
Analysis Performance Evaluation of Measuring Building (BM1) and
Cipoletti (BM3) Buildings in the Mambal Irrigation Network
of the Ayung River Irrigation Area
I Made Budiadi, Made Mudhina, Ketut Wiwin Andayani, Igag Suryanegara and I Wayan Wiraga
Department of Civil Engineering Bali Sate Polytechnic, South Kuta, Bali, Indonesia
Keywords: Mambal Irrigation Area, Measuring Building, Cipoletti, Performance Evaluation.
Abstract: The discharge canal in the Mambal irrigation area is a very important structure because it distributes water
proportionally to the paddy fields. The results of field observations show that the current formula is no
longer suitable for the canal characteristics due to changes in the physical shape of the building. Therefore,
it is necessary to evaluate the performance of the Cipoletti measuring channel and measuring channel to
obtain the actual flow coefficient. This research was conducted by testing the flow formula compared to
factual discharge measurements to obtain the actual flow coefficient. Instantaneous discharge measurements
are carried out with various variations of discharge in order to obtain a discharge coefficient that is truly in
accordance with the characteristics of the measuring building. The results showed that for BM 1 the new
formula was obtained Q = 1.430 Bh
3/2
. In BM 3 a new formula is obtained as follows Q = 1.78 b h
3/2
.
1 INTRODUCTION
The development carried out by the Government in
increasing food self-sufficiency is to improve
irrigation network services by revamping buildings
and canals that are in the same area. Until now, the
biggest water loss for irrigation water distribution is
the loss of water in secondary and tertiary canals,
which ranges from 20-30% of the water distributed
(Nugroho 2014), (Perdana and Wiguna 2019).
Improvement of buildings and canals from semi-
technical irrigation to technical irrigation has a very
positive effect in reducing water loss along the way.
Irrigation in Bali departs from the traditional Subak
irrigation agricultural system combined with a
modern irrigation system that is more technical in
nature to give a touch in the building management
system. This combination provides a more technical
farming system than previous farming
(Prastyadewia, Susilowati, and Iskandara 2020),
(Asmiwyati et al. 2015), (Budiasa et al. 2015)
Associated with the distribution of water to the
plots of irrigated rice fields have been arranged
through existing buildings along the network.
Buildings on irrigation networks in primary and
secondary canals were built by the government
through relevant agencies while buildings on tertiary
and quarter canals were built by farmers. Buildings
located in the primary and secondary canals consist
of several buildings such as share buildings, for
tapping, crossing dives, mud bags, measuring
buildings and other buildings. (Ahmed 2020),
(Akkuzu, nal, and Karataş 2007). The measuring
building is one of the important buildings in the
irrigation network because it has a function related
to the accuracy of the amount of water distributed to
the rice fields. This measuring building provides the
amount of water as needed by setting the water level
in the measuring building.
The building measuring the width threshold and
Cipoleeti in the Tukad Ayung irrigation area at the
Mambal weir drainage condition has undergone
many changes in shape as a result of the condition of
the building undergoing several changes such as
cracked walls, rusted sills and the presence of
sediment upstream and downstream of the building.
measuring. As a result of this condition, it is felt that
there is a mismatch of water distributed to farmers'
fields. This situation has a direct effect on the
decline in optimal growth of rice plants which can
reduce grain production at the farmer level.
Condition. From the preliminary research conducted,
352
Budiadi, I., Mudhina, M., Andayani, K., Suryanegara, I. and Wiraga, I.
Analysis Performance Evaluation of Measuring Building (BM1) and Cipoletti (BM3) Buildings in the Mambal irrigation Network of the Ayung River Irrigation Area.
DOI: 10.5220/0011801800003575
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2022), pages 352-357
ISBN: 978-989-758-619-4; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright © 2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

it shows that the flow formula in the measuring
building used today has been used since the building
was built and has never been adjusted until now. In
order to obtain the actual flow coefficient from the
current condition of the measuring structure, it is
very necessary to carry out an analysis of the flow in
the existing measuring structure. The results of this
study can be an important reference related to the
actual flow coefficient so that the distribution of
water by measuring structures is the same as that
required by farmers for irrigating their fields. Thus,
the results of this study can also be used as a guide
for the operation and maintenance system of
irrigation areas in the Mambal irrigation area. The
problem in this research is what is the flow
coefficient applied to the existing measuring
building and what is the actual flow coefficient
based on the test results? The purpose of this study
is to determine the currently applied coefficient and
compare it with the actual flow coefficient of the
measurement results
2 METHOD
Calibration is one of the steps to determine the
stability of a measuring object to get the actual
measurement results. (Shock, Barnum, and Seddigh
1998), (Collectives n.d.), (Santos et al. 2021). The
research was designed for six months by conducting
research activities both in the field and analytically
involving a research team of lecturers and students.
Field research was carried out by coordinating with
several parties including the Bali Provincial Public
Works Service and irrigation observers based in
Lukluk Kapal. Coordination is carried out to
determine the timing of the implementation of the
instantaneous discharge measurement so that it does
not interfere with irrigation operations that are
already running. While the analysis is carried out by
analyzing the instantaneous discharge juxtaposed
with the flow formula in a measuring building. Field
surveys to determine the condition of the measuring
building include: the location of the measuring
building. difficulty level of measurement, temporary
method of measurement, physical condition of
measuring building, current flow formula and
problem of measuring accuracy of building
Measurement of instantaneous discharge is
carried out in several ways depending on the needs
and field conditions, for example with a current
meter, buoys and others (Setiawan and Purwanto
2018), (Indonesian National Standard 2015).
Instantaneous discharge measurement requirements
are carried out with the following requirements: in a
straight location, not affected by trees or roots,
evenly distributed and it is estimated that there is no
circular velocity distribution, there are no other
factors that can cause a sudden rise in water level,
the measurement depth should be 3 times to 5 times
the diameter of the propeller. Measurement
personnel requirements: have experience in taking
measurements at least in the same job and have
received instructions on how to measure before and
have a healthy body condition (Busscher 2009)
(Jaiswal et al. 2012) (Kroc and Zumbo 2018), (Liu
and Henze 2005)
Examination of the current meter includes that
the battery used is new, the panel is visible when the
measurement is taken, when taking the
measurement, it is expected to wear a life jacket,
there is a handle that can be used in an emergency
and a measurement form is available
Figure 1: Current Meter.
Calibration is an activity to test the current ar
flow formula by comparing the factual discharge
with the theoretical discharge. The series of
activities include determining the measurement
point, measuring the cross-sectional width,
determining the depth of the water, measuring the
instantaneous discharge, analyzing the instantaneous
discharge and calibration.
The steps of calibration activities start from
building inventory, instantaneous flow
measurement, discharge analysis and calibration.
Instantaneous discharge measurements are carried
out at least 10 times to obtain valid measurement
data. Complete calibration steps as shown in Figure
2.
Analysis Performance Evaluation of Measuring Building (BM1) and Cipoletti (BM3) Buildings in the Mambal irrigation Network of the
Ayung River Irrigation Area
353

Figure 2: Research flow chart.
The Measurement Building DI Mambal is located in
two locations, namely in Kapal BM1 Village. and
BM3. In general, the condition of the building is
very well maintained and can operate well. The
problem, in general, is the presence of sediment in
the channel which affects the flow. This
sedimentation is caused by the remnants of the
building downstream which enter the channel
causing disturbances upstream. A complete picture
of the condition of the building can be seen in the
image below.
Building Measure BM1
This measuring building is in the form of a wide
threshold with a masonry construction with a plunge
downstream as shown in Figure 3 below:
Figure 3: Measuring building BM1.
Building Measure BM3, This measuring building is
a cipoletti measuring building whose threshold is a
sharp threshold made of steel. More details can be
seen in Figure 4 below.
Figure 4: Measuring Building BM3.
2.1 Inventory
Inventory is carried out to determine the current
condition of the building and the planned
measurement activities to be carried out. This
inventory records the location of the building, the
condition of the building, the current flow formula,
as well as the current debit measurement technique
plan that will be carried out.
2.2 Instantaneous Discharge
Measurement
Instantaneous discharge measurements are carried
out to determine the actual discharge conditions by
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
354
measuring repeatedly for at least 10 trials. The
instantaneous dbit measurement is carried out in the
measuring building using the measurement form that
has been provided with a calibrated current meter.
Measurements were carried out with different
variations in water height so as to produce varying
discharges (Xu et al. 2021).
2.3 Analysis
The analysis was carried out after knowing the
actual discharge data from the measurement results.
This analysis was conducted to obtain the value of
the flow coefficient (Cd and CV). After obtaining
the Cd and CV values, a regression analysis was
carried out to determine the actual magnitude of the
coefficient.
3 RESULTS
Calibration shows that each water level has different
Cv and Cd values. The higher the water, the higher
the discharge as well as the values of Cv and Cd
which show varying values. More details can be
seen in Table 1 below:
Table 1: Calculation of the value of C (Cd,Cv) in BM 1.
buildings.
Exp. Discharge h
3/2
1,705Bh
3/2
C
(m3/dt) (m)
1 0.04 0.01 0.09 0.43
2 0.28 0.06 0.39 0.72
3 0.43 0.08 0.52 0.82
4 0.49 0.09 0.59 0.84
5 0,89 0.16 1.07 0.84
6 1.24 0.21 1.45 0.86
7 1.48 0.25 1.71 0.87
8 1.87 0.34 2.33 0.80
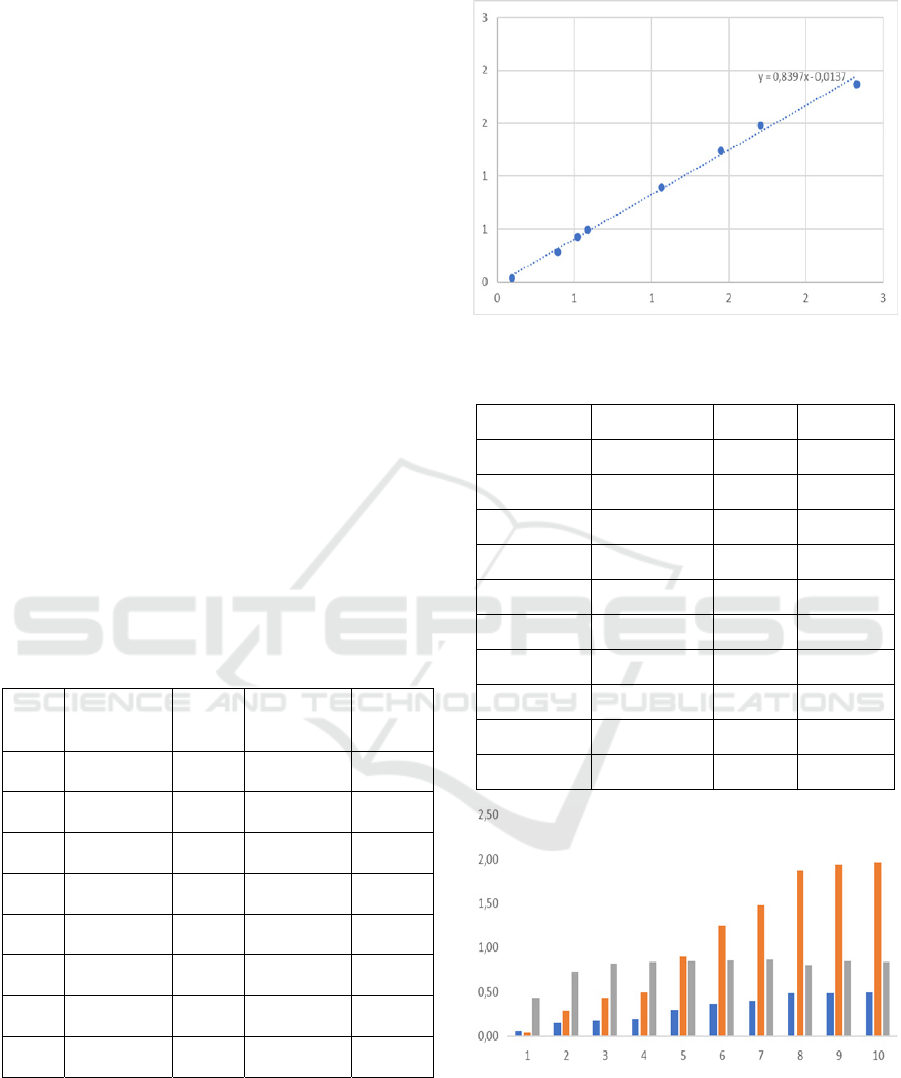
Figure 5: Relationship between Cv and Cd in BM 1.
Table 2: Comparison between H with Q and Cd, Cv.
Experiment H average Q Cd,Cv
1 0.06 0.04 0.43
2 0.15 0.28 0.72
3 0.18 0.43 0.82
4 0.2 0.49 0.84
5 0.29 0.90 0.84
6 0.36 1.24 0.86
7 0.40 1.48 0.87
8 0.49 1.87 0.80
9 0.48 1.94 0.85
10 0.49 1.96 0.83
Figure 6: Relationship Between H, Q and Cd,Cv in BM 1.
Analysis Performance Evaluation of Measuring Building (BM1) and Cipoletti (BM3) Buildings in the Mambal irrigation Network of the
Ayung River Irrigation Area
355

Table 3: Calculation of the value of C (Cd,Cv) in BM 3.
buildings.
Exp. Discharge h3
/2
2.95 Bh
3/2
C
(m
3
/dt) (m)
1 0.34 0.033 0.587 0.58
2 0.73 0.062 1.094 0.67
3 1.12 0.096 1.697 0.66
4 1.56 0.131 2.327 0.67
5 1.38 0.147 2.603 0.53
6 1.73 0.175 3.109 0.56
7 2.51 0.202 3.583 0.71
8 1.76 0.189 3.351 0.52
9 1.78 0.187 3.321 0.53
10 2.36 0.181 3.215 0.73
Figure 7: Relationship Between H, Q and Cd,Cv in BM 3.
Figure 8: Relationship between Q and 2,95 BH3/2 in BM 3.
4 CONCLUSION
Based on the results of the discussion that has been
carried out, several conclusions can be drawn as
follows:
1. The formula for the drainage system in the
building measuring BM1 A and BM 3 is
currently Q = 1.71 B h1,5
2. Based on the results of observations made, it
shows that the formula of the research results
shows the formula for the drainage system as
follows:
a. In buildings measuring BM 1
From the analysis results, the magnitude of Cd x
Cv = 0.839 is obtained so that the calibration of
the old formula Q = 1.71 B h0.5 becomes the
new formula as follows: Q = 1.705 Cd Cv B h
3/2
,
so that it becomes: Q = 1.705 0.839 B h
3/2
or Q =
1,430 B h
3/2
b. On Buildings Measure BM 3
By entering the value of 2g 0.5, then Q = 2.95
Cd b h
3/2
based on the results of the analysis
obtained a cd value of 0.604 so that the new
formula is obtained as follows Q = 1.78 b h
3/2
Suggestion What can be suggested is when the
instantaneous discharge measurement is carried out
carefully so as to produce calibration results that are
truly in accordance with field conditions.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
On this occasion, the authors would like to thank all
those who have helped in this research, especially
the Department of Civil Engineering at the Bali
State Polytechnic and friends from the Hydraulics
Laboratory of the Civil Engineering Department
who have provided assistance in thinking and
measuring activities in the field.
REFERENCE
Ahmed, Bayan. 2020. “Research Article Issn : 2321-7758
Characterization And Redesigning Of Mada Batu
Small Scale Irrigation Scheme , West Arsi Zone of
Oromia Region International Journal of Engineering
Research-Online.” 8(3).
Akkuzu, Erhan, Halil Baki Ünal, and Bekir Sitki Karataş.
2007. “Determination of Water Conveyance Loss in the
Menemen Open Canal Irrigation Network.” Turkish
Journal of Agriculture and Forestry 31(1): 11–22.
Asmiwyati, I Gusti Agung Ayu Rai, Made Sudiana
Mahendra, Nurhayati Hadi Susilo Arifin, and
Tomohiro Ichinose. 2015. “Recognizing Indigenous
Knowledge on Agricultural Landscape in Bali for
Micro Climate and Environment Control.” Procedia
Environmental Sciences 28(SustaiN 2014): 623–29.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2015.07.073.
Budiasa, I. Wayan et al. 2015. “The Role of the Subak
System and Tourism on Land Use Changes within the
Saba Watershed, Northern Bali, Indonesia.” Journal of
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
356

the International Society for Southeast Asian
Agricultural Sciences 21(2): 31–47.
Busscher, W. J. 2009. “Field Estimation of Soil Water
Content: A Review.” Journal of Soil and Water
Conservation 64(4): 116A-116A.
Collectives, Recherches. N O . 326 M AY 2015
Calibration of Acoustic Instruments.
Jaiswal, Shiv Kumar, Sanjay Yadav, A. K.
Bandyopadhyay, and Ravinder Agarwal. 2012.
“Global Water Flow Measurement and Calibration
Facilities: Review of Methods and Instrumentations.”
Mapan - Journal of Metrology Society of India 27(2):
63–76.
Kroc, Edward, and Bruno D. Zumbo. 2018. “Calibration
of Measurements.” Journal of Modern Applied
Statistical Methods 17(2).
Liu, Simeng, and Gregor P. Henze. 2005. “Calibration of
Building Models for Supervisory Control of
Commercial Buildings.” IBPSA 2005 - International
Building Performance Simulation Association 2005:
641–48.
Nugroho, Anton Priyo. 2014. “Analisis Kebutuhan Air
Irigasi (Studi Kasus Pada Daerah Irigasi Sungai Air
Keban Daerah Kabupaten Empat Lawang).” Teknik
Sipil Dan Lingkungan 2: 457–70.
Perdana, Putu, and Kusuma Wiguna. 2019. Perhitungan
Kebutuhan Air. Denpasar: Udayana University Press.
Prastyadewia, Made Ika, Indah Susilowati, and Deden
Dinar Iskandara. 2020. “Preserving the Existence of
Subak in Bali: The Role of Social, Cultural, and
Economic Agencies.” Economia Agro-Alimentare
22(3): 1–20.
Santos, Fernando Ferreira Lima dos et al. 2021.
“Confidence Analysis and Calibration of a Fc-28 Soil
Moisture Sensor Mounted on a Microcontroller
Platform.” Nativa 9(1): 123–28.
Setiawan, RIsdiyana, and Yuli Purwanto. 2018.
“Perbandingan Pengukuran Debit Sungai Metode
Pelampung Dan Current Mater.” Jurnal Prosiding
Hasil Penelitian dan Kegiatan Tahun 2018: 67–74.
Shock, Clinton C, J Michael Barnum, and Majid Seddigh.
1998. “Calibration of Watermark Soil Moisture
Sensors for Irrigation Management.” Proceedings of
the International Irrigation Show (September): 139–
46. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/2287629
44.
Standar Nasional Indonesia. 2015. “Tata Cara Pengukuran
Debit Aliran Sungai Dan Saluran Terbuka
Menggunakan Alat Ukur Arus Dan Pelampung.”
Jakarta : Badan Standardisasi Nasional: 8066.
Xu, Hu, Zhenhua Wang, Wenhao Li, and Qiuliang Wang.
2021. “Assessment of Water Measurements in an
Irrigation Canal System Based on Experimental Data
and the CFD Model.” Water (Switzerland) 13(21).
Analysis Performance Evaluation of Measuring Building (BM1) and Cipoletti (BM3) Buildings in the Mambal irrigation Network of the
Ayung River Irrigation Area
357
