
Research on the Teaching Reform of "Building Construction" Course
in the Network Information Age: Green Low Carbon Transformation
as the Center
Guanghu Jin
a
Department of Architecture, Yanbian University, Yanji, China
Keywords: Network Information Technology, Building Construction, Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutrality, The
Teaching Reform.
Abstract: The highly developed network information technology makes it possible for us to learn more about the
latest foreword knowledge at the first time. Achieving carbon peaking and carbon neutralization is the only
way for China to promote high-quality development in the new development stage. As the highland of talent
training in the construction industry, colleges and universities should coordinate the construction of carbon
neutral related courses to provide solid support for talents in the construction field to achieve the ambitious
goal of carbon peak and carbon neutral. As the core course of the architecture major, "Building
construction" combines carbon peaking and carbon neutralization to reform the teaching content of building
materials, building modules, building energy conservation, building doors and windows, etc.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9935-0785
1 INTRODUCTION
The construction industry is a pillar industry in
China and one of the industries with the highest
carbon emissions. Computer information technology
analysis results In 2018, the carbon emissions of the
whole process of building operation in China's urban
and rural construction accounted for 51.3% of the
national total. In order to achieve the goal of carbon
peaking and carbon neutralization in the field of
urban and rural construction, it is necessary to
continuously promote innovation in all aspects based
on the management of the whole construction
process, so as to make the whole construction
process green, intelligent and sustainable. The
Implementation Plan for Carbon Peak in Urban and
Rural Construction issued in June 2022, the main
goal of which is to control the peak carbon
emissions in urban and rural construction by 2030,
and strive to achieve green and low-carbon
transformation in urban and rural construction mode
and modernization of carbon emission governance in
urban and rural construction by 2060, The full text
of the Plan can be viewed through the network
information platform (Fig 1).
As a basic course and a technical course in the
undergraduate education system of architecture
specialty, the content of "Building construction"
course is closely related to the diversification of
architectural technology, construction technology,
material technology and various systematic design
methods. However, in the past, the teaching content
of "Building construction" was mainly based on
traditional construction methods and building
materials, and there were few new materials and
technologies related to green and low carbon.
Therefore, this paper will make full use of the
cutting-edge direction of the network new media to
compare the latest national green and low-carbon
norms, procedures and standards with the relevant
content of the current "Building construction"
textbook, supplement and improve the teaching
content of the "Building construction" course, so that
the teaching content of the "Building construction"
course is closer to the requirements of today's green
and low-carbon development (JIN, 2017).
250
Jin, G.
Research on the Teaching Reform of "Building Construction" Course in the Network Information Age: Green Low Carbon Transformation as the Center.
DOI: 10.5220/0011909800003613
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education (NMDME 2022), pages 250-255
ISBN: 978-989-758-630-9
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
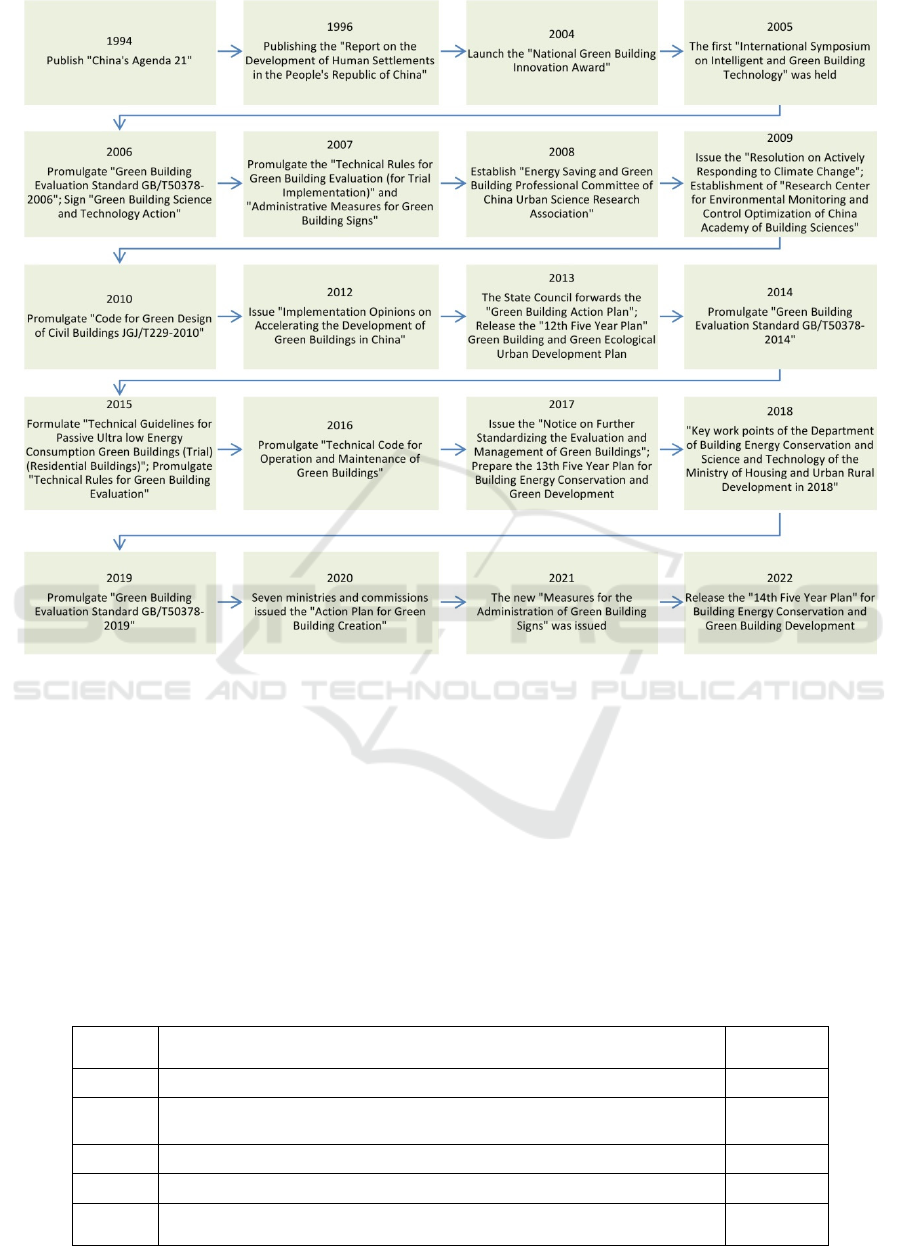
Figure 1: Development history of green buildings in China.
2 RESEARCH PURPOSE AND
METHOD
In order to thoroughly implement the decision and
deployment of the CPC Central Committee and the
State Council on carbon peaking and carbon
neutralization, and make the teaching content of the
"Building construction" course more close to the
requirements of green and low-carbon development
in today's society, on the premise of collecting and
sorting out relevant green and low-carbon
documents, norms, procedures and standards
through various online and offline methods, consult
the shortcomings of the current "Building
construction" teaching materials and deepen and
supplement them, Put forward reasonable
suggestions for the teaching reform of "Building
construction" course of architectural specialty in
colleges and universities (
Table 1).
Table 1: Current green low carbon related specifications
Serial
No
Specification name Revision
1 Design standard for energy efficiency of public buildings (GB50189-2015) 2015
2
Design Standard for energy efficiency of residential buildings in severe
cold and cold zones (JGJ 26-2018)
2018
3 Assessment standard for green building (GB/T50378-2019) 2019
4 Standard for Building Carbon emission calculation (GB/T 51366-2019) 2019
5
General code for energy efficiency and renewable energy application in
b
uildings (GB55015-2021)
2021
Research on the Teaching Reform of "Building Construction" Course in the Network Information Age: Green Low Carbon Transformation
as the Center
251

3 REQUIREMENTS FOR GREEN
AND LOW-CARBON
DEVELOPMENT IN URBAN
AND RURAL CONSTRUCTION
3.1 Long Term Development
Requirements of Green and
Low-Carbon
Carry out digital review of construction drawings
based on network information technology, and
supervise the sustainable development of green and
sustainable building design. All new buildings in
domestic cities and towns will be constructed
according to the green building design standards by
2025. The buildings that meet the green building
standards will reach more than 30%, and all new
public construction projects invested by the
government will reach the standard of one star green
building or above (MOC & MSA, 2019). By 2030,
the energy efficiency rate of new residential
buildings in severe cold and cold regions will
increase from 75% to 83%; The energy efficiency
rate of new residential buildings in other climate
zones has increased from 65% to 75%; The energy
efficiency rate of new public buildings has increased
from the current 72% to 78%. We will promote the
large-scale development of low-carbon buildings,
and encourage all regions to actively build zero
carbon buildings and near zero energy consumption
buildings. By 2030, all public buildings in key cities
above prefecture level will be renovated, and the
energy saving rate will be increased by more than
20% on the original basis (MOC & MSA, 2022).
3.2 Green and Low-Carbon
Development Requirements at this
Stage
From April 2022, the energy consumption of new
residential buildings will be reduced by 30% on the
original basis, that is, the energy efficiency rate of
residential buildings in severe cold and cold regions
will increase from 65% to 75%, and that of
residential buildings in other climatic regions will
increase from 50% to 65%; The energy consumption
of new public buildings is reduced by 20% on the
original basis, that is, the energy saving rate is
increased from 65% to 72%. It also requires that the
carbon emissions of new buildings be reduced by
40% on the original basis and reported to the
competent department platform through network
information technology. The calculation method of
total carbon emissions (CM) in the whole phase of
building operation is:
CM
∑
EiEFi
Cp
y
A
Where Ei is the energy consumption of class i of
buildings; EFi is the carbon emission factor of class i
energy; i is the type of terminal energy consumed by
buildings; Cp is the annual carbon reduction of
building green space carbon sink system; y is the
design life of the building; A is the building area
(MOC & MSA, 2019).
4 TEACHING CONTENT
REFORM OF "BUILDING
CONSTRUCTION" COURSE
4.1 Teaching Content Reform of
Building Materials
Building materials are the main contributors to
carbon emissions in the construction industry.
According to statistics, 41.3% of the carbon
emissions in the production stage of building
materials account for the total life cycle carbon
emissions of buildings. In addition, the proportion of
carbon emissions during the transportation of
building materials will be higher. Therefore,
reasonable selection of building materials in
architectural design will play an absolute role in
reducing carbon emissions in the construction
industry (
Table 2
).
Table 2: Carbon Emission Factors of Main Building
Materials.
Category of building materials
Carbon emission
facto
r
Ordinar
y
Portland cement 735k
g
CO
2
e/t
Concrete bric
k
336 k
g
CO
2
e/m
3
Autoclaved fl
y
ash bric
k
341 k
g
CO
2
e/m
3
Fired fly ash solid bric
k
134 kg CO
2
e/m
3
Shale solid bric
k
292 kg CO
2
e/m
3
Shale hollow bric
k
204 kg CO
2
e/m
3
Gan
g
ue solid bric
k
22.8k
g
CO
2
e/m
3
Coal
g
an
g
ue hollow bric
k
16.0k
g
CO
2
e/m
3
C30 concrete 295 k
g
CO
2
e/m
3
Cla
y
2.69 kg CO
2
e/t
Lime production (market
avera
g
e
)
1190 kg CO
2
e/t
Steelmaking pig iron 1700 kg CO
2
e/t
Natural gypsum 32.8 kg CO
2
e/t
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
252
Cast
p
i
g
iron 2280 k
g
CO
2
e/t
san
d
(f=1.6~3.0) 2.51 kg CO
2
e/t
Ordinary carbon steel 2050 kg CO
2
e/t
Polyvinyl chloride (market
average)
7300kg CO
2
e/t
Rock wool boar
d
1980kg CO
2
e/t
Polystyrene foam boar
d
5020kg CO
2
e/t
Plastic steel window 121k
g
CO
2
e/m
2
Aluminum
p
late with 28500k
g
CO
2
e/t
Universal woo
d
178 k
g
CO
2
e/m
3
Plywoo
d
487 kg CO
2
e/m
3
Particleboar
d
336 kg CO
2
e/m
3
At present, the building structure design in the
"Building construction" textbooks used in China is
all around traditional building materials, but from
the perspective of carbon peaking, carbon
neutralization and the use of network information
technology, more materials with low carbon
emission factors are selected. For example, the
traditional method of flat roof slope making layer in
roof construction is to use expanded perlite, but the
carbon emission factor of expanded perlite has
reached 2880kgCO
2
e/t. The materials of slope
making layer should be changed to light aggregate
concrete, vermiculite cement mortar, slag cement
mortar and other materials with low carbon emission
factors according to the requirements of building
roof use, so as to reduce carbon emissions (MOC &
MSA, 2019).
4.2 Teaching Content Reform of
Building Module and Wall
In order to make building materials universal and
improve production efficiency, China has stipulated
a unified modular series for building materials. In a
large number of architectural designs, the opening,
depth and door and window dimensions of buildings
must be coordinated according to this module. In
order to achieve the ambitious goal of carbon
peaking and carbon neutralization, the country has
formulated a forward-looking policy of reducing the
proportion of building materials consumed at the
construction site by 2030 by 20% on the basis of
2020, and comprehensively promoting green
building materials on projects that meet the StarCraft
green building standards by 2030, And use network
information technology to supervise at any time.
Although the thickness of common brick walls is
included in the teaching material of "Building
construction" currently used in China, it is not
expanded and extended by combining wall materials
and modulus. In the selection of masonry bricks, the
building materials with low carbon emission factors
and the carbon emission factors in the transportation
process of building materials should be considered
first. Therefore, the coal gangue porous bricks and
hollow bricks with low carbon emission factors
produced locally should be selected as far as
possible through network information technology; In
addition, considering the loss rate of building
materials, the door and window buttresses, walls
between doors and windows, molding pilasters, etc.
shall be designed in combination with the brick
modulus as much as possible in the architectural
design. For example, walls with a length of less than
1 m shall be 120 mm, 180 mm, 250 mm, 370 mm,
500 mm, 680 mm, 750 mm and other dimensions to
avoid wasting materials and labor caused by brick
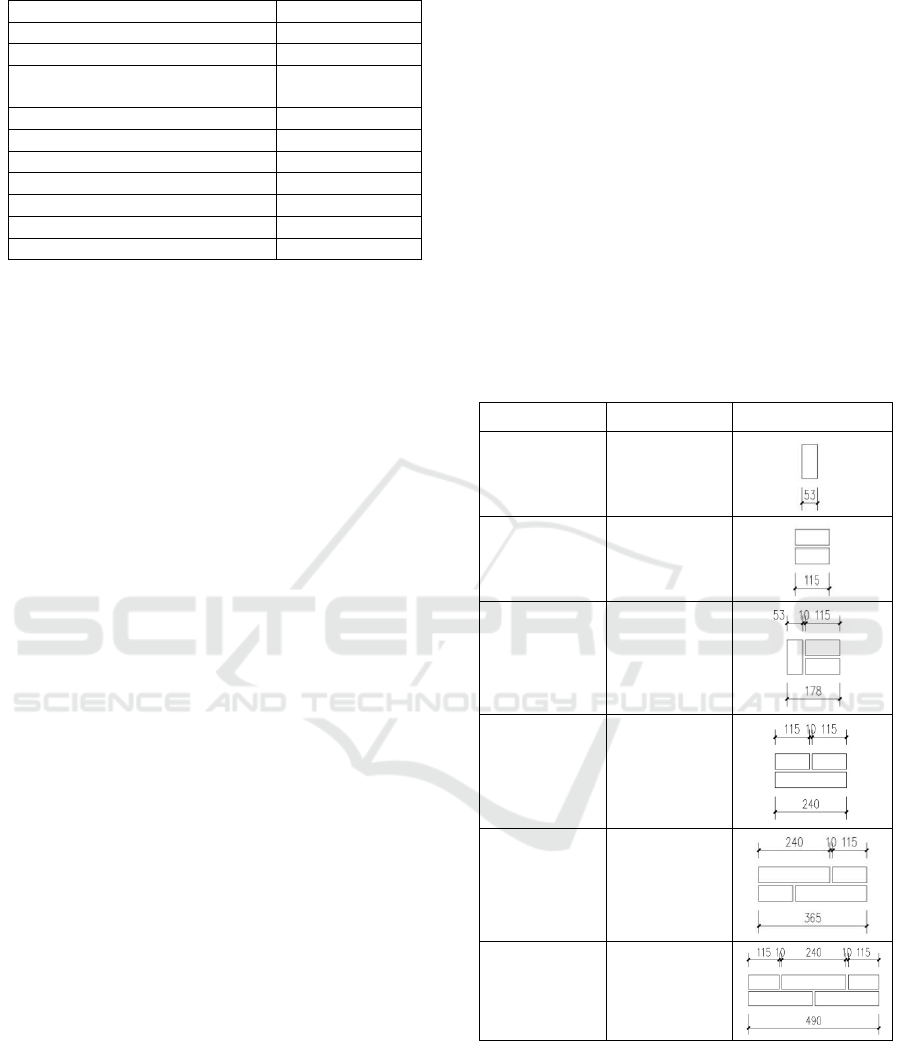
cutting during construction (
Table 3).
Table 3: Standard Brick Laying Method.
name Wall thicness legend
6 thick wall 1/4 brick wall
12 thick wall 1/2 brick wall
18 thick wall 3/4 brick wall
24 thick wall 1 brick wall
37 thick wall 3/2 brick wall
49 thick wall 2 brick wall
4.3 Teaching Content Reform of
Building Energy Conservation
China's building energy conservation started in the
1980s, but China has always attached importance to
the development of building energy conservation,
and has successively issued and updated the design
standards for building energy conservation in
Research on the Teaching Reform of "Building Construction" Course in the Network Information Age: Green Low Carbon Transformation
as the Center
253
various climatic regions, promoting the healthy and
rapid development of China's building energy
conservation field. Proper thermal insulation
materials for buildings can effectively improve
energy efficiency and promote green, sustainable
and low-carbon development. In order to protect the
ecological environment and cope with climate
change, implement the decision-making and
deployment of carbon peaking and carbon
neutralization, improve the efficiency of energy
resource utilization, promote the use of renewable
energy, promote low-carbon development, create a
good indoor space environment, and meet the needs
of high-quality development of the whole society,
the country has continued to pay attention to
building energy conservation design, successively
issued building energy conservation design
standards, green building evaluation standards,
building carbon emission calculation standards As of
now, the average energy efficiency rate of
residential buildings and public buildings in severe
cold and cold regions in China needs to reach 75%
and 72% respectively, according to the general
specifications and regulations for building energy
efficiency and renewable energy utilization (MOC &
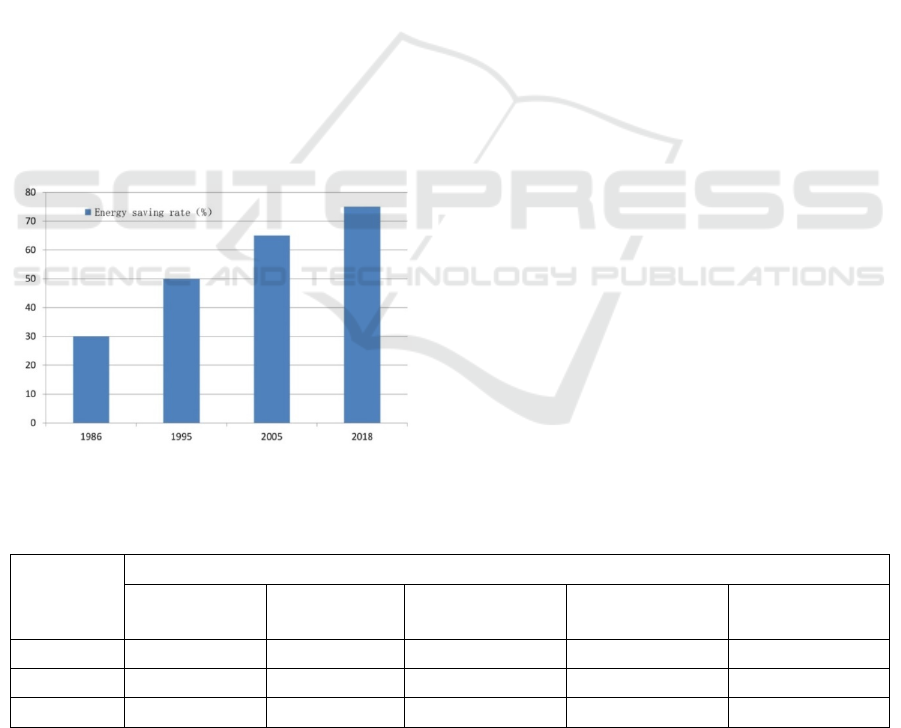
MSA, 2015;
Fig 2).
Figure 2: Evolution of China's civil building energy
efficiency rate.
At present, the content of "Building
construction" textbooks used in China involves little
in building energy conservation, especially in the
current society where the national policy on carbon
peaking, carbon neutralization and deployment is
only reflected in the wall and roof chapters of
"Building construction" textbooks. The energy
saving rate of civil buildings is mainly achieved
through the improvement of the thermal insulation
function of the building envelope. Therefore, it is
necessary to add this part to the teaching content of
"Building structure", and pay attention to relevant
foreword knowledge through network information
technology at any time.
4.4 Teaching Content Reform of Doors
and Windows
Doors and windows are part of the building
envelope, and also an important link to ensure
building energy conservation, which needs to meet
many relevant indicators. At present, the content of
"Building construction" textbook used in China has
supplemented the content of energy conservation of
doors and windows, but the length is only one and a
half pages, without detailed description. The current
national codes and regulations describe the energy
conservation of windows and doors in residential
buildings, public buildings and industrial buildings
in more detail, such as the area ratio of windows to
walls, the area of roof skylights, and the thermal
performance of windows and doors, which should be
deepened in combination with the relevant computer
software for building energy conservation design.
(
Table 4)Extend this aspect for the green and low
carbon transformation of the construction industry to
lay the foundation for the realization of green and
low carbon national policies as soon as possible
(MOC, 2018).
Table 4: Requirements for window wall ratio of residential buildings.
orientation
Window wall area ratio
Frigid region Cold region
Hot summer and
cold winter area
Hot summer and
warm winter areas
Moderate Zone A
north ≤0.25 ≤0.30 ≤0.40 ≤0.40 ≤0.40
East, West ≤0.30 ≤0.35 ≤0.35 ≤0.30 ≤0.35
south ≤0.45 ≤0.50 ≤0.45 ≤0.40 ≤0.50
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
254

5 CONCLUSIONS
Carbon peaking and carbon neutralization have
become the key direction of national development
and the strategic goal of green and low-carbon
transformation of the construction industry. In
today's society with highly developed network
information technology, we should learn more about
the latest foreword knowledge at the first time to
enrich the teaching content. As the highland of talent
training in the construction industry, colleges and
universities should closely follow the national
guidelines and policies, coordinate the construction
of relevant courses, provide solid support for
building professionals to achieve the ambitious goal
of carbon peaking, carbon neutralization, and
provide constructive suggestions for other colleges
and universities to reform the "building structure"
curriculum.
By analyzing the teaching content of the course
"Building construction", the following aspects
should be reformed. 1) For the selection of building
materials, try to choose materials with low carbon
emission factor and produced in local or surrounding
cities; 2) The building is designed according to the
modulus to reduce the material loss rate and reduce
carbon emissions; 3) In combination with the
requirements of the current national energy
conservation rate standard, building energy
conservation design runs through most chapters of
the "building construction" curriculum; 4) Improve
the performance of building doors and windows, and
make the weak links of the exterior enclosure
structure meet the current standard requirements.
REFERENCES
Guanghu JIN. (2017). On the application of school
enterprise cooperation in the course of "building
construction" in colleges and universities. J. Chinese
and foreign architecture, 73-75.
Lin Qin & Hongyang Wei. (2019). Building construction
(Part 1). M. Beijing: China Architecture Press.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the
People's Republic of China & State Administration for
Market Regulation. (2022). General code for energy
efficiency and renewable energy application in
buildings GB55015-2021. M. Beijing: China
Architecture Press.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the
People's Republic of China & State Administration for
Market Regulation. (2019). Standard for Building
Carbon emission calculation GB/T 51366-2019. M.
Beijing: China Architecture Press.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the
People's Republic of China & State Administration for
Market Regulation. (2019). Assessment standard for
green building GB/T50378-2019. M. Beijing: China
Architecture Press.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the
People's Republic of China. (2018). Design Standard
for energy efficiency of residential buildings in severe
cold and cold zones JGJ 26-2018. M. Beijing: China
Architecture Press.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the
People's Republic of China & State Administration for
Market Regulation. (2015). Design standard for
energy efficiency of public buildings GB50189-2015.
M. Beijing: China Architecture Press.
Research on the Teaching Reform of "Building Construction" Course in the Network Information Age: Green Low Carbon Transformation
as the Center
255
