
The Effect of Paint Thickness Coating on Power Radiated in Above
Ground Carbon Steel Pipe for Fire Hydrant System
Ni’matut Tamimah
1 a
, Ika Erawati
1
, Dianita Wardani
1 b
, Pekik Mahardhika
1 c
and Aslam Chitami Priawan Siregar
2 d
1
Department of Marine Engineering, Politeknik Perkapalan Negeri Surabaya, Sukolilo, Surabaya, Indonesia
2
Department of Physics, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember, Sukolilo, Surabaya, Indonesia
aslamsiregar01@gmail.com
Keywords: Coating, Thickness, Power Radiated, Carbon Steel, Fire Hydrant.
Abstract: Corrosion is a primary cause of material failure, especially in the fire hydrant system that uses carbon steel
placed above ground. Corrosion protection is performed on the pipeline to prevent or reduce the occurrence
of corrosion. The most common method for corrosion protection is coating with a layer protective.
Corrosion is applied to the entire panel with a primer coat of red epoxy resin before assembling to pipes. In
this research, the variable coating thickness of the paint used was 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, and 400 μm. The
result showed that the highest radiation occurred at the 200 μm of coating thickness and the lowest radiation
was 350 μm. It can be concluded that 350 μm coating thickness was the lowest absorbed by the material.
Therefore, it was better to be applied to protect the carbon steel pipe for fire hydrants system from
corrosion.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5234-2737
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6465-0086
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5239-9741
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4972-5769
1 INTRODUCTION
Coating is one of the methods to resist the materials
from corrosion. Coating is also applied as a
decorative, protective, and some others specific
purposes (Wicks, 2007). The first attempt to control
corrosion in pipelines is to use coating materials.
Corrosion can be prevented as the pipeline metal can
be isolated from the contact with the natural
environment. Moreover, the coating can be as an
effective protection against corrosion because it is an
effective electrical insulator and it can be applied
without any damage and will be easily to repair.
(Peabody, 2001).
For the protection of a fire hydrant system that
uses Carbon Steel Pipe on the ground surface which
may daily exposed to sunlight and other
environmental factors, protection in the form of a
coating is needed (Maulana, 2020). However, the
optimum thickness that can be applied to reach the
best performance and without incurring the
excessive costs for coatings are required.
In this study, the thickness using FDTD (Finite
Difference Time Domain) method of the pipe
coating was varied. The optimum thickness with low
power radiated was also obtained to increase the
protection of carbon steel pipes that were used for
the fire hydrants which placed above ground.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Materials
In this study, corrosion-resistant metals such as
Carbon Steel ASTM A53 gr A with NPS 4" Sch 40
for fire hydrants were used to reduce the corrosion
rate. Figure 1 below shows the simulation of carbon
steel pipe with 4 m length.
434
Tamimah, N., Erawati, I., Wardani, D., Mahardhika, P. and Siregar, A.
The Effect of Paint Thickness Coating on Power Radiated in Above Ground Carbon Steel Pipe for Fire Hydrant System.
DOI: 10.5220/0011811900003575
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2022), pages 434-436
ISBN: 978-989-758-619-4; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright © 2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
Figure 1: Carbon steel pipe simulation.
While the material specifications of carbon steel
pipe used in the simulation are shown in the Table 1.
Table 1: Carbon steel material specifications.
Specification Value
Electric cond. 6.993e+06 [S/m]
Density 7870 [kg/m^3]
Thermal cond. 65.2 [W/K/m]
Heat capacity 0.45 [kJ/K/kg]
Diffusivity 1.84103e-05 [m^2/s]
Young's modulus 205 [kN/mm^2]
Poisson's ratio 0.29
Thermal expand 13.5 [1e-6/K]
On the other side, a red epoxy resin material was
used as the protective layer of coating paint. The
epoxy resin specifications are shown in the Tabel 2.
Table 2: Epoxy resin material specifications.
Specification Value
Density 1500 [kg/m^3]
Thermal cond. 0.2 [W/K/m]
Young's modulus 13 [kN/mm^2]
Poisson's ratio 0.45
2.2 Methods
FDTD (Finite Difference Time Domain) is a
differential numerical method that is often used in
simulation of electromagnetic waves (Siregar, 2021).
The FDTD method uses a differential approach in
the spatial domain explicitly and a differential
approach in the time domain implicitly. First
introduced by Yee, the FDTD method has been used
in a variety of application problems (Gregory, 1999).
The algorithm used is quite simple in numerical
approximation of Maxwell's equations of differential
form.
Then, an electric field grid (E) and magnetic
field (H) intermittent in space and time were used,
so that computation can be done by calculating the
field equation as a function of the previous field.
The basis of the Yee algorithm is approximation
with a second-order Taylor expansion in space and
time. Numerical dispersion and lattice-induced
errors Irregularity can be minimized by giving the
number of lattice spaces per unit length appropriate
wave (Pozar, 2005).
3 RESULTS
The energy of sunlight received by a surface on the
earth is about 1000W/m
2
. It means that each location
of 1 m
2
has the potential to generate 160-200W of
solar electricity. Therefore, this study used 200 W
for solar electricity lighting in simulation. The result
of simulation showed that the addition of a paint
coating could affect to the power of sunlight
reflected on the pipe.
Table 3: Irradiation simulation results on carbon steel
pipe.
Thickness
(μm)
Power Radiated
(10
-5
W)
Frequency
(GHz)
150 0.27 1
200 0.46 1
250 0.33 1
300 0.31 0.921
350 0.22 1
400 0.35 1
Based on Table 3 above, the reflected power of
sunlight was affected by coated pipe (the thickness).
Most coated pipe received normal energy absorption
(1 GHz) although they were varied in value of power
radiated. The greatest energy absorption happened at
the 300 μm paint coating. It occurred at a frequency
of 0.921 GHz which was in the same phase with the
wave of sunlight on the carbon steel pipe affected.
Here, the thickness of the coated was able emit
electromagnetic waves at the UHF (Ultra High
Frequency). Means here, the 300 μm has fast
responses for sunlight irradiated compared to others.
The Effect of Paint Thickness Coating on Power Radiated in Above Ground Carbon Steel Pipe for Fire Hydrant System
435
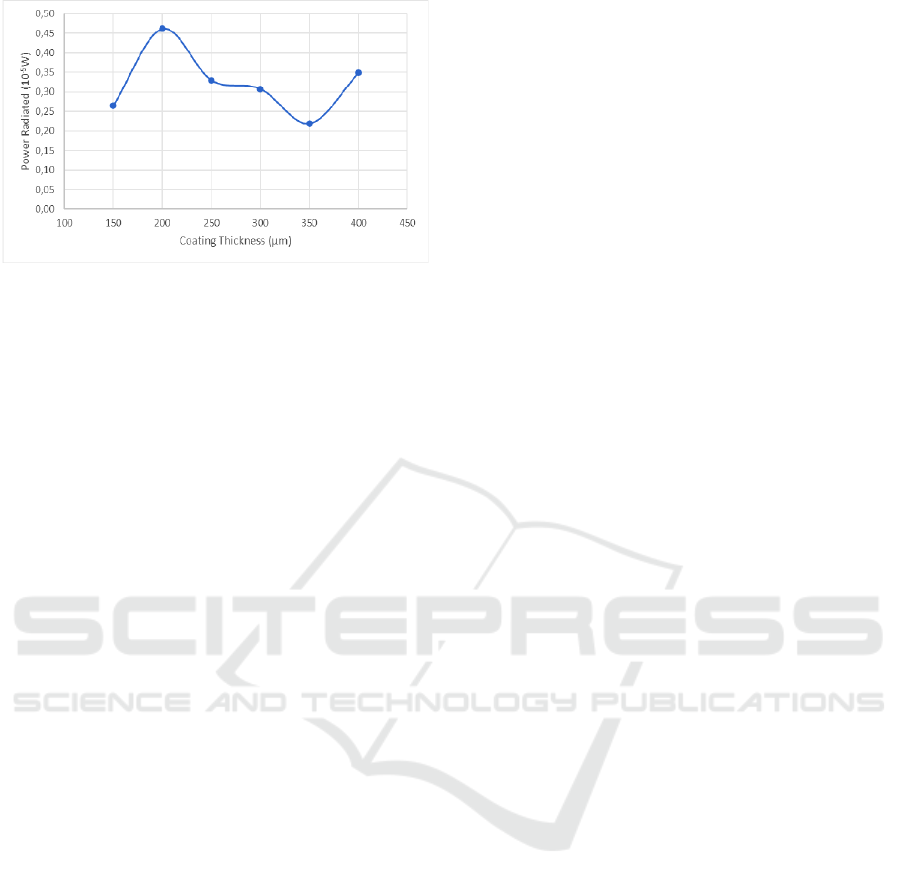
Figure 2: Graph between thickness of coating pipe and
power radiation.
While in the Figure 2, it can be shown that the
highest radiation occured at the 200 μm coating
thickness and the lowest radiation was at 350 μm.
The higher power radiated value indicated that there
was more sunlight absorption into the material. In
other hand, the lower power radiated value indicated
less sunlight absorption into the material.
From the Figure 2, it also can be indicated that
350 μm coating thickness was the lowest sunlight
absorption by the materials. Less sunlight absorption
also indicated low of corrosion rate. Therefore, the
350 μm was better applied to protect the carbon steel
pipe for fire hydrants system from corrosion.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the research result, the best coating
thickness to protect carbon steel pipe for fire
hydrants was the coating thickness which had the
minimum power radiated value. Furthermore, with
the appropriate coating thickness applied to the
materials, it could minimize the corrosion rate which
later it also could affect to the lifetime of the
materials.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank to Allah SWT, the almighty, who has
granted us countless blessings, knowledge, and
opportunity to finish this research.
REFERENCES
Gregory M. T., & Christos C. (1999). FDTD Analysis of
Phased Array Antennas. IEEE Transactions on
Antennas and Propagation, (Vol. 47, No. 4)
Maulana, R. E., & Poernomo, H. (2020). Pemilihan Jenis
dan Spesifikasi Pompa Pada Desain Sistem
Firefighting Jenis Hydrant, Sprinkle dan Fire Monitor
Pada Pabrik Gula. In Proceedings Conference on
Piping Engineering and its Application (Vol. 5, No. 1,
pp. 146-151).
Peabody, A. W. (2001). Control of Pipeline Corrosion.
Texas, NACE International the Corrosion Society.
Pozar, D.M. (2005). Microwave Engineering Third
Edition. US, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Sullivan, D. M. (2000) Electromagnetic Simulation Using
The FDTD Method, IEEE Press.
Siregar, A. C. P., Yudoyono, G., & Pramono, Y. H.
(2021). A Study of Silicon Effect as a Switch on Folded
Dipole Antenna (No. 6970). EasyChair.
Wicks Jr. Z. W, Joes F. N. Pappas S. P. and Wicks D. A.
(2007). Organic Coatings Science and Technology.
US, John Wiley & Sons Inc.
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
436
