
Knowledge Atlas of Online Education Research in China Based on
Visual Analysis
Xiao Xiao
*a
and Guanghua Yang
b
School of business administration, Wuhan Business University, Wuhan 430056, China
Keywords: Online Education, Citespace, Visualized Analysis, Knowledge Map.
Abstract: By analyzing the situation of my country's online education research, we summarize the research hotspots and
future trends, with the purpose of providing reference and reference for my country's online education
innovation research. Combined with Citespace, this paper draws a scientific knowledge map of my country's
online education research based on the online education related literature in the CSSCI database. It is found
that my country's online education research is significantly affected by national policies and the new crown
epidemic, the number of published articles shows a steady growth trend, and the research group is scattered
Therefore, scholars need to strengthen cooperation with institutions, further scientific and objective in-depth
practice, and combine qualitative and quantitative research methods to promote a more comprehensive
development of online education research.
1 INTRODUCTION
Compared with Western countries, China's online
education started relatively late. Technically
restricted by Internet technology; conceptually
shackled by traditional classrooms, although various
platforms and companies are trying their best to
explore and move forward, the industry is developing
slowly. In October 2019, 11 departments including
the Ministry of Education jointly issued guidelines,
proposing to promote the healthy development of
online education. The new crown epidemic in 2020
has caused an unprecedented interruption of
education services. The Ministry of Education called
for "suspending classes without stopping school".
The "China Education Modernization 2035" issued
by the State Council clearly proposed to "accelerate
the educational reform in the information age". Based
on this, this paper uses Citespace software to analyze
the literature on the theme of "online education" in
my country in recent years, and presents the research
progress through visual means, in order to provide
decision-making reference for practical work.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9577-9517
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6150-2977
2 RESARCH METHODS AND
DATA SOURCES
2.1 Research Methods
2.1.1 Scientific Collaboration Analysis
The research hotspots and frontiers in the field of
"online education" are investigated through
bibliometrics, and the evolution characteristics of
research in this field are revealed in an objective,
quantitative, direct and visual way through data
mining and graph analysis, which can effectively
avoid traditional literature research methods.
Questions that are biased towards inductive reasoning
and are too subjective.
This study uses Citespace's visual analysis of
online education research, and uses a combination of
quantitative and qualitative methods to cluster the
knowledge base and keyword co-occurrence of the
literature, and then analyze the research context and
trends of online education.
Xiao, X. and Yang, G.
Knowledge Atlas of Online Education Research in China Based on Visual Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0011913100003613
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education (NMDME 2022), pages 421-428
ISBN: 978-989-758-630-9
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
421

2.1.2 Price's Law
The square root of the total number of scientists,
produces 50 percent of all scientific papers. If the
number of papers published by the most productive
scientist is set as nmax, and the total number of papers
published by scientists is denoted as x(1,nmax),
price's law can be expressed as follows:
(1/2) × (1 ,𝑛𝑚𝑎𝑥) =𝑥(𝑚 ,𝑛𝑚𝑎𝑥)
= 𝑥(1,𝑚)
(1)
Where, M is such a number assumed by Price, that
is, the total number of papers published by scientists
whose individual number of papers is greater than m
is exactly equal to half of the total number of papers,
and the meaning of X (m, nmax) in the equation
exactly represents this half of papers.
Based on lowe's law and mathematical
conclusion, price deduced that m≈0.749(nmax 1/2).
2.1.3 The K-Mean Clustering Algorithm
K-means is a clustering algorithm based on the
partition of sample sets. K-means clustering divides
the sample set into K subsets to form K classes, and
divides N samples into K classes. The distance from
the center of each sample to its class is the smallest,
and each sample belongs to only one class. For large
data sets, k-means clustering is relatively scalable and
effective.
Given the data sample X, n objects are included
X={X
1
, X
2
, X
3
, ...., X
n
},Where each object has
properties of m dimensions. The goal of the K-means
algorithm is to cluster n objects into the specified k
class cluster based on the similarity between the
objects, and each object belongs to and only to one
class cluster with the smallest distance from the
center of the class cluster. For K-means, the k
clustering centers need to be initialized first{C
1
, C
2
,
C
3
, ...., C
k
}, 1<k≤n ,Then, by calculating the
Euclidean distance from each object to each cluster
center, as follows:
dis(Xi,Cj)=
(𝑋
− 𝐶
)
(2)
In the above formula the X
i
represents the i-th
(1≤i≤n) object, the C
j
represents the j-th(1≤j≤k)
cluster center, the X
it
represents the t-th attribute of
the t-th (1≤i≤m) object, The C
jt
represents the t-th
attribute of the j-th cluster center. Comparing each
object from distance to each cluster center in turn,
assigning objects to the class cluster from the nearest
cluster center, yields k class clusters{S
1
, S
2
, S
3
, ...,
S
k
}.
The K-means algorithm defines the prototype of
the cluster with the center. The cluster center is the
mean of all the objects in the cluster in each
dimension. The calculation formula is as follows:
𝐶
=
∑
𝑋
∈
|
𝑆
|
(3)
In the formula, C
l
represents the center of the l-
th(1≤i≤k) cluster,│S
l
│ represents the number of
objects in the l-th class cluster, X
i
represents the i-th
object in the l-th class cluster, 1≤i≤│S
l
│.
Therefore, the visual analysis of online education
research in this paper mainly focuses on the
clustering of knowledge base and keyword co-
occurrence of the literature, and then analyzes the
research context and trend of online education.
2.2 Data Sources
The data of this article comes from the Chinese Social
Science Citation Index (CSSCI). Searching "online
education" in the "all fields" method yields 314
search results. After manual screening, reviews,
reviews, reports, etc. were removed, and finally 286
papers (1998-2022) with reference value were
obtained as research objects, and the acquisition time
was July 12, 2022. By systematically sorting and
summarizing 286 literatures, it shows the history of
online education research in my country.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Analysis of Publication Time
An analysis of the time distribution of the number of
publications is helpful to understand the degree of
attention paid to online education research.
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
422
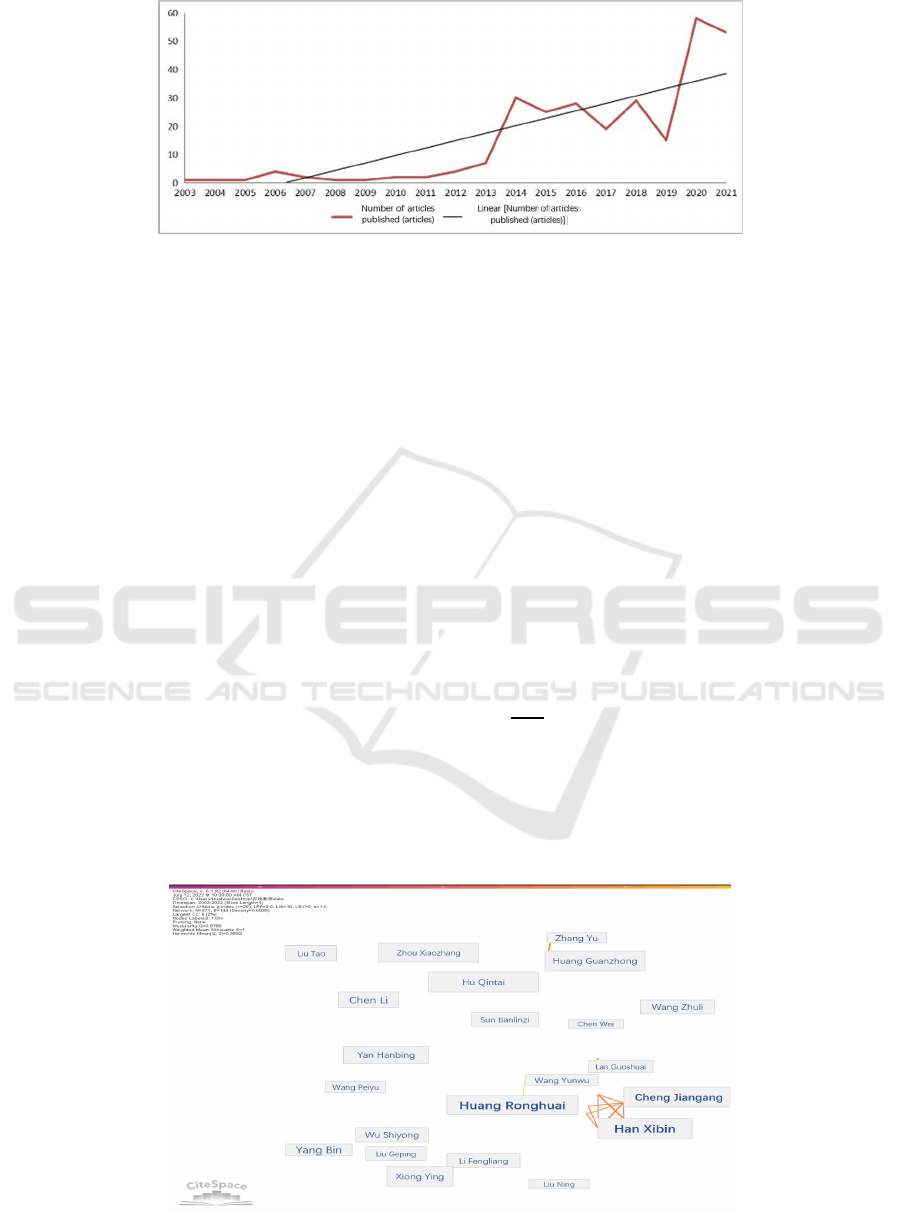
Figure 1: Time distribution of online education research in China.
As shown in Figure 1, the number of published
papers on online education research in my country is
on the rise, especially after 2014, and it will explode
in 2020. 2003-2012 was the initial stage of online
education research. Affected by the development of
information technology, the academic circles paid
less attention to this field, with fewer research groups,
less research efforts, and few published papers. 2014-
2019 is the development stage of online education
research. Although it has grown rapidly, it has
occasional ups and downs, and the fluctuations are
not large. 2020 has been an explosive growth stage of
online education research. Affected by the epidemic,
the scope of online education has been continuously
expanded, the forms of online education have become
more diverse, the research field has been broadened,
the research content has been in-depth, and the
research methods have been diversified.
3.2 Author Analysis
By analyzing the author symbiotic collaboration
network diagram, we can understand the important
scholars in the field and their collaborations.
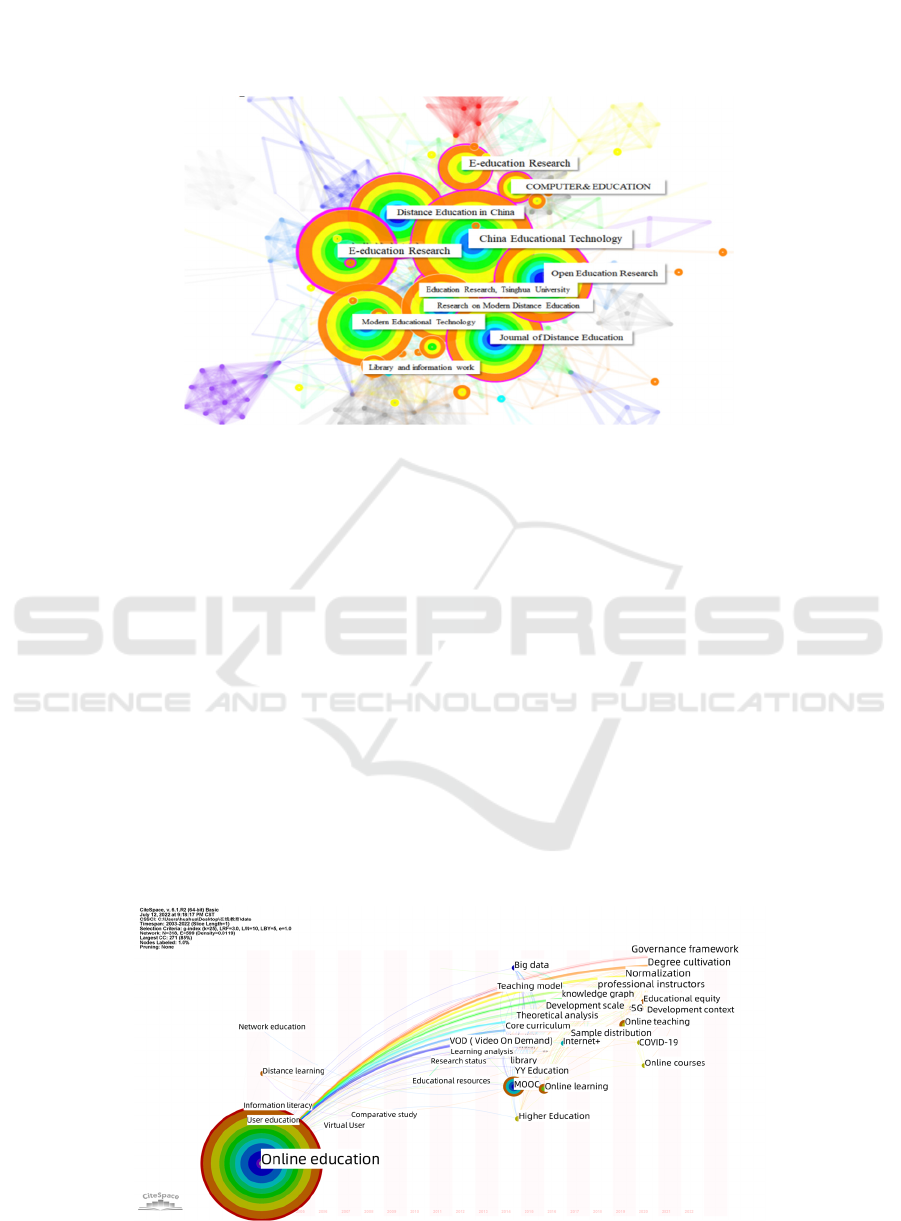
The knowledge map of author cooperation
network in my country's online education research is
shown in Figure 2. The size of the nodes (solid
circles) in the figure represents the number of
documents. The larger the author's name is, the more
the author publishes. The lines between the nodes
represent the author's cooperation. , there are 271
nodes and 144 links in the figure, and the network
density is 0.0039, which indicates that the
cooperation between domestic researchers in the field
of online education is not close. In this field, there is
only a 7-person cooperation network headed by
Cheng Jiangang and Han Xibin, and the rest of the
people are scattered, and there are a large number of
independent research scholars.
According to Price Law (Price Law): the total
number of scientists square root, the number of
people who have written 50% of all scientific papers.
According to the number of nodes, the number of
authors in the field of online education research is
271, so the number of core authors in this field should
be
√
27116.However, more than half of the papers
in this field have more than 16 authors, so there are
no more authors in this field. No core author group
has been formed.
Figure 2: Co-occurrence map of authors in online education research in China
Knowledge Atlas of Online Education Research in China Based on Visual Analysis
423
3.3 Source Analysis of Important
Journals
Academic journals are an important channel for the
dissemination of scientific research results. Co-
citation analysis of journals can provide the
distribution of important knowledge sources in a
certain field.
Figure 3: Journal co-citation network for online education research in China.
Citespace selected Cited Journal to obtain the co-
citation network of journals in the field of online
education in my country, as shown in Figure 3. There
are 484 nodes in the graph, 1929 links, and a density
of 0.0165. In Citespace, nodes whose centrality
exceeds 0.1 are key nodes. It can be seen from the
network of co-cited journals that "China Electronic
Education" has the highest citation frequency, and the
journals are mainly electronic education, which has a
strong concentration.
3.4 Evolutionary Path Analysis
My country's online education research can be
divided into three periods, the first stage is 2003-
2012, the second stage is 2014-2017, and the third
stage is 2019-present.
The first stage of research on online education in
my country is mainly in two aspects: on the one hand,
through the analysis of the advanced experience of
the United States and other university libraries, it is
proposed to promote online information literacy
education in my country and build a related education
system, and its main development object is university
books. The main purpose is to enhance the
information quality of teachers and students; on the
other hand, when China enters the Internet 1.0 era, it
proposes to use the Internet to conduct research on
distance education. The articles at this stage are few
and scattered, limited by the limitations of the
popularization of the Internet, the research mainly
focuses on the feasible discussion and analysis of
online education for a small number of groups or
institutions, which belongs to the theoretical research
stage.
Figure 4: Evolutionary path of online education research in China
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
424

The second stage originated from the "Ten-Year
Development Plan for Education Informatization
(2011-2020)" issued by the Ministry of Education of
China. The document proposed to "build an
intelligent teaching environment, provide high-
quality digital education resources and software
tools, and advocate network inter-school
collaboration learning and improving the level of
information-based teaching". In 2010, my country's
Internet development entered the era of 2.0, that is,
the mobile Internet stage, with a large-scale increase
in Internet users. In 2013, MOOC was introduced into
China, setting off a frenzy on MOOC research, and
proposed new development directions such as flipped
classroom, open university, big data + online
education development. This stage focuses on the
practical exploration stage of large-scale online
education platforms.
The third stage started with the global outbreak of
the new crown epidemic. In order to curb the spread
of the new crown epidemic, Chinese schools were
suspended on a large scale, and online learning has
become the only option for China to “suspend classes
and continue learning”. Therefore, online education
has once again ushered in a golden period of
development, and scholars at this stage have begun to
focus on research on the diversification of online
education. The research is centered on online
education, including four aspects: the implementation
of teaching activities, the guarantee of teaching
operation, the reform of education and teaching, and
the balanced development of education.
3.5 Keywords Co-Occurrence Analysis
Keywords are the author's highly generalized and
centralized description of the content of the literature.
Co-occurrence analysis of keywords can reflect the
research hotspots in this field to a certain extent. The
keyword co-occurrence network knowledge map of
my country's online education research is shown in
Figure 5. There are 318 nodes, 599 chains, and a
network density of 0.0119. The top 20 high-
frequency keywords are extracted and sorted in
descending order, see table 1.
Figure 5: Keyword co-occurrence network of online education research in China
Table 1: Top10 keywords of online education research in China.
serial number
Fre
q
uenc
y
ke
y
words
1 208 online education
2 16 MOOC
3 12 Online learnin
g
4 11 Big data
5 8 Hi
g
her education
6 7 The remote education
7 7 COVID-19
p
andemic
8 7 Education fai
r
9 7 Online teachin
g
10 6 Factors affecting the
Knowledge Atlas of Online Education Research in China Based on Visual Analysis
425

3.5.1 MOOC
With the rapid development of Internet technology
and knowledge economy, and the popularity of the
worldwide resource openness movement, massive
open online courses "MOOC" have begun to emerge.
Liu Hehai believes that the essence of "MOOC" is
online education, and the key point lies in its
"autonomy, collaboration, and interaction", which are
embodied in three aspects: curriculum design,
teaching philosophy, and learning process. (Liu,
Zhang, Zhu, 2014) Wang Xiao and Wang Zhiquan
believe that MOOCs have brought opportunities for
the reform and development of teaching in my
country's colleges and universities, but they have
obvious limitations in teaching concepts, teaching
processes and teaching effects. The positioning of
courses in college teaching, the construction of
excellent courses of MOOCs, and the teaching mode
of flipped classroom for reference, realize the organic
combination of MOOCs and traditional college
teaching. (Wang, Wang, 2015)
3.5.2 Online Learning
Online learning is not simply to copy the offline
classroom to online, but to understand its essence and
connotation, through careful design and organization,
and a new form of future education that organically
integrates with offline classrooms. Huang Ronghuai
and Zhang Muhua, from the perspective of super-
large-scale Internet education organizations, clearly
pointed out that smooth communication platforms,
appropriate digital resources, convenient learning
tools, diverse learning methods, flexible teaching
organizations, effective support services, and close
government-enterprise relationships The seven
elements of school collaboration are the basic
guarantee for the smooth progress of online learning.
(Huang, 2020) From the perspective of user
experience, Liu Shu believes that learning platforms
have a tendency to homogenize basic functions, and
user experience will become an important driving
force for the development of online learning
platforms. (Liu, 2019) Miao Dongling, Wu Zhao, and
Yan Hanbing constructed an influencing factor model
of online learning from the perspective of
comprehensive learning theory. They believed that
the three dimensions of content, interaction, and
motivation have a significant impact on the stickiness
of online learning. (Miao, Wu, Yan, 2021)
3.5.3 Big Data
The "big data" produced with the transformation of
computer and Internet technology provides a new
opportunity for educational reform and the
improvement of educational quality. Zhu Jiayi
pointed out that educators, educational institutions
and related managers should not overestimate the
impact of big data on educational reform. Personal
success is the result of a combination of factors such
as family, society, and school. (Zhu, 2016) Wang
Shuaiguo takes the smart teaching tool Rain
Classroom as an example to discuss the development
paths of colleges and universities to carry out
teaching reform and use teaching tools to carry out
blended teaching under the background of big data.
(Wang, 2017)
3.5.4 Higher Education
Under the interactive influence of multiple factors
such as information technology innovation,
commercial value promotion and the development of
educational equality and lifelong education concepts,
modern information technology represented by
artificial intelligence has triggered profound changes
in the higher education ecosystem. Wang Cixiao
pointed out that online education in colleges and
universities is faced with three opportunities and
challenges: innovation of educational service system,
reform of talent training system, and structural
development of educational resources. (Wang, 2020)
Hu Dexin and Li Linlu pointed out that the multi-
linkage of online education and higher education
reform has triggered a profound revolution in
learning methods and content, and promoted
subversive changes in teaching methods, content and
teams. (Hu, 2021) Zhang Nanxing believes that the
construction of online higher education courses and
their platforms in my country has a relatively high
starting point in the past 20 years. There is a certain
gap. (Zhang, 2021)
3.5.5 COVID-19 Pandemic
Affected by the new crown epidemic, the school
closure policies of various countries have affected
hundreds of millions of children and adolescents. In
March 2020, the Organization for Economic
Cooperation and Development conducted a global
survey on how education systems are responding to
the epidemic and the challenges faced by large-scale
online education. The study found that the digital
divide is exacerbating inequity in education; the
epidemic has highlighted the social functions of
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
426

schools and put forward higher requirements for
teachers' expectations; China has certain advantages
in school resources and teachers' professional
preparation for online education, but There is an
imbalance in the distribution of resources among
individual students. (Xu,2020)
4 CONCLUSIONS
4.1 Conclusions
Based on the online education-related research
literature published by CSSCI from 1998 to 2022, and
using the information visualization tool Citespace as
the research method, this paper systematically studies
my country's online education research from the
aspects of publication time, authors and journals,
research hotspots and evolution paths. analysis, the
following conclusions are drawn:
The time distribution shows that the number of
articles in online education research, especially after
2014, has shown a significant growth trend,
indicating that the attention of this field is
continuously increasing, which can be divided into
three stages: slow development, rapid development
and explosive growth.
The distribution of authors shows that the online
education research groups in my country are small
concentrated and scattered, with less group
cooperation and more independent research. Only a
cooperation network headed by Cheng Jiangang and
Han Xibin is formed. At the same time, online
education research institutions are scattered, with less
cooperation, and most of them are Colleges of
Education and Information Colleges.
The published journals show that online
education research papers are mainly published in
distance education, open education and education-
related journals. These publications, such as "China
Electronic Education", are highly authoritative
journals in the field of online education, and their
citation frequency is also high. The highest,
"Electronic Education Research" has the highest
centrality, and they are all knowledge carriers and
important communication channels for online
education research.
The analysis of keywords and evolution paths
shows that the hotspots of online education research
are mainly concentrated in MOOC, online learning,
big data, higher education, distance education, etc.
The research content is also drawn from foreign
experience, the domestic macro-educational
environment, and developed into practical teaching
strategies. Research.
4.2 Discussion
With the introduction and development of online
education concept to popularization, the research on
online education in academia has also experienced a
development process from theory to practice, from
macro to micro, and from simple to complex, but
there are still shortcomings.
First of all, online education research generally
emphasizes theory rather than practice, focusing
more on macro-level and theoretical research, and
less on tools and platforms that can effectively guide
online teaching. Secondly, there are more qualitative
researches and less quantitative researches in online
education research, and the researches are more
inclined to the proposal and solution of problems,
with less effect and feedback. Finally, the number of
researchers in online education is large but the
number of leaders is small, the core research team has
not yet been formed, and there is a lack of effective
interaction between research institutions.
In the future, exchanges and cooperation among
scholars should be strengthened to jointly promote a
more comprehensive, in-depth, scientific and
objective research on online education in my country.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank the fund for its support: The National
Business Education, Training and Scientific Research
"Fourteenth Five Year Plan" project in
2022"Ideological and Political Construction and
Practice Research on Core Courses of E-commerce"
(Project No. SKKT-22068).
REFERENCES
Cixiao Wang. Development Venation, Application Status,
and Transformation Opportunities of Online Higher
Education [J]. Modern educational technology, 2020:5-
14
Dexin Hu. Crossover and integration: linkage mechanism
and pattern reconstruction of online education and
higher education reform [J]. College education
management, 2021:77-86
Dongling Miao, Zhao Wu, Hanbing Yan. Factors affecting
online learning viscosity from the perspective of leris’s
(2007) theory [J]. Distance education in China
(Comprehensive Edition), 2021:68-75
Knowledge Atlas of Online Education Research in China Based on Visual Analysis
427

Hehai Liu, Shuyu Zhang, Lilan Zhu. Discussion of
Essence,Connotation and Value of MOOCs [J].
Modern educational technology, 2014:5-11
Jiayi Zhu. Education reform triggered by big data: a ripple
or a huge wave? [J]. Theory and Reform, 2016:118-123
Jinjie Xu. Responses to COVID-19 and Challenges to
Large-scale Online Learning for Global Education
System: Findings and Insights Based on Results from
OECD Survey across Nations [J]. Journal of Distance
Education, 2020: 3-10
Nanxing Zhang. The Status Quo and Further Development
Strategy of China’s Online Higher Education in the
Perspective of International Comparison [J]. Chinese
Higher Education Research, 2021:48-55
Ronghuai Huang. Research on the Core Elements of
Running a Huge Scale of Cyber-learning: A Case Study
of \"Disrupted Class, Undisrupted Learning\"
Supported Effectively by Online Education [J]. E-
education Research, 2020:10-19
Shu Liu. Research on Online Learning Platform Experience
from the Perspective of Users [J]. E-education
Research, 2019:47-52
Shuaiguo Wang. Rain Classroom: The Wisdom Teaching
Tool in the Context of Mobile Internet and Big Data [J].
Modern educational technology,2017: 26-32
Xiao Wang, Zhiquan Wang. Research on the Teaching
Mode of Chinese Universities in the Context of MOOC
[J]. Journal of National Academy of Education
Administration, 2015:41-45
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
428
