
Multi-Domain Data Enhanced Network for Task-Oriented Dialogue
Yuanyuan Cai
1a
, Yutong Shi
1
and Haitao Xiong
2b
1
National Engineering Research Centre for Agri-Product Quality Traceability, Beijing Technology and Business
University, Beijing, China
2
School of International Economics and Management, Beijing Technology and Business University, Beijing, China
Keywords: Multi-Domain, Task-Oriented Dialogue, End-to-End, Transfer Learning, Neural Network.
Abstract: Intelligent dialogue system is a new approach to human-machine interaction, replacing highly repetitive and
standardized customer service. It has been applied widely for various purposes in many domains, such as
weather inquiry and hotel booking. However, the performance of dialogue systems is limited to domain-
specific data which is insufficient to train a high-quality dialogue model. To address this issue, we purpose a
multi-domain data enhanced neural model with an end-to-end framework. This model fuses integrated-
domain features and individual-domain features to improve the performance on dialogue generation in each
specific domain. The experimental results on the two datasets show that our dialogue model outperforms
existing methods, which indicates it has high flexibility in domains with small-scale data.
1 INTRODUCTION
As the core research in artificial intelligence, human-
machine dialogue technology is widely used in
various common scenarios, such as customer service
and intelligent assistants. Thus, it has attracted
extensive attention from academia and industry. For
the past few years, benefiting from the breakthrough
progress in natural language processing under the
wave of deep learning, more and more scholars have
applied deep learning to dialogue systems and
achieved new improvements. Generally speaking,
there are two kinds of dialogue systems according to
the application domain: open-domain and task-
oriented dialogue systems
(Bordes et al., 2016)
. Open-
domain dialogue is an essential branch of the dialogue
system, which refers to chat that is not limited to
topics and has no clear purpose for dialogue.
However, compared with the task-oriented dialogue,
it has strong randomness and uncertainty. Task-
oriented dialogue has a clear purpose, and the
speakers know exactly what they want the machine to
help them accomplish (Le and Mikolov, 2014).
Therefore, it is applied in various industries to help
users complete predetermined tasks or actions, such
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1310-033X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3505-4925
as booking airline tickets, hotels, and restaurants,
which is the focus of our research.
Early researches mainly focus on pipeline-based
dialogue systems. In order to achieve task-oriented
dialogue generation, the pipeline-based dialogue
consists of three essential components(Wei et al.,
2018): The question will be processed in the first
module to extract the intent and the implicit
information. Then, the second module will update the
state according to the user intent and generate
corresponding system actions. The last module
converts the system actions into natural language.
However, the limits of pipeline-based methods are
obvious. It requires a lot of manual annotation for
each independent module. The errors of the upstream
modules will influence the downstream because of its
interdependence structure (Wei et al., 2018; Wen et
al., 2016). Therefore, in recent years, academia has
gradually studied modeling dialog systems in an end-
to-end manner to eliminate error accumulation in
conventional methods. Inspired by the recent success
of the recurrent neural network (RNN) (Chen et al.,
2017) and the memory network (Lei et al., 2018;
Madotto et al., 2018) in machine translation, most of
the newly task-oriented dialogue systems use a
sequence-to-sequence framework. It takes the
conversation as input, and converts the statement into
Cai, Y., Shi, Y. and Xiong, H.
Multi-Domain Data Enhanced Network for Task-Oriented Dialogue.
DOI: 10.5220/0011923700003612
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing (ISAIC 2022), pages 299-305
ISBN: 978-989-758-622-4; ISSN: 2975-9463
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
299

a latent feature representation, then generates a
response in a natural language. The end-to-end
dialogue system can directly generate responses
through the dialogue history based on the encoder-
decoder framework. It does not generate error
accumulation compared to the pipeline-based
method. However, it still has some problems that
need to be solved urgently. Most of end-to-end
dialogue systems can only generate responses based
on the dialogue history (Joshi et al., 2017). When the
training data is concentrated in a single domain, this
framework cannot adapt to other domains well, so the
response of the system is relatively slow, and it
cannot be adjusted according to the relevance of each
domain. Even if there are some multi-domain fusion
models, they are not very accurate in learning the
features of each domain.
To address the above issues, we further propose a
multi-domain data enhanced network (MDN), which
finely learn each domain's relevance and fully use
data from existing domains to establish dialogue
system in less-data domains. The MDN model
divides domains into groups and uses attention
mechanism to fuse the features of each domain to
obtain the individual-domain features. In addition, to
emphasize shared knowledge between different
domains, the MDN trains data of all domains to get
integrated-domain features, then combines them with
individual-domain features. Experiments show that
this structure captures the features of each domain
more accurately, and helps to improve the
effectiveness of each domain. The contributions of
the paper are summarized as follows:
Our proposed model captures the correlations
between the current domain and relevant
domains to accomplish transfer learning, which
indicates it has high flexibility in emerging
domains.
We apply an attention mechanism to capture
fine-grained correlations between different
domains.
The experimental results on two public datasets
show that our proposed model outperforms the
previous models.
2 RELATED WORKS
The end-to-end neural network is being hotly debated
in contemporary academics and increasingly
establishing itself as promising research in dialog
systems. Earlier, scholars first proposed the theory of
applying end-to-end networks in dialogue system
models (Wen et al., 2016). According to the theory,
an end-to-end dialogue system based on memory
networks is proposed. (Bordes et al., 2016).
Subsequent studies have followed the experiment and
get deliverables phase by phase. For example, a
scalable sequence-to-sequence dialog framework
introduced a memory network for the encoder-
decoder framework (Lei et al., 2018). This storage
network is used to generate hidden vectors of session
content. Since then, end-to-end task-oriented
dialogue systems typically employ a Sequence-to-
Sequence model to generate system responses from
dialogue histories. (Raghu and Gupta, 2018; Williams
and Zipser, 1989; Serban, Sordoni et al., 2015; Park
and Kim, 2022). Based on the above two models, the
combination of memory network and sequence
structure, Mem2Seq is proposed (Madotto et al.,
2018). It uses global multi-hop attention for memory
retrieval and finally uses probability distribution to
generate dialogue responses in a sequence. At the
same time, the replication mechanism of human
dialogue history and knowledge base is added to the
generation process. A global-to-local memory pointer
network addresses the noise problem (Wu et al.
2019). The model adopts the framework of encoder-
decoder to generate a global memory pointer while
encoding, which is used in the knowledge base
retrieval process.
When the task-oriented dialogue system faces a
small amount of training data, its training effect will
be significantly reduced, because the dependence of
models on prior knowledge is too high, and the
adaptability to a new domain is too weak. Scholars
are increasingly turning their attention to building
less-data-driven dialogue systems. Researchers
analyze APIs beyond the domain scope and designed
a new method based on adaptive representation
learning, which can perform task-oriented dialogue
on a zero-shot dataset (Jin et al., 2021). In order to
solve the shortage and diversity of knowledge base, a
technical means (Kulhánek et al., 2021) reverses
translation to increase the variety of training data sets.
For multi-domain problems, the core concept is to
transfer domain knowledge while focusing on
specific domain information and shared domain
knowledge (Qin et al., 2019).
End-to-end task-based dialogue systems have
been extensively studied. In addition to the
underlying model architecture, the research direction
of end-to-end task-oriented dialogue systems is
gradually moving closer to multi-domain dialogue.
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
300
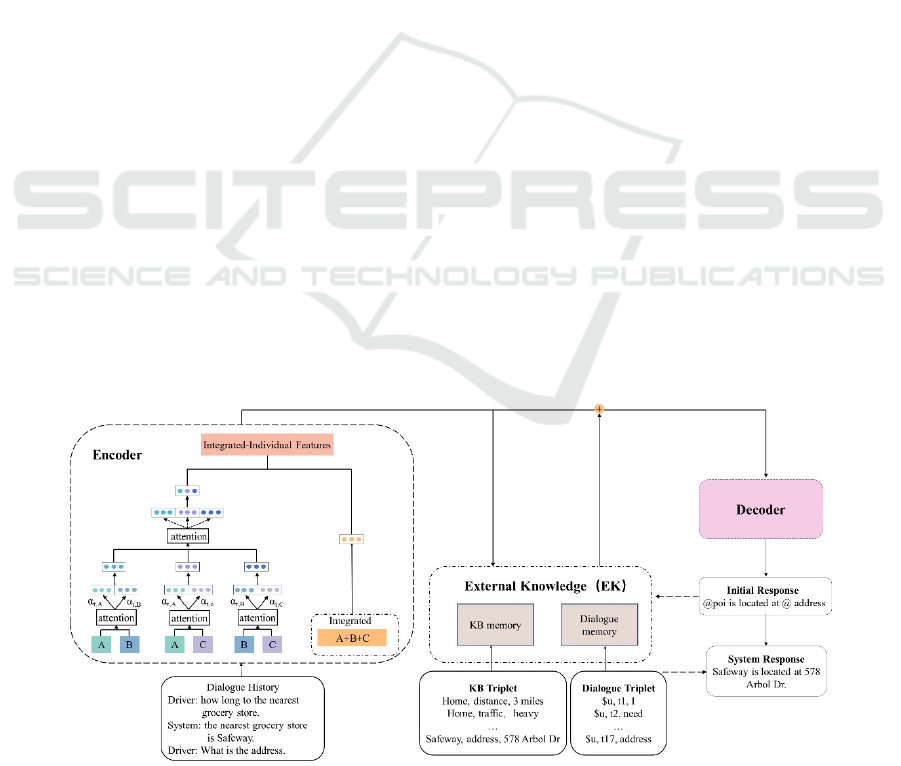
3 MODEL
Our proposed model groups multiple domains and use
attention mechanism to accurately capture the fine-
grained correlation of the current input and each
domain, which achieves transfer learning. As shown
in Figure 1, the MDN model consists of two parts:
encoder and decoder. First, the input sequence is
encoded to integrated-individual features through an
integrated encoder and several domain encoders.
Then the feature vector serves as a query vector to
search the external knowledge (which is composed of
knowledge base and memory). The filtered relevant
information from external knowledge is passed to the
decoder to guide the response generation. The
decoder generates a preliminary response with sketch
tags and searches the external knowledge again to get
the most potential word and replace sketch tags. To
better understand our method, we will elaborate the
construction of our decoder and encoder in 3.1-3.2,
respectively.
3.1 Encoder
To facilitate understanding, we can consider that there
are two types of encoders in the MDN model. One is
integrated encoder, which is trained by mixing data
from different domains, and the output features are
available to all domains. The other is domain encoder,
which is trained separately over each domain and
captures specific features of each domain. We group
domain encoders in pairs and perform both in-group
and out-group fusion to learn fine-grained
correlations between specific domain subsets and get
the individual-domain features. Finally, we fuse
integrated-domain features and individual-domain
features to obtain integrated-individual features.
Both encoders consist of a bi-directional gated
recurrent unit (GRU) (Chung et al., 2014). Encoders
encode the dialogue history to generate context-
sensitive hidden states
()
()
i,A enc 1
BiGRU ,
emb
ii
hxh
φ
−
=
(1
)
As shown in Equation 1,
,iA
h
represents the
hidden state generated by A-domain encoder, where
()
emb
φ
⋅
is the word embedding matrix. As shown in
Figure 1, the MDN uses the attention mechanism
(Guo et al., 2018) to fuse the features of domains A
and B. The same fusion occurs between domains A
and C, domains B and C. Compared with directly
fusing three domains, grouping them provides a more
focused understanding of their relationship and can
capture the fine-grained correlation between domains.
The following are the detailed instructions on how to
fuse the domain features in encoder. Suppose all
domain features at t timestep are represented as
𝒉
,
||
, |D| is the total amount of domains. The
mechanism takes
𝒉
,
as input and outputs the
attention weight score
𝛼
,
through softmax function,
which refers to the degree of relevance between input
and each domain.
()
*
enc ,
Softmax
d
tt
W
α
=+hb
(2
)
The feature vector of group AB is mixed by
domain A and B according to the weight score. The
final individual-domain feature is the optimal domain
fusion feature, generated by the output feature vectors
of the three groups in the same way.
Figure 1: The framework of our model.
Multi-Domain Data Enhanced Network for Task-Oriented Dialogue
301

Unlike domain encoder, which trains over a single
domain data, integrated encoder trains over a multi-
domain data, so its output features are domain
integrated and available for each domain. Finally, we
combine the integrated-domain features with the
individual-domain features:
()
()
enc 2 1 enc enc
LeakyReLU ,
sd
ρ
=
HW WHH
(3)
In order to facilitate the understanding, it can be
assumed that the integrated-individual feature is the
combination of
end
S
H
and
enc
d
H
. Besides, we adopt a
self-attention mechanism to obtain contextual
information, effectively capturing the semantic
relevance between all words in the context. We obtain
the context vector
enc
f
c
by using self-attention over
en
f
H
. Then we use the query vector, which contains
both integrated and individual features to search the
external knowledge.
1
enc enc
f
=qc
(4)
It loops k hops and calculate the attention weight
at each hop k.
()
(
)
enc
Softmax
kkk
ii
=
•
pqc
(5
)
The external knowledge of the MDN model is a
set of trainable embedding matrices, where
k
i
c
is the
embedding in
th
i
memory position. The model
executes the function
()
(
)
enc
Sigmoid
kkk
ii
g = c
•
q
. The
resulting memory distribution is the global memory
pointer
()
1
,,
bT
Gg g
+
=…
, it passes retains relational
knowledge to the decoder and instantiate slot. As
shown in equation,
enc
k
q
is the query vector of the
th
K
hop,
k
i
p
is soft attention. After reading the memory
enc
k
o
according the weighted sum of
1k
i
+
c
, the new
query vector
1
enc
k +
q
is update.
11
enc enc enc enc
,
kkkkkk
ii
i
++
==+
opcqqo
(6
)
can be seen as encoded external knowledge
information, which filter out useless information.
Then it is transmitted to the decoder with the encoded
dialogue history. Therefore, the model can enhance
the interaction between the model and the external
knowledge by querying knowledge to improve
accuracy.
3.2 Decoder
The decoder first generates a response with sketch
tags. Then the hidden state and global memory
pointer are used to query external knowledge again,
copy the word with the highest probability and
replace tags to generate finally response.
The decoder consists of a single-layer GRU called
sketch RNN. Its generative vocabulary has sketch
tags, which represent special entity types. The
decoder will generate “It will @Weather on @Date in
@Location.” instead of “It will rain on Sunday in
Mountain vie” first. At each time step, the hidden
state has two functions, first is to predict the
generation of the next word. When there are no sketch
tags in the preliminary responses, the generated
words can be considered as the final response. In
order to generate output token
t
y
, The MDN
calculates the attention representation
dec,t
′
h
of the
dialogue history first, and then combines it with
dec,t
h
, finally it projects the combination to the vocabulary
space V and U as follow:
dec, dec,
,
ttt
U
′
=
ohh
(7
)
t
o
is the score, which determine the probability of
next word, and the probability
t
y
ν
∈
is finally
calculated as:
()
()
11
,, ,, Softmax
tt t
py y y XB
−
…=∣ o
(8
)
When the preliminary response generates sketch
tags, the global memory pointer will be passed to the
external knowledge and modify the global context
representation with its attention weight. Then h
queries the External knowledge on the pointer
network (Vinyals et al., 2015). The resulting
distribution is the local memory pointer, and the word
with the highest probability is the output. Finally,
copy mechanism (Gu et al., 2016) copies the words
from external knowledge into the reply. This process
is called instantiated sketch tags.
4 EXPERIMENT
In this section, we introduce our experimental
environment and parameter settings. Then we
compare the experimental results with different
models.
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
302

4.1 Experiment Settings
The dataset selected for our experiment are public
dataset SMD (Eric and Manning, 2017) and Multi-
WOZ 2.1 (Budzianowski et al., 2018), as shown in
Table 1.
Table 1: Statistics of two datasets.
Datasets Domains Train Dev Test
SMD
Navigate,
Weather,Schedule
2425 302 304
Multi-
WOZ2.1
Restaurant,
Attraction, Hotel
1839
117 141
The implementation details of the specific
experimental settings are as follows: We set the
dimensionality of the embedding and the number of
GRU hidden units as 128, batch size as 16, and select
3 as the number of memory network's hop. The
number of hop K is set to 1,3,6 to compare the
performance difference. In this experiment, the
dropout rate is selected in the range of [0.1-0.5], and
other weight parameters are initialized by randomly
sampling the values from the uniform distribution.
The model uses the Adam optimization algorithm to
adjust the parameters (Kingma and Ba, 2014).
4.2 Benchmark
This paper selects several representative models as
baseline models to verify the performance of our
model in task-based dialogue.
Mem2Seq (Madotto et al., 2018): The model
proposed global multi-hop attention to copy
words directly from the knowledge base and
dialogue history, effectively combining
knowledge base information.
KB-retriever (Qin et al, 2019): The model
proposes a two-step framework for querying
the knowledge base. It adopts the KB retrieval
component to retrieve the relevant rows of the
knowledge base to filter unnecessary
information and then uses the attention
mechanism to lock the relevant columns.
GLMP (Wu et al., 2019): This model is a
variant of Mem2Seq and proposes a global-to-
local memory pointer network, which designs
a global encoder and a local decoder to filter
the knowledge base.
DF-Net (Qin et al., 2020): Based on GLMP
model, it proposes a dynamic fusion
mechanism, realizes task- oriented intelligent
dialogue in multiple domains, and achieves
state-of-the-art performance.
We implement the public code of DF-Net with the
reported parameters to obtain results, and adopt the
reported results of Mem2Seq, DSR, KB-retriever as
well as GLMP.
4.3 Evaluation Criterion
Following previous work (Eric et al., 2017; Mardoto
et al., 2018; Wen, 2018; Wu, 2019; Qin et al., 2019),
we use BLEU and micro entity F1 metrics to evaluate
model performance.
BLEU: The BLEU score is designed based on
precision (Papineni et al., 2002). It is a commonly
used evaluation indicator for tasks such as machine
translation in natural language processing. Therefore,
we use the BLEU-4 score as the evaluation criterion
to calculate the cumulative score from 1-gram to 4-
gram for our experiments, and primarily test the
performance of models in terms of generating fluent
language over the data.
Entity F1: This metric evaluates the ability of models
for generating relevant entities from external
knowledge and captures the semantics of user-
initiated dialog flows. Both datasets contain dialogues
from three domains, so we compute the per-domain
entity F1 and the aggregated dataset entity F1 to
evaluate the retrieval ability of the model in
individual domain and integrated domains.
4.4 Experimental Results
The performances of MDN versus the previous model
on the SMD dataset and Multi-WOZ2.1 dataset are
shown in Table 2 and Table 3 respectively. It
significantly outperforms the baseline model overall.
We can observe that our proposed model achieves the
highest BLEU scores on both datasets, which is 0.8
and 1.1 higher than the second model. It indicates that
our framework surpasses the prior models, generates
more accurate and fluent responses, and produce
highly readable replies. For the SMD dataset, the
MDN model has the highest entity F1 scores in the
weather domain, schedule domain, and aggregated
domain, which is 0.1%, 3%, and 0.5% higher than the
second baseline model. For the Multi-WOZ2.1
dataset, our model achieves the best performance in
aggregated domain and hotel domain, which
surpasses the second model 3.4% in hotel domain.
The high entity F1-score certifies that this grouping
framework helps sift relevant entities from the
knowledge base in different domains. These
remarkable advances show that it is effective to
improve the performance of most domains by
grouping domains and dynamically fusing features. It
Multi-Domain Data Enhanced Network for Task-Oriented Dialogue
303
can accurately capture the correlation between
domains and enhance the performance of the model.
Table 2: Compared results of different models on SMD.
Model BLEU F1
Navigate
F1
Weather
F1
Schedule
F1
Mem2Seq
(Madotto et al., 2018)
12.6 33.4
20 32.8 49.3
KB-retriever
(Qin et al, 2019)
13.9 53.7
54.5 52.2 55.6
GLMP
(Wu et al., 2019)
13.9 60.7
54.6 56.5 72.5
DF-Net
(Qin et al., 2020)
15.2 60.0
56.5 52.8 72.6
MDN
(ours)
16.0 61.2 55.1 56.6 75.6
Table 3: Compared results of different models on Multi-
WOZ2.1.
Model BLEU F1
Restaurant
F1
Attraction
F1
Hotel
F1
Mem2Seq
(Madotto et al., 2018)
6.6 21.6
22.4 22.0 21.0
GLMP
(Wu et al., 2019)
6.9 32.4
38.4 24.4 28.1
DF-Net
(Qin et al., 2020)
7.8 34.2
37.4 40.3 30.4
MDN
(ours)
8.9 34.2
34.5 35.4 33.8
5 CONCLUSION
In this work, we propose a multi-domain data
enhanced network to explicitly strengthen domain
knowledge for multi-domain dialogues. We adopt
attention mechanism to evaluate the correlation
between the current input and each domain, using the
correlation as a criterion for individual-domain
feature generation. In addition, both encoder and
decoder use query vectors to retrieve external
knowledge to improve response accuracy.
Experiments on two public datasets demonstrate that
our model outperforms the prior models. Besides, our
model is highly adaptable to different domains since
it uses the semantic similarity between domains to
accomplish knowledge transfer in the specific
domains with small datasets.
REFERENCES
Bordes, A., Boureau, Y.-L., & Weston, J. (2016). Learning
end-to-end goal-oriented dialog. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1605.07683.
Chen, H., Liu, X., Yin, D., & Tang, J. (2017). A survey on
dialogue systems: Recent advances and new frontiers.
Acm Sigkdd Explorations Newsletter, 19(2), 25-35.
Chung, J., Gulcehre, C., Cho, K., & Bengio, Y. (2014).
Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks
on sequence modeling. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1412.3555.
Eric, M., & Manning, C. D. (2017). Key-value retrieval
networks for task-oriented dialogue. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1705.05414.
Gu, J., Lu, Z., Li, H., & Li, V. O. (2016). Incorporating
copying mechanism in sequence-to-sequence learning.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1603.06393.
Guo, J., Shah, D. J., & Barzilay, R. (2018). Multi-source
domain adaptation with mixture of experts. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1809.02256.
Jin, D., Gao, S., Kim, S., Liu, Y., & Hakkani-Tur, D.
(2021). Towards zero and few-shot knowledge-seeking
turn detection in task-orientated dialogue systems.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.08820.
Joshi, C. K., Mi, F., & Faltings, B. (2017). Personalization
in goal-oriented dialog. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1706.07503.
Kingma, D. P., & Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A method for
stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1412.6980.
Kulhánek, J., Hudeček, V., Nekvinda, T., & Dušek, O.
(2021). AuGPT: Auxiliary Tasks and Data
Augmentation for End-To-End Dialogue with Pre-
Trained Language Models. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2102.05126.
Le, Q., & Mikolov, T. (2014). Distributed representations
of sentences and documents. Paper presented at the
International conference on machine learning.
Lei, W., Jin, X., Kan, M.-Y., Ren, Z., He, X., & Yin, D.
(2018). Sequicity: Simplifying task-oriented dialogue
systems with single sequence-to-sequence
architectures. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the
56th Annual Meeting of the Association for
Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers).
Madotto, A., Wu, C.-S., & Fung, P. (2018). Mem2seq:
Effectively incorporating knowledge bases into end-to-
end task-oriented dialog systems. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1804.08217.
Papineni, K., Roukos, S., Ward, T., & Zhu, W.-J. (2002).
Bleu: a method for automatic evaluation of machine
translation. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the
40th annual meeting of the Association for
Computational Linguistics.
Park, N., & Kim, S. (2022). How Do Vision Transformers
Work? arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.06709.
Qin, L., Che, W., Li, Y., Wen, H., & Liu, T. (2019). A
stack-propagation framework with token-level intent
detection for spoken language understanding. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1909.02188.
Qin, L., Xu, X., Che, W., Zhang, Y., & Liu, T. (2020).
Dynamic Fusion Network for Multi-Domain End-to-
end Task-Oriented Dialog.
Raghu, D., & Gupta, N. (2018). Disentangling language and
knowledge in task-oriented dialogs. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1805.01216.
Serban, I. V., Sordoni, A., Bengio, Y., Courville, A., &
Pineau, J. (2015). Hierarchical neural network
generative models for movie dialogues. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1507.04808, 7(8), 434-441.
Vinyals, O., Fortunato, M., & Jaitly, N. (2015). Pointer
networks. Advances in neural information processing
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
304

systems, 28.
Wei, Z., Liu, Q., Peng, B., Tou, H., Chen, T., Huang, X.-J.,
. . . Dai, X. (2018). Task-oriented dialogue system for
automatic diagnosis. Paper presented at the Proceedings
of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for
Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers).
Wen, T.-H., Vandyke, D., Mrksic, N., Gasic, M., Rojas-
Barahona, L. M., Su, P.-H., Young, S. (2016). A
network-based end-to-end trainable task-oriented
dialogue system. arXiv preprint arXiv:1604.04562.
Williams, R. J., & Zipser, D. (1989). A learning algorithm
for continually running fully recurrent neural networks.
Neural computation, 1(2), 270-280.
Wu, C.-S., Madotto, A., Winata, G., & Fung, P. (2017).
End-to-end recurrent entity network for entity-value
independent goal-oriented dialog learning. Paper
presented at the Dialog System Technology Challenges
Workshop, DSTC6.
Wu, C.-S., Socher, R., & Xiong, C. (2019). Global-to-local
memory pointer networks for task-oriented dialogue.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1901.04713.
Multi-Domain Data Enhanced Network for Task-Oriented Dialogue
305
