
The Application based on the Theory of BPM Applied to CMS
Mei Feng, Kunying Li, Xiaolian Li, Ji Zhang, Xu He, Ying Shi, Xiaoqiang Nan and Yuling Jiang
Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development, China
Keywords: BPMN, BPM, CMS, Work Flow.
Abstract: A large number of graphical process modeling languages has been developed to aid organizations in the
documentation of their processes. These languages range from simple flowchart techniques to more advanced
languages capable of capturing information required for process simulation and execution. The latest
representative from the large camp of process modeling languages has become known under the acronym
BPMN – the Business Process Modeling Notation. On the basis of representation above, there are a series of
description in the paper written by programmers who have ever taken part in the process to make the CMS.
(Contract Management System). these description has to do with something in field of BMP from developing
history, commercial value, system design to the achievement from making CMS online application form.
CMS created flow processes based on BPMN that clearly lays out the steps CMS’s business takes to
accomplish a task and these steps should construct CMS own specific diagram. The flow process has been
brought more transparent management and a variety of ways to approve contracts submitted in CMS. It
reduces the approved period of contract cycle and provides specific ideas to other systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 The Way to Flow Management
A new approach to process work gains attention and
the corporate world experiences another burst of
enthusiasm. In the early Eighties, it was Six Sigma.
In the early Nineties, it was business process
reengineering and then ERP. In the early zeros, it was
BPM and BPMS.
1.2 The Background of Development
Based on the above, the contract project team first
considered BPMN when developing the approval
process of the CMS2.0. with the rapid development
of business, the CMS1.0 has been unable to meet all
the demands. This paper starts with the system design
and implementation, expounding the whole process
of CMS2.0 application based on BPMN extension
and custom development process.
2 SYSTEM DESIGN AND
IMPLEMENTATION
2.1 Application Architectures
2.1.1 Thinking to Flow Process Design
The Business process of CMS2.0 has the following
characteristics :1. More complicated, 2. More elastic.
It provides lots of graphical representation of the
modeling process and character for understanding
different sections as the effective means of Co-
ordination. Because of satisfied standards provided
by BMPN2.0, it has taken to set up the application
service of flow modeling in CMS2.0 (Chang 2005).
2.1.2 Implementing architectures
Those data generated in different stages of CMS will
be send to the Module of lifecycle that is responsible
for driven each case of contract to different stages in
running time (Chang 2005). The Engine of ruler will
take action which analyzes business data produced at
some stage of CMS, to get the instances of modeling
process, then take them to the Engine of flow process,
finally creates many waiting tasks for flowing to the
contact, which given by the Engine of flow process.
868
Feng, M., Li, K., Li, X., Zhang, J., He, X., Shi, Y., Nan, X. and Jiang, Y.
The Application Based on the Theory of BPM Applied to CMS.
DOI: 10.5220/0011836700003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 868-872
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
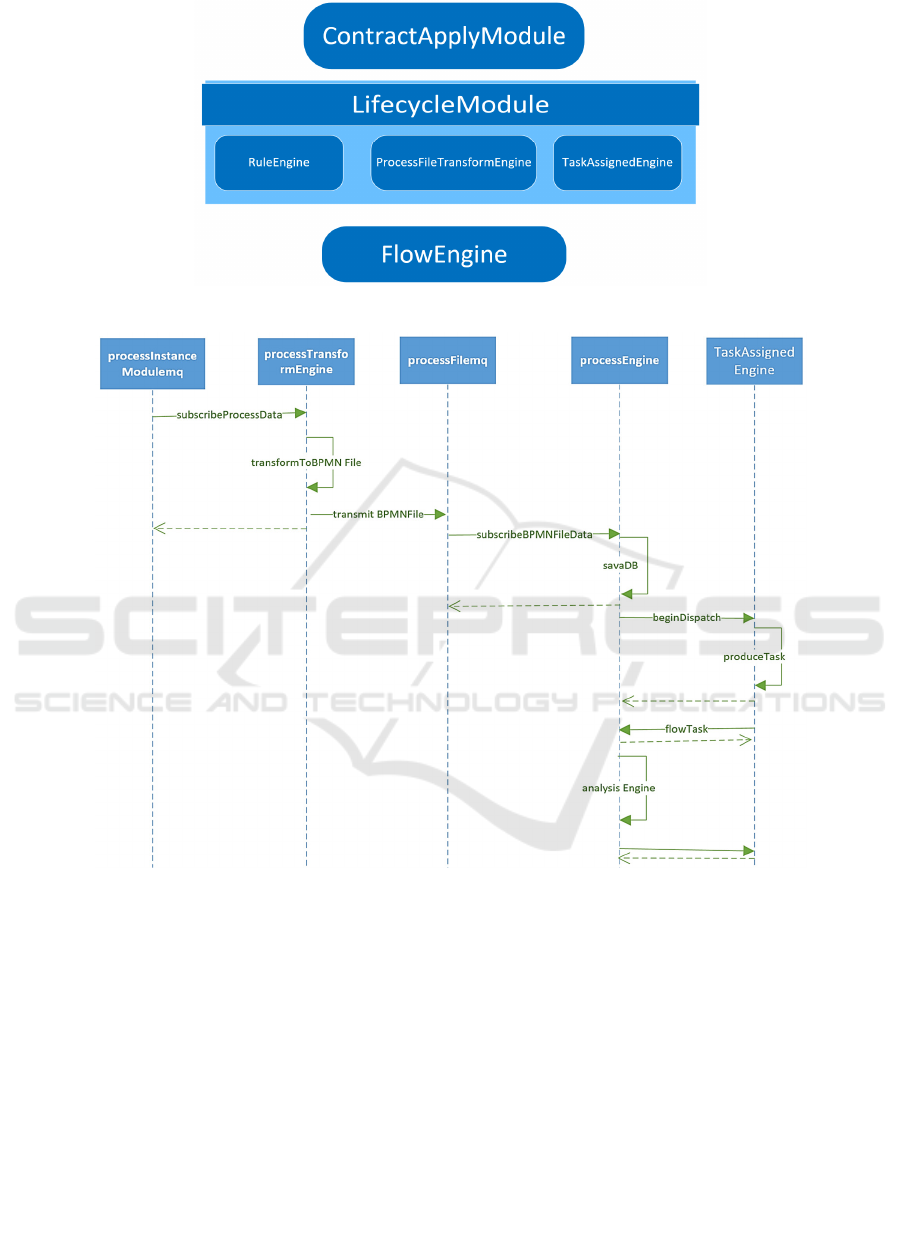
Figure 1: Process architecture diagram.
Figure 2: Process sequence diagram.
2.2 Architecture
2.2.1 The Ruler Engine
The Applications of CMS2.0 will transfer business
data to the ruler engine, at this time the ruler engine
takes out of data from message body, matches the
process rule, finally outputs matching result
(Browning 2009).
2.2.2 Conversion
The engine of conversion in CMS2.0 will converts
available objects of flow process into definition
followed by specification from BPMN2.0 (Penicina
2009).
2.2.3 Waiting Tasks Assignment
The waiting tasks are produced by business rules
driven from the engine of flow process.
Sequence diagram as figure 2.
The Application Based on the Theory of BPM Applied to CMS
869
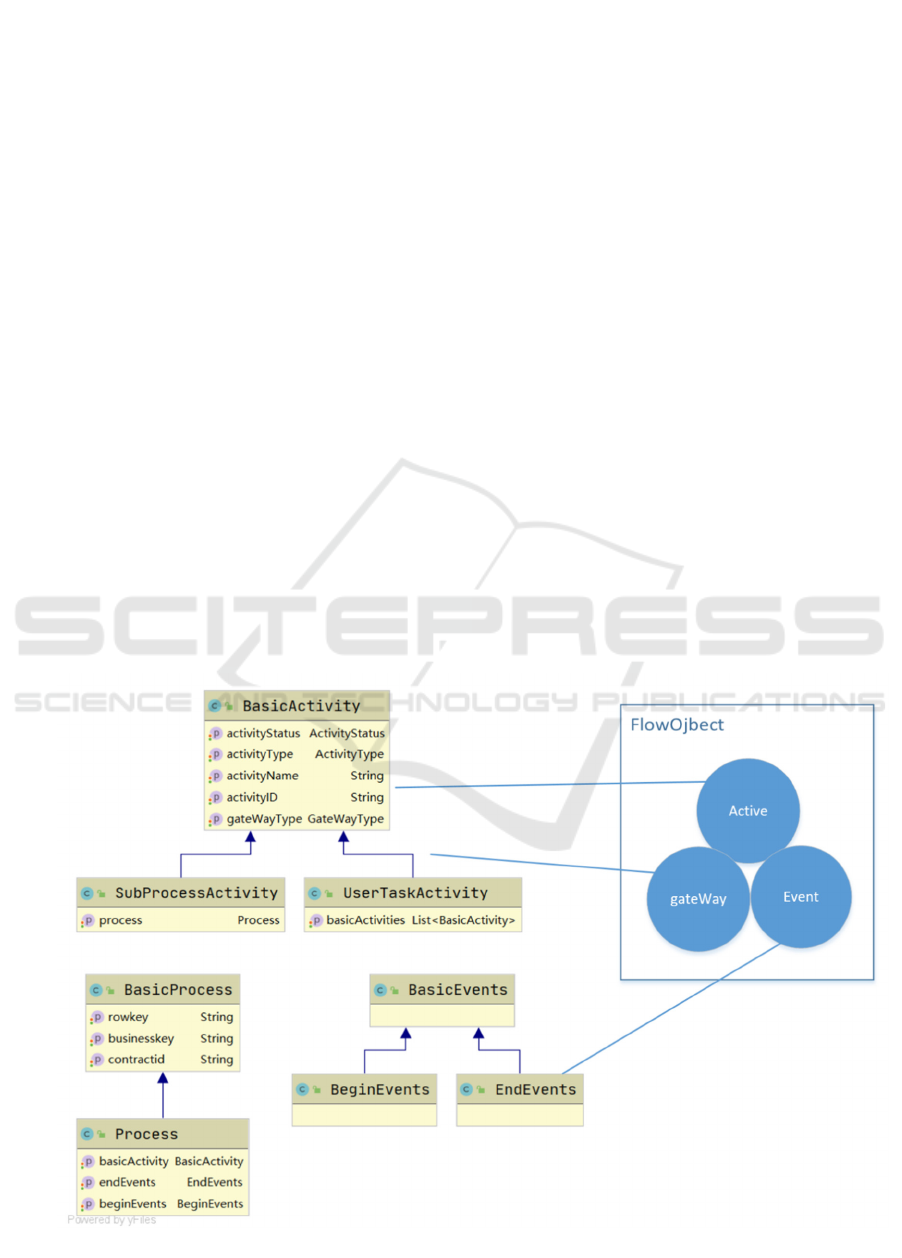
2.3 Design in Detail
2.3.1 The Flow Node Specification Combined
with BPMN2.0
In despite of providing professional graphical
symbols for five elements, which provided by
BPMN2.0, it is difficult to users, who has been
applied from the beginning of CMS, to make use of
modeling symbols with accuracy and distinction and
draw them on the chain of flow process as a big task
(Correal 2007). CMS2.0 will take tasks of
transformation to package into code, so users only
focus on flow towards, not care of how to set the flow
attributes relate to activity, event or gateway. the way
enormously decreases burden in process of using.
For implementing the output standard drafted by
BPMN, design as follow: the mapping between
business modeling processes and flow objects
Design model as below.
2.4 Implementing Flow Engine
2.4.1 Application in CMS2.0
BPMN consists of a series of entire flow objects by
self. It completely depends on those objects for
creating and analysing templates. CMS does not do
any changes to the objects, but extends more
functions through the way of injecting. it is
convenient to us in deal with flow process.
2.4.2 Driven Flow Process
Message Acceptance
The Entry of engine of flow process is responsible for
receiving the data from other modules, then handling
them according to orders from those data .the input
parameter is` Flow Request Message <T Content>`as
business object . it consists of form objects and
collections. These services are not influence in
workflow management system, So generic objects
are used for carrying out functions. Flow Request
Message as the required data handled by the engine
of flow process is handed by strong type.
The Workflow Management
The Workflow Management is mainly
responsible for the connection from each node. while
each of the nodes have finished own work, the move
of workflow would stepped into next node. Because
of what is next node is unknowing, at this time The
Workflow Management should be necessary. The
Workflow Management also has another task that
look up data in the node. the object such as Data
Object or Data
Figure 3: Flow instance module diagram.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
870
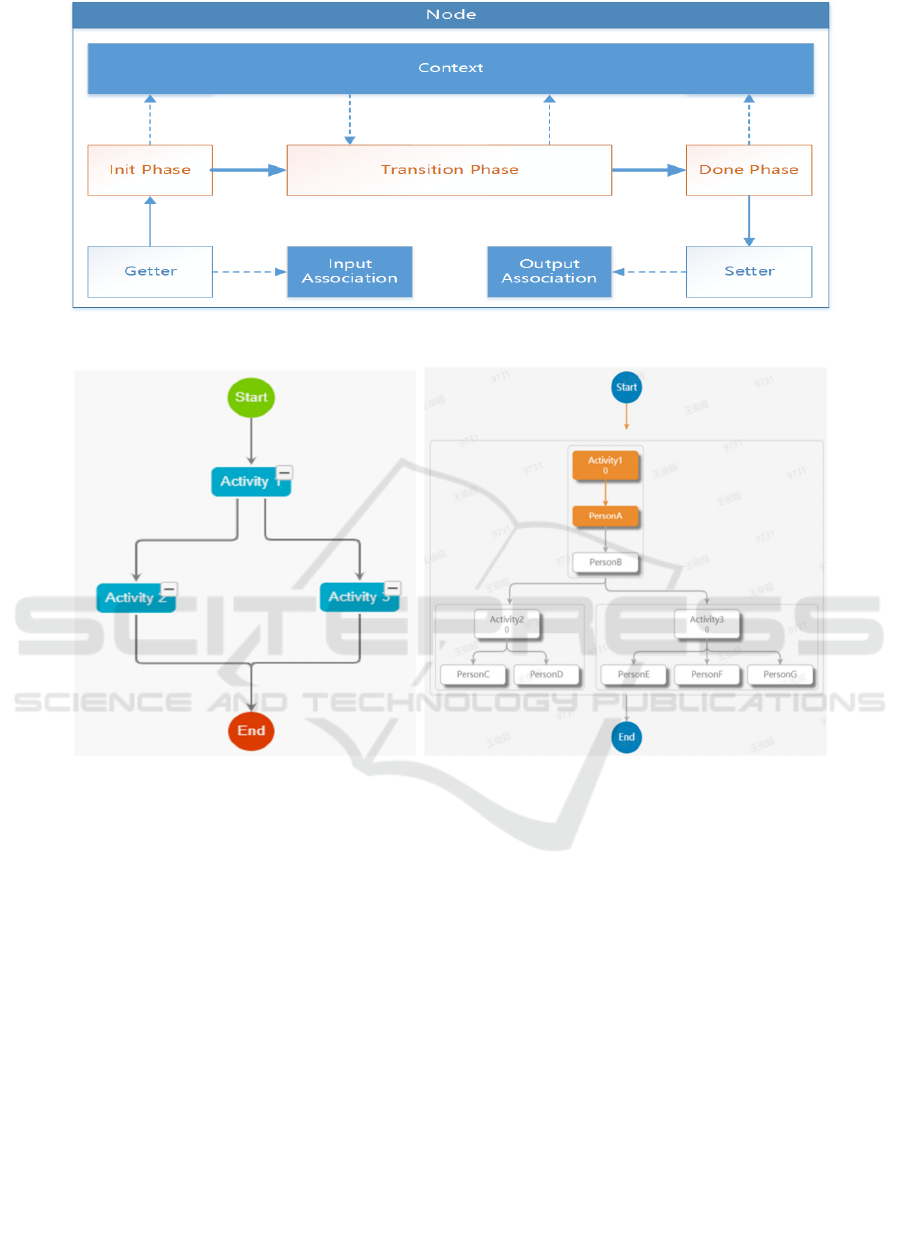
Figure 4: Node context diagram.
Figure 5: Predefined flow process diagram. Figure 6: Process instance diagram.
Object Reference is outside of nodes, so it is
necessary that The Workflow Management
dispatches and inserts data.
The Node Controller
The controller of node will be in charge of functions
from various nodes, for instance, the changing status
inside node. it loads work instead of The Workflow
Management at all.
The changing status should decide whether or not
flow process will be continued. According to the
proposal from BPMN, the status of active node will
be divided into Inactive, Ready, Active, Withdraw,
Completing, Completed, Failing, Failed, Terminating,
Terminated, Compensating, Compensated and
Closed. The source of Each status will be clear. The
standard methods have been implemented by the way
of simplicity. the class, which is extended, is overrode.
2.5 The Achievement of Development
2.5.1 The Better Transparent Workflow
Management
The Flow process not only shows predefined flow
process in graphical form (as shown as blow figure 5),
it is convenient to administrators for modifying flow
process, but also will be shown as flowchart with
implementation (as shown as blow figure 6).
Each of persons who is approver all can directly
view the framework of flow process, it keeps
transparence in the process.
2.5.2 The Main Achievement
The coordination with persons and the multi-approval
can all decrease running time in the process.
The Application Based on the Theory of BPM Applied to CMS
871

Comparison Among Different approval period
(CMS2.0 AND CMS1.0), it was found out that the
period has been apparently saved by one-third.
It was the first project of flow process based on
BPMN within the enterprise of PetroChina. as a result,
the practice taken by this project will provide new
ideas and choices for other projects. it fully changed
the traditional mode that has been applied within
enterprises in PetroChina.
3 CONCLUSION
The flow process of CMS2.0 officially has been
launched on may 2020, the numbers of flow
processes in CMS2.0 have been increasing. The Flow
process shows predefined flow process in graphical
form, supports the better transparent workflow
management and the multi-approval and the shorter
period to approve. Hence one could see that it has
taken a remarkable achievement in the development
of flow process. It was the first project of flow
process based on BPMN within the enterprise of
PetroChina. As a result, the practice taken by this
project will provide new ideas and choices for other
projects. It fully changed the traditional mode that has
been applied within enterprises in PetroChina.
REFERENCES
Browning, T.R. The many views of a process: Toward a
process ’08 architecture framework for product
development processes. Syst. Eng. 12, 1 (2009), p. 69–
90
Chang, J.F. Business Process Management Systems:
Strategy and Implementation. Auerbach Publications,
September 2005.
Correal, D., Casallas, R. Using domain specific languages
for software process modeling. In ACM OOPSLA,
Workshop on Domain-Specific Modeling (2007).
Penicina, L. The approach of transformation between
business process dimensions in BPMN modeling tool.
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on
Informat (Lithuania, Kaunas, April 2009), p. 72–81.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
872
