
Needs Fulfillment Analysis of Social Media for Gen Y and Gen Z in
Medan City
Munzaimah and Moulita
Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. Dr. T. Mansyur No. 9, Medan
Keywords: Social Media, Uses & Gratification, Dependency Theory, Gen Y, Gen Z
Abstract: This article attempts to explain the analysis of Gen Y and Gen Z characters in using social media using Uses
& Gratification theory and Dependency theory. As the main objective of this theory, this article also focuses
on the work on the interdependence between the media system, the larger social system, and the media users.
We conducted a survey on 400 respondents from Gen Y and Gen Z in the city of Medan. This survey
summarizes three external aspects of dependence on media according to theory, namely cognitive, affective
and behavioral aspects. From the survey data, we then tested the dependence on media at two levels of
approach, namely the macro level approach and the micro level approach. At the micro-level approach we
look more specifically at the role of media in individual lives, analyzing how people use and depend on media
to meet specific goals or needs. In a macro-level approach, we analyze the interdependence between the user
(audience), the media system, and the wider social system. The conclusion of this research work is how social
institutions can build media systems that are appropriate and compatible with Gen Y and Gen Z characters as
part of the largest social media audience.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Research Background
In this digital era, interpersonal communication and
ways of consuming mass media are also experiencing
a shift from people who communicate in closed
channels such as letters, telephones, e-mails to people
who like to broadcast video and text in messaging and
media sharing applications. Likewise, the way they
get or search for news and other information,
newspapers, magazines, and tabloids have become
extinct and have been replaced by online news portals
with digital news formats that are presented faster and
are immediately accepted in the user's hand (mobile
phone).
Medan is home to multi-ethnic people who come
from the areas surrounding the city of Medan as the
capital of the province of North Sumatra as well as
ethnic immigrants from outside North Sumatra who
migrated because of the economic attractiveness of
the city of Medan which from the start was a strategic
business and trade city on the edge of the Malacca
strait. Thus, Medan is worthy of being called a
miniature of multicultural Indonesia. Its population is
around 2 million people, making it the third largest
city in Indonesia. As a big city, the internet service in
this city can be said to be better than other areas
outside the city of Medan. About network
availability, price, and network speed. Therefore,
Generation Y and Generation Z in Medan are very
close to the demographic profile of Generation Y and
Generation Z nationally.
Previous studies have shown that teenagers spend
a lot of time on the internet, and half of that time is
spent on social media (Scott et al., 2016). Research
conducted by Spring (2018) states that the most
popular social media platform for teenagers is
Snapchat, followed by Instagram and Twitter
(Statista, 2018). Younger people are moving away
from Facebook and embracing different platforms
instead (Statista, 2018). This shows that each
generation interacts with social media in different
ways and for different purposes.
In Indonesia, according to the Association of
Indonesian Internet Service Providers (APJII), in
2018, more than 98 million Indonesians were
connected to the internet and 95% of the activities
carried out were opening social media. (Ardi and
Putri 2020) According to the 2020 population census
which conducted by the Central Statistics Agency
426
Munzaimah, . and Moulita, .
Needs Fulfillment Analysis of Social Media for Gen Y and Gen Z in Medan City.
DOI: 10.5220/0011824200003460
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Social and Political Development (ICOSOP 2022) - Human Security and Agile Government, pages 426-430
ISBN: 978-989-758-618-7; ISSN: 2975-8300
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

(BPS) of Indonesia, the composition of the
Indonesian population is currently dominated by
productive age. The two largest age groups are
Generation Y or better known as Millennials and
Generation Z. The proportion of Generation Z (Gen
Z) is 27.94% and Millennial Generation (Gen Y) is
25.87% of the total population of Indonesia.(BPS,
2021)
Gen Y and Gen Z are each the earliest generation
to adapt to the digital world, they have been in contact
with the digital world from an early age (digital
native). These two generations no longer have the
need to consume conventional media such as
newspapers and printed magazines, even electronic
media such as radio and TV are products that they
rarely consume.
Social media is currently very influential on the
formation of individual communication interactions
between generations and intra generations. On social
media, Gen Y and Gen Z get information, satisfaction
(leisure), and entertainment (Bolton et al. 2013).
According to Hasbullah, social interactions that occur
in cyberspace are built on a pattern of reciprocal and
mutually beneficial interrelationships built on trust
and supported by norms, positive and strong social
values. There is also the principle of voluntary and
willing to involve themselves in a network of social
relations. (Hasbullah, 2006)
Knowing the behavior of using social media Gen
Y and Gen Z is the entrance to find out and
understand what is going on and where the generation
is moving. Because most stereotypes about Gen Y or
Gen Z come from assumptions, which can keep us
from understanding the truth about these two
generations (IDN Millenial Report 2020)
1.2 Focus of Discussion
This article focuses on the discussion of three
variables in the uses and gratification theory as well
as dependency, namely cognitive, affective and
behavioral aspects to see the specific role of social
media in individual (micro) lives and the role of social
media on dependency relations between users
(audience), media systems, and the wider social
system (macro).
This article is based on research that uses a
quantitative approach with a descriptive type of
research. To get a picture of the character and
behavior of social media users in gen Y and gen Z,
the author has conducted a survey on respondents in
the city of Medan.
2 METHODOLOGY
The population in this study are residents of Medan
city who fall into the Gen Y and Gen Z categories.
Several researchers from various countries have
conducted separate studies on Gen Y and social
media, such as what was done (Pyöriä, Pasi. Ojala,
Satu. Saari, Tiina and Järvinen 2017), (Meechunek
2018), (Werenowska and Rzepka 2020) and (Bolton
et al. 2013). All of these researchers classify Gen
Y/millennials as those born in the early 1980s to the
late 1990s. There are differences in determining the
final range of Gen Y, some limiting it to 2000, 1999,
some only until 1994.
Meanwhile, Gen Z is generally associated with
those born after 2000. The range of years of birth of
Gen Z is more varied in some previous studies than
Gen Y. Previous literature describes Gen Z as a group
of individuals born from 1995 to 2009. Tapscott
(2008) limits this generation between 1998-2008,
Dimock (2019) starts Gen Z from 1997, Lyons,
LaVelle, and Smith (2017) defines the year of birth of
Gen Z members between 1993-1999, Kissinger
(2019) says Gen Z people born between 1997-2012,
but for Madden (2017) anyone born between 1995
and 2009 is considered a member of Generation Z.
(VITELAR 2013); Kissinger 2019)
The very large number of populations is the
reason for researchers to use samples by using a
sampling technique first. The sample is used to reduce
the use of time, effort, and costs in cross-sectional
research or research that is conducted only at one time
(Neuman, 1997: 28). The number of samples in this
study were four hundred respondents (400) which
were divided equally between Gen Y and Gen Z. The
number of respondents between women and men was
also divided equally for each generation. Sampling in
this study using purposive sampling technique.
The data obtained through the process of
collecting data through surveys were then analyzed
using descriptive statistical analysis techniques. The
data will be presented in the form of a single data
frequency distribution or cross data tabulation. The
results of data analysis are then presented in the form
of a diagram that can describe the results of the study.
Statistical data obtained through data processing
using SPSS.
Needs Fulfillment Analysis of Social Media for Gen Y and Gen Z in Medan City
427

3 THEORIES
3.1 Uses & Gratification Theory
The uses & gratifications approach is one of the
proper theoretical foundations for analyzing the
motives of media users. Because this theory assumes
users who actively choose the media used and the
second is that the media used can provide
gratification for the goals to be achieved. (Alyusi
2018) This theory suggests that audiences have
complex needs that need to be met through the use of
media (Bungin: 2006)
Katz, Gurevitch and Hazz (Effendy: 2000) say
that there are several reasons for the fulfillment of
someone who wants to be fulfilled in using the media,
namely:
1. Cognitive Needs; namely needs related to
information, knowledge and understanding.
This need is based on the desire or urges to
understand and master the environment, it
also satisfies curiosity and the urge to
investigate
2. Affective Needs; i.e. needs related to
aesthetic, pleasurable and emotional
experiences
3. Personal integration needs are needs related
to credibility, confidence or trust, stability
and individual status. These things are
obtained from the desire for self-esteem.
4. Social integration needs, namely needs
related to the addition of contact with family,
friends and the outside world. These things
are based on a desire for affiliation.
5. Escapist needs are needs related to the desire
to escape from conditions of tension,
emotion, loneliness and lack of social
support, requiring entertainment as a
solution.
3.2 Depedency Theory
Dependency theory is considered one step ahead of
uses & gratification theory in showing the influence
of media. The uses & gratification approach views the
audience as an active and goal-directed audience
instead of being used passively by the media.
Audiences are very responsible for selecting media to
meet their own needs. However, in the process of
using media, users may develop certain dependencies
that give the media more power than the uses &
gratification theory imagines. (Littlejohn and Foss
2009)
The dependency theory was first proposed by
Sandra Ball-Rokeach and Melvin De Fleur. They
both use a systems-wide approach, in one model they
propose an integral relationship between the
audience, the media, and the larger society.
There are two factors that determine how
dependent users are on media according to Ball-
Rokeach and DeFleur. First, users will become more
dependent on media that satisfy some of a person's
needs than on media that satisfy only a few of their
needs. For example, for a group of people, the
function of the news reporting media is more
important than sports. then the dependence on
information from a media that presents news
increases, because the media provides more important
information for the group.
The second source of dependence is social
stability, as social change and conflict escalate,
established institutions, beliefs, and activities are
challenged, prompting a reassessment and perhaps
new choices regarding media consumption. At such
times the dependence on the media will increase.
Conversely, the more stable the situation, the
dependence of a person on the media will decrease.
4 RESULT & DISCUSSION
Comparison table of respondents' opinion percentage about
using social media to fulfill cognitive needs
We summarize respondents' opinions regarding the
use of social media to fulfill cognitive needs. There
are five (5) criteria of cognitive needs that we ask;
firstly using social media can get learning from
others, secondly being able to exchange opinions
freely with anyone on social media, thirdly meeting
people who have the same views/interests, fourthly
being able to see interesting comments about the
latest news through social media, lastly can free to
discuss trivial topics when interacting with others.
From the results of respondents' answers, the two
generations majority chose 'agree' and 'strongly agree'
Kategori
Jawaban
Mendapatkan
pembelajaran
dari orang lain
Dapat bertukar
opini secara
bebas dengan
siapa saja di
media sosial
Bertemu dengan
orang yang
mempunyai
pandangan/
ketertarikan
yang sama
Dapat melihat
komentar menarik
tentang berita
terbaru melalui
media sosial
Dapat bebas
membahas topik
remeh saat
berinteraksi
dengan orang
lainO
K
Gen Y Gen Z Gen Y Gen Z Gen Y Gen Z Gen Y Gen Z Gen Y Gen Z
San
g
at setu
j
u 14.72 30.80 11.66 17.72 15.95 25.32 17.79 27 11.66 25.74
Setuju 71.17 57.38 57.06 64.98 57.67 54.85 59.51 54.85 49.08 45.57
Kurang setuju 11.6 10.13 28.22 15.61 20.86 17.30 20.25 15.61 31.90 23.63
Tidak setuju 2.45 1.69 3.07 1.69 5.52 2.53 2.45 2.53 7.36 5.06
Total 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
ICOSOP 2022 - International Conference on Social and Political Development 4
428
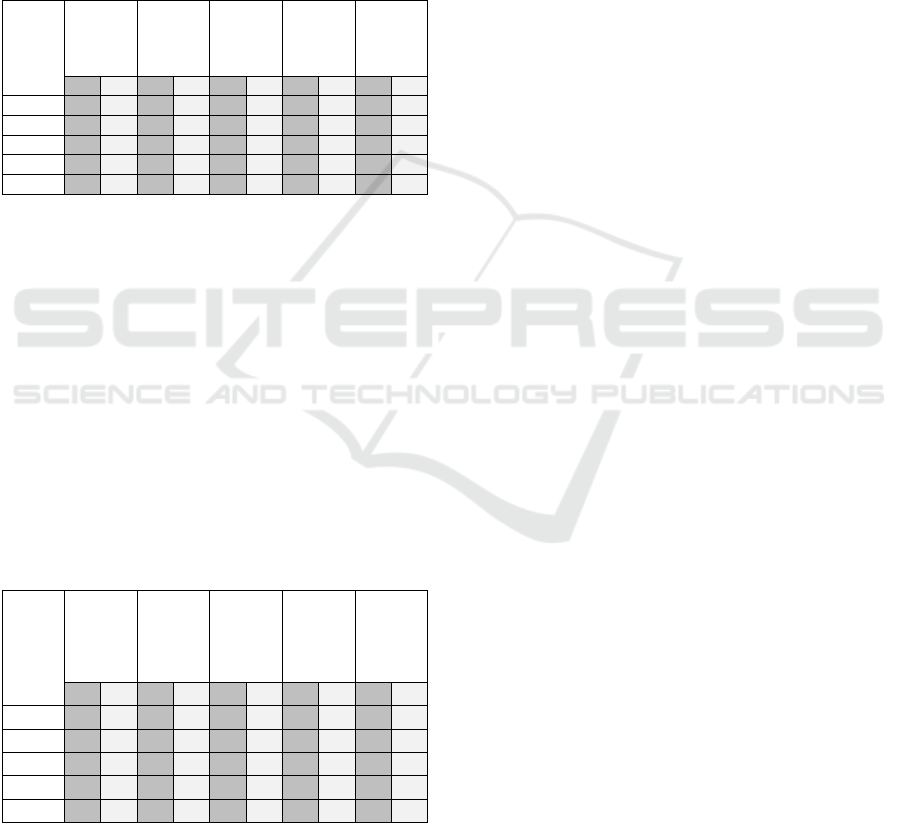
for the first four categories. As for the last category,
although the two generations still prefer to 'agree', the
second most is the choice of 'less agree'. We can
conclude from the category of social media to fulfill
this cognitive need, both generations are very
enthusiastic about using social media to get learning
from others. Then some of the second generation
population seems to have decreased interest in
discussing trivial topics when interacting with other
people on social media.
Comparison table of respondents' opinion percentage about
using social media to fulfill affective needs
In addition to cognitive aspects, we also
summarize respondents' opinions regarding the
fulfillment of affective aspects in using social media.
There are five affective criteria that we propose,
firstly getting the latest information about friends and
family, second feeling mutually reinforcing even
though they have never met, third more connected to
what is happening in friends' lives, fourth place to
find different perspectives, and fifth form feelings
closer with friend. From the results of the responses
we received, the majority of these two generations
chose 'agree' for all criteria.
Comparison table of respondents' opinion percentage about
using social media as a means of release
Social media is also a means for release by using
it as the following criteria; firstly looking for the latest
information in the community, secondly using social
media for looking for idol artist gossip, third using
social media to find news with certain topics. The
fourth uses social media to find funny things, the fifth
uses social media to share new ideas. Both
generations overwhelmingly chose the agree and
strongly agree categories for the first criterion.
However, for the second criterion, Gen Y even
though the criteria for agreeing remained in the
majority, the category that did not agree was the
second highest, Gen Z even those who chose not to
agree became the majority followed by those who
chose to agree in the second position. The rest for
criteria 3, 4 and 5 the majority of respondents chose
to agree and strongly agree. From these results we can
conclude that both generations really use social media
to find out the latest information and developments in
society. Most of Gen Y likes to look for celebrity
gossip on social media, while Gen Z mostly doesn't
even like looking for celebrity gossip on social media.
Social media is also used by these two generations to
find news on a certain topic, or just to find
entertainment with funny posts. Both generations also
predominantly agree that social media is used to share
new ideas.
5 CONCLUSION & FOLLOW UP
5.1 Micro Approach
At the micro-level approach we look more
specifically at the role of media in individual lives,
analyzing how people use and depend on media to
meet specific goals or needs. First on cognitive needs,
namely needs related to information, knowledge and
understanding.
In today's digital generation, there is a
phenomenon called fear of missing out (FOMO). Fear
of missing out is a psychological syndrome in the
form of fear that arises in individuals, when other
people have fun without their presence (Przybylski,
Murayama, DeHaan, & Gladwell, 2013 in (Risdyanti,
Faradiba, and Syihab 2019). In this FOMO syndrome,
social media is not only a tool to find out everything
that they feel is important like normal people, they
have feelings of fear, anxiety, anxiety or worry if they
are not involved in social activities with the people
around them, they will tend to be more attached to the
media. social life to cause negative consequences for
him.
From table 1 of the survey results above, we can
see that the majority of Gen Y and Gen Z do use social
media to fulfill their cognitive needs such as getting
learning from others, being able to exchange opinions
KATEGORI
Mendapatkan
informasi terbaru
tentang teman
dan keluarga
Merasa saling
menguatkan
meskipun belum
pernah bertemu
Lebih terhubung
dengan apa yang
terjadi di
kehidupan teman
Tempat
menemukan cara
pandang berbeda
Membentuk
perasaan lebih
dekat dengan
teman
Gen Y Gen Z Gen Y Gen Z Gen Y Gen Z Gen Y Gen Z Gen Y Gen Z
Sangat setuju
20.25 28.27 11.66 23.21 12.27 21.94 15.95 24.05 14.11 21.94
Setuju
68.10 63.29 60.12 51.90 61.96 54.43 62.58 55.70 56.44 57.38
Kurang setuju
10.43 7.59 25.15 23.21 20.86 21.94 19.63 17.30 26.99 18.14
Tidak setu
j
u
1.23 0.84 3.07 1.69 4.91 1.69 1.84 2.95 2.45 2.53
Total 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
KATEGORI
Menggunakan
media sosial
karena mencari
informasi terbaru
di masyarakat
Menggunakan
media sosial
karena mencari
gosip artis idola
Menggunakan
media sosial
untuk mencari
berita dengan
topik tertentu
Menggunakan
media sosial
untuk mencari
hal-hal yang lucu
Menggunakan
media sosial
untuk berbagi ide
yang baru
Gen Y Gen Z Gen Y Gen Z Gen Y Gen Z Gen Y Gen Z Gen Y Gen Z
Sangat setuju 19.63 34.18 12.88 15.61 22.09 26.16 19.63 29.96 16.56 20.68
Setuju 71.17 56.96 40.49 32.49 57.06 60.34 59.51 58.65 65.64 68.35
Kurang setuju 9.20 8.44 30.06 37.55 19.02 13.08 19.63 10.55 15.34 9.70
Tidak setuju - 0.42 16.56 14.35 1.84 0.42 1.23 0.84 2.45 1.27
Total 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
Needs Fulfillment Analysis of Social Media for Gen Y and Gen Z in Medan City
429

freely with anyone on social media, meeting people
who have the same views/interests, and can see
interesting comments about the latest news through
social media.
Thus, there is no doubt that Gen Y and Gen Z's
dependence on social media can meet the needs of
various types of information, be it knowledge
information or trivial information circulating among
their friends. The social media platforms used are also
relevant to what information they need, so we find
that in generation Y and generation Z there are
different social media platforms dominated by each
generation.
5.2 Macro Approach
In a macro-level approach, we analyze the
interdependence between the user (audience), the
media system, and the wider social system. An
example of the phenomenon that the author chooses
for this macro approach is the presence of influencers
on social media who then become a mouthpiece to
amplify values, attitudes and choices that are
considered correct by a community group to an
audience on social media.
The audience here is not seen as users who are free
(rational) to choose, social media audiences are
automatically collected by the social media system
into a bubble containing like-minded people. The
social media algorithm system is increasingly
creating social divisions in society, starting on social
media where people are met only with those who have
the same understanding, then they are unable to
tolerate the differences they encounter in real society,
social conflicts occur starting from the social
divisions that occur. on social media.
The author is still conducting further studies for a
case study of this macro approach, this research work
will be continued by determining a topic that has
occurred in the world of social media which then has
an impact on the social situation and condition of the
community. Determine the influencers that will be
used as resource persons and the social media
audience that is the target market of the influencers.
REFERENCES
Alyusi, Shiefti Dyah. 2018. MEDIA SOSIAL; Interaksi,
Identitas Dan Modal Sosial. Kedua. Jakarta.
Ardi, Zadrian, and Shania Andrisa Putri. 2020. “The
Analysis of the Social Media Impact on the Millennial
Generation Behavior and Social Interactions.” 1(2): 70–
77.
Bolton, Ruth N. et al. 2013. “Understanding Generation Y
and Their Use of Social Media: A Review and Research
Agenda.” Journal of Service Management 24(3): 245–
67.
Kissinger, Taylor. 2019. “Generation Z ’ S Hidden Social
Media Rule Book.” (June).
Littlejohn, Stephen W, and Karen A Foss. 2009. Teori
Komunikasi; Theories of Human Communication. 9th
ed. Jakarta: Salemba Humanika.
Meechunek, Krishnapong. 2018. “Using Social Media
Affecting Lifestyle and Social Behaviors of Generation
Y in Bangkok Metropolitan, Thailand.” SSRN
Electronic Journal 6(2): 103–10.
Pyöriä, Pasi. Ojala, Satu. Saari, Tiina. and Järvinen, Katri-
Maria. 2017. “The Millennial Generation.” SAGE
Open: 1–14. https://us.sagepub.com/en-us/nam/open-
access-at-sage.
Risdyanti, Keyda Sara, Andi Tenri Faradiba, and Aisyah
Syihab. 2019. “Peranan Fear of Missing Out Terhadap
Problematic Social Media Use.” Jurnal Muara Ilmu
Sosial, Humaniora, dan Seni 3(1): 276.
Vitelar, Alexandra. 2013. “Like Me: Generation Z and the
Use of Social Media for Personal Branding.”
Management Dynamics in the Knowledge Economy
7(2): 257–68.
Werenowska, Agnieszka, and Maciej Rzepka. 2020. “The
Role of Social Media in Generation Y Travel Decision-
Making Process (Case Study in Poland).” Information
(Switzerland) 11(8): 1–14.
ICOSOP 2022 - International Conference on Social and Political Development 4
430
