
Construction of Teacher Performance Evaluation System in Private
Higher Vocational Colleges Based on AHP and Factor Analysis
Wanqing Chen
1
,
Qili Gan
1,*
, Junxia Sun
1
and Yu Wang
2
1
Chongqing Vocational College of Building Technology, Shapingba, Chongqing, 401330, China
2
Chongqing Vocational College of Science and Technology, Dazu, Chongqing, 402360, China
Wanqing Chen, Email: 850425529@qq.cn
Junxia Sun, Email: 773546815@qq.cn
Yu Wang Email: 309341980@qq.cn
Keywords: Private Vocational College, Teachers' Performance, The Performance Evaluation, AHP, Factor Analysis
Method.
Abstract: On the basis of sorting out the related research on teacher performance in private higher vocational colleges,
this paper constructs the teacher performance evaluation system in private higher vocational colleges from
the perspective of teacher ability composition, aiming at the existing problems in the current teacher per-
formance evaluation in private higher vocational colleges. In the selection of indicators of the system, litera-
ture analysis, social research and policy interpretation are adopted to screen out the preliminary evaluation
indicators, which are revised and improved through expert interviews to determine the evaluation indicators.
The importance of each index was scored by questionnaire survey, and the recovered data were analyzed by
SPSS software combined with AHP (analytic hierarchy process) and factor analysis, and the weight of each
index was finally determined.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the Opinions on Promoting the High-quality De-
velopment of Modern Vocational Education, it is
mentioned that the income of vocational schools
through school-enterprise cooperation, technical
services, social training and self-run enterprises can
be used as the source of performance pay in a certain
proportion (Opinions on Promoting the High-quality
Development of Modern Vocational Education,
2021). The implementation of performance evalua-
tion is a general trend, but at present, the perfor-
mance evaluation of private higher vocational col-
leges has some problems, such as lagging evaluation
index, unreasonable setting of index weight, imper-
fect evaluation mechanism, and inconsistent with the
running characteristics of private higher vocational
colleges, which restrict the development of private
higher vocational colleges to a certain extent (North
China University of Water Resources and Electric
Power, 2020). In order to change this situation,
many scholars have conducted researches from mul-
tiple directions and multi-dimensions. Cheng Weiku
(Cheng 2021) constructed the evaluation system
from five dimensions: teacher evaluation orientation,
annual evaluation, teaching quality evaluation meth-
od, professional title evaluation and employment,
and post-employment management. Yang Chunmei
(Yang 2019) constructed an evaluation system from
four dimensions: benefit, stakeholders, teaching
process and teacher learning and growth; Zhang Lu
(Journal of ecological engineering vocational col-
lege, 2014) used analytic hierarchy process (AHP) in
the construction of the system. The system evalua-
tion index constructed by Wang Jihua (Wang 2020)
comes from five aspects: teaching evaluation, pro-
fessional promotion, teacher training, competition
and campus culture construction. Wang Yan (Wang
2020) took the construction of ethics, work process,
work performance and social service ability as the
main evaluation indicators; Liu Xin (Liu 2017) used
the balanced scorecard method when building the
system. These methods are worthy of reference in
this paper, but most of these scholars are based on a
specific college to analyze, general adaptation is not
strong. This paper aims to build a set of private
higher vocational college teacher evaluation system
based on the requirements of vocational education
Chen, W., Gan, Q., Sun, J. and Wang, Y.
Construction of Teacher Performance Evaluation System in Private Higher Vocational Colleges Based on AHP and Factor Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0011899800003613
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education (NMDME 2022), pages 123-129
ISBN: 978-989-758-630-9
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
123

reform on teachers' ability and quality, expand and
improve the theory of teacher management, apply to
the daily management and evaluation of teachers,
provide ideas for the construction of teachers, so as
to promote the continuous progress of vocational
education.
2 CURRENT SITUATION OF
TEACHERS' PERFORMANCE
EVALUATION IN PRIVATE
VOCATIONAL COLLEGES
The current performance evaluation of private high-
er vocational colleges mainly has the following
problems:(1) Unreasonable evaluation index setting.
Modern vocational education pays attention to
teachers' abilities in many aspects, attaches more
importance to theoretical basic education than to
teachers' practical ability, and attaches importance to
both skill training and humanistic quality. However,
the current evaluation of teachers' performance
mainly focuses on academic level and scientific
research ability, but not on professional and tech-
nical practical ability, vocational education and
teaching research, social service and evaluation
(Wang 2012). The index setting of "emphasizing
birth, neglecting ability, emphasizing theoretical
teaching, neglecting practical teaching, emphasizing
academic research, neglecting technology applica-
tion" is the most important problem in teacher eval-
uation of higher vocational colleges at present (Zhou
2019). This is contrary to the requirements of mod-
ern vocational education, so it is necessary to build a
new evaluation system. (2) Lack of teachers' partici-
pation in the formulation of performance evaluation
system. The teacher performance system in most
schools is formulated by administrative personnel in
accordance with the intention of superior leaders and
their own experience, combined with the evaluation
methods of teachers in other similar institutions, and
teachers rarely participate in the formulation pro-
cess. Due to the different positions, the performance
evaluation system has many unreasonable points,
which will affect the enthusiasm of work over time.
(3) The evaluation method is unreasonable. At pre-
sent, the main methods of teacher performance eval-
uation include 360-degree evaluation method, lead-
ership evaluation method and democratic evaluation
method. All of these methods have the problem of
strong subjectivity and lack of objective authenticity
of evaluation results. Li Peili et al. believe that
"speaking by numbers" is easier to convince teachers
than other ways (Li, Zhang, 2007), so it is necessary
to establish a set of evaluation methods using sys-
tems and standards. (4) Unclear positioning. At pre-
sent, the evaluation system of few schools takes into
account the characteristics of private colleges and
universities, which have less financial funds and
need to be responsible for their own profits and loss-
es. As a result, the performance management mech-
anism is not consistent with the development strate-
gy and school-running orientation of the college, and
does not fully reflect the school-running characteris-
tics of the college.
3 OVERALL CONSTRUCTION
IDEA
The goal of this study is to solve the existing private
vocational college teacher performance evaluation
system unreasonable. To be specific, it is necessary
to closely follow the national strategic deployment
in vocational education, investigate the demand of
society and enterprises for talents, and clarify the
core quality of talent training in vocational colleges.
This paper analyzes what kind of vocational teach-
ing ability teachers in vocational colleges should
have in order to achieve the corresponding training
objectives, and evaluates the ability of teachers in
vocational teaching. Therefore, the essence of teach-
er performance evaluation is the evaluation of teach-
ers' vocational teaching ability. The key point of the
construction of evaluation system is the identifica-
tion of teachers' vocational teaching ability, and the
conversion of ability into evaluation index and the
setting of weight. In order to ensure that the evalua-
tion system is scientific and reasonable, many as-
pects of research are carried out when the index is
established, and the SPSS software is used to com-
bine factor analysis and AHP to analyze the data
when the weight is determined.
4 ESTABFIGURE LISHMENT OF
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
SYSTEM INDICATORS
4.1 Selection of Indicators
The indicator establishment process in this paper
includes the following steps:(1) Policy analysis. This
paper analyzed seven policy documents related to
modern vocational education from 2014 to 2021,
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
124

and extracted 17 items of teachers' competence and
quality in vocational colleges, such as teachers' eth-
ics and style, production-education integration, and
practical teaching ability. (2) Social research and
statistics on vocational education. In March 2021,
Educator magazine and relevant institutes of educa-
tion conducted an extensive survey for vocational
colleges, families and enterprises across the country
and formed a Large-scale Questionnaire Report on
the Development of China's Vocational Education
[114]. According to the data of the report, 21 items
of teachers' competence and quality are extracted,
such as the ability to guide students' skill competi-
tion and social service ability. (3) Literature analy-
sis. In this paper, the literature related to "higher
vocational teacher performance" was sorted out and
26 evaluation indicators were extracted, such as
professional practice and scientific research perfor-
mance (4) Expert interview. The teachers' abilities
extracted in the first three steps are sorted into the
first draft of the evaluation index system. Eleven
vocational education experts were invited to verify
the index system based on the characteristics of
private colleges and universities, eliminate unrea-
sonable indicators and add other indicators that are
not perfect.
4.2 Establishment of Indicators
In accordance with the practice of expert interviews
and field investigations in schools during index
screening, this paper takes teachers' ethics as the
index of the one-vote rejection system and does not
participate in weight calculation. In addition, 6 first-
level indicators, 11 second-level indicators and 34
third-level indicators were finally determined.
Figure 1. Teacher performance evaluation index
Construction of Teacher Performance Evaluation System in Private Higher Vocational Colleges Based on AHP and Factor Analysis
125

5 DETERMINATION OF WEIGHT
OF PERFORMANCE
EVALUATION SYSTEM
Since the importance of each indicator is different, it
is necessary to assign weight to each indicator. In
this paper, the index system is made into a quantita-
tive evaluation table, which is distributed to front-
line teachers, teaching administrators, teaching aux-
iliary staff, administrative staff and other teaching
related personnel in the way of questionnaire survey,
and the recovered questionnaire data is used as the
basic data to determine the weight of the index.
SPSS software was used for statistical processing of
questionnaire data, combined with AHP and factor
analysis to determine the final weight.
5.1 Questionnaire Survey
In this survey, questionnaires were distributed
through the questionnaire star, with 34 three-level
evaluation indicators as variables and six first-level
indicators as six dimensions, and the importance of
each variable was scored by the five-level system
respectively. A total of 183 questionnaires with valid
data were collected.
5.2 Sample Data Analysis
The data analysis of the sample includes reliability
analysis and validity analysis. This study first car-
ried out reliability analysis (Cronbach's α coeffi-
cient) from the six dimensions of teachers' ethics,
education and teaching ability, scientific research
ability, professional practice ability, external com-
munication ability and professional relearning abil-
ity, and then conducted validity analysis of the
above indicators in order (KMO and Bartley sphere
test). In order to test the validity of the questionnaire
data answers and the rationality of the questionnaire
design.
5.2.1 Sample Reliability Analysis
This paper used SPSS software to analyze the relia-
bility of questionnaire data and sample validity. The
Cronbach 'Salpha coefficients of the six first-level
indicators were all greater than 0.8, indicating the
high reliability of the questionnaire. Then, validity
test was conducted. Since the evaluation indicators
of this paper come from policy interpretation, litera-
ture research and expert interviews, the content is
true and valid, and the content validity meets the
requirements, so the construction validity was main-
ly tested here. After analysis, the KMO of the ques-
tionnaire was 0.907, greater than 0.6, and the Bart-
lett sphericity test showed that P =0.000, less than
0.05, indicating that the data met the condition of
structural validity test by factor analysis. Then factor
information concentration analysis and validity
analysis were carried out, a total of 6 factors were
extracted, and the characteristic root values were all
greater than 1. The variance explanation rate values
of the 6 factors were 14.462%, 14.242%, 13.743%,
10.783%, 6.737%, 5.450%, and the cumulative vari-
ance explanation rate after rotation was 65.417%.
More than 50%. Factor loading coefficient absolute
value is greater than 0.4, the organization discipline
corresponding factor 4, corresponding education
teaching ability factor 2, corresponding factor 6
scientific research ability and professional practice
ability corresponding factor 3, foreign exchange
capacity corresponding factor 1, professional learn-
ing ability corresponding factor 5, factors and re-
search items and consistent with the expected re-
sults, the relation between data effective degrees.
5.3 Selection of Indicator Weight
Determination Method
Because there are three levels of indicators in this
paper, it is suitable to use the analytic hierarchy
process to determine the weight of indicators, but the
analytic hierarchy process has certain subjectivity.
At the same time, there are a large number of indica-
tors in this paper, and dimensionality reduction is
needed in the analysis, which is just suitable for
factor analysis to determine the weight. Therefore,
this paper combines the two methods. The weight of
the first-level index is determined by factor analysis
method, and the weight of the second-level and
third-level indexes is determined by reuse analytic
hierarchy process, which can avoid the defects
caused by a certain method.
5.3.1 Determining the Weight of First-Level
Indicators
According to the variance interpretation rate values
of the six factors and the cumulative variance inter-
pretation rate value after rotation in the sample reli-
ability analysis, the corresponding weights of each
index are shown in Figure 2:
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
126
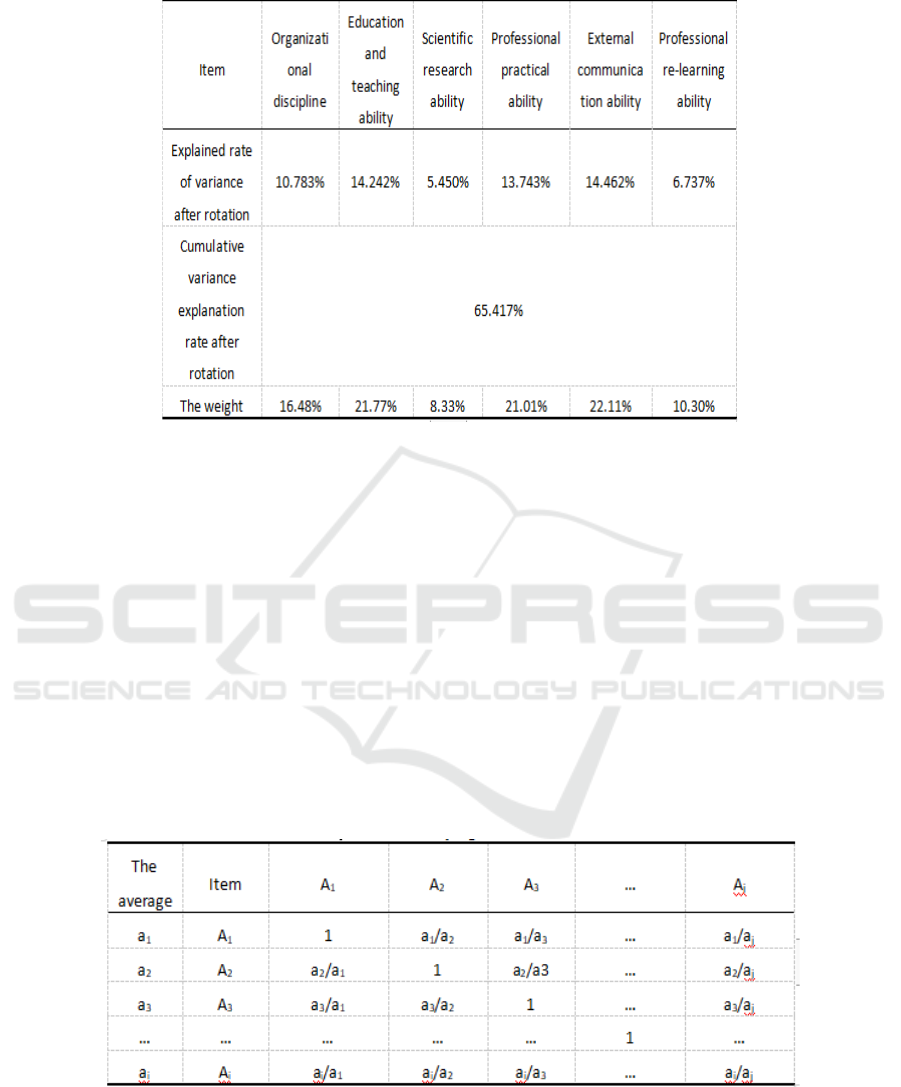
Figure 2. Weight of first-level indicators
5.3.2 Determination of Three-Level Index
Weight
This paper uses the AHP to determine the weight of
the secondary index and the tertiary index.
Establish a Hierarchical Structure System.
The hierarchical structure system consists of three
levels, the top level is the construction of higher
vocational teachers, the middle level is 6 first-level
indicators, the bottom level is 11 second-level indi-
cators, and each second-level indicator contains
several third-level indicators, a total of 34 third-level
indicators.
Construct Pairwise Comparison Matrices. In
order to judge the importance of each indicator in
the performance evaluation index system, it is nec-
essary to construct a judgment matrix to make a
pairwise comparison of each indicator layer by lay-
er. Firstly, the average scores of 183 questionnaires
of 34 third-level indicators were calculated respec-
tively. Then, each second-level indicator was taken
as a dimension, and the average scores of third-level
indicators of this dimension were divided by two to
obtain the judgment matrix, as shown in Figure 3:
The data in the judgment matrix of row I and
column j are denoted as aij, aij=ai/aj, where ai-- the
average score of Ai term and aj -- the average score
of Aj term.
Figure 3. AHP judgment matrix
Calculate the Eigenvector and Weight Value,
and do Consistency Check.
The maximum
eigenroot and corresponding eigenvector of each
pairwise comparison matrix are calculated, and the
consistency test of the evaluation results of the
judgment matrix is made. If the test passes, the
weight calculation results in the judgment matrix are
valid. When CR<0.1, consistency is considered to be
Construction of Teacher Performance Evaluation System in Private Higher Vocational Colleges Based on AHP and Factor Analysis
127
satisfied; otherwise, pairwise comparison matrices
are reconstructed.
CI
CR
RI
=
Where: CI is the consistency test index,CI =
, λmax-- is the maximum characteristic root
of the judgment matrix.
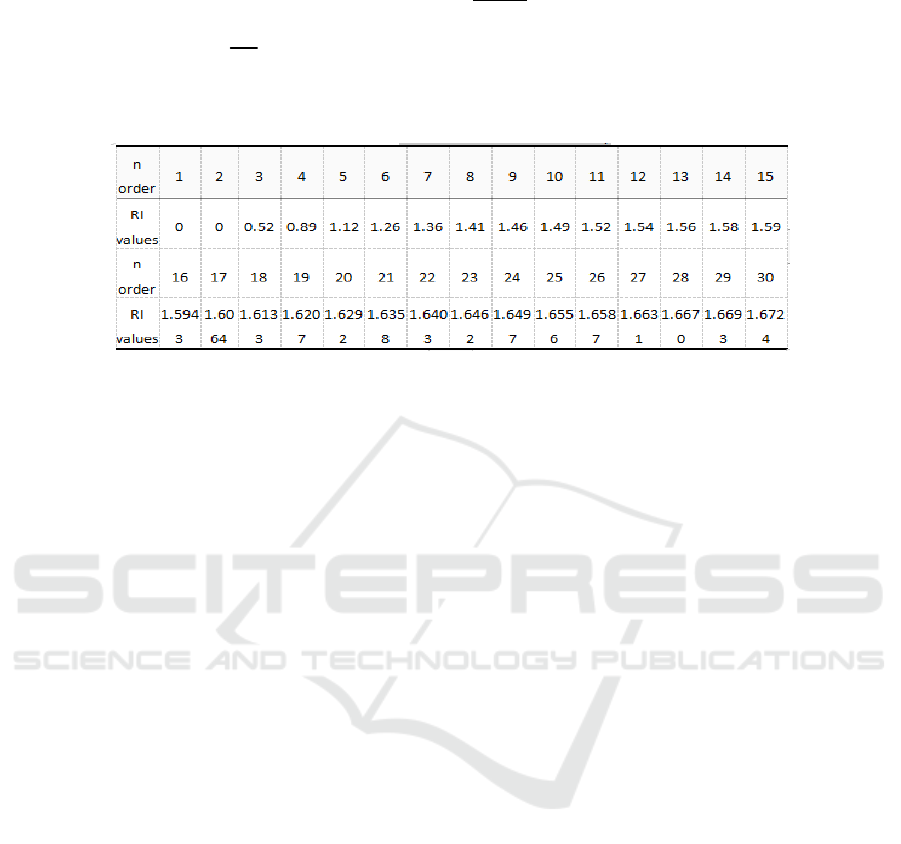
RI-- Random consistency proportional coeffi-
cient, the value of RI is related to the order “n” of
the judgment matrix, and the specific value is shown
in Figure 4:
Figure 4. RI table of random consistency
5.3.3 Determination of the Weight of
Second-Level Indicators
The calculation method of the weight of the second-
level index is the same as that of the third-level in-
dex. Each first-level index is taken as a dimension,
and the second-level index below each dimension is
scored by experts, so as to construct the judgment
matrix, calculate the feature vector and weight value,
and do the consistency test.
5.3.4 Determination of Comprehensive
Weight
The comprehensive weight formula of each index is:
= the weight of first-level indicators* weight of sec-
ond-level indicators*Three-level indicator weight
6 CONCLUSION
In the process of designing the index system, this
paper investigates the current situation and social
needs of performance evaluation of private higher
vocational colleges. When setting the index weight,
it fully considers the wishes of front-line teachers,
which can promote the development of private high-
er vocational colleges more than the existing per-
formance evaluation system. SPSS software com-
bined with AHP and factor analysis is used to set the
weight for each evaluation index, and a quantifiable
evaluation index system is constructed. In the pro-
cess of using, each school can set the scoring stand-
ard for each index, and the combination of weight
and standard is fairer than the current evaluation
method. The weight scale of the evaluation system
constructed in this paper shows that, among the six
competencies that teachers should possess, teaching
and education ability, professional practice ability
and external communication ability can most affect
the results of teacher performance evaluation.
REFERENCES
Aizhen Wang. Reconstruction of Teachers' Performance
Appraisal System in Private Jing Wang. Research on
the performance evaluation of university teachers [J].
Value engineering,2012,31(17):197-199.
Chunmei Yang, Edge occupy water. Research on the per-
formance appraisal of teachers in private universities
[J]. Think Tank Times,2019(35):82+85.
Higher Vocational Colleges Based on KPI: A Case Study
of A College [D]. North China University of Water
Resources and Electric Power.2020
Journal of ecological engineering vocational col-
lege,2014,27(01):57-58.
Jihua Wang. Research on the Construction of Incentive
Mechanism for Teachers in private Higher Vocational
Colleges under 360° Assessment Method [J]. Econom-
ic Research Guide, 2020(21):132-133.]
Opinions on Promoting the High-quality Development of
Modern Vocational Education [EB/OL]. [2021-10-12]
http://www.moe. gov. Cn/jyb_xwfb/s271/202110 /
t20211012_571650. HTML
Peili Li, Liyun Zhang. Problems and countermeasures of
university teachers' performance evaluation [J]. Jour-
nal of Adult Higher Education,2007(03):18-20.
Weiku Cheng. Design and Application of Teacher Evalua-
tion and Assessment System in Private Undergraduate
Universities -- A Case study of Guangzhou Institute of
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
128

Software [J]. Journal of guangdong polytechnic of
communications,2021,20(01):121-125.
Wenjie Zhou. Analysis on the reform path of teachers'
performance evaluation in higher vocational colleges
[J]. Modern Vocational Education,2019(26):88-89.
Xin Liu, Research on Performance Appraisal of Private H
College Based on Balanced Scorecard [D]. Shenyang
University of Technology, 2017:1-3.
Yan Wang. Study on Optimization of Performance Ap-
praisal System of K College [G]. Shandong Jianzhu
University.2020
Construction of Teacher Performance Evaluation System in Private Higher Vocational Colleges Based on AHP and Factor Analysis
129
