
The Analysis of Tensile Strength of High-Density Polyethylene for
Shipbuilding
I Putu Arta Wibawa, Kharis Abdullah
a
, Sumardiono, Abdul Gafur,
Eriek Wahyu Restu Widodo
b
and Zaini Aris Musthofa
Politeknik Perkapalan Negeri Surabaya, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: HDPE, Ship, Tensile Strength.
Abstract: Since years ago, ships have been made using various types of materials. The materials that be used, such as
wood, steel, aluminium, and others. However, some of materials still have disadvantages, such as easily
weathered, unrecyclable, and expensive. There is still a need for alternative materials that are cheap and
environmentally friendly. HDPE can be used as an alternative because it has the above characteristics. It is
necessary to analyse its mechanical properties first before applicated because of related to the strength of the
material. One of its mechanical properties is tensile strength. Therefore, this study was conducted to analyse
the mechanical properties of HDPE by testing. This research was conducted to determine the mechanical
properties of tensile testing for the three brands of HDPE which were applied as the basic material for
shipbuilding by referring to the Turk Loydu acceptability standard. The HDPE material was processed into
test specimens and tested for tensile strength. Based on the tests that have been carried out, the highest
mechanical properties of HDPE material were obtained, ultimate tensile strength and yield strengths of 32.7
and 26.89 MPa (Local HDPE), respectively. Fracture tensile strength and maximum strain of 29.60 MPa and
46.92% (HDPE ROCHLING), respectively. While the strain at yielding point was 2.39% (HDPE AGRU).
Based on the acceptance standards of Turk Lyodu, HDPE ROCHLING could be used as a basic material for
shipbuilding in terms of the acceptability of mechanical properties after tensile testing.
1 INTRODUCTION
Along with the development of technology, various
types of materials have been used as basic materials
for shipbuilding. The materials that have been used
are wood, steel, aluminium, and fiberglass. Some of
the above materials still have weaknesses, such as
wood that is easily weathered, steel and aluminium
which are expensive, or fiberglass which
unrecyclable. Meanwhile, currently the use of
materials that are durable, environmentally friendly,
and has an economical price is a new concern for ship
owners. Thus, from these problems, other alternative
materials are still needed that can be applied as basic
materials for shipbuilding.
HDPE (high density polyethylene) can be an
alternative base material for shipbuilding. Currently,
more than 70% of the plastics produced or used by the
community are Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7859-4783
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4424-0351
(PP), Polystyrene (PS), and Polyvinyl Chloride
(PVC) so that many or even most of the current
studies and research must relate to these four the type
of polymer (Praputri et al, 2016). HDPE has
characteristics which is durable against aging and
corrosion, and recyclable (Siswandi, 2016). Before
applied as a ship structural material, it was necessary
to know in advance about the physical and
mechanical properties of HDPE. Mechanical
properties describe the characteristics of the material
when it is subjected to loading.
Knowing the mechanical properties of HDPE
were certainly related to the strength of the material.
The strength of a material is needed to determine the
level of resistance of the material to deformation that
occurs due to loading. As for one of the mechanical
properties that need to be known, namely tensile
strength (tensile strength). Tensile strength can be
generated through a series of tensile tests (tensile
334
Arta Wibawa, I., Abdullah, K., Sumardiono, ., Gafur, A., Restu Widodo, E. and Aris Musthofa, Z.
The Analysis of Tensile Strength of High-Density Polyethylene for Shipbuilding.
DOI: 10.5220/0011769900003575
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2022), pages 334-336
ISBN: 978-989-758-619-4; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright © 2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

strength tests). Therefore, to determine the tensile
strength of HDPE and determine whether the material
can be applied as a basic material for shipbuilding, the
authors made a solution through tensile strength
testing.
2 EXPERIMENTS
The material was used in this research was HDPE
sheet with three different brands (HDPE AGRU,
Local, ROCHLING). The manufacture of test
specimens was carried out by directly attaching a
specimen mall whose dimensions have been designed
based on the ASTM D-638 part type I standard. The
dimensions of the test specimens that have been
regulated in ASTM D-638 are listed in Table 1.
Table 1: The dimension of tensile test specimen according
the ASTM D-638.
Dimension
7 or under
(Thickness, mm)
Tolerances
I II
W 13 6 0.5
L 57 57 0.5
WO 19 19 6.4
LO 165 153 no max
G 50 50 0.25
D 115 135 5
R 76 76 1
(Source: ASTM D-638, 2004)
The shape of the test specimen has also been adjusted
to the ASTM D-638 standard as can be seen in Figure
1.
Figure 1: The specimen of tensile strength according ASTM
D-638.
After the test specimens were made, tensile
strength testing was carried out using a universal
testing machine (UTM) with the SHIMADZU UH-
600kNI brand with a testing speed of 50 mm/min. As
for after the test, the results will be processed to reveal
the mechanical properties after the tensile strength
test, such as maximum tensile strength and yield
strength.
3 RESULTS
The research conducted by Jamal in 2017 showed that
fishing boats/pompong boats made of HDPE can be
used as a substitute for wood-based materials, this
research was carried out only on the design side of
fishing boats, without calculating the size of the
construction (Jamal, 2017). Fitria also conducted a
similar study in 2021 on tourist boats made of HDPE,
where in determining the construction size of HDPE
ships using the rules from DNVGL-ST-0342 (Fitria,
2021). Based on these two studies, this time the
research is focused on knowing the mechanical
properties of HDPE material before it is applied and
calculated as ship construction.
Based on the characterization carried out with the
tensile testing machine, the mechanical properties
data after the tensile test were obtained in the form of
tensile strength, strain, and modulus of elasticity as
shown in the following table.
Table 2: Tensile strength of HDPE materials.
No. Merk
Ultimate Tensile
Strength (MPa)
1 AGRU HDPE
25.43
2 Local HDPE 32.75
3
ROCHLING
HDPE
25.37
According to The Table 1 above, it shown that the
results of the tensile strength test produce maximum
tensile strength values for the three HDPE brands.
The maximum tensile strength value is owned by
Local HDPE, which is 32.75 MPa. Meanwhile,
HDPE AGRU has the smallest maximum tensile
strength, which is 25.37 MPa. The size of the tensile
strength of a material is influenced by factors, such as
the type of material, crystallinity, type of resin and
additives used.
Table 3: Yield strength of HDPE materials.
No. Merk
Yield Strength
(MPa)
1 AGRU HDPE 14.06
2 Local HDPE 26.89
3
ROCHLING
HDPE
20.54
The Analysis of Tensile Strength of High-Density Polyethylene for Shipbuilding
335
Based on Table 2 above, it shows that the results
of the tensile strength test produce yield strength
values for the three HDPE brands. The value of the
largest yield tensile strength is owned by Local
HDPE, which is 26.89 MPa. Meanwhile, HDPE
AGRU has the smallest maximum tensile strength,
which is 14.06 MPa. There are previous studies that
analyze the tensile strength of HDPE materials.
Research conducted by Eva in 2016 on the effect of
fillers on the mechanical properties of nano
composites showed that the tensile strength of HDPE
material was 22.59 MPa (Ginting, 2016). This
concludes that the tensile strength values of the three
HDPEs studied are above the tensile strength values
of other HDPE studies.
After knowing the value of the mechanical
properties of HDPE material that has been raised
from the tensile strength test, it will then be referred
to one of the accepted standards for mechanical
properties of HDPE material for shipbuilding basic
materials, namely Turk Lyodu for Polyethylene
Crafts. The criteria and minimum acceptance set by
Turk Lyodu on the mechanical properties of HDPE
material can be seen in Table 3.
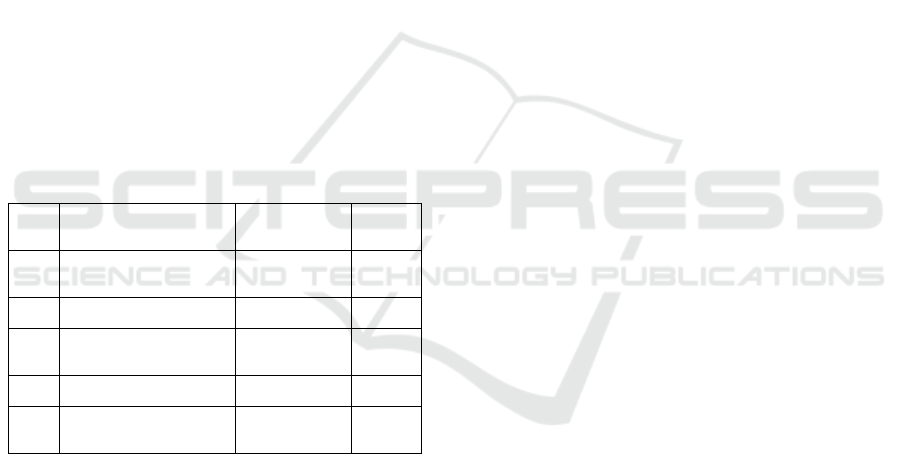
Table 4: Standar Keberterimaan HDPE dalam Türk Loydu
Tentative Rules for Polyethylene Crafts.
No Property
Properties
o
f
HDPE
Unit
1
Tensile ultimate
s
tress
Min. 24 MPa
2
Tensile yield stress Min. 17 MPa
3
Tensile break
s
tress
Min. 14 MPa
4
Elongation at yield 1 to 27 %
5
Elongation at
brea
k
10 to 1500 %
Based on Table 8 above, it shows that the results
of the acceptance of the mechanical properties of
HDPE material after tensile testing resulted in the
conclusion that only ROCHLING brand HDPE met
the Turk Lyodu acceptability standard for mechanical
properties after tensile strength testing. Meanwhile,
Local HDPE does not meet the acceptability standard
only for the value of the maximum strain. AGRU's
HDPE does not meet the acceptable standards for
maximum tensile and yield strength values. So from
this, only HDPE ROCHLING material can be
implemented as a basic material for shipbuilding
based on mechanical properties after tensile strength
testing.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the tensile strength tests that have been
carried out, each of the highest mechanical properties
of HDPE material is obtained, namely the maximum
tensile strength of 32.7 MPa (Local HDPE); yield
tensile strength of 26.89 MPa (Local HDPE); fracture
tensile strength of 29.60 MPa (HDPE ROCHLING);
strain at yielding point of 2.39% (HDPE AGRU);
maximum strain of 46.92% (HDPE ROCHLING).
Based on the acceptance standard of HDPE
material mechanical properties regulated by Turk
Lyodu, HDPE ROCHLING material can be used as a
basic material for shipbuilding based on the
acceptability of mechanical properties after tensile
strength testing.
REFERENCES
ASTM International. (2014). ASTM D-638. Standard Test
Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. United
States: ASTM International.
Diniardi, E. d. (2014). Analisis Kekuatan Mekanik dan
Struktur Mikro pada Polimer Penyusun Kipas Radiator.
Jurnal Teknologi Vol.6 No.1, pp. 55-67.
Fitria, Indah Lestari. (2021). Tugas Akhir Perancangan
Kapal Bertenaga Listrik untuk Meningkatkan
Pariwisata di Waduk Gondang Lamongan. Surabaya:
PPNS.
Ginting, E., & Padang, M. (2016). Analisis Sifat Mekanis
Dan Struktur Nanokomposit Abu Sekam. Jurnal
Einstein Volume 4 No 2, pp. 42-26.
Jamal dan Haryanto, Edy. (2017). Penetapan Bentuk Kapal
Nelayan Berbahan Dasar Plastik High Density
Polyethylene diperairan Selat Malaka. Jurnal Inovtek
Polbeng, Vol. 07, No. 2.
Praputri, E., Mulyazmi, E., Sari, M., Martynis. (2016).
Pengolahan Limbah Plastik Polypropylene Sebagai
Bahan Bakar Minyak (BBM) dengan Proses Pyrolysis.
Seminar NasionalTeknik KimiaTeknologi Oleo Petro
Kimia Indonesia. Pekanbaru.
Siswandi and Dwi Aryawan, Wasis. (2016). High Density
Polyethylene (HDPE) Vessel of Pompong as a Fishing
Vessel for Bengkalis Fisherman. Prosiding pada The
2nd International Seminar on Science and Technology.
2 Agustus, Surabaya, Indonesia.
Turk Loydu. (2014). Tentative Rules For Polyethylene
Crafts 2014. Turk Loydu: Istambul.
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
336
