Berry-Stlzle T R, Cummins J D. (2019)
Enterprise risk management and economies of scale
and scope: evidence from the German insurance
industry. Annals of Operations Research, 3:1-35.
Aamer, S, Abu-Qarn. (2019) Reassessment of the
Proximate Determinants of Income Levels and Growth
of Nations. Atlantic Economic Journal, 4: 463-483.
An Q, Wu Q, Li J, et al. (2019) Environmental efficiency
evaluation for Xiangjiang River basin 816: 95-103.
Hiebl M R W, Duller C, Neubauer H. (2019) Enterprise
Risk Management in Family Firms: Evidence from
Austria and Germany. The Journal of Risk Finance,
1:39-58.
Huang X. (2019) Reform of state﹐wned enterprises and
productivity growth in China. Asian-Pacific Economic
Literature, 1: 64-77.
Huang Y, Liu S. (2020) Efficiency evaluation of a
sustainable hydrogen production scheme based on
super efficiency SBM model. Journal of Cleaner
Production, 256:120447.
Johnston J, Soileau J. (2020) Enterprise Risk Management
and Accruals Estimation Error. Journal of
Contemporary Accounting and Economics, 3: 100209.
Kuo Y F, Lin Y M, Chien H F. (2020) Corporate social
responsibility, enterprise risk management, and real
earnings management: Evidence from managerial
confidence. Finance Research Letters, 10: 101805.
LO González, Santomil P D, Herrera A T. (2020) The effect
of Enterprise Risk Management on the risk and the
performance of Spanish listed companies. European
Research on Management and Business Economics,
3:111-120.
Oliveira K, Mexas M, Meirino M, et al. (2019) Critical
success factors associated with the implementation of
enterprise risk management. Journal of risk research, 7-
8: 1004-1019.
Oliveira K, Mexas M, Meirino M, et al. (2019) Critical
success factors associated with the implementation of
enterprise risk management. Journal of risk research, 7-
8: 1004-1019.
Ojeka S A, Adegboye A, K Adegboye, et al. (2019) Chief
financial officer roles and enterprise risk management:
An empirical based study. Heliyon, 6: 01934.
Polly, Stevens, Jordan, et al. (2019) Integrated (Enterprise)
Risk Management in Canadian Healthcare
Organizations: Common Barriers and a Shared
Solution for Effective and Efficient Implementation in
Canada. Healthcare quarterly (Toronto, Ont.), 1: 48-53.
RGF Corrêa, Neto F, Souza J S, et al. (2019) Enterprise risk
management in integrated crop-livestock systems: A
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
818

method proposition. The Journal of Agricultural
Science, 10: 1-11.
Silva M Z, Fernandes F C. (2019) The influence of
contingencies factors strategy and structure in the
enterprise risk management in a hospital. Gesto &
Produo, 1: 1-16.
Shi Q, Wang C, Wang W. (2019) Liquidity Shock, Credit
Constraint and the Development of Private vs. State-
Owned Enterprises. Frontiers of economics in China,
4:583-603.
Saeidi P, Saeidi S P, Sofian S, et al. (2019) The impact of
enterprise risk management on competitive advantage
by moderating role of information technology.
Computer standards & interfaces, 3: 67-82.
Vij M. (2019) The emerging importance of risk
management and enterprise risk management strategies
in the Indian hospitality industry: Senior managements'
perspective. Worldwide Hospitality and Tourism
Themes, 4: 392-403.
X Lin, X Zhu, Y Han, et al. (2020) Economy and carbon
dioxide emissions effects of energy structures in the
world: Evidence based on SBM-DEA mode. Science of
The Total Environment, 6: 138947.
Zhu C, Zhu N, Shan W. (2021) Eco-Efficiency of Industrial
Investment and Its Influencing Factors in China Based
on a New SeUo-SBM-DEA Model and Tobit
Regression. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 1:
1-16.
Enterprise Credit Risk Management Model Based on Super
S
BMModel
819
