
Intellectual Intelligence Moderation on the Influence of Fintech
Transformation and Fintech Innovation on Women's Financial
Literacy Capacity
Sihar Tambun and Fitri Nurwanti
Universitas 17 August 1945 Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Fintech Transformation, Fintech Innovation, Intellectual Intelligence, Women's Financial Literacy Capacity
Abstract: This study provides empirical evidence regarding the effect of fintech transformation and fintech innovation
on women's financial literacy capacity with intellectual intelligence as a moderating variable. The results of
this study indicate that fintech transformation has a positive effect on women's financial literacy capacity.
Where fintech transformation creates convenience for individuals, especially women, in digitally transacting,
the convenience created by fintech transformation has a significant effect on women's financial literacy
capacity. Fintech innovation has a significant effect on women's financial literacy capacity. Innovation fintech
provides convenience by adopting cashless payments that provide a safer mode of payment for individuals,
the ease of digital transactions has a significant influence on women's financial literacy capacity. 425
respondents from among women in Indonesia were sampled in this study. Data analysis using structural
equation modeling partial least squares (PLS-SEM). Based on the results of the study, shows that fintech
transformation has a significant effect on women's financial literacy capacity which is moderated by
intellectual intelligence, and fintech innovation has a positive effect on women's financial literacy capacity
which is moderated by intellectual intelligence. The results of this study recommend for women that the
existence of fintech transformation and fintech innovation can facilitate women in financial matters. Digital
transactions make financial activities more effective and efficient. In addition to the convenience provided by
fintech, women must have intellectual intelligence to minimize the risks that may occur from fintech, and
with intellectual intelligence, women are expected to be able to use fintech as well as possible. The existence
of fintech transformation and fintech innovation moderated by intellectual intelligence is believed to be able
to help increase the capacity of financial literacy and financial inclusion for women in Indonesia.
1 INTRODUCTION
Now, Indonesian is entering the era of “society 5.0”
characterized by high competition in various sectors
that are in direct contact with needs, because at this
time every individual, especially 'women', is required
to live side by side with technology and be able to
master and utilize technology as well as possible.
Today's increasingly sophisticated digital technology
is making big changes to the world, with innovations
and transformations in the digital world making it
easier for every individual to access information in
many ways, and can enjoy the facilities of digital
technology freely and in control. According to
(IInternational Telecomunication Union
Development sector, 2022) The number of internet
users in the world has now reached 5 billion. This
figure represents 63% of the world's population
which is now estimated at 7.93 billion people.
Globally, internet use consists by 62% of men and
57% of women. In Indonesia, based on data from the
Association of Indonesian Internet Service Providers
(APJI, 2022) the number of internet network users in
Indonesia reaches 210 million people. The internet
penetration rate in Indonesia grew by 77.02%, from a
total of 275.77 million Indonesians. Furthermore, the
results of the APJI survey also show that the
penetration rate based on gender in internet use in
Indonesia is 77.5% for men and 76.48% for women.
With the growth of the internet in society, which is
increasing every year, it can create attractive digital
innovations for the community, which in principle is
carried out to provide services that are can the
expectations and needs of the community.
22
Tambun, S. and Nurwanti, F.
Intellectual Intelligence Moderation on the Influence of Fintech Transformation and Fintech Innovation on Women’s Financial Literacy Capacity.
DOI: 10.5220/0011864900003582
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Seminar and Call for Paper (ISCP) UTA â
˘
A
´
Z45 Jakarta (ISCP UTA’45 Jakarta 2022), pages 22-31
ISBN: 978-989-758-654-5; ISSN: 2828-853X
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

Currently, technology in Indonesia has brought
Indonesia towards a large-scale digital transformation
of most economic sectors, especially in the financial
sector by being able to produce software, web, and
financial services which are the gateway to the
industrial revolution called fintech transformation.
(Barroso & Laborda, 2022). In addition, the existence
of financial technology innovations that have been
present in the financial world has also spurred
transactions to become more cashless and provide
high-efficiency values for the business world which
we can call fintech innovation (Zhao et al., 2022).
With the existence of fintech innovation, it can play a
big role in increasing financial literacy capacity,
especially for women (women's financial literacy
capacity). (Luo et al., 2022) . Financial literacy itself
is a skill or ability in terms of managing finances,
women who aspire to be prosperous, happy, and
independent, must increase their capacity in
managing finances so that their future is as expected
(Darriet et al., 2021). Based on the results of the
National Financial Literacy and Inclusion Survey
(SNLIK) conducted by (Otoritas Jasa Keuangan,
2019) Yesterday, the level of financial literacy and
financial inclusion in 2019 reached 38.03% and
76.19%, respectively. This figure shows a significant
increase from the previous survey in 2016 where
there was an increase in public financial
understanding by 8.33% and an increase in access to
financial products and services by 8.39%.
Furthermore, the results of the OJK survey also show
that based on gender, the level of male financial
literacy and inclusion is 39.94% and 77.24%,
relatively higher than women at 36.13% and 75.15%,
respectively. Based on the findings of the
phenomenon above, examining the relationship
between fintech transformation, fintech innovation
and women's financial literacy capacity is an
interesting focus to discuss, whether the existence of
fintech innovation and fintech transformation
moderated by intellectual intelligence will encourage
Indonesian women to be able to increase women's
financial literacy capacity. so that the gender gap in
financial literacy and financial inclusion can be
equalized.
Previous researchers have proven that fintech
transformation has been women’s financial literacy
capacity (Prete, 2022; Zarifis & Cheng, 2022 ; Lyons
et al., 2022). Fintech innovation has been studied
about women's financial literacy capacity (Ioannou &
Wójcik, 2022 ; Sun & Tang, 2022 ; Tay et al., 2022).
Intellectual intelligence has been investigated in
women's financial literacy capacity (Lin & Bates,
2022 ; Martins et al., 2022 ; Schoofs, 2022).
However, no research places intellectual intelligence
as a moderating variable on the effect of fintech
transformation on women's financial literacy
capacity. Furthermore, another recent finding from
this study lies in the intellectual intelligence variable
as a moderating variable that moderates the fintech
innovation variable on the variable of women's
financial literacy capacity. This will be discussed in
this study and become evidence to fill the gaps in
previous research.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Theory Technology Acceptance
Model & Theory of Planned
Behavior
Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) is a theory
introduced by (Davis, 1985) The purpose of the
Technology Acceptance Model describes the
determinants of acceptance of a technology which
will then explain user behavior on various end-user
computing technologies by testing perceived
usefulness and perceived ease of use. Another theory
that explains the acceptance of individuals in using
technology is the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB)
is a theory introduced by (Ajzen, 1991)this theory can
explain that trust and risk can influence individuals to
be interested or have a desire to use technology. TPB
has the advantage of being able to analyze situations
when individuals cannot control their behavior. By
using this two theory approach, the research model is
studied systematically to see the fintech
transformation that will affect women's financial
literacy capacity. Financial literacy capacity is
influenced by fintech transformation and fintech
innovation and is moderated by intellectual
intelligence as a moderating variable. Thus, fintech
transformation and fintech innovation have the ability
to affect women's financial literacy capacity, which is
moderated by intellectual intelligence. Based on these
arguments, the results of previous studies were traced
and a research hypothesis was formed.
2.2 The Effect of Fintech
Transformation on Women's
Financial Literacy Capacity
With the existence of fintech transformation, it can
make it easier for individuals, especially women, to
use digital payment tools and platforms, this can be
one way to increase financial literacy capacity (Prete,
Intellectual Intelligence Moderation on the Influence of Fintech Transformation and Fintech Innovation on Women’s Financial Literacy
Capacity
23

2022) High financial literacy capacity can also foster
a high sense of individual trust in the use of fintech,
both of which have an important role to play (Zarifis
& Cheng, 2022). Fintech transformation is proven to
make it easier for individuals to save, borrow, and
send money digitally. The existence of fintech that
continues to transform is believed to be able to
increase the number of financial inclusion which is
part of financial literacy (Lyons et al., 2022). Thus,
fintech transformation has the potential to have an
important influence on women's financial literacy
capacity. This is certainly an important thing and has
the ability to form a positive perception for every
woman. According to the previous research statement
and the arguments above, hypothesis H1: Fintech
transformation has the potential to have a positive
effect on women's financial literacy capacity.
2.3 The Effect of Fintech Innovation on
Women's Financial Literacy
Capacity
Fintech innovation is believed to be able to increase
the profit potential in the financial sector of each
country, fintech innovation can be a ladder to increase
the number of financial inclusion and financial
literacy (Ioannou & Wójcik, 2022). In addition,
fintech is the most effective digital financial inclusion
in encouraging sustainable economic growth by
increasing loans from financial institutions, the
amount of citizen savings, and the quantity of citizen
consumption (Sun & Tang, 2022). Therefore, with the
existence of fintech innovation, the community must
continue to be encouraged to adopt cashless payments
that provide a safer mode of payment (Tay et al.,
2022). Thus, fintech innovation has the potential to
have an important influence on women's financial
literacy capacity. This is certainly an important thing
and has the ability to form a positive perception for
every woman. According to the previous research
statement and the arguments above, hypothesis H2:
Fintech innovation has the potential to have a positive
effect on women's financial literacy capacity.
2.4 Influence of Intellectual
Intelligence on Women's Financial
Literacy Capacity
Women with high intellectual intelligence have a
greater awareness of the function of the economy and
increase the use of economic information that can
increase financial literacy capacity to achieve lifelong
financial prosperity (Lin & Bates, 2022). The ability
of women's intelligence related to financial literacy
can measure how well a person understands and uses
information related to their finances (Martins et al.,
2022). Likewise, intelligence in terms of better
financial understanding will encourage women to use
digital financial services that are convenient and easy
for women to transact (Schoofs, 2022). Thus,
intellectual intelligence has the potential to have an
important influence on women's financial literacy
capacity. This is certainly an important thing and has
the potential to form a positive perception for every
woman. According to the previous research statement
and the arguments above, hypothesis H3: Intellectual
intelligence has the ability to have a positive effect on
women's financial literacy capacity.
2.5 Moderation of Intellectual
Intelligence on the Effect of Fintech
Transformation on Women's
Financial Literacy Capacity
Individuals with a high level of intellectual
intelligence have greater potential in using fintech
transformation such as buying an item online and
make payments digitally (Isaia & Oggero, 2022). The
current fintech transformation has many positive
effects on its users, especially women, the unlimited
transactions offered by fintech make it easier for
individuals to transact anywhere and anytime
(Sumardi et al., 2022). The fintech transformation
also has a positive impact on women entrepreneurs,
with the fintech transformation being able to facilitate
digital business transactions (Karim et al., 2022). By
the previous research statement and the arguments
above, hypothesis H4 is determined: Intellectual
intelligence has the potential to influence and
moderate the influence of fintech transformation on
women's financial literacy capacity.
2.6 Moderation of Intellectual
Intelligence on the Effect of Fintech
Innovation on Women's Financial
Literacy Capacity
Fintech includes many innovative technology-based
financial services, fintech innovation makes the
financial system grow better and affects all financial
aspects including financial literacy capacity (Huarng
& Yu, 2022). Fintech innovation provides efficiency
for all users, especially in the current digital era
(Yang & Wang, 2022). In addition, after the
convenience provided by fintech to its users, a risk
will be created, understanding the risks needs to be
known so that payments with fintech can still take
ISCP UTA’45 Jakarta 2022 - International Seminar and Call for Paper Universitas 17 Agustus 1945 Jakarta
24

place more securely, therefore each individual must
use his intelligence to know the risks of fintech (Xia
et al. ., 2022). By the previous research statement and
the arguments above, hypothesis H5 is determined:
Intellectual intelligence has the potential to influence
and moderate the influence of fintech innovation on
women's financial literacy capacity.
3 METHODS
This study used research samples from women with a
selected sample of 425 female respondents in
Indonesia. 15 variable indicators studied in this study.
There are four variables in this study. First, the fintech
transformation variable is an independent variable.
Fintech transformation is a large-scale digital
transformation of most economic sectors, especially
in the financial sector by being able to produce
software, web, and financial services that are the
gateway to the industrial revolution. The fintech
transformation variable consists of three indicators,
namely technology that accelerates and facilitates
transaction processes, technology that provides
functionality for users, and technology that provides
flexibility for users. (Barroso & Laborda, 2022).
Second, is the fintech innovation variable. Fintech
innovation is a financial technology innovation that
has been present in the financial world and has
spurred transactions to become more cashless and
provide high-efficiency values for the business world.
The fintech innovation variable consists of five
indicators, namely maintaining monetary stability,
maintaining financial system stability, efficient
payment system, smooth payment system, and secure
payment system. (Zhao et al., 2022). Third, the
variable of women's financial literacy capacity is the
dependent variable. Financial literacy can be
interpreted as skills or abilities in terms of managing
finances, women who aspire to be prosperous, happy,
and independent, must increase their capacity in
managing finances so that their future is as expected.
The financial literacy variable consists of four
indicators, namely the ability to read finance, analyze
finances, manage finances, and communicate about
personal financial conditions that affect material
welfare. (Darriet et al., 2021). Fourth, the intellectual
intelligence variable is a moderating variable.
Intellectual intelligence is a person's ability to explain
basic abilities, such as the ability to reason, plan,
solve problems, think abstractly, understand ideas,
use language, capture power, and learn. The
intellectual intelligence variable consists of three
indicators, namely figure ability, verbal ability, and
numerical ability (Mulatningsih et al., 2022). The
data for this study were taken using the statements in
the questionnaire in Google Form that uses a Likert
scale of 1 to 5. All statements in the research
questionnaire follow the indicators of each variable
being studied. Respondents' answers collected were
recapitulated to be analyzed using partial least
squares structural equation (PLS-SEM). The
SmartPLS (Partial Least Square) software that is used
to prove the hypothesis of this study uses the
bootstrapping method. The PLS-SEM analysis
consists of two sub-models, namely the measurement
model or outer model and the structural model or
inner model. The outer model test uses the MultiTrait-
MultiMethod or MTMM approach by testing the
convergent and discriminant validity. While the
reliability test was carried out in two ways, namely
with Cronbach's Alpha and Construct Reliability
(Hair & Alamer, 2022). Convergent Validity value >
70 is considered high, a loading factor value of 0.50
to 0.60 is interpreted as still acceptable (Hair &
Alamer, 2022). Discriminant validity, which is
comparing the square root of the average variance
extracted (√AVE), AVE > 0.50 is considered good
(Hair & Alamer, 2022). Reliability test is declared
reliable if the value of construct reliability and
Cronbach alpha > 0.70 (Hair & Alamer, 2022). Test
structural models or inner models in showing the
relationship or strength of estimates between latent
variables or constructs based on substantive theory.
Reliability is measured using 3 criteria, namely R-
Square, F-Square, and Estimate for Path Coefficients.
R-Square which is the goodness-fit test of the model,
if the R-Square value is 0.75, it is considered that the
model is strong, 0.50 is considered to be a moderate
model and 0.25 is considered to be a weak model
(Golzarri-Arroyo et al., 2022). If the F-square value
of 0.02 is interpreted as having a weak influence on
the latent variable, 0.15 is interpreted as having a
medium effect on the latent variable and 0.35 is
interpreted as having a large weak influence on the
structural level (Golzarri-Arroyo et al., 2022).
Estimate For Path Coefficients looks at the
significance of the effect between variables by
looking at the parameter coefficient values and the T
statistical significance value, namely through the
bootstrapping method (Golzarri-Arroyo et al., 2022).
Intellectual Intelligence Moderation on the Influence of Fintech Transformation and Fintech Innovation on Women’s Financial Literacy
Capacity
25
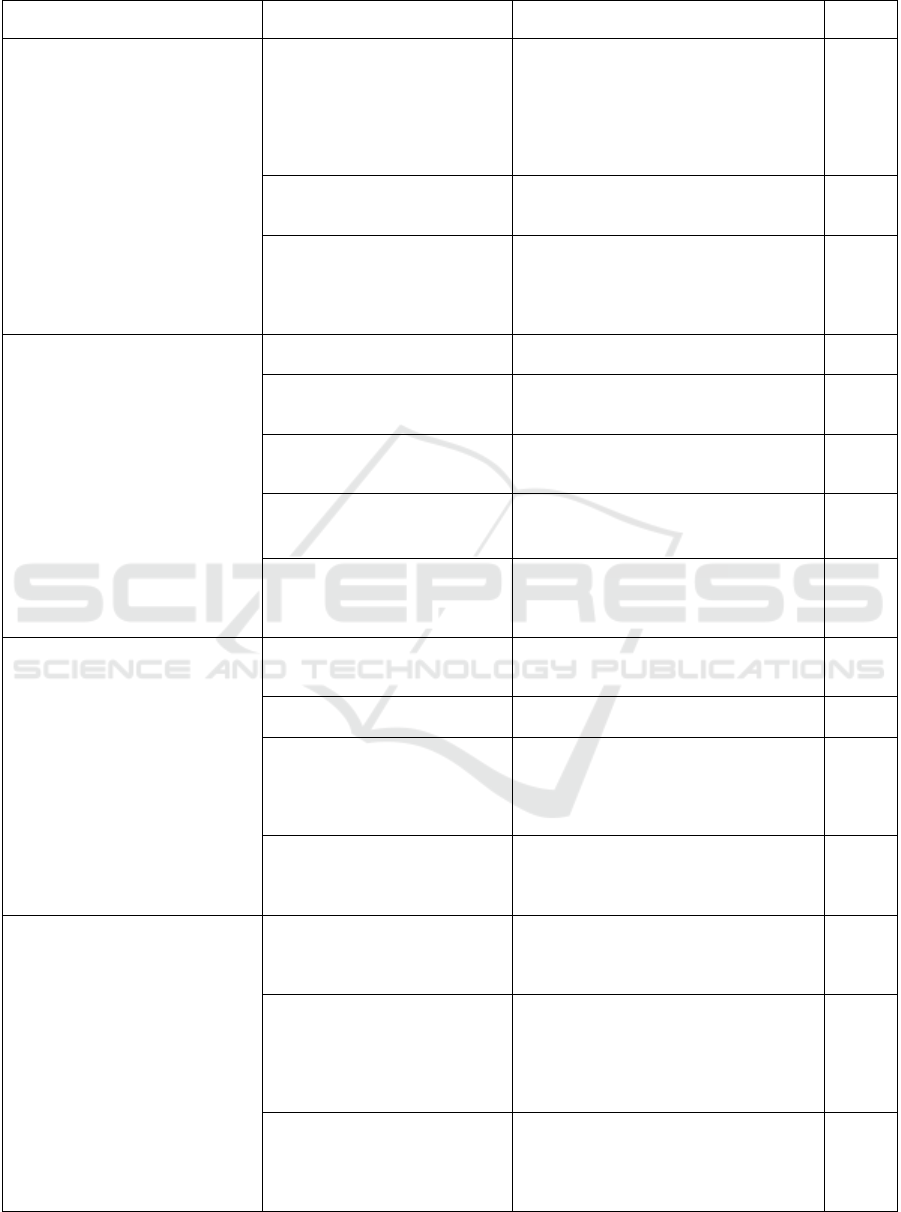
Table 1: Operationalization of Research Variables.
Variable Indicator Rating Size Items
Fintech Transformation (X1)
Financial technology
transformation is a large-scale
digital transformation of most
economic sectors, especially in the
financial sector by being able to
produce software, web, and
financial services that are the
gateway to the industrial revolution
(Barroso & Laborda, 2022).
Technology that speeds up and
facilitates the transaction process
1. fintech transformation has
accelerated and simplified your financial
transactions.
2. Fintech transformation helps you
become more efficient and economical in
terms of buying and selling transactions
and payment systems.
1
2
Technology that provides
functionality for its users
1. With the fintech transformation, it
helps you to maximize the business you
have.
3
Technology that provides
flexibility for users
1. flexibility of fintech makes it easier
for you to run a business.
2. The use of technology, software, and
data collected by fintech can be used as
p
art of a risk analysis of your business.
4
5
Fintech Innovation (X2)
Financial technology innovation is
a financial technology innovation
that has been present in the
financial world and has spurred
transactions to become more
cashless and provide high-
efficiency values for the business
world (Zhao et al., 2022).
Maintaining monetary stability
1. Fintech innovations have made your
financial system better and more stable.
6
Maintaining financial system
stability
1. Innovation in fintech makes your
financial system grows sustainably on an
ongoing basis.
7
Efficient payment system 1. Innovation in fintech makes your
financial system grows sustainably and
stably on an ongoing basis.
8
Smooth payment system
1. With fintech innovation, you feel
that financial transactions can be carried
out more smoothly.
9
secure payment system 1. With fintech innovation in the
disruptive era, it will have a good impact
on you because financial technology is
safer.
10
Women's Financial Literacy
Capacity (Y)
Financial literacy can be
interpreted as skills or abilities in
terms of managing finances,
women who aspire to be
prosperous, happy, and
independent, must increase their
capacity in managing finances so
that their future is as expected
(Darriet et al., 2021).
Financial reading skills. 1. As a woman you can read finances
intelligently, wisely, and reliably in,
managing
f
inances.
11
Analyzing finances. 1. You can analyze or check the
financial health you have.
12
Manage finances. 1. Before managing finances, you have
learned how to manage finances properly
and correctly.
2. You can manage finances well to
financial welfare goals.
13
14
Communicate about personal
financial conditions that affect
material well-being.
1. At the end of every month you
always evaluate your financial statements
for that month so that your financial
condition is guaranteed to be stable.
15
Intellectual intelligence (Z)
Intellectual intelligence is a
person's ability to explain basic
abilities, such as the ability to
reason, plan, solve problems, think
abstractly, understand ideas, use
language, capture power, and learn.
(Mulatningsih et al., 2022). .
Figure ability. 1. It is very important and necessary for
you to equip yourself with financial
literacy, especially related to critical
reasoning skills to avoid forms of fraud.
16
Verbal ability. 1. You can analyze if there are
problems with the financial statements you
have.
2. Verbally you can read financial
statements either personal or belonging to
the organization.
17
18
Numerical ability. 1. You can read the data in the financial
statements carefully.
2. You can calculate quickly and
precisely calculate the financial statements
you have.
19
20
ISCP UTA’45 Jakarta 2022 - International Seminar and Call for Paper Universitas 17 Agustus 1945 Jakarta
26
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The results of the data in this study were obtained
from questionnaires distributed to respondents using
Google Forms. The questionnaire in this study
contains statement items related to research variables
as shown in Table 1. Operationalization of Research
Variable. The sample in this study used as many as
425 respondents among women in Indonesia. The
criteria for respondents with a minimum age of 18
years with the latest education, among others consist
of SMA/K which are filled by 29.3% women,
Diploma is filled by women as many as 13.9%
women, Strata 1 is filled by women as many as 53.1%
women, and from Strata 2 the rest is filled by 3.7%
women. The descriptive statistics of the respondents'
answers are presented as follows:
Table 2: Descriptive Statistics.
Variables N Min Max Mean
Std.
Deviation
FT 425 3.00 5.00 4.3948 0.71234
FI 425 3.00 5.00 4.4113 0.70461
WFLC 425 3.00 5.00 4.4334 0.72079
II 425 3.00 5.00 4.4612 0.69759
Source: SPSS Statistics Processed Data
The results of descriptive statistics can be
explained by the achievement of each variable. First,
fintech transformation has a minimum value of 3.00,
a maximum of 5.00, and a mean of 4.3948. The mean
value of 4.3948 out of a maximum of 5 indicates that
the achievement of this fintech transformation is
87.90%. The average score for fintech transformation
is the lowest among the four variables. Both fintech
innovations have a minimum value of 3.00, a
maximum of 5.00, and a mean of 4.4113. The mean
value of 4.4113 out of a maximum of 5 indicates that
the achievement of this fintech innovation is 88.23%.
The three women's financial literacy capacity has a
minimum value of 3.00, a maximum of 5.00, and a
mean of 4.4334. The mean value of 4.4334 out of a
maximum of 5 indicates that the achievement of
women's financial literacy capacity is 88.67%. The
four intellectual intelligence have a min value of 3.00,
a max of 5.00, and a mean of 4.4612. This mean score
is the highest among the other four variables. The
mean value of 4.4612 out of a maximum of 5
indicates that this intellectual intelligence
achievement is 89.22%.
The data quality test in this study used partial least
squares (PLS-SEM) structural equation modeling. By
using software SmartPLS (Partial Least Square). The
reliability value for all variables tested with Rho,
Cronbach's Alpha and Construct Reliability results >
0.70, which means that the reliability test is declared
to meet the criteria with a high value. The average
variance extract (√AVE) value to test the validity has
a result > 50, which means the validity test is
acceptable and considered good. The inner model test
which is measured using 3 criteria, namely R-Square,
F-Square, and Estimate for Path Coefficients has
results for the R-Square value of the dependent
variable of women's financial literacy capacity of
0.94 so that it can be interpreted that the R-Square
value is in the category strong. The F-Square value
for the moderating intellectual intelligent variable is
0.63. It can be concluded that the intellectual
intelligent variable has a moderate influence on the
structural level. The variable loading factor value for
each construct > 0.5 can be interpreted as all valid
data. The results of Estimate for Path Coefficients
used to see the significance of the influence between
variables have significant results for all hypothesis
testing. The following are the results of testing the
research hypothesis:
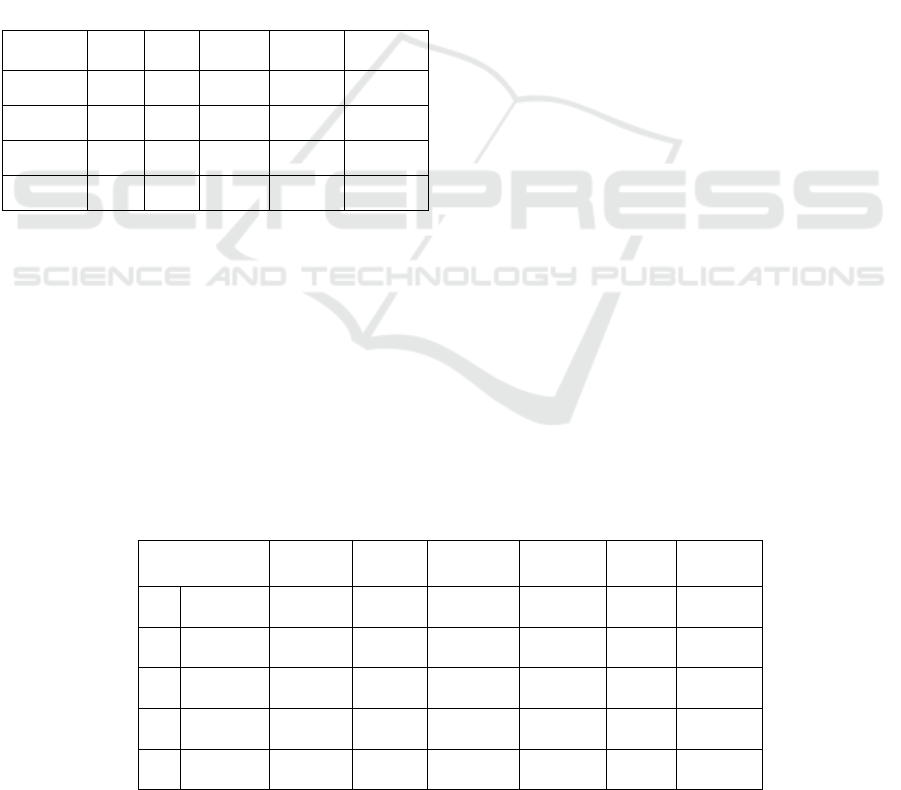
Table 3: Hypothesis testing.
Hypothesis
Original
Sample
Sample
Mean
Standard
Deviation
T
Statistics
P
Values
Decision
H1
FT
WFLC
0.256 0.264 0.066 3,909 0.000 Accepted
H2
FI
WFLC
0.106 0.105 0.052 2.036 0.021 Accepted
H3
II
WFLC
0.589 0.582 0.074 8,010 0.000 Accepted
H4
II * FT
WFLC
0.191 0.193 0.054 3,521 0.000 Accepted
H5
II * FI
WFLC
0.153 0.156 0.052 2,955 0.002 Accepted
Source: SmartPLS Processed Data
Intellectual Intelligence Moderation on the Influence of Fintech Transformation and Fintech Innovation on Women’s Financial Literacy
Capacity
27

ISCP UTA’45 Jakarta 2022 - International Seminar and Call for Paper Universitas 17 Agustus 1945 Jakarta
28

From the results of the hypothesis testing, it can
be described as follows. Evidence of the first
hypothesis, fintech transformation has a significant
effect on women's financial literacy capacity. With
the existence of fintech transformation, it can help
make it easier for women to use digital payment tools
and platforms. The convenience created by fintech
transformation can increase financial literacy
capacity, especially for women. The evidence of this
study supports and complements previous research
conducted by Prete, (2022), Zarifis & Cheng, (2022),
and Lyons et al., (2022). Thus, based on the analysis
and research test results, it can be concluded that
hypothesis H1: Fintech transformation has a
significant effect on women's financial literacy
capacity. Evidence of the second hypothesis, fintech
innovation has a positive effect on women's financial
literacy capacity. With individual fintech
innovations, they will be introduced to safer and more
effective payment modes. Fintech innovation is
believed to be able to increase profit potential in the
financial sector and encourage economic growth in
every country and can increase financial literacy
capacity, especially for women. This research
evidence supports and complements previous
research conducted by Ioannou & Wójcik, (2022),
Sun & Tang, (2022), and Tay et al., 2022). Thus,
based on the analysis and research test results, it can
be concluded that hypothesis H2: Fintech innovation
has a significant effect on women's financial literacy
capacity. Proving the third hypothesis, intellectual
intelligence has a positive effect on women's financial
literacy capacity. Women with high intellectual
intelligence will be able to keep up with the times, one
of which is by being able to use digital financial
services that will make transactions easier. The
intelligence possessed by women in terms of finance
can increase the capacity for financial literacy and
financial inclusion. The evidence of this study
supports and complements previous research
conducted by Lin & Bates, (2022), Martins et al.,
(2022), and Schoofs, (2022). Thus, based on the
analysis and research test results, it can be concluded
that hypothesis H3: Intellectual intelligence has a
significant effect on women's financial literacy
capacity. Proving the fourth hypothesis, intellectual
intelligence has a significant and moderate effect on
the influence of fintech transformation on women's
financial literacy capacity. Individuals with a high
level of intellectual intelligence have a greater
potential in using fintech which will make it easier for
individuals to transact anywhere and anytime. The
convenience provided by the fintech transformation
can increase women's financial literacy capacity. The
evidence of this study supports and complements
previous research conducted by Isaia & Oggero,
(2022), Sumardi et al., (2022), and Karim et al.,
(2022). Thus, based on the analysis and research test
results, it can be concluded that hypothesis H4:
Intellectual intelligence has a positive effect and can
moderate the influence of fintech transformation on
women's financial literacy capacity. Proving the fifth
hypothesis, intellectual intelligence has a significant
and moderate effect on the influence of fintech
innovation on women's financial literacy capacity.
The existence of fintech innovation provides
efficiency for every individual, fintech innovation can
make the financial system grow better and affect all
financial aspects including financial literacy capacity,
in addition to the convenience provided by fintech to
its users there will be risks that arise, these risks can
be minimized with intelligence owned by the
individual. The evidence of this study supports and
complements previous research conducted by
Hzuarng & Yu, (2022), Yang & Wang, (2022), and
Xia et al., (2022). Thus, based on the analysis and
research test results, it can be concluded that
hypothesis H5: Intellectual intelligence has a positive
effect and can moderate the influence of fintech
innovation on women's financial literacy capacity.
5 CONCLUSION
This study provides empirical evidence regarding the
effect of fintech transformation and fintech
innovation on women's financial literacy capacity
with intellectual intelligence as a moderating
variable. The results of the research in this article
indicate that the transformation of fintech has a
positive effect on women's financial literacy capacity.
Where fintech transformation creates convenience for
individuals, especially women, in digitally
transacting, the convenience created by fintech
transformation has a significant effect on women's
financial literacy capacity. Fintech innovation has a
significant effect on women's financial literacy
capacity. Innovation fintech provides convenience by
adopting cashless payments that provide a safer mode
of payment for individuals, the ease of digital
transactions has a significant influence on women's
financial literacy capacity. Intellectual intelligence
has a significant effect on women's financial literacy
capacity. An individual with high intellectual
intelligence can minimize every risk, one of which is
the risk of digitally transacting through fintech.
Intellectual intelligence possessed in terms of finance
can influence the capacity of financial literacy to be
Intellectual Intelligence Moderation on the Influence of Fintech Transformation and Fintech Innovation on Women’s Financial Literacy
Capacity
29

better. Moderation of intellectual intelligence can
strengthen the influence of fintech transformation on
women's financial literacy capacity. Individuals with
high intellectual intelligence can follow the
transformation in the current digital era, one of which
is the fintech transformation as well as possible.
Fintech transformation moderated by intellectual
intelligence will have a significant effect on women's
financial literacy capacity. In addition, intellectual
intelligence can strengthen the influence of fintech
innovation on women's financial literacy capacity.
Individuals who have intellectual intelligence can
take advantage of the efficiency created by fintech
innovation, one of which is cashless, individuals will
be facilitated by digital payments anywhere and
anytime. With fintech innovation moderated by
intellectual intelligence, it will have a significant
effect on women's financial literacy capacity. The
results of this study recommend for women that
fintech transformation and fintech innovation can
facilitate women in terms of finance, digital
transactions make financial activities more effective
and efficient, in addition to the convenience provided
by fintech women must have intellectual intelligence
to minimize the risks that may occur from fintech, and
with intellectual intelligence, women are expected to
be able to use fintech as well as possible. There is
fintech transformation and fintech innovation
moderated by intellectual intelligence are believed to
be able to help increase the capacity of financial
literacy and financial inclusion for women in
Indonesia.
In designing and developing this research, there
are still many limitations that still need to be
improved. The limitation of this research is that the
number of respondents who become the sample is
very limited.
For further researchers, the utilization of the
fintech variable can be added as an independent
variable to complete the model that affects women's
financial literacy capacity. Because the utilization of
fintech can encourage the flow of economic turnover
in the digital financial sector to be faster and more
practical. This will affect women's financial literacy
capacity. Therefore, by looking at the utilization of
fintech as an independent variable, the effect will
strengthen the influence of fintech transformation and
fintech innovation on women's financial literacy
capacity. Women will be able to increase their
financial literacy capacity if they have adequate
intellectual intelligence regarding the utilization of
fintech.
REFERENCES
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior.
Organizational Behavior and Human Decision
Processes, 50(2), 179–211.
https://doi.org/10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-T
APJI. (2022). Hasil Survey Profil Internet Indonesia 2022.
Apji.or.Od, June. apji.or.id
Barroso, M., & Laborda, J. (2022). Digital transformation
and the emergence of the Fintech sector: Systematic
literature review. Digital Business, 2(2), 100028.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.digbus.2022.100028
Darriet, E., Guille, M., & Vergnaud, J.-C. (2021). Financial
literacy and numeracy. The Routledge Handbook of
Financial Literacy, December, 96–109.
https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003025221-10
Davis, F. D. (1985). A technology acceptance model for
empirically testing new end-user information systems:
Theory and results. Management, Ph.D.(January 1985),
291. https://doi.org/oclc/56932490
Golzarri-Arroyo, L., Dickinson, S. L., Jamshidi-Naeini, Y.,
Zoh, R. S., Brown, A. W., Owora, A. H., Li, P., Oakes,
J. M., & Allison, D. B. (2022). Evaluation of the type I
error rate when using parametric bootstrap analysis of a
cluster randomized controlled trial with binary
outcomes and a small number of clusters. Computer
Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 215, 106654.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.106654
Hair, J., & Alamer, A. (2022). Research Methods in
Applied Linguistics Partial Least Squares Structural
Equation Modeling ( PLS-SEM ) in second language
and education research : Guidelines using an applied
example. Research Methods in Applied Linguistics,
1(3), 100027.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmal.2022.100027
Huarng, K.-H., & Yu, T. H.-K. (2022). Causal complexity
analysis for fintech adoption at the country level.
Journal of Business Research, 153, 228–234.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.08.030
IInternational Telecomunication Union Development
sector. (2022). Global Connectivity Report 2022.
Ioannou, S., & Wójcik, D. (2022). The limits to FinTech
unveiled by the financial geography of Latin America.
Geoforum, 128, 57–67.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoforum.2021.11.020
Isaia, E., & Oggero, N. (2022). The potential use of robo-
advisors among the young generation: Evidence from
Italy. Finance Research Letters, 103046.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.frl.2022.103046
Karim, S., Naz, F., Naeem, M. A., & Vigne, S. A. (2022).
Is FinTech providing effective solutions to Small and
Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in ASEAN countries?
Economic Analysis and Policy.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2022.05.019
Lin, C. A., & Bates, T. C. (2022). Smart people know how
the economy works: Cognitive ability, economic
knowledge and financial literacy. Intelligence,
93(June), 101667.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2022.101667
ISCP UTA’45 Jakarta 2022 - International Seminar and Call for Paper Universitas 17 Agustus 1945 Jakarta
30

Luo, S., Sun, Y., & Zhou, R. (2022). Can fintech innovation
promote household consumption? Evidence from China
family panel studies. International Review of Financial
Analysis, 82(October 2021), 102137.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irfa.2022.102137
Lyons, A. C., Kass-Hanna, J., & Fava, A. (2022). Fintech
development and savings, borrowing, and remittances:
A comparative study of emerging economies. Emerging
Markets Review, 51, 100842.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ememar.2021.100842
Martins, A., Madaleno, M., & Ferreira Dias, M. (2022). Are
the energy literacy, financial knowledge, and education
level faces of the same coin? Energy Reports, 8, 172–
178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2022.01.082
Mulatningsih, M., Indartono, S., & Efendi, R. (2022). The
Effect of Emotional Intelligence and Intellectual
Intelligence on Student Discipline. International
Journal of Multicultural and Multireligious
Understanding, 9(3), 10–16.
https://doi.org/10.18415/ijmmu.v9i3.3449
Otoritas Jasa Keuangan. (2019). Survei Nasional Literasi
dan Inklusi Keuangan Indonesia 2019. Survey Report,
1–26. www.ojk.go.id
Prete, A. Lo. (2022). Digital and financial literacy as
determinants of digital payments and personal finance.
Economics Letters, 213, 110378.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econlet.2022.110378
Schoofs, A. (2022). Promoting financial inclusion for
savings groups: A financial education programme in
rural Rwanda. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental
Finance, 34, 100662.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbef.2022.100662
Sumardi, Azizah, U. S. Al, Mulyono, H., & Suryana, A. M.
(2022). The determinants of willingness to
continuously use financial technology among
university students: Dataset from a private university in
Indonesia. Data in Brief, 44, 108521.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2022.108521
Sun, Y., & Tang, X. (2022). The impact of digital inclusive
finance on sustainable economic growth in China.
Finance Research Letters, 50, 103234.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.frl.2022.103234
Tay, L. Y., Tai, H. T., & Tan, G. S. (2022). Digital financial
inclusion: A gateway to sustainable development.
Heliyon, 8(6), e09766.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09766
Xia, H., Wang, Y., Gauthier, J., & Zhang, J. Z. (2022).
Knowledge graph of mobile payment platforms based
on deep learning: Risk analysis and policy implications.
Expert Systems with Applications, 208, 118143.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.118143
Yang, L., & Wang, S. (2022). Do fintech applications
promote regional innovation efficiency? Empirical
evidence from China. Socio-Economic Planning
Sciences, 101258.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seps.2022.101258
Zarifis, A., & Cheng, X. (2022). A model of trust in Fintech
and trust in Insurtech: How Artificial Intelligence and
the context influence it. Journal of Behavioral and
Experimental Finance, 100739.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbef.2022.100739
Zhao, J., Li, X., Yu, C.-H., Chen, S., & Lee, C.-C. (2022).
Riding the FinTech innovation wave: FinTech, patents
and bank performance. Journal of International Money
and Finance, 122, 102552.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jimonfin.2021.102552
Intellectual Intelligence Moderation on the Influence of Fintech Transformation and Fintech Innovation on Women’s Financial Literacy
Capacity
31
