
Business English Listening and Speaking Course Blended Learning
Activities: Evaluation Model Construction and Application
Yang Song
Foreign Languages Department, Dalian Neusoft University of Information, Ganjingzi District, Dalian, China
Keywords: Business English Listening and Speaking Courses, The Third-Generation Activity Theory, Blended Learning,
PLS-SEM Formula.
Abstract: Based on the third-generation activity theory and blended learning instructions, this study explores the
evaluation model of factors in on-line and off-line BL learning activities in Business English Listening and
Speaking courses. The result shows that students’ learning motivation positively influences their attitude
towards the teaching resources and compliance with rules. The effective correlation of on-line and off-line
resources integration further influence students’ overall learning outcomes and gains. Teachers’ on-line and
off-line feedback shows great effect on the overall performance. The model contributes greatly to the solution
of blended learning effects evaluation. The study provides meaningful and practical implications for applying
the third-generation activity theory in blended learning activities evaluation model construction.
1 INTRODUCTION
Blended learning is a way to combine traditional
teaching activities with online teaching activities. At
present, BL based on SPOC and MOOC is a new form
of teaching innovation. And the focus of BL has been
shifted from the teaching resources design to the
design of teaching activities. The third-generation
activity theory focuses on the conflicts of internal
factors in an activity system and the integrations of
these factors. The third-generation activity theory can
provide theoretical bases and guidance for BL
activities design and better learning outcomes. BL in
foreign language teaching has exhibited its unique
characteristics. Its flexibility and effectiveness has
been recognized widely. However, the studies on how
to evaluate the effectiveness of foreign languages BL
activities have been deficient. Business English
Listening and Speaking course is the core curriculum
for Business English major students. The course aims
to improve students’ listening and speaking ability in
the business environment. Business knowledge,
listening strategy, and communication skills are all
important knowledge input for the course. The course
is a big challenge for both teachers and students.
Based on the third-generation activity theory, the
study will focus on the conflicts and interactions in
the blending learning activities of Business English
Listening and Speaking course. And the study aims to
deepen the application of BL in Business Listening
and Speaking courses and also to provide effective
reference for the evaluation of BL activities.
2 RELATED THEORY AND
RESEARCH
2.1 Blended Teaching Activities Design
in Business English Speaking and
Listening Course
Blended learning is a new approach that combines
online teaching materials and resources with off-line
classroom-based teaching activities (Guan, 2020).
Blended learning is to enhance the teaching and
learning experiences for teachers and students by
combining face-to-face learning activities with on-
line learning activities. In recent years, many cases
showed that BL can achieve better learning outcomes.
Also more efficient teaching and better course
management can be seen in BL, as it provides more
diversified ways of knowledge input and teaching
methods. Technology advancement provides new
opportunities and tools for students to learn in multi-
medium environment. BL is designed and delivered
in a way that enhances and changes the teacher’s role
486
Song, Y.
Business English Listening and Speaking Course Blended Learning Activities: Evaluation Model Construction and Application.
DOI: 10.5220/0011914200003613
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education (NMDME 2022), pages 486-491
ISBN: 978-989-758-630-9
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
from a lecturer to a facilitator, from a dominator to a
helper. BL on-line platforms can further support class
activities like group discussions, deliverables
submissions, and feedbacks provisions. Varied BL
materials increase the availability and richness of
learning resources for students to interact with each
other and collaborate.
2.2 The Third-Generation Activity
Theory
Activity theory views that in the process of human
leaning activity, the role of mediations is very
important and it is the key factor for the learning
subject to change the objects and to realize the
cognition development (Vygotsky,1978). Activity
theory has evolved for generations. Vygostky in 1978
firstly proposed the first generation of activity theory
as part of the social cultural theory. The idea of
Vygostky is that human interactions are based on
mediations and interactions with the surrounding
environment. And in n1981, Leont forms the second
generation of activity theory based on the first one.
With the increased interest on individual and common
complexity, together with the existing of social
mediators, the second generation of activity theory
contains more levels of activities. In 1999, Engestrom
and Miettient further propose that human activities
are realized through practices and collaborations.
This is the third generation of activity theory and it
includes at least two sets of interaction activities.
Based on the third-generation activity theory, the
imbalance and mismatch between interactions is
dynamic (Kuutti,1996), and the resolving of conflicts
are helpful in realizing extended learning activity
design. That is to say, the conflicts in the activities are
conducive for the learning object to do extended
learning (Vygotsky,1978). Combining the theoretical
model of third-generation activity theory and the
classification of conflicts, BL design in Business
English Listening and Speaking courses should
consider the very basic activity system, that is the
offline teaching system, which includes the internal
conflicts like students’ learning motivations, teaching
resources, and the learning experience. What’s more,
the conflict between the basic activity system with the
new activity system, that is the BL system is very
obvious as well. Finally, the conflict between the
basic activity system and the on-line SPOC system,
like the integration with SPOC on-line tools with
offline class teaching. The first two conflicts are the
internal conflicts within the basic activity system, and
the third conflict is the conflict between the basic
activity system and the new activity system, the forth
conflict is the conflict in the integration of on-line and
off-line teaching activities. These conflicts are
dynamic due to the characteristics of the learning
subjects. The learning subject continuously interact
and compromise with the conflicts to develop and
evolve further (Kuutti, 1996). The third-generation
activity theory not only provide the theoretical bases
for the design of blended teaching activities, but also
provided the framework and guidance for blended
teaching evaluation model construction and
application.
2.3 PLS-SEM Formula
PLS-SEM is short for Partial Least Square-Structural
Equation Modelling. PLS-SEM includes
measurement scheme, modelling scheme, and the
weighting scheme. And the two main categories of
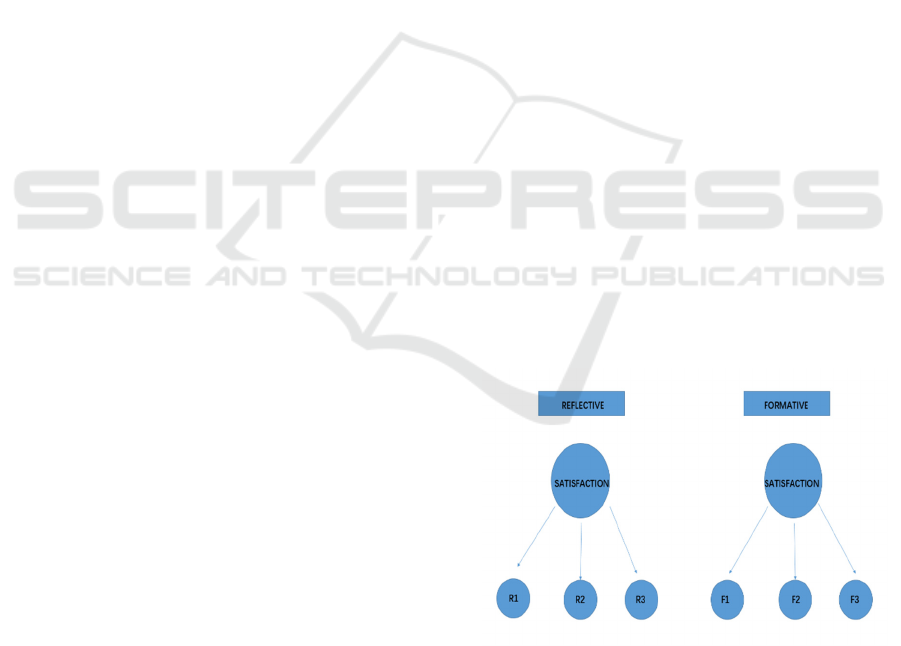
PLS-SEM are Reflective measurement and
Informative measurement, as it is shown is Figure 1.
Partial least squares (PLS) is an iterative estimation
that combines principal component analysis with
multiple regression. It is a causal modelling method,
which is used in Sweden, the European Union and the
United States. PLS method has many advantages:
there is no distribution requirement, while LISEREL
method, one of the other methods, assumes that the
joint distribution of explicit variables is multivariate
normal, and the goal is to predict according to the
block structure, internal relationship, and causal
prediction relationship. PLS estimation is consistent
and basically consistent when the sample size is large
and there are many explicit variables for each hidden
variable.
Figure 1: PLS-SEM Formula.
For Reflective measurement, it can be clearly seen
that the latent variable Y causes items, which are
expressed through indicators. For Informative
measurement, it is obvious that the latent variable Y
is caused by items, that is, the indicator forms the
Business English Listening and Speaking Course Blended Learning Activities: Evaluation Model Construction and Application
487

latent variable. In fact, before 2010, the most
commonly used method was CB-SEM, Covariance-
based Structural Equation Modelling based on
Covariance, which was a typical confirmatory
method. The advantage of the model is used to
determine whether the researcher result is consistent
with the actual data. PLS-SEM evaluates the
parameters based on the variance of the data. It
focuses on what are the exogenous variables that
affect the dependent variable. Thus, what are the Xs
that affect Y. PLS-SEM focuses on multiple X
explaining their respective Y (multiple Y), that is,
multiple indicators explaining a single X, and how
multiple X affects Y.
x
y
x
y
ξ
δ
η
ε
=Λ +
=Λ +
(1)
In the above measurement equation, it describes
the relation between variables and indicators, like the
BL influential factors and the mediation tools in the
teaching process. And X is the exogenous variable. Y
is the endogenous variable. The measurement
equation model is to study the relationship between
the variables like the satisfaction rate and the
credibility of the certain items. The equation model
sets the potential rules and inter connections between
different variables and the influential items.
3 EVALUATION MODEL
CONSTRUCTION
3.1 BL Framework of Business English
Speaking and Listening Course
The SPOC based BL model for Business English
Listening and Speaking courses is to adopt and
combine unit topic related SPOCs into the pre-class,
in-class and after-class teaching procedures. SPOCs
can be used as lead-in learning materials for students
to learn about the unit topics. Also SPOCs are very
important in the difficult and important knowledge
points teaching, as they can provide basic concept
explanations with varied examples and business cases
combined. SPOCs can also be used in after-class
course review and course assignment. We provide
business case study materials and case analysis
requirements for the students. SPOC is a good way to
present business cases to the students after class
through varied blended learning platforms, like Blue
Ink Cloud Class, Rain Class and others. By using
SPOCs in their blended learning process, students can
better their self-study before class and get prepared.
They can internalize the knowledge in class and
consolidate the knowledge after class (Zheng, 2019).
In this way, SPOC is in every phase of the course
learning and its flexibility can greatly promote
independent learning online and offline.
Before class, teachers determine the teaching
objectives and teaching contents according to the
course requirement. Teachers need to prepare
teaching materials for the course including PPTs,
micro lectures, and other video and audio files, and
publish them on blended learning platforms for
students to do pre-class self-learning and get prepared
for the class. Students need to preview micro lectures
for the unit key points which are about listening
strategies and then finish the basic and challenging
exercises for the micro lectures. Also students need to
preview the micro lectures for the unit difficult points
which are about business communication skills and
then upload the oral discussion group work to Blue
Ink Cloud Class. Thirdly, students need to preview
the Business Background Information part of the
textbook. Supplementary micro lectures are also
provided for students to watch and learn. Unit Study
Guide and Unit Resource Usage Guide are also
available for students' pre-class self-study usage.
Students can enter the SPOC teaching platform to
learn related relevant expanded contents to the unit
topic and complete the online discussion and self-
check activities. In class, teachers check and monitor
students online learning process through Q&A
session, group discussion and pair work. Teachers
design various forms of classroom activities such as
role-plays, case analysis, presentations, listening and
dubbing tests and other offline activities to improve
the interaction with students. More importantly,
teachers must play the role as the scaffolder to give
students timely feedback and comment according to
the students in-class performance so that students can
find their weaknesses and make rectified plans to
complete the tasks better and make progress. Finally,
teachers need to summarize and evaluate classroom
teaching activities and review the key and difficult
points. After class, students can access the after-class
assignment and learning materials on the blended
learning platform as well. The after-class study tasks
mainly include oral debates and discussion oral work
related to the business communication skills of the
unit and the basic listening exercises, which are
compulsory. The optional study tasks are the extra
business case studies and the TED listening and
speaking practices. The course blended learning
model is shown in Figure 2.
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
488
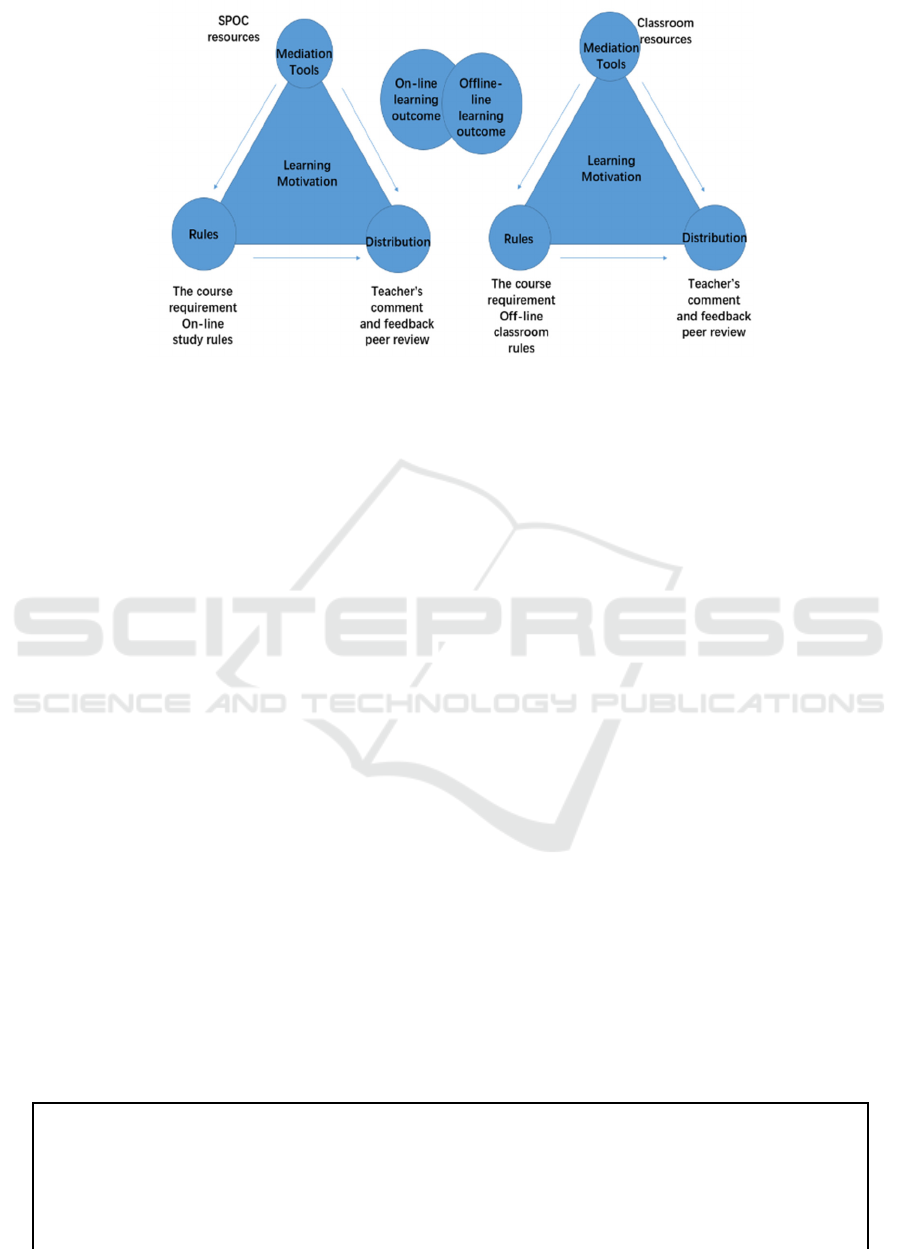
Figure 2: Blended teaching framework based on the third-generation activity theory
As it is shown in Figure 2, the SPOC teaching
activity system includes the students learning
motivation, the online learning effect, which, SPOC
resources, and the course requirements, together with
the teacher and student collaboration and the work
distribution factors. What’s more, how the students
use the resources, whether the students obey the rules,
and whether the students can finish the online study
tasks are all critical factors in evaluating the
realization of the course objectives in Business
English Listening and Speaking courses. And on the
left, it is the off-line teaching activity system. The
mediation tools include the textbooks, the course
resources and the related class activities, together
with the classroom rules and regulations, the group
work division, and the teacher’s feedback are all very
important in the internalization of the course input.
Only through combining the off-line teaching with
online teaching and deepening its integration, the
utmost learning outcome can be achieved. BL design
in Business English Listening and Speaking courses
can promote the integration of on-line and off-line
teaching effectively. Teachers served as mentors and
guidance providers in the teaching process. The
students are the subjects. SPOC resources and off-
line teaching resources served as mediation tools. The
on-line and off-line classroom rules, the work
distribution, and the interaction and collaboration all
work together to realize the teaching objectives of the
course.
3.2 The Bl Activities Evaluation Model
Design
Based on the third-generation activity theory and BL
of the Business English Listening and Speaking
course, and referring to the existing research results
by previous scholars, the study designed the
following evaluation model to evaluate the teaching
effects and effectiveness of the Business English
Listening and Speaking course BL teaching. The
evaluation model considers the course related item
including the students’ learning motivation, teaching
resources, the course assessment, and the on-line /off-
line classroom rules. All the factors are set according
to the third-generation theory, including, the subject,
the mediation tools, the object, and the rules. And the
specific evaluation perspectives are set in details
according to course settings, including 6 factors. The
evaluation model includes open questions to get the
students comment and feedback on on-line and off-
line teaching effects. The corresponding evaluation
model setting with all the relating factors are as
follows:
Table 1: Business English Listening and Speaking course blended teaching evaluation model.
Activit
y
Factor BL Learnin
g
Elements Evaluation Content
Subject Learning Motivation
Based on the knowledge of the Business English Listening
and Speaking Course
Mediation Tools
SPOC Resources
Based on the variety, quality and relevance of the SPOC
resources
Classroom Resources
Based on the text material and classroom quality and the
interaction with SPOC resources
Business English Listening and Speaking Course Blended Learning Activities: Evaluation Model Construction and Application
489
Object Learning Outcome
Based on the satisfaction of business knowledge, Listening
strate
gy
a
pp
lication, and oral communication abilit
y
Rules
Evaluation Rules
Based on the requirements of online and offline rules and its
relevance
On-line Study Rules
To obey the on-line learning rules and the blended learning
p
latform usa
g
e data
Off-line Study Rules
To obey the off-line classroom rules and the involvement
and com
p
letion of classroom tasks
Feedback
On-line Feedbac
k
Based on teachers on-line comment and feedback effect
Off-line Feedbac
k
Based on teachers off-line comment and feedback effect
3.3 Data Collection
The study was done through Sojump online survey
tool. It is used as part of the course on-line test
platform as well. The sample covers all together 135
Business English major students who are currently
taking the course, and the survey was done three
times respectively at the beginning of the term, the
middle of the term, and the end of the term. The
survey was designed covering all the activity factors
as discussed above, and all together 27 questions were
asked regarding the students learning motivation, the
resource using experience, and the on-line and off-
line task feedback, and etc. The study of the learning
outcomes covered the three aspects of business
English learning, including the listening
comprehension ability, the oral communication
ability in business environment, and also the ability
to involve and participate in certain business
occasions with cross-cultural backgrounds.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Evaluation Model to Solve the
Blended Teaching Conflicts
The driving power in the evaluation model design is
to solve the possible conflicts in the BL teaching
process of Business English Listening and Speaking
courses. And the ultimate goal is to improve the
overall learning effect of the course. Firstly, the
students’ learning motivation is the most important
factor when considering students’ learning outcomes.
Only through the promotion of students’ learning
outcomes, the learning effects can be improved
greatly. Teachers can do research on the students’
learning motivations, and try to understand its variety
and characteristics. After sufficient research, teachers
can analyse the existing problems and weak points in
the learning motivation, and set personalized study
plans to effectively improve students learning
motivation. Secondly, the mediation tools, which are
the on-line and off-line teaching resources, are the
most important mediation tools between the study
subject and the object. Thus, in the process of course
teaching, students use SPOC and off-line learning
resources available to realize the internalization of the
course input, the listening strategy, business
knowledge, and the oral communication ability in the
business context. In this whole process, teachers
should focus on the teaching resources and teaching
activity design, to make sure the natural integration of
the on-line and off-line content. Only in this way, the
course intended input can be reconstructed, so as to
realize the transition from knowledge learning to
skills application. Thirdly, the rules and work division
in the class activity setting are important to control
and supervise the whole process of class activity
implementation. In the Business English Listening
and Speaking course teaching, teachers should focus
on the unified goals of both on-line and off-line
teaching. Also teachers should set measurable and
realizable teaching objectives. The coherence
between online and offline teaching is also very
important, as BL is not about multiple teaching goals
nor teaching methods, it is the integration of on-line
and off-line teaching that really matters in the
teaching process.
4.2 Data Analysis
Based on the evaluation model we have constructed,
we set all the components and factors that are
included in the model as F, standing for different
factors. In the SPOC on-line activity system,
students’ study motivation is heavily influenced by
the Quality of SPOC Resources, that is F1. Also the
Obedience of On-line Study Rules(F2) is also an
important factor effecting the students’ learning
motivation. And at the same time, F1 and F2
influence greatly on F8(Students Learning Effect).
And between these two factors, the former influences
the latter as well, that is to say the students’ attitude
towards the SPOC resources highly impact their
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
490

obedience of the on-line study rules. In the offline
teaching activity system, Students Learning Effect are
influenced by F3 (Off-line Study Attitude) and F4
(Obedience of Classroom Rules). And at the same
time, F3 and F4 influence greatly on F8(Students
Learning Effect). And likewise, the students’ attitude
towards the off-line classroom teaching materials
influences the indicators in the obedience of the
classroom rules. Last but not least, the teachers’
mediation during the whole process plays an
important role, as can be seen from the indicator
F5(On-line Feedback) and F6(Off-line Feedback).
On-line and off-line feedback both influences the
F8(Students Learning Effect). And we can see from
the below table that the off-line feedback is more
effective, or to say more impactful.
Figure 3: Blended teaching effect evaluation model.
Using the PLS-SEM formula to do the data
calculation, we found that we set each factor with 3-
4 relevant survey questions. The credibility of this
setting is among 0.6-0.8. And the corresponding
influencing factor has certain differentiability with
other factors question setting. Also the credibility for
each question is above 0.07, and it is an indicator to
show that the questions and the factors are well set
and has great corresponding relations. As it is shown
in Figure 3, in the upper part, it shows the
interrelations in the on-line SPOC activity system.
We can see that the students learning motivation has
positive impact on the students’ attitude towards the
SPOC resources(F1=0.34). Also the study motivation
influences the obedience of online rules (F2=0.27). It
is also a positive influence. All together, the overall
influence on the students learning effect is great
(F8=0.67) In the lower part, we can see the
interrelations between students learning motivation
and its relation with the off-line classroom resources.
It has obvious positive impact as we the indicator
F3=0.36, which is little bit higher than the indicator
between online resources. The same rules go with the
correlation with the obedience of the offline
classroom rules (F4=0.24). Both the off-line
classroom resources and the obedience of on-line
rules account for the overall students learning effects.
The on-line and off-line feedback provided by
teachers and peers also has positive influence on the
overall learning effects, as it is indicated F5=0.20 and
F6=0.36. We can conclude that the mediation on the
above factors are quite obvious and has positive
relations.
5 CONCLUSION
Based on the third-generation of activity theory, take
the evaluation model of Business English Listening
and Speaking courses blended teaching model as an
example, the paper discussed the possible and
potential conflicts in the BL process, and to extend
the current understanding of BL practice. And the
study has its limitations, as the evaluation model is set
from the prospective of students only, not considering
the perspective of teachers and other aspects. Also the
evaluation model didn’t include all the evaluation
factors like the students’ personal interest and the
complexity of the teaching resources. Hopefully, in
the future, the current model can be constantly
improved through the future rounds of teaching and
this teaching model can shine some light on the other
coursed blended teaching design.
REFERENCES
Guan Enjing. The Research on the Effectiveness of Blended
Teaching - Take 68 Courses from Shan Technology
University as Examples [J]. Modern Education
Technology, 2020, (3):39-44.
Horn M B& Staker H. Blended: Uising Disruptive
innovation to improve schools [M]. San Francisco, CA:
Jossey-bass,2014.
Kuutti K. Activity theory as a potential framework for
human computer interaction research [A]. In Nardi B
A(ed). Context and Conciousness: Activity Theory and
Human-Computer Interaction [C]. Cambridge,MA:The
Mit Press, 1996. 17-44.
Vygotsky L S. Mind in Society: The Development of
Higher Psychological Processes [M]. Cambridge, MA:
Harvard University Press, 1978.
Zheng Yongyan. The Research on the Promotion Effect on
SPOC Based Blended Teaching of English Academic
Writing [J]. Computer-assisted Foreign Language
Education, 2019, (5): 50-55.
Business English Listening and Speaking Course Blended Learning Activities: Evaluation Model Construction and Application
491
