
Research on the Teaching Evaluation System of Art Courses
Lijun Shi
1,2
1
Universiti Putra Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
2
Yunnan College of Business Management, Kunming, China
Keywords: Art Majors, Curriculum Teaching, Evaluation System.
Abstract: Aiming at the characteristics of solid subjectivity in the evaluation of student performance of art course
teaching, this study introduces the concept of a quantitative assessment of art courses, decomposes
evaluation indexes, incorporates learning process evaluation and teaching results assessment into the
complete assessment and evaluation system, constructs the design model of teaching evaluation system of
art courses to analyze the case; evaluates the teaching effect of methods through the analysis of the
achievement of course objectives, to promote teaching activities and promote the cultivation of applied
talents.
1 INTRODUCTION
Art majors have the characteristics of solid
application and practice. The course teaching
evaluation has a significant role in the construction
of the curriculum system of art design majors, which
serves as an essential link to measure the teaching
results of the course. Teachers should grasp the
traditional classroom teaching class and the practical
teaching with the project-based carrier in the course
evaluation to promote the healthy, rational, and
sustainable development of art design majors and
improve its role in the new The position of
innovative composite talents training quality (Song
2010). As an essential part of course teaching, the
course evaluation system supervises teaching and
learning, improves the overall quality of classroom
teaching in continuous evaluation and correction,
and achieves the effect of mutual promotion of
education and evaluation. The school academic
affairs office or the corresponding teaching
management department can use the assessment to
understand the teaching situation of teachers and
students and then carry out the evaluation of the
teaching effect and reasonably propose the
personnel training program (Jiang 2015).
2 THE CURRENT SITUATION
AND PROBLEMS OF THE
CURRENT ART COURSE
EVALUATION SYSTEM
2.1 Single Form of Examination
Method
The traditional way of examination is usually
conducted by submitting works at the end of the
period, which is a single form of analysis. Artistic
creation takes a certain amount of time to take
shape. The progress of artistic level is a gradual
process; not a single score can indicate the level of
learning, and the artwork itself has no uniform
answer and is difficult to quantify (Long 2009).
Therefore, the assessment form of scoring based on
a single work is too homogeneous.
2.2 Focus on Results, Not Process
The traditional teaching course evaluation is through
the final works provided by students and scored.
This way can't reflect the students' design level and
can't make a comprehensive judgment on the
students' progress and complete quality
improvement. Therefore, this evaluation method is
not exhaustive, and art and design majors emphasize
the process of learning, which needs to be advanced
gradually. Teachers should train and exercise
20
Shi, L.
Research on the Teaching Evaluation System of Art Courses.
DOI: 10.5220/0011897400003613
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education (NMDME 2022), pages 20-25
ISBN: 978-989-758-630-9
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

students in a targeted manner according to their
foundation and characteristics and make a
comprehensive evaluation of student's learning in
the learning process to see their progress and
improvement to evaluate their learning objectively.
Therefore, we should focus on the overall
assessment of student's learning process and include
students' learning, progress, and development and
students' attitude, ability, and character in the
general evaluation.
2.3 Teacher Evaluation, Single
Evaluation Subject
Teachers usually give corresponding evaluation
scores to students' assignments or works in
traditional art teaching evaluation. Such unilateral
evaluation is often too subjective. Teachers'
preferences and impressions of students will affect
the evaluation results, and even teachers' moods at
the time of assessment will involve the evaluation
scores. Moreover, each teacher's learning
experience, knowledge background, mastery of the
profession, and understanding of design will be
different, and their knowledge of the same work will
be further. Therefore, relying solely on the class
teacher as the subject of evaluation is too
homogeneous. When teachers encounter two similar
or similar results, they often hesitate and are likely
to intervene in the end to give emotional scores.
Such teachers' subjective judgment will inevitably
become the primary criterion for evaluating students'
performance, resulting in the evaluation results
relying too much on the teacher's subjectivity in
charge of the class.
3 IDEAS FOR THE STUDY OF
THE COURSE EVALUATION
SYSTEM
According to the teaching process and results and
the characteristics of the subject curriculum system,
we put the leading focus indicators of art and design
on teaching system setting, the content of teaching
goal setting, teaching effect and course teaching
management, and innovation of teaching results.
3.1 Evaluation Setting of Teaching
Goal Concerns Professional
Courses
The focus is first to observe whether the course
teaching objectives are clear, whether the design of
its course teaching objectives can support the
objectives of talent training, and the relevance of the
course teaching objectives and talent training.
3.2 Assessment Design of Teaching
System Concerns for Major Art
Courses
The problems of the course teaching system include
the conditions of course teaching resources, teaching
content setting, teaching methods, and assessment
and evaluation methods (Lv 2017). The course
teaching content framework is clear, the module
objectives are clear, the modules are closely
connected, and they are properly set up with the
previous and subsequent courses. The latest research
results of professional development and professional
development requirements can be introduced into
the teaching design in time. The practical teaching
content system of art design practice teaching is also
an aspect of the mandatory assessment of the
curriculum teaching system setting. This module
should reflect the results and skip the process of
student participation (Xu 2009).
3.3 Course Teaching Management and
Evaluation Design of Teaching
Effectiveness Observation Points
The observation points of course teaching
management and teaching effectiveness include
course management, evaluation of teaching
effectiveness, and teaching file management. The
observation of course management is refined to
whether there is a detailed plan for course
management and whether diverse methods can be
adapted to monitor the process and achieve excellent
quality, not only limited to classroom teaching
management. The evaluation of teaching effect
includes student evaluation, process evaluation, and
course result evaluation. Art and design courses will
directly produce some visual teaching results,
mainly from two aspects of the assessment: the
course teaching results based on the organization,
planning, counseling students to participate in the
corresponding professional competitions students
won high-level awards and the promotion of the
Research on the Teaching Evaluation System of Art Courses
21

course exhibition and other professional media
reports (Li 2018).
3.4 Establishment and Observation of
Art and Design Course Evaluation
Observation Index System
To establish a curriculum evaluation system, we
must first memorize the thinking of evaluating the
observation indicators. Secondly, we must also
consider the load-bearing and connection of the
evaluation and evaluation indicators. We have
assigned weights to each hand: the importance of the
teaching goal design is 10%, and the importance of
the curriculum teaching system design. 50%,
teaching management and teaching effect weight
20%, teaching achievement characteristic item
weight 20%. The implementation of the observation
of the curriculum evaluation system must also have
evaluation committees with a reasonable structure.
We choose a high-level, cross-border diverse team in
terms of committee composition. This evaluation
system promotes curriculum construction in art and
design curriculum construction and teaching and
establishes its unique brand effect (Bi 2016).
4 DESIGN MODEL OF
TEACHING EVALUATION
SYSTEM FOR ART COURSES
4.1 Art Course Teaching Evaluation
Methods
Evaluation of course goal attainment can be based
on a comprehensive evaluation method according to
the characteristics of the course, which can be based
on both direct evaluation and indirect evaluation
(Yao, 2015). Direct evaluation methods include, but
are not limited to, standardized exams,
non-standardized exams, midterm exams, process
assessments, learning portfolios, and other methods.
Indirect evaluation methods include, but are not
limited to, self-evaluation, student evaluation, peer
evaluation, a supervisory evaluation, interviews,
questionnaires, and feedback from students on
achievement evaluation at the end of the semester
(Zhao 2014).
The indirect evaluation process can collect
students' opinions and suggestions on the course in
the form of midterm talks and faculty talks; use
multiple evaluation methods such as supervisory
evaluation + peer evaluation + student evaluation +
self-evaluation to monitor and evaluate the course
teaching; conduct a questionnaire survey on the
achievement of course objectives at the end of the
course to give feedback on students' evaluation of
course achievement.
4.2 The Weight Distribution of
Teaching Evaluation of Art
Courses
A combination of direct and indirect assessment can
be used, with immediate evaluation accounting for
70-100% and indirect evaluation accounting for
0-30%, and the proportion can be adjusted
appropriately according to the characteristics of the
course.
4.3 Separate Use of Direct Evaluation
The direct evaluation of the achievement of course
objectives should include at least two categories of
process assessment and standard tests. Process
assessment includes but is not limited to course
attendance, extra-curricular assignments, practical
training, classroom performance, group cooperative
learning effects, course mini-papers, etc.; standard
tests are conducted according to the assessment
methods specified in the course syllabus, such as
final exam results, midterm exams, unit tests,
reading reports, lab reports, etc.
5 DESIGN MODEL AND A CASE
OF TEACHING EVALUATION
SYSTEM OF ART COURSES
5.1 Course Objective Weighting
The calculation method of target weights should be
combined with the support relationship of course
objectives to graduation requirements. If the course
objectives play a strong support role to the
achievement of the corresponding graduation
requirements, make its support intensity value 1.0; if
the course objectives play a medium support role,
make its support intensity value 0.5; if the course
objectives play a weak support role, make its
support intensity value 0.2. After normalization, the
weight of each course objective is obtained, which
indicates the importance of each course objective to
the achievement of graduation requirements and is
used to calculate the overall achievement value of
the course for the evaluation of graduation
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
22
requirements. Suppose there are 3-course objectives
in a system, and the weight of each course objective
is M1, M2, and M3.
5.2 Calculation of the Degree of
Achievement of Course Objectives
The course objectives are designed with a full score
of 100, and the expectations of all items in the
assessment session are 100. Assuming that the final
work in course objective one accounts for 60%, the
average student score is A1; the midterm work
accounts for 10%, the average student score is A2;
the stage test accounts for 20%, and the average
student score is A3; the written work accounts for
10%, the average student score is A4, then the
achievement of course objective 1 is
%10%20%10%60
43211
×+×+×+×= AAAAH
Assuming that 20% of the final work in Course
Objective 2, the average student score is B1, 10% of
the midterm work, the average student score is B2,
10% of the stage tests, the average student score is
B3, 50% of the group work, the average student
score is B4, and 10% of the classroom performance,
the average student score is B5, then the
achievement of course objective 2 is
21 234 5
20% 10% 10% 50% 10%HB B B B B=× +× +× +× +×
Assuming that 10% of the classroom performance in
Course Objective 3, the average student score is C1,
60% of the course papers, the average student score
is C2, and 30% of the group learning, the average
student score is C3, then the achievement of Course
Objective 3 is
%30%60%10
3213
×+×+×= CCCH
Total goal achievement:
332211
HMHMHMH ×+×+×=
A course goal attainment score above 60
indicates that the course goal was effectively
achieved.
5.3 Case Study of Teaching Evaluation
of Art Courses
A. Examples of major art courses
According to the condition of a school art major
to confer a degree, the goal achievement standard
was determined to be 60 or more, and the
comparison of the results of the goal achievement
evaluation and the actual score of course
achievement with the standard value of each course
of the established assessment system is shown in
Figure 1 below. To further analyze the students'
learning achievement, the results of the course goal
1 achievement distribution chart are shown in Figure
2 below, the results of the course goal 2 achievement
distribution chart are shown in Figure 3 below, and
the results of the course goal 3 achievement
distribution chart are shown in Figure 4 below.
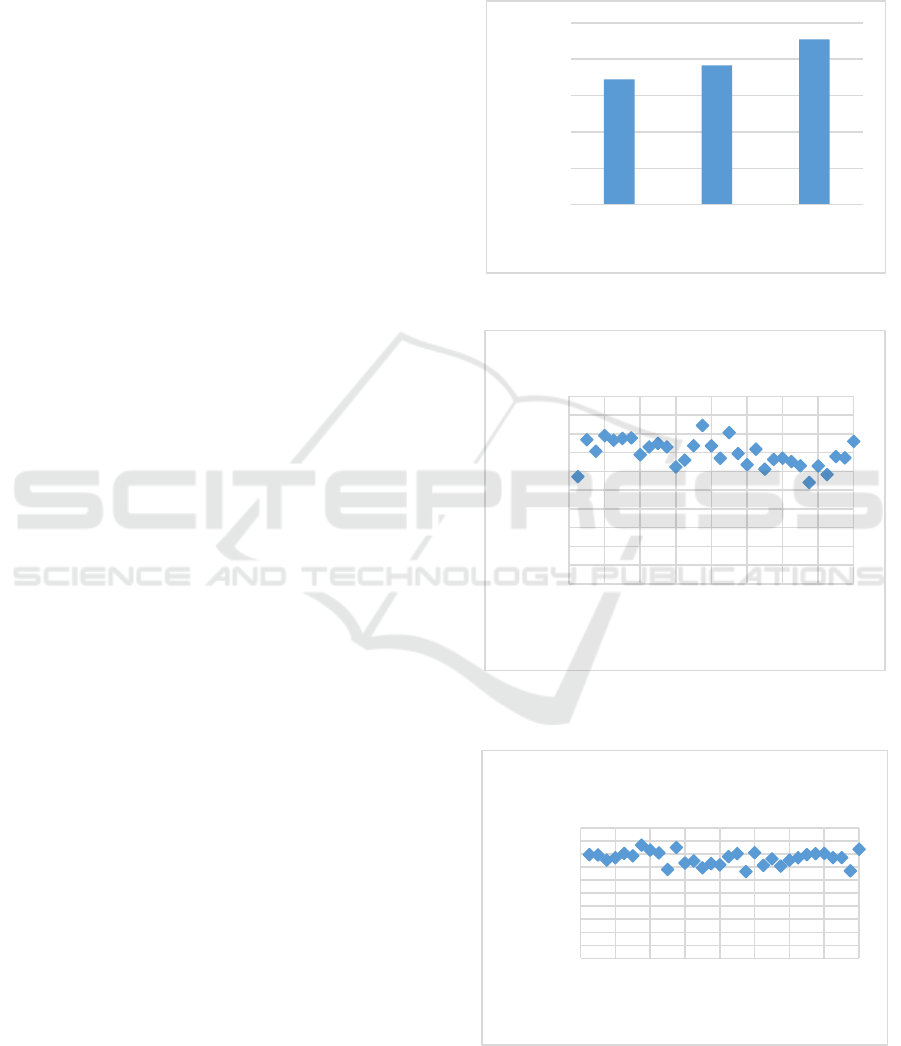
Figure 1 achievement degree of curriculum objectives
Figure 2 distribution of students' achievement of course
objective 1 in art design class
Figure 3 distribution of students' achievement of course
objective 2 in art design class
68,90
76,61
91,03
0,00
20,00
40,00
60,00
80,00
100,00
course
objective 1
course
objective 2
course
objective 3
0,00
10,00
20,00
30,00
40,00
50,00
60,00
70,00
80,00
90,00
100,00
0 4 8 121620242832
SERIAL NUMBER
COURSE OBJECTIVE 1
0,00
10,00
20,00
30,00
40,00
50,00
60,00
70,00
80,00
90,00
100,00
0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32
SERIAL NUMBER
COURSE OBJECTIVE 2
Research on the Teaching Evaluation System of Art Courses
23

Figure 4 distribution of students' achievement of course
objective 3 in art design class
Course Objective 1 corresponds to the
Knowledge Objective, with an achievement level of
69.90; the standard value was achieved, and it was
basically achieved. Course Objective 2 corresponds
to the Competency Objective, with an achievement
level of 77.61. The achievement level is higher than
the standard value, and the course objectives are
better achieved. Course objective 3 corresponds to
the quality objective, with an attainment rating of
91.09, higher than the standard value, and better
achieves the course objectives. The distribution of
individual evaluations reflects that most students
could complete the standard. For course objective 3,
all students met the middle, and students were
usually actively involved in their studies.
5.4 Evaluation of the Reasonableness
of the Evaluation Results
The scientific rationality of the evaluation method:
In each aspect of teaching, the process evaluation
mainly adopts the combination of works, stage tests,
group learning, classroom performance, and course
paper, but the rationality of the corresponding
scoring criteria needs further optimization. For the
weight setting of the evaluation indexes, the primary
basis is the judgment of the strength of the course
objectives on the support of the graduation
requirement index points, which will have some
influence on the accuracy of the final evaluation
results. From the scores of different evaluation index
items, we can see that the data of test-based items,
such as stage tests, midterm works, and final works,
are relatively objective. In contrast, the data of
non-test things are supplemented to effectively avoid
emphasizing results over process and a single
evaluation subject so that the evaluation results can
generally reflect the achievement of students' course
objectives. The quantitative evaluation has the
accomplishment of knowledge objectives relatively.
It is easy to evaluate the accomplishment of
knowledge objectives, but it is more difficult to
assess the ability and quality objectives accurately.
From the actual evaluation results, the achievement
of course objective three is high, mainly because the
evaluation data of course objective three comes from
subjective evaluation. The assessment increases the
participation of evaluation scoring. It allows the
whole class to participate in scoring to take the
average result, effectively avoiding the influence of
a single subjective evaluation on the development.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND
RECOMMENDATIONS
In this paper, the art course system is changed from
changing the single examination-based evaluation
form to a flexible and diversified evaluation form to
be integrated into the course teaching and play the
role of testing, regulating, supervising, and
motivating. Through the research on the design
mode of the teaching evaluation system of art
courses, the comprehensive evaluation method is
used to study the achievement of course objectives
according to the characteristics of the classes, which
can be based on direct evaluation and indirect
evaluation. The immediate assessment of course
goal achievement includes process assessment and
standard test. The indirect evaluation process
collects students' opinions and suggestions on the
course in mid-term talks and teachers' lectures; uses
various evaluation and assessment modes to monitor
and evaluate the course teaching to decompose the
evaluation index and quantify the assessment.
The design model of the teaching evaluation
system of art courses adopts the calculation method
of target weights, establishes the consequences of
each assessment factor according to the supportive
relationship of course objectives to graduation
requirements, analyzes the situation of course
attainment from the process assessment and
result-based assessment results, combines the
results, of course, objective attainment evaluation
and the comparison between the actual scores of
course attainment and traditional values, and
comprehensively evaluates the effect, of course,
teaching to promote teaching activities and promote
the cultivation of application-oriented talents.
The evaluation link items of the teaching
evaluation system of art courses are not set in stone,
0,00
10,00
20,00
30,00
40,00
50,00
60,00
70,00
80,00
90,00
100,00
0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32
SERIAL NUMBER
COURSE OBJECTIVE 3
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
24

and we can increase and decrease the evaluation
links according to the situation and also adjust the
weights according to the characteristics of the
courses as appropriate so that the evaluation results
are closer to the courses.
REFERENCES
Bi Linlin. A brief discussion on the construction of the
evaluation system of the teaching ability of art
teachers [J]. Times Education,2016(03):111+113. (in
Chinese)
Jiang Dayuan. Basic information about the German
education system [J]. Vocational Education Forum:
2005, (07). (in Chinese)
Long Fang. Research on higher vocational project-based
teaching courses [J]. Science and Technology
Information, 2009, (2):23-25. (in Chinese)
Li Wei. Exploration on the reform of teaching base
construction of digital media art majors [J]. New
Course Research (Midterm Journal), 2018(02):
20-21+29. (in Chinese)
Lv Jiangyin. A school-based study on the implementation
and evaluation of teaching and learning of practical
training courses in secondary preschool education--a
case study of preschool education in Shaoxing Art
School [J]. Literature and Education Materials,
2017(15): 239-240. (in Chinese)
Song Kun. Exploration of the reform of assessment
methods of project-based teaching courses [J]. Science
and Technology Information, 2010, (15): 7-9. (in
Chinese)
Xu Hui. Learner-centered teaching - Five key changes to
teaching practice [M]: Zhejiang University Press,
2006: 94. (in Chinese)
Yao Lu. Research on the design of the teaching paradigm
of imaginative thinking and the evaluation system of
its effect in the course of "Modeling Foundation" in
higher education [J]. Curriculum Education Research,
2015(17):243. (in Chinese)
Zhao Meichuan. Constructing a practical teaching
evaluation system for art design majors in independent
colleges [J]. Times Education, 2014(12): 25-26(in
Chinese)
Research on the Teaching Evaluation System of Art Courses
25
