Analysis of the SERVQUAL Based Mixed Teaching Model in
Colleges
Yinghong Li
a
Shandong Institute of Commerce and Technology, Shandong, China
Keywords: Hybrid Teaching Model, SERVQUAL Model, Quality Assessment Information.
Abstract: Teachers' information technology teaching level and teaching quality can be improved by combining online
and offline teaching. This paper constructs the SERVQUAL model to measure the service quality of college
professional teaching from the perspective of service quality management. Using factor analysis and entropy
weight method, this paper determines the dimension coefficient of the model, analyzes each index, and dis-
cusses the priority order of index action. The purpose of this paper is to provide a reference for improving the
quality of professional teaching services in colleges and universities.
1 INTRODUCTION
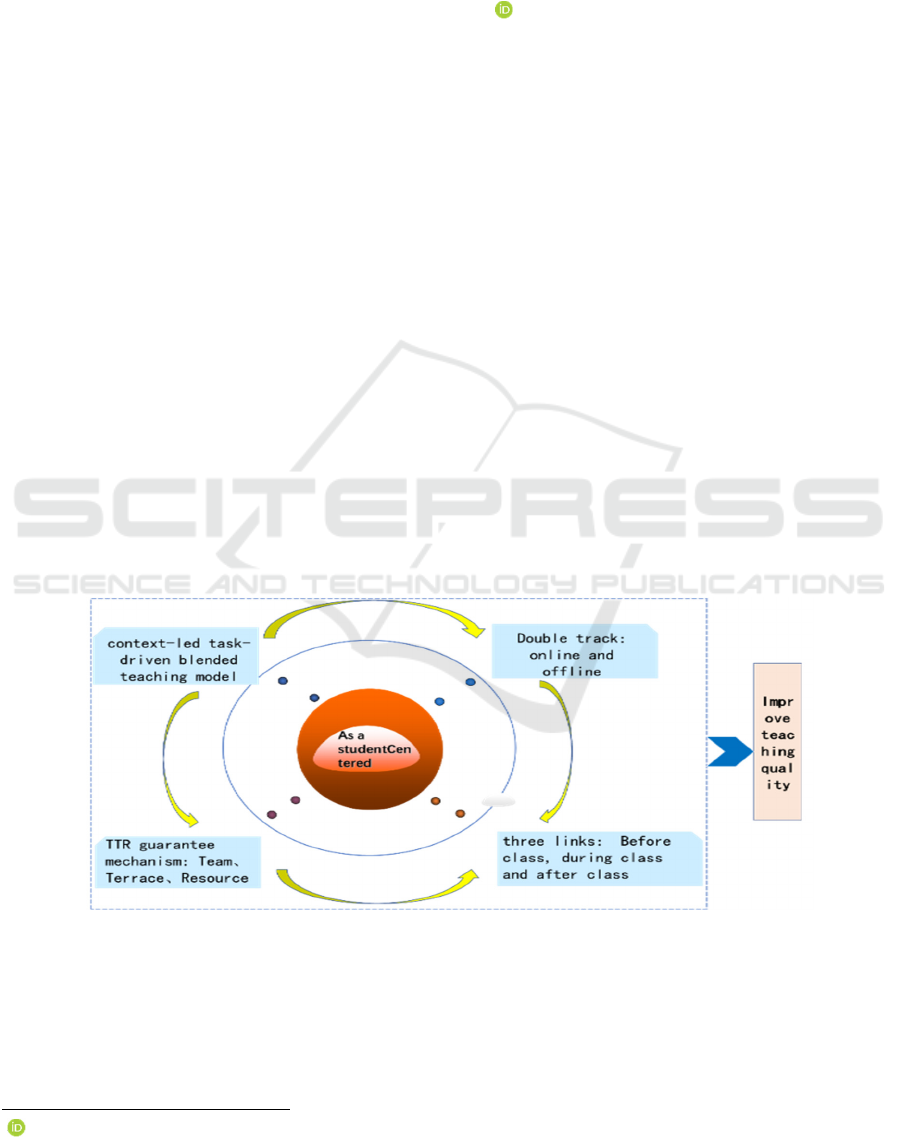
The teaching model is built around student-centered
learning and development, designing teaching situa-
tions according to real job scenarios, further refining
teaching tasks according to the teaching situations,
and turning students into workplace people, playing
different roles and completing various work tasks.
With the TTR mechanism as the guarantee, the mo-
bile classroom and the physical classroom, the pre
class and post class double track and three links run
alternately, and finally achieve the teaching goal. The
student-centered, context-led task-driven hybrid
teaching model is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Context-led task-driven hybrid teaching model
The use of data mining technology in educational
research is a common method of exploring the rela-
tionship between evaluation object and evaluation in-
dex. The development trend in teaching evaluation
and teaching management is to improve the quality of
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1854-2751
teaching through effective evaluation standards and
methods. The teaching model emphasizes student-
centered learning and development. Making the
teaching environment and experience as realistic as
possible, refine the teaching tasks accordingly, and
Li, Y.
Analysis of the SERVQUAL Based Mixed Teaching Model in Colleges.
DOI: 10.5220/0011910800003613
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education (NMDME 2022), pages 295-300
ISBN: 978-989-758-630-9
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
295

convert students into professionals. Using the TTR
mechanism, the mobile classroom and physical class-
room, operating before and after class, in a double
track, three-way alternating pattern, finally achieve
their educational objectives (Luo 2022).
SERVQUAL model is based on the difference
theory. It believes that service quality has five dimen-
sions, namely, tangibility, reliability, responsiveness,
assurance and empathy. Evaluators' perception of ser-
vice quality is evaluated from these five dimensions.
SERVQUAL model is to set 22 secondary indicators
(questions) based on five dimensions. Evaluators
score the psychological expectations and actual feel-
ings of secondary indicator questions according to
their own experiences and actual needs. The differ-
ence between the two scores is the evaluator's evalu-
ation of service quality. The smaller the difference,
the higher the evaluation.
2 THE PURPOSE OF THIS
STUDY IS TO CONSTRUCT AN
EVALUATION AND ANALYSIS
MODEL OF MIXED TEACHING
QUALITY IN COLLEGES.
Each index score is evaluated based on the difference
between psychological expectation and actual experi-
ence, As shown in Formula (1), the difference is the
students' evaluation of the teaching quality.
𝑆𝑄=𝑊
𝑃
−𝐸
1
5
1
(1)
Where, 𝑅is the number of second-level indicators to
which each attribute belongs; 𝑃
is students' psycho-
logical expectation score for the 𝑖 th question; 𝐸
is
the score of students' actual feelings about the ith
question, and 𝑊
is the weight of each dimension.
Because different attributes have different degrees
of influence on the evaluation of teaching quality, us-
ing the same weight assignment will result in large
deviation. The research uses entropy weight method
to determine the weight of each secondary indicator
of the model. Because the secondary indicators of
each attribute have strong relevance (factor analysis
can be used to extract factors for verification), the
weight of each attribute is the accumulation of the
weight values of the secondary indicators.
As a result of the different properties of the teach-
ing quality evaluation, the weight of the same assign-
ment will produce large deviations. To determine the
weights of each secondary index in the model, the re-
search uses the entropy weight method. Because sec-
ondary indicators have strong correlations, the weight
of each attribute is part of the secondary index
weights.
With online teaching quality evaluation to illus-
trate the basic principle of entropy weight method,
there are 𝑚 students participating in online teaching
quality evaluation, 𝑛 secondary index of evalua-
tion, the statistical value of student evaluation index
is marked 𝑋
, indicating the evaluation of the JTH
index by the 𝑖 th student. The extreme value method
is used to standardize statistical data to eliminate the
influence of different units among indicators. The
standardized formula is as follows:
𝒚
𝒊𝒋
=
𝒙
𝒊𝒋
𝟏
𝒎𝒊𝒏
𝒙
𝒊𝒋
𝒎𝒂𝒙
𝒋
𝒙
𝒊𝒋
−𝒎𝒊𝒏𝒙
𝒊𝒋
𝟏
(2)
After quantifying the same degree of standardized
indicators, the proportion of the 𝑖 th student's eval-
uation value of the 𝑗 th indicator is:
𝑷𝒊𝒋=
𝒚
𝒊𝑱
𝒚
𝟐
′
𝒋
𝒎
𝒊𝟏
(3)
Weight of each attribute:
𝑾
𝒋
=𝒘
𝒋
𝑹
𝒊𝟏
(4)
Score gaps between multiple evaluators on a sin-
gle index increase with the larger the gap. The smaller
the entropy and the larger the entropy weight, the
greater the entropy, indicating that the index can pro-
vide more information about the research topic and
play a greater role in sample comparison.
The perceptual difference (psychological expecta-
tion-actual feeling) of 230 samples was calculated to
obtain the perceptual matrix of online teaching eval-
uation, and the entropy weight of 26 second-level in-
dicators was calculated by entropy weight method (as
shown in Table 1).
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
296
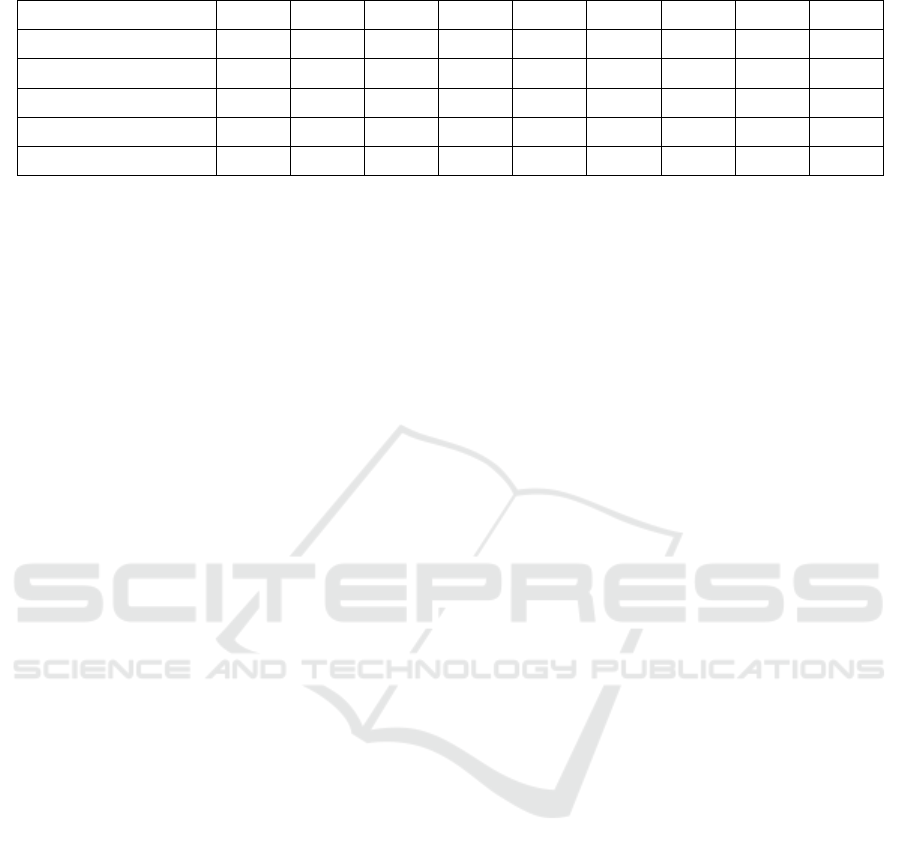
Table 1. Entropy weight, the second-level index of SERVQUAL Scale for teaching Quality in Colleges
Number A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9
Entropy weight 0.0457 0.0547 0.0214 0.0277 0.0369 0.0147 0.0258 0.0369 0.0124
Number B10 B11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 D17 D18
Entropy weight 0.0248 0.0325 0.0244 0.0257 0.0235 0.0741 0.0239 0.0258 0.0147
Number D19 D20 D21 E22 E23 E24 E25 E26
Entropy weight 0.0147 0.0741 0.0258 0.0357 0.0159 0.0753 0.0852 0.0458
3 TEACHERS' DIGITAL
TEACHING ABILITY AND
INNOVATION AND
ENTREPRENEURSHIP
ABILITY
Online and offline hybrid teaching puts forward un-
precedented high standards and requirements for
teachers' digital processing ability, information teach-
ing ability and innovation and entrepreneur-ship abil-
ity.
As a result of online and offline hybrid teaching,
teachers are expected to demonstrate unprecedented
levels of digital processing ability, information teach-
ing ability, and innovation.
3.1 Transforming Teachers' Teaching
Philosophy
Traditional teaching has formed a teacher-centered
closed classroom model, teachers guide and act by
themselves, blindly instill knowledge into students,
only to complete teaching tasks, and completely
ignore students' independent learning and
personalized development. If teachers can't adapt to
the development of the times, change the outdated
educational ideas, and change their roles in education,
they will certainly mislead students. So, teachers must
break through the old and create new ones, establish
the information mixed teaching concept, and adopt
the most advanced teaching technology and means
(Liu 2020, Yu 2022).
3.2 Teachers are Encouraged to
Participate in Various IT Teaching
Ability Trainings
The school has created all conditions, invited IT
teaching experts, digital processing experts,
innovation and entrepreneurship entrepreneurs to
give lectures in the school, encouraged teachers to
actively participate in various forms of online and
offline modern teaching ability training, digital
processing ability training, digital quality training and
innovation and entrepreneurship ability training, held
symposiums and exchanges, and discussed and
consulted with each other.
3.3 Teachers Are Encouraged to
Participate in Various Levels of
Teacher Teaching Ability
Competitions
By learning the content of the competition, forming
pairs to participate, preparing for the competition,
participating in the competition, exchanging the
competition and reflecting on the competition, a set of
process, even if they do not win the prize, the teachers'
informatization teaching level must have improved.
3.4 Build an Intelligent Teaching
Platform Centered on Active
Student Learning
Blended online and offline teaching requires teachers
to upload digital resources, students to be able to learn
locally when and where they want, and to be able to
implement interactive online and offline teaching.
This requires teachers to build a platform. To
successfully build a teaching platform in a short
period of time, the following steps are required.
Step 1: Understand the dual interface and dual
ports of the platform. Dual interface refers to the
teacher interface and student interface, and dual ports
refer to the computer side and mobile side.
Step 2: Build the platform. To build a platform,
you have to build a course first, and give all your
courses a good framework and columns. Then upload
digital resources (Liang 2021). Set up before, during
and after class activities.
By building a platform course and implementing
online and offline hybrid teaching, the teacher
uploads digital materials before class, allowing
Analysis of the SERVQUAL Based Mixed Teaching Model in Colleges
297
students to pre-study online and discuss problems
with the teacher and classmates at any time, the
teacher explains the important and difficult problems
offline during class, and through online questions,
discussions, salons, quizzes and quizzes, the online
and offline interleaved operation improves students'
motivation, and the teacher assigns homework and re-
leases extended materials after class to Classroom
knowledge is further enhanced.
4 AN EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS OF
BLENDED TEACHING IN
COLLEGES AND
UNIVERSITIES
4.1 Data Sources and Processing
This paper selects the online teaching quality
evaluation data of business administration majors in
a university in Shandong Province for empirical
analysis. Each student (considering that there are few
theoretical courses for senior students and the sample
size is insufficient, this paper does not do research)
scores the expectation and actual perception of 38
indicators, and uses formula (1) to calculate the
evaluation of individual students on the current online
teaching quality. The online questionnaire
(questionnaire star) was used to eliminate invalid
samples, and a total of 230 samples were determined,
including 85 marketing majors and 145 business
administration majors.
4.2 Construction of Comprehensive In-
dicators of Teaching Evaluation
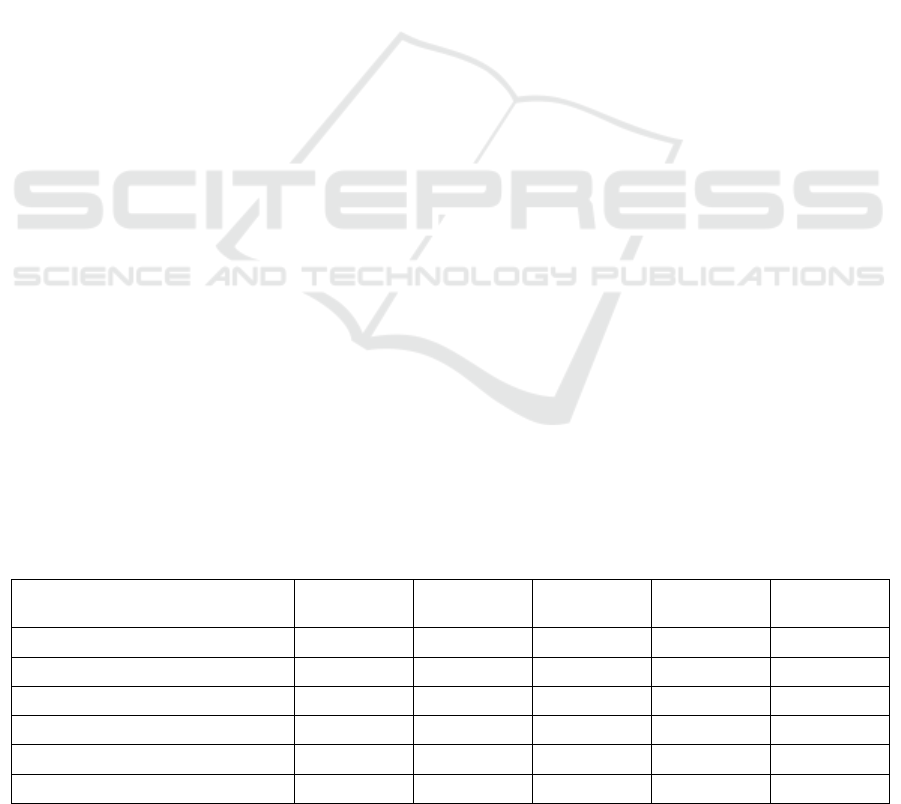
1. Ensure the reliability of the SERVQUAL scale and
each dimension subscale by conducting a reliability
analysis, it is necessary to conduct reliability, validity
and paired sample 𝑇 -test on the collected question-
naires to determine the designed online teaching qual-
ity scale for colleges and universities. At the same
time, the differences in the scores of students' psycho-
logical expectations and actual feelings about the in-
dicators in the questionnaire were compared. The rel-
evant indexes obtained by SPSS software are shown
in Table 2.
Service quality and gap The SQ value of the over-
all service quality of professional education is 0.358,
and its percentile score is 92.12; The service quality
SQ value of each indicator is 0.07-1.2 (Table 2), in
which the mean values of the "curriculum setting",
"curriculum teaching" and "teaching resources" di-
mensions are 0.0658, -0.0998 and 0.195 respectively.
The paired t-test results showed that there were statis-
tically significant differences between students' ex-
pectations and perceptions of various indicators of
professional education services (P<0.05, Table 2).
Digital resources should not only achieve sharing
with the paper content of the textbook, but also
achieve interaction with the platform. Ping The plat-
form includes resource platform, teaching plat-form,
training platform, etc. The digital content of the
teaching materials should be shared with the platform
content to facilitate teachers and students to access
and learn anytime and anywhere using different web
tools and mobile tools, and to promote more interac-
tive learning between teachers and students. To facil-
itate students' reading and use, loose-leaf textbooks
can be developed according to the characteristics of
the course.
In order to ensure the reliability of SERVQUAL
and its sub scales, it is necessary to conduct reliabil-
ity, validity and paired sample T tests on the collected
questionnaires to determine the designed online
teaching quality scale for colleges and universities,
and compare the differences between the students'
psychological expectations and actual feelings of the
indicators in the questionnaire. Relevant indexes ob-
tained by SPSS software are shown in Table 2
Table 2. SERVQUAL Scale for Teaching Quality in Colleges and Universities: Reliability and Validity
Scale α KMO
Bartlett's test
for sphericity
Factor load-
ings
Factor load-
ings
SERVQUAL Total 0.897 0.997 0.000 - -
Tangibility Quality Scale 0.810 0.784 0.000 0.547 0.000
Reliability Quality Scale 0.904 0.946 0.000 0.577 0.000
Responsiveness Quality Scale 0.987 0.863 0.000 0.641 0.000
Assurance Quality scale 0.901 0.897 0.000 0.487 0.000
Empathy Quality Scale 0.963 0.904 0.000 0.701 0.000
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
298
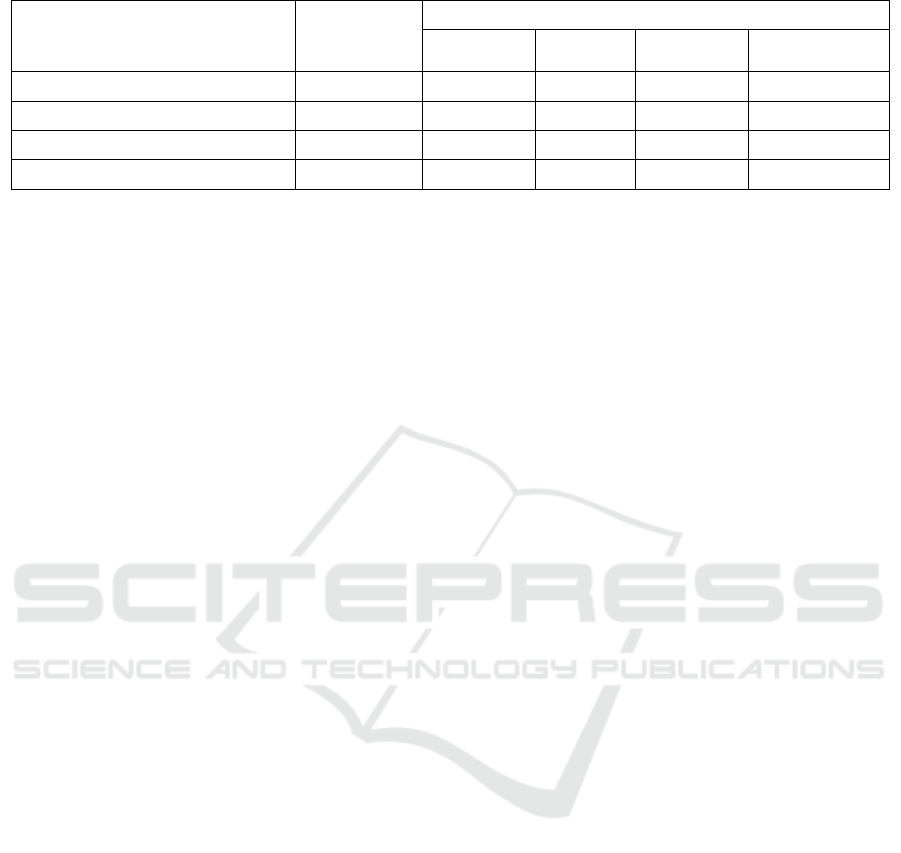
Table 3. KMO and Bartlett spherical tests and Cronbach's coefficient of correlation
Dimension Index number
Cronbach’s α KMO
Expectation
subscale
Perceptual
subscale
Expectation
subscale
Perceptual
subscale
The curriculum 7 0.721 0.856 0.851 0.829
Course teaching 4 0.851 0.744 0.732 0.873
Teaching resources 8 0.744 0.893 0.799 0.805
Toatal 19 0.825 0.862 0.816 0.844
5 CONCLUSION
Combining factor analysis and entropy weight
method, the five-dimension weight coefficients of the
SE-VQUAL model can effectively reflect the im-
portance of each dimension, and the SE-VQUAL
model based on the weight coefficients can reasona-
bly score online teaching quality. The result shows
that the score of online teaching quality is propor-
tional to the grade and major. In view of the curricu-
lum setting in colleges and universities, it shows that
colleges and universities should strengthen the im-
provement of online teaching quality of basic courses;
There is a gap in the teaching quality scores of differ-
ent majors, which indicates that there are differences
between the secondary majors of business administra-
tion. Colleges and universities should improve or
evaluate the secondary majors based on the particu-
larity of the secondary majors.
1. Cronbach's α coefficient was used to test the re-
liability of SERVQUAL model. The overall
Cronbach's α coefficient of the scale was greater than
0.900, and each dimension was between 0.802 and
0.859 (Table 1). Based on KMO and Bartlett spheri-
cal tests, all dimensions had KMO values greater than
0.5 (Table 1), and the differences were statistically
significant (P<0.05). The results of factor analysis of
SERVQUAL model validity showed that the factor
matrix was orthogonal rotated with maximum vari-
ance, and the three factors with characteristic root
greater than 1 accounted for 94.930% and 64.304%
of the perceived and expected variation.
2. Using the SERVQUAL model scale, the empir-
ical study builds an online teaching quality evaluation
scale for colleges and universities., and the Reliability
and validity are tested. In each dimension index, there
is a significant difference between psychological ex-
pectation and actual perception. This shows that the
SERVQUAL model can be used to evaluate colleges'
and universities' teaching quality. Additionally, it
combines the generality of service quality manage-
ment theory with the specificity of university teaching
and learning quality management. Provide new ideas
for studying teaching quality management in colleges
and universities, and improve the theory of teaching
quality management.
By building a platform course and implementing
online and offline hybrid teaching, the teacher up-
loads digital materials before class, allowing students
to pre-study online and discuss problems with the
teacher and classmates at any time, the teacher ex-
plains the important and difficult problems offline
during class, and through online questions, discus-
sions, salons, quizzes and quizzes, the online and of-
fline interleaved operation improves students' moti-
vation, and the teacher assigns homework and re-
leases extended materials after class to Classroom
knowledge is further enhanced.
REFERENCES
Dado, Taborecka–Petrovicova, J. Riznic, D, & Rajic, An
Empirical Investigation into the Construct of Higher
Education Service.
Foropon, Seiple, Kerbache, Using SERVQUAL to Exam-
ine Service in the Classroom: Analyses of Undergradu-
ate and Executive Education Operations Management
Courses [J]. International Journal of Business & Man-
agement, 2013(20): 105 - 116
Guo Lijun Current Situation and Trend of Research on Uni-
versity Teaching Evaluation since the 21st Century [J].
Modern University Education, 2019 (6)
Guruler H, Istanbullu A. Modeling student performance in
higher education using data mining [J]. Educational
Data Mining, 2014 (1) :105 - 124.
Int. Conf. on Information Technology Interfaces. Cavtat:
IEEE, 2012. 207-212.
Jia Yanhong, Zhao Jun, Zhao Chuanyan, Wang Shengli.
Evaluation of Grassland Ecological Security based on
entropy weight Method: A Case study of Gansu Pasto-
ral areas [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2006(8):
1003-1008.
Krpan D. , Stankov S. Educational data mining for grouping
students in E-learning system [C]. Proceedings of the
ITI 2012 34th
Analysis of the SERVQUAL Based Mixed Teaching Model in Colleges
299

Liang Shan. Discussion on the construction of digital re-
sources for accounting majors in higher education insti-
tutions -taking financial accounting course as an exam-
ple. Journal of Yan'an Vocational and Technical Col-
lege, August 2021: Vol. 35, No. 4.
Liu Jian, Huang Yuying, Yan Lichao. Data Mining and
Analysis of Classroom Teaching Evaluation [J]. Journal
of Education Science, Hunan Normal University,
2019(2): 118-124.
Liu Xiao. Exploring the improvement of teachers' ability in
blended teaching mode. Journal of State Grid Technical
College,2020 05): Vol. 23, No. 5.
Liu Xiaozhe. Some Thoughts on Promoting the Construc-
tion of Undergraduate Teaching Evaluation Index Sys-
tem [J]. China University Teaching, 2014 (7)
Luo Zhiyong, Gan Mengyu, Luo Yiwen. Research on the
construction of a blended teaching model of university
chemistry based on flipped classroom. University Edu-
cation, July, 2022.
Quality [J]. Serbian Journal of Management, 2012(2): 203
-218.
Shan Wengui. College Teaching Evaluation Index System
and Information Processing [J]. Work Viewpoint, 2004
(10)
Wu Zhenggang, Yan Ming, Zhang Ruihong. The Construc-
tion of Student centered University Quality Evaluation
System [J]. Heilongjiang Education (Higher Education
Research and Evaluation), 2019 (4)
Yu Haijiao. Exploration and practice research of "flipped
classroom" in electronic information class based on
"online+offline" hybrid teaching mode. Computer
Knowledge and Technology, July 2022: Vol.18, No.21.
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
300
