
HDPE as a New Alternative Material for Small Vessel Boat Strength
Topan Firmanda, Sony Anggara, M. Rizqi Hariadi and Akbar Rakanda Prakasa
PT. Biro Krasifikasi Indonesia, Indonesia
Keywords: HDPE, Small Vessel, Classification, FEM.
Abstract: In the last decade, the use of HDPE as an alternative material for boat is increasingly. At least there are several
reasons for using HDPE as substitute for FRP material, from zero corrosion, marine growth resistance, and
the most important is the issues of environmentally friendly (recyclable). However, the use of HDPE as boat
structures must meet shipbuilding standards, which are regulated in Classification rules, and Biro Klasifikasi
Indonesia (BKI) as the only national class does not yet have detailed rules regarding of HDPE. The study was
conducted to see the feasibility of HDPE as boat structures, starting from rules gap analysis (ISO 12215-5,
IRS polyethylene rules, BKI rules small vessel), verification of the strength of boat construction and the effect
of thermal on HDPE sheet using Finite Element Method by commercial software. The results showed that
HDPE as an alternative material can be used as a boat/small vessel with the global stress results in test model
at 15 MPa in transverse structures and 8 MPa in longitudinal structures (allowable stress 0.8Fy) both sagging
and hogging conditions. As for thermal effects, HDPE panels are tested up to 70°C and produce elastic
deformation up to 50mm for 1m frame spacing.
1 INTRODUCTION
Polyethylene is one of the simplest and most
preferred polymers, and also most widely used
polymeric raw material for plastics around the world.
Polyethylene is generally divided into three
categories based on density: Low density
polyethylene (LDPE), Medium density polyethylene
(MDPE), and High density polyethylene (HDPE).
High density polyethylene (HDPE), as well as the
grades of polyethylene processed from it, are used in
places where more mechanical, physical or thermal
properties are required (Mikko, 2015).
Compared to other types of plastic, HDPE has
mechanical properties that allow it, to further utilized
in the field of Engineering (Prihatmoyo P.E. et.al,
2018). By increasing the density, the yield strength,
toughness, modulus of elasticity, hardness and heat
resistance of polyethylene can be increased.
Increasing the density also reduces solubility and
swelling, gas permeability, and impact strength
(Nuryosuwito N. et.al., 2019)
In the last decade, the use of HDPE as an
alternative material for boat/small vessel is
increasingly, especially for professional use. At least
there are several reasons for using HDPE as substitute
for FRP or wood material, from durable against
material aging, zero corrosion, marine growth
resistance (Wahyudin et.al., 2021), lighter vessel
weight (up to 30% compared to wood (Wilma A.,
2019)), easier to assemble, UV and fire resistance,
and the very most important is the issues of
environmentally friendly (100% recyclable) (Jamal,
2015). There are two main types of materials that can
be used as a boat or small vessels, HDPE plastic in
the form of plate-shaped and powder or pellets
(Siswandi, 2016), HDPE with base material shaped
like grains as shown in Figure 1 and in the form of
plate-shaped as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 1: Grain of plastic HDPE (Siswandi,2016).
Firmanda, T., Anggara, S., Hariadi, M. and Prakasa, A.
HDPE as a New Alternative Material for Small Vessel Boat Strength.
DOI: 10.5220/0011814700003575
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2022), pages 473-477
ISBN: 978-989-758-619-4; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright © 2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
473

Figure 2: Plate-shape of plastic HDPE (Wahyuddin et.al.,
2021).
However, the use of HDPE as boat structures
should meet shipbuilding standards which are usually
regulated in the Classification rules, therefore the
government oblige classification for several type of
vessels sailing in Indonesia waterways (Perhubungan
P.M., 2019), and Biro Klasifikasi Indonesia (BKI) as
the only national class in Indonesia does not yet have
detailed regulation regarding of HDPE, BKI rules
only regulates vessels with metal, wood, FRP and
composite materials (Indonesia, B.K, 2021).
The study was conducted to see the feasibility of
HDPE material as boat/small vessel hull, and will
focus on the strength aspect of vessel construction
made of HDPE plate-shape / HDPE sheet, and not
discuss the stability, seakeeping or material quality
aspects..
2 METHODOLOGY
The study methodology to see the feasibility of HDPE
as boat/small vessel structures, starting from rules gap
analysis and perform manual calculations according
to the respective reference rules, followed by
verification of the strength of boat/small vessel
construction and also thermal effect on HDPE sheet
using Finite Element Method by commercial
software.
2.1 Rules Gap Analysis
Rules gap analysis is carried out to see the different
requirement given by each rule, then reconciled with
some adjustments. HDPE vessel models with lengths
of 14m and 17m (Class Approved) as structural
geometry assumptions and verification of manual
calculations supplied by one of the HDPE shipyards.
The standard/rules that will be used as a manual
calculate comparison and gap analysis are:
BKI rules for small vessels up to 24m (BKI,
2021)
ISO 12215-5 Small craft - Hull construction
and scantlings (ISO, 2008)
Class Partner Indian Register Shipping
Guidelines on Hull Structure of Thermoplastic
Vessels (IRS, 2021)
Other Class Partner rules like Turk Lloyd
Tentative Rules for Polyethylene Crafts (TL,
2014) and Det Norske Veritas Standard for
certification no.2.21 (Veritas, D.N., 2010) are
exactly same as IRS guidance mentioned
before.
2.2 Numerical Verification
Numerical verification is needed as an additional
analysis after the rules gap, because the existing rules
do not consider the global strength or longitudinal
strength of small vessels, furthermore the facts
regarding the effect of solar heat will also be
simulated numerically using the commercial software
Poseidon and ANSYS.
3 RESULTS AND DISSCUSION
IRS Thermoplastic vessels guidelines provide only
the requirements for hull bottom and side thickness as
following:
t = kꞏs [P
F
/(6.7L)]
0.5
ꞏ (14+3.6L) (mm) (1)
where:
k = 0.72 for HDPE; s = stiffener spacing (m); PF =
Pressure factor and L = vessels length (m)
And the requirement of thickness for inner hull
shall not be less than 0.8t from eq.(1). However,
vessel constructions are complex structures, many
part have not been covered in those guidance
therefore the other rules will be used to cover this
shortfall.
Assumption to calculate the strength of HDPE
small vessels structure is with Aluminium material
approach, because although they are different in
terms of metallic types, but in terms of mechanical
properties both of these materials have same patterns,
even in ANSYS software these two materials belong
to one family of linear elastic isotropic materials as
shown in Figure 3.
3.1 Rules Manual Calculation
Before calculating the local structural strength,
design stress adjustments are made for each rule
based on aluminium material, in general the basic
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
474

design stress used in several standards / rules follows
the mechanical properties of HDPE stated in IRS
Guidelines, finally the adjustments of rules as shown
in Table 1 below.
Figure 3: Material Properties Comparison of HDPE and
Aluminium.
Table 1: Design stress adjustment for several rules.
BKI ISO IRS*
Rp
0.2
17 MPa
Rm 24 MPa
k 15,5
SF
plate
17 MPa
SF
stiff
15,4 MPa
Yield 17 MPa
Break 14 MPa
Ultimate 24MPa
*All in Tensile
Table 2: Manual calculation vs actual.
Ite
m
BKI ISO IRS Actual
Bottom
p
late 18.74 14.6 19.50 15
Side Plate 13.47 9.22 16.03 10
Deck Plate 10.8 - - 10
Bulkhead P. 4.04 9.22 15.6 12
Bar Keel 52x340 - - 40x250
Rect. Ste
m
42x302 - - 40x250
Floo
r
393 - - 360
Centre Girde
r
393* - - 360
Side Transv. 150 - - 360
Deck Transv. 67.3 - - 73.5
* BKI requires the fitted a centre girder for vessels
above 15 m with aluminium material, with a beam
deflection approach (ML/(8EI)) then a new criterion is
obtained, "All HDPE craft shall have a centreline
g
irder "
Manual calculation is carried out for each
standard/rules. Regulations that cover almost all parts
of the ship are BKI rules, but some results exceed
actual conditions, while the ISO standard provides
requirements of hull plate thickness that are very
close to actual, while IRS Guidance provides the
greatest requirement. Therefore, combining several
standards/rules is the aim of this study. The results of
local strength calculations can be seen in Table 2
below.
3.2 Numerical Calculation
3.2.1 Global Strength of Midship
When the vessels sails, it will receive loads due to
waves (sagging and hogging) in addition to the loads
due to hydrostatic pressure and cargo. This wave load
has not been considered in the previous rules/
standards, and is used to calculate the longitudinal
strength of vessels, especially the influence of centre
girder on global strength. The midship section model
can be seen in Figure 4 below:
Figure 4: Midship cross section.
The assessment of the longitudinal strength of this
HDPE vessel uses Poseidon commercial software,
with the following input parameters:
Length of model 3.2 m (fr.15~fr.23)
E 1.08E+6 kN/m
2
dan F
y
25 MPa
Bending load 391 kNm (BKI, 2022)
The results of numerical analysis as shown in
Figure 5, and show that the total stress (vonmiss) in
the longitudinal structure is 8 MPa and in the
transverse structure is 15 MPa, while the allowable
stress is 19MPa (0.8Fy) given by Standard For
Certification Craft (Veritas D.N., 2010). This analysis
proves that the centre girder installation reduces stress
of the transverse structure significantly by dividing
the floor in two equal length, however the assessment
of global strength of the longitudinal structure is not
HDPE as a New Alternative Material for Small Vessel Boat Strength
475
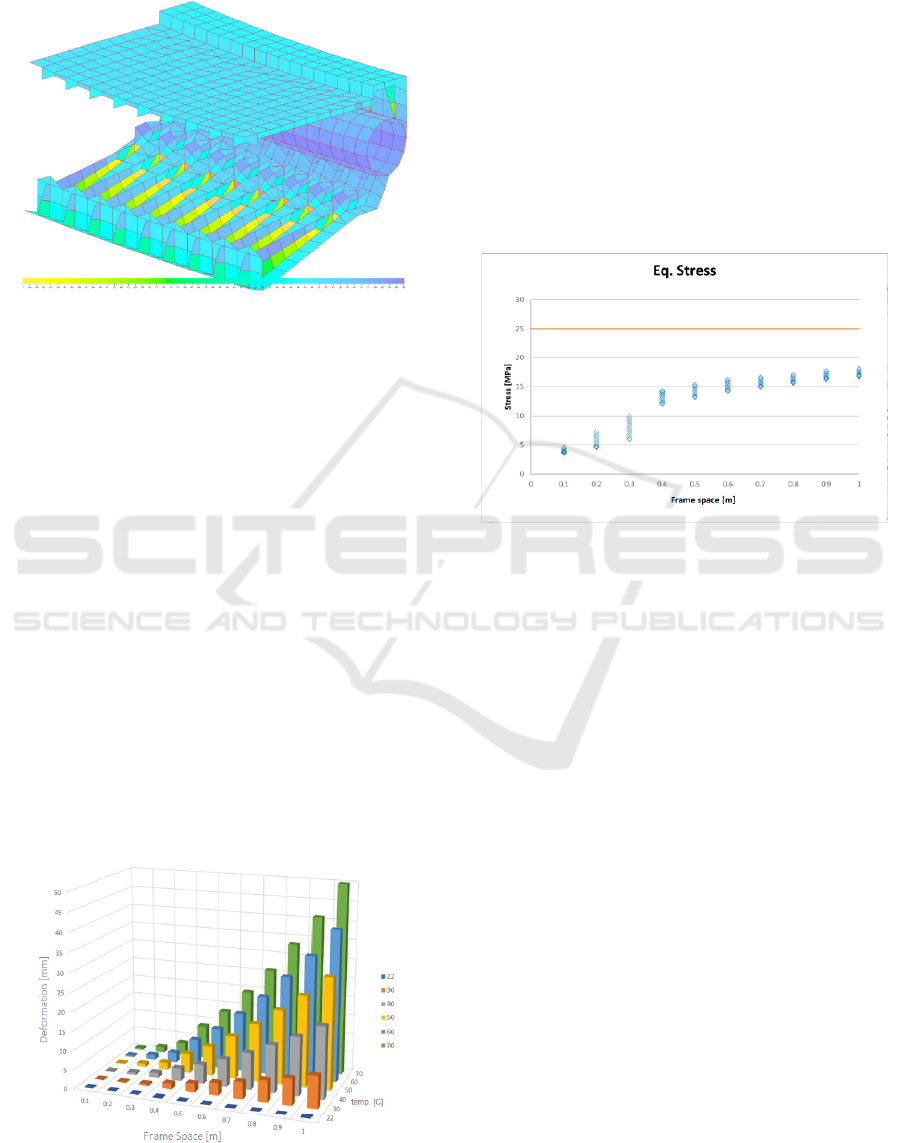
required for vessels under 24m due to the stress in the
longitudinal structure is less than half the allowable
stress.
Figure 5: Vonmiss stresses in Sagging condition.
3.2.2 Thermal Effect on HDPE
Thermal analyses were carried out to relate the
behaviour of HDPE sheets in areas of the ship's
structure that are frequently exposed to the sunlight
(eg. decks and superstructures), and also based on
information from builders who stated that HDPE
vessels decks which exposed to sunlight often
deformed, but returned to normal at night.
This analysis uses ANSYS commercial software,
with the following input parameters:
Model consist of 9 panel (3x3)
Variation of plate thickness 5 ~ 15mm
Variation of frame space 0.1 ~ 1 m
Variation of thermal load 22~70 °C
Film coefficient 5E-6 W/mm
2
°C
The results of the analysis can be seen in Figure 6.
The greater frame space as the thermal load increases,
will increase the total deformation, and maximum
deformation of 50 mm is obtained with a combination
of 70°C thermal load and 1 m frame space of stiffener.
Figure 6: Deformation of HDPE sheet.
IACS provides a deformation tolerance limit, for
stiffener with 1 m of frame space will give maximum
allowable deformation limit of 3 mm (IACS rec.47,
2013), so by this standard, assuming an average
temperature at sea level is 30°C, then only 0.3 m of
frame space or less can meets the criteria.
However this deformation not only related to
material safety, but also related to passenger/crew
safety. For material safety, the analysis will be
continued until the material stress limit is obtained.
The analysis results are shown in Figure 7, and show
that the deformation that occurs is entirely elastic
deformation, which is indicated by the stresses that
never exceeds the yield of HDPE material.
Figure 7: Thermal stress versus yield material.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Recommendations for the development of BKI
HDPE regulation regarding vessels strength are to
combine several standard/rules and some methods
with the following details:
Calculation of shell (bottom and side) and
transverse bulkhead thickness according to IRS
Guidelines
Other structural calculations using BKI Rules
for small vessels using aluminium formulations
with adjustment of design stress Rp
0.2
17 MPa,
Rm 24 MPa and k 15.5
Additional requirement as follows "All HDPE
craft shall have a centreline girders"
Other part that are not regulated by the two
references above can be solved numerically
with an acceptance criterion limit of 0.8F
y
It is recommended to take the smallest elastic
deformation (see Figure 6) for passages way
area and also for the area of equipment whose
performance will be impaired due to such
deformation.
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
476

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Acknowledgments are conveyed to PT. Iqra Visindo
Technology which has shared technical drawings of
HDPE vessels
REFERENCES
Perhubungan P.M. (2019). PM 61 Kewajiban Klasifikasi
bagi Kapal berbendera Indonesia pada Badan
klasifikasi
BKI (2021). BKI Rules for small vessel
BKI (2022). BKI Rules for hull
ISO (2008). 12215-5 Small craft - Hull construction and
scantlings
IRS (2021). IRS Guidelines on Hull Structure of
Thermoplastic Vessels
Loydu, T. (2014). Tentative Rules for Polyethylene Crafts
Veritas, D.N (2010). Standard for certification no.2.21
IACS (2013). IACS Rec. no.47 Shipbuilding and Repair
Quality Standard
Mikko M. (2015). Structural dimensioning of polyethylene
boat, urn.fi/URN:NBN:fi:amk-201505086920
Prihatmoyo P.E., et.al. (2018). Rancang Bangun Mesin
Destilator Pengubah Limbah Plastik Menjadi Minyak.,
In Proceedings Conference on Design Manufacture
Engineering and its Application (Vol. 2, No. 1)
Nuryosuwito, N., et.al. (2018). Pengaruh Campuran
Sampah Plastik dengan Katalis Alam terhadap Hasil
Produk Pyrolisis. Rekayasa Mesin, 9(2), pp. 85-91
Wahyuddin et.al, (2021). Material Cost Analysis for 35 GT
Passenger Ships with High Density Polyethylene
Materials, Repository.unhas.ac.id.
Wilma A. (2019). Analisa Teknis Ekonomis Penggunaan
Kulit Plastik HDPE Sebagai Pengganti Kulit Kayu Pada
Lambung Perahu Katamaran, Kapal: Jurnal Ilmu
Pengetahuan dan Teknologi Kelautan
Jamal (2015). Strength Evaluation of Pompong Structure
Made from High Density Polyethylene Plastics as Basic
Materials, The 4th International Seminar on Fisheries
and Marine Science
Siswandi (2016). High Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
Vessel of Pompong as a Fishing Vessel for Bengkalis
Fisherman, The 2nd International Seminar on Science
and Technology.
HDPE as a New Alternative Material for Small Vessel Boat Strength
477
