
Sentiment Analysis of Electronic Social Media Based on Deep Learning
Vasily D. Derbentsev
1 a
, Vitalii S. Bezkorovainyi
1 b
, Andriy V. Matviychuk
1 c
,
Oksana M. Pomazun
1 d
, Andrii V. Hrabariev
1 e
and Alexey M. Hostryk
2 f
1
Kyiv National Economic University Named After Vadym Hetman, 54/1 Peremogy Ave., Kyiv, 03680, Ukraine
2
Odessa National Economic University,8 Preobrazhenskaya Str., Odessa, 65082, Ukraine
Keywords:
Sentiment Analysis, Social Media, Deep Learning, Convolutional Neural Networks, Long Short-Term
Memory, Word Embeddings.
Abstract:
This paper describes Deep Learning approach of sentiment analyses which is an active research subject in the
domain of Natural Language Processing. For this purpose we have developed three models based on Deep
Neural Networks (DNNs): Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), and two models that combine convolutional
and recurrent layers based on Long-Short-Term Memory (LSTM), such as CNN-LSTM and Bi-Directional
LSTM-CNN (BiLSTM-CNN). As vector representations of words were used GloVe and Word2vec word em-
beddings. To evaluate the performance of the models, were used IMDb Movie Reviews and Twitter Sentiment
140 datasets, and as a baseline classifier was used Logistic Regression. The best result for IMDb dataset
was obtained using CNN model (accuracy 90.1%), and for Sentiment 140 the model based on BiLSTM-CNN
showed the highest accuracy (82.1%) correspondinly. The accuracy of the proposed models is a quite accept-
able for practical use and comparable to state of the art models.
1 INTRODUCTION
The rapid development of electronic mass media and
social networks has given a new impetus to the de-
velopment of automated Natural Language Process-
ing (NLP) systems.
NLP is an interdisciplinary field at the intersection
of Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence and Lin-
guistics, dedicated to how computers analyze natural
(human) language models.
The range of tasks that NLP solves is quite wide.
For example, NLP can be used to build automatic
systems like machine translation, speech recognition,
named entity recognition, text classification and sum-
marization, sentiment analysis, question answering,
autocomplete, predictive text input, and so on (N1,
2021; Mayur et al., 2022; N43, 2018).
One of the important tasks of NLP is Sentiment
Analysis (SA), also known as opinion mining. SA is
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8988-2526
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4998-8385
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8911-5677
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9697-1415
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6165-0996
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6143-6797
an attempt to extract subjective characteristics from
the text: emotions, sarcasm, confusion, suspicion etc.
The main goal of SA is to classify the polarity of a
given document, and to determine whether the opin-
ion expressed in a document or sentence is positive,
negative, or neutral.
It is a very popular text classification technique
because sentiment can convey a wealth of informa-
tion about one’s point of view on a subject under dis-
cussion. It helps to conduct a comprehensive anal-
ysis of feedback, polarity of messages or reactions.
SA is widely used among businessmen, marketers and
politicians.
In the analysis of public opinion on sensitive so-
cial and political issues, identifying common themes
and tone of discussion can greatly simplify the work
of experts in the field of sociology, political science
and journalism (Iglesias and Moreno, 2020; Pozzi
et al., 2016).
Due to the permanent increase in the amount of
information, previously developed technologies lose
their effectiveness. The ability to quickly monitor and
control public opinion is still the key to success.
Traditionally, this problem has been solved by
dictionary or rule-based approaches (Karamollao
˘
glu
et al., 2018; Dhaoui et al., 2017; Khoo and Johnkhan,
Derbentsev, V., Bezkorovainyi, V., Matviychuk, A., Pomazun, O., Hrabariev, A. and Hostryk, A.
Sentiment Analysis of Electronic Social Media Based on Deep Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0011932300003432
In Proceedings of 10th International Conference on Monitoring, Modeling Management of Emergent Economy (M3E2 2022), pages 163-175
ISBN: 978-989-758-640-8; ISSN: 2975-9234
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
163

2018; Alessia et al., 2015). These approaches are sta-
tistical methods that use pre-assembled sentiment dic-
tionaries containing different words and their corre-
sponding polarities for determining a given word as
“positive” or “negative”.
However, construction complete dictionaries for a
large amount of unstructured data generated by mod-
ern electronic media and social networks are quite a
tedious task.
Machine Learning (ML) methods help solves this
problem. Such approaches are based on algorithms
for classifying words according to the corresponding
sentiment marks. That’s why ML models are pre-
ferred for SA due to their ability to processing with
the large amount of texts compared to dictionary-
based approaches.
In recent decade, Deep Neural Networks (DNNs)
have been actively used to solve many NLP tasks, in-
cluding SA (Li, 2017; Trisna and Jie, 2022; Kamath
et al., 2019). This became possible due to:
• the progress in designing DNNs of various ar-
chitectures (recurrent, convolutional, encoder-
decoder, transformer, hybrid);
• an increasing in computing performance, includ-
ing through the use of graphics processors units
and the availability of various cloud computing
services;
• the creation of labeled datasets for various NLP
tasks;
• development such models of pre-trained vector
representations of words (word embedding) as
Word2vec, FastText (Mikolov et al., 2013; Pen-
nington et al., 2014; Bojanowski et al., 2017)
which are available for many languages.
In the last few years, large pre-trained models
based on the Transformer architecture and Attention
mechanism such as GPT-3, BERT, ELMo etc. has had
a significant impact in the solving of various NLP
tasks (Durairaj and Chinnalagu, 2021; Geetha and
Karthika Renuka, 2021; Deng et al., 2022; Tabinda
Kokab et al., 2022). These models can be interpreted
as language models which formed probability distri-
butions over sequences of words.
Such models are universal and capable of “extract-
ing” features from the text that are useful for solving
many problems of text analysis. But they are quite
“heavy”, contain hundreds of millions parameters and
require significant computational resources.
Therefore, for the most NLP practical applica-
tions, traditional approaches based on ML and Deep
Learning (DL) have been successfully used.
The purpose of our research is to develop set
models for sentiment classification based on different
DNNs architecture and compare their performance on
IMDb and Sentiment 140 Twitter datasets.
2 RELATED WORKS
Drus and Khalid (Drus and Khalid, 2019) provided a
report of review on sentiment analysis in social media
that explored the common methods and approaches
which used in this domain. This review contains an
analysis of about 30 publications published during
2014-2019 years. According to their results most of
the articles applied opinion-lexicon method to analy-
ses text sentiment in social media in such domain as
world events, healthcare, politics and business.
Recently Jain et al. (Jain et al., 2021) published re-
port on ML applications for consumer sentiment anal-
ysis in the domain of hospitality and tourism. This re-
port based on 68 research papers, which were focused
on sentiment classification, predictive recommenda-
tion decisions, and fake reviews detection.
They have shown a systematic literature review to
compare, analyze, explore, and understand ML pos-
sibilities to find research gaps and the future research
directions.
Sudhir and Suresh (Sudhir and Suresh, 2021) pub-
lished comparative study of various approaches, ap-
plications and classifiers for sentiment analysis. They
have discussed the advantages and disadvantages of
the different approaches such as Rule-based, ML and
DL approaches used for SA as well as compared
the performances of the classification models on the
IMDb dataset.
The authors note that, in general, ML-based ap-
proaches provide greater accuracy than Rule-based
ones. At the same time, Conventional ML models
(Support Vector Machine, Decision Trees, and Lo-
gistic Regression) provide classification accuracy at
the level of 85-87% for the IMDb dataset. DL-based
models (CNN, LSTM, GRU) shows higher accuracy:
about 89% on the IMDb dataset.
Trisna and Jie (Trisna and Jie, 2022), presented
a comparative review of DL approaches for Aspect-
Based SA. The results of their analysis show that
the use of pre-trained embeddings is very influential
on the level of accuracy. They also found that ev-
ery dataset has a different method to get better per-
formance. It is still challenging to find the method
that can be flexible and effective for using in several
datasets.
There are several papers devoted to developing
new methods of word embeddings.
Thus, Biesialska et al. (Biesialska et al., 2021)
proposed a novel method which uses contextual em-
M3E2 2022 - International Conference on Monitoring, Modeling Management of Emergent Economy
164

beddings and a self-attention mechanism to detect and
classify sentiment. They performed experiments on
reviews from different domains, as well as on lan-
guages (Polish and German).
Authors have shown that proposed approach is on
a par with state-of-the-art models or even outperforms
them in several cases.
Rasool et al. (Rasool et al., 2021) proposed a
novel word embedding method novel word-to-word
graph (W2WG) embedding method for the real-time
sentiment for word representation. He noted that per-
formance evaluation of proposed word embedding ap-
proach with integrated LSTM-CNN outperformed the
other techniques and recently available studies for the
real-time sentiment classification.
Recently have been published several research pa-
pers devoted using DNNs different architecture based
on CNN-LSTM models for SA task (Elzayady et al.,
2021; Hern
´
andez et al., 2022; Khan et al., 2022;
Priyadarshini and Cotton, 2021; Haque et al., 2020).
Elzayady et al. (Elzayady et al., 2021) presented
two powerful hybrid DL models (CNN-LSTM) and
(CNN-BILSTM) for reviews classification. Experi-
mental results have shown that the two proposed mod-
els had superior performance compared to baselines
DL models (CNN, LSTM).
Khan et al. (Khan et al., 2022) evaluated the
performance of various word embeddings for Roman
Urdu and English dialects using the CNN-LSTM ar-
chitecture and compare results with traditional ML
classifiers. Authors mentioned that BERT word em-
bedding, two-layer LSTM, and SVM as a classifier
function are more suitable options for English lan-
guage sentiment analysis.
Priyadarshini and Cotton (Priyadarshini and Cot-
ton, 2021) proposed a novel LSTM-CNN grid search-
based DNN model for sentiment analysis. As to the
experimental results they observed proposed model
performed relatively better than other algorithms
(LSTM, Fully-connected NN, K-nearest neighbors,
and CNN-LSTM) on Amazon reviews for sentiment
analysis and IMDb datasets.
Haque et al. (Haque et al., 2020) analyzed differ-
ent DNNs for SA on IMDb Movie Reviews. They
have compared between CNN, LSTM and LSTM-
CNN architectures for sentiment classification in
order to find the best-suited architecture for this
dataset. Experimental results have shown that CNN
has achieved an F1 −score of 91% which has outper-
formed LSTM, LSTM-CNN and other state-of-the-art
approaches for SA on IMDb dataset.
Quraishi (Quraishi, 2020) evaluated of four ML
algorithms (Multinomial Na
¨
ıve Bayes, Support Vec-
tor Machine, LSTM, and GRU) for sentiment anal-
ysis on IMDb review dataset. He found that among
these four algorithms, GRU performed the best with
an accuracy of 89.0%.
Derbentsev et al. (Derbentsev et al., 2020) also
explored the performance of four ML algorithms (Lo-
gistic Regression, Support Vector Machine, Fully-
connected NN, and CNN) for SA on IMDb dataset.
They used two pre-trained word embeddings GloVe
and Word2vec with different dimensions (100 and
300) as well as TF-IDF representation. They reported
that the best classification accuracy (90.1%) was per-
formed by CNN model with Word2vec-300 embed-
ding.
3 BASE CONCEPT OF NLP
APPLYING TO SENTIMENT
ANALYSIS
3.1 ML Approach of NLP
To solve NLP problems using ML methods, it is nec-
essary to represent the text in the form of set fea-
ture vectors. The text can consist of words, numbers,
punctuation, special characters of additional markup
(for example, HTML tags). Each such “unit” can be
represented as a vector in various ways, for example,
using unitary codes (one-hot encoding), or context-
independent (depended) vector representations.
The base idea of applying ML to NLP was intro-
duced by Bengio et al. (Bengio et al., 2003). They
proposed to jointly learn an “embedding” of words
into an n-dimensional numeric vector space and to use
these vectors to predict how likely a word is given its
context.
In the case of text, features represent attributes
and properties of documents including their content
and meta-attributes, such as document length, author
name, source, and publication date. Together, all doc-
ument features describe a multidimensional feature
space to which ML methods can be applied.
Thus, in the most general terms, the application
of ML to SA problems consists of the following: text
data preprocessing, feature extraction, classification,
and interpretation of results.
3.2 Data Pre-Processing
The quality of the result depends on the input data.
Therefore, it is important that they are prepared in
the best possible way. In general, pre-processing
stage consists of the following steps (Brownlee, 2017;
Sentiment Analysis of Electronic Social Media Based on Deep Learning
165

Hobson et al., 2019; Camacho-Collados and Pilehvar,
2018):
• Text cleaning. First of all, we need to clean up the
text. Depending on the task, cleaning includes re-
moving non-alphabets, various tags, URLs, punc-
tuation, spaces, and other markup elements;
• Segmentation and tokenization. They are relevant
in the vast majority of cases, and provide division
of the text into separate sentences and words (to-
kens). As a rule, after tokenization all words are
converted to lower case;
• Lemmatization and stemming. Typically, texts
contain different grammatical forms of the same
word, and there may also be words with the same
root. Lemmatization is the process of reducing
a word form to a lemma - its normal (dictio-
nary) form. Stemming is a crude heuristic pro-
cess that cuts off “excess” from the root of words,
often resulting in the loss of derivational suffixes.
Lemmatization is a subtler process that uses vo-
cabulary and morphological analysis to eventually
reduce a word to its canonical form, the lemma;
• Definition of context-independent features that
characterize each of the token, which not depen-
dent on adjacent elements;
• Refining significance and applying a filter to stop
words. Stop words are frequently used words
that do not add additional information to the text.
When we apply ML to texts, such words can add
a lot of noise, so it is necessary to get rid them;
• Dependency parsing. The result is the formation
of a tree structure, where the tokens are assigned
to one parent, and the type of relationship is es-
tablished;
• Converting text content to a vector representation
that highlights words used in similar or identical
contexts.
3.3 Features Extraction
ML algorithms cannot work directly with raw text, so
it is necessary to convert the text into sets of numbers
(vectors) – construct a vector representation. In ML
this process is called feature extraction.
Vector representation is a general name for vari-
ous approaches to language modeling and represen-
tation training in NLP aimed at matching words (and
possibly phrases) from some dictionary of vectors.
The most common approaches for construction
vector representations are Bag of Words, TF-IDF, and
Word Embeddings (Hobson et al., 2019).
3.3.1 Bag of Words
Bag of words (Bow) is a popular and simple feature
extraction technique used in NLP. It describes the oc-
currences of each word in the text.
Essentially, it creates a matrix of occurrences for
a sentence or document, ignoring grammar and word
order. These frequencies (“occurrences”) of words
are then used as features for learning.
The basic idea of applying Bow is that similar doc-
uments have similar content. Therefore, basis on con-
tent, we can learn something about the meaning of the
document.
For all its simplicity and intuitive clarity, this ap-
proach has a significant drawback. The Bow encoding
uses a corpus (or set, collection) of words and repre-
sents any given text with a vector of the length of the
corpus. If a word in the corpus is present in the text,
the corresponding element of the vector would be the
frequency of the word in the text.
If individual words are encoded by one-hot vec-
tors, then the feature space will have a dimension
equal to the cardinality of the collection’s dictionary,
i.e. tens or even hundreds of thousands. This dimen-
sion rises along with the increasing of the amount of
dictionary.
3.3.2 N-Grams
Another, more complex way to create a dictionary is
to use grouped words. This will resize the dictionary
and give Bow more details about the document.
This approach is called “N-gram”. An N-gram
is a sequence of any entities (words, syllable, letters,
numbers, etc.). In the context of language corpora, an
N-gram is usually understood as a sequence of words.
A unigram is one word, a be-gram is a sequence
of two words, a trigram is three words, and so on. The
number N indicates how many grouped words are in-
cluded in the N-gram. Not all possible N-grams get
into the model, but only those that appear in the cor-
pus.
3.3.3 TF-IDF
Term Frequency (T F) is the ratio of the number of
appearing a certain word to the total number of words
in the document. Thus, the importance of a word t
within a single document d
i
is evaluated:
T F(t, d
i
) =
n
t
∑
k
n
k
, (1)
where n
t
is the number of occurrences of the word
t in the document d
i
, and in the denominator of the
fraction is the total number of words in the document.
M3E2 2022 - International Conference on Monitoring, Modeling Management of Emergent Economy
166

But frequency scoring has a problem: words with
the highest frequency have, accordingly, the highest
score. There may not be as much information gain for
the model in these words as there is in less frequent
words.
One way to remedy the situation is to downgrade a
word that appears frequently in all similar documents.
This metric is called T F − IDF (short for Term Fre-
quency – Inverse Document Frequency).
In this metric IDF is the inverse of the frequency
with which a certain word occurs in the documents of
the collection:
IDF(t, d
i
, D) = log
|D|
|{d
i
∈ D|t ∈ d
i
}|
. (2)
Here |D| is the number of documents in the collec-
tion (corpus), {d
i
∈ D|t ∈ d
i
} is the number of docu-
ments in the collection D that contain word t.
There is only one IDF value for each unique word
within a given collection of documents. IDF metric
reduces the weight of commonly corpusused words.
T F − IDF is a statistical measure for estimating
the importance of a word in a document that is part of
a collection or corpus:
T F-IDF(t, d
i
, D) = T F(t, d
i
) × IDF(t, d
i
, D). (3)
T F − IDF scoring increases in proportion to the
frequency of occurrence of the word in the document,
but this is compensated by the number of documents
containing this word.
The disadvantage of the frequency approach based
on this metric is that it does not take into account the
context of a single word. Moreover, it does not dis-
tinguish the semantic similarity of words. All vectors
are equally far from each other in the feature space.
3.3.4 Word Embedding
Word embedding is one of the most popular represen-
tations of document’s vocabulary. This is a technique
that maps words into number vectors, where words
which have similar meanings will be close to each
other with their vector representation in terms of some
distance metric in the vector space.
Word embedding gives the impressive perfor-
mance of DL methods on challenging NLP problem.
Recently, several powerful word embedding models
have been developed:
• Word2vec (short from Words to Vectors, provided
by Google in 2013 (Mikolov et al., 2013);
• GloVe (short from Global Vectors, provided by
Stanford University in 2014 (Pennington et al.,
2014);
• FastText (provided by Facebook in 2017 (Bo-
janowski et al., 2017);
• BERT (short from Bidirectional Encoder Repre-
sentations from Transformers, provide by Google
in 2018 (Devlin et al., 2018).
These models are pre-trained on large corpuses of
texts, including Wikipedia and specific domain.
Word2vec is a set of ANN models designed to ob-
tain word embedding of natural language words. It
takes a large text corpus as input and maps each word
to a vector, producing word coordinates as output. It
first generates a dictionary of the corpus and then cal-
culates a vector representation of the words by learn-
ing from the input texts.
The vector representation is based on contextual
proximity: words that occur in the text next to the
same words (and therefore have a similar meaning)
will have close (by cosine distance) vectors.
Word2vec implements two main learning algo-
rithms: CBoW (Continuous Bag of Words) and Skip-
gram (figure 1).
Figure 1: Simplified representation of the CBoW and Skip-
gram models (Mikolov et al., 2013).
CBoW is an architecture that predicts the current
word based on its surrounding context. Architecture
like Skip-gram does the opposite: it uses the current
word to predict surrounding words.
Building a Word2vec model is possible using
these two algorithms. The word order of the context
does not affect the result in any of these algorithms.
GloVe focuses on words co-occurrences over the
whole corpus. Its embeddings relate to the proba-
bilities that two words appear together. So, GloVe
combines features of Word2vec and singular co-
occurrence matrix decomposition.
In the present study, we applied both Word2vec
and GloVe models to obtain vector representations of
words.
The main application effect of using pre-trained
language models is to obtain high-quality vector rep-
resentations of words that take into account contex-
tual dependencies and allow you to achieve better re-
sults on targets.
Sentiment Analysis of Electronic Social Media Based on Deep Learning
167

4 DNNs Classification Models
Design
After previous stage, we can start building a clas-
sification model. The model type and architec-
ture depends on the research task of SA which can
be performed at different hierarchical levels of text
documents (document-level, sentence-level, word or
aspect-level), domains (reviews about travel agencies,
hotels, movies, election opinion prediction, analysis
of public opinion on acute social and political issues),
binary or multiclass classification.
If we have a dataset of texts with class labels
(for example, with binary labels “positive” and “neg-
ative”), we could apply Supervised ML techniques, in
particular, binary classification algorithms.
Mathematically, this problem can be formulated
as follows: given training sample of texts X =
{x
1
, x
2
, ...x
m
}, for each text there is a class label Y =
{y
i
}, y
i
∈ {0, 1}, i = 1, 2, ...m.
It is necessary to build a classifier model
b(X, w): X → Y , where w is a vector of unknown pa-
rameters or weights.
At the same time, it is necessary to minimize the
Loss function that determines the total deviation of
real class labels from those predicted by the classifier.
For binary classification problems, the most common
is binary cross-entropy:
Loss = −
1
N
"
N
∑
i=1
(y
i
log(p
i
) + (1 − y
i
)log(1 − p
i
))
#
(4)
where N is the size of the training sample, y
i
= {0, 1}
is the true class label for the i-th data sample, p
i
is the
probability of belonging to the positive class for the
i-th data sample provided by the classifier.
4.1 Logistic Regression
Since the task of SA in the general case is reduced to
the binary classification problem (negative, positive),
we chose the Logistic Regression (LR) model as the
baseline classifier b(·):
b(X, w) = σ (⟨w, x⟩), (5)
where ⟨w, x⟩ - denotes the scalar product, σ(·) is a
Sigmoid (logistic) function
σ(z) =
1
1 + exp(−z)
. (6)
LR has such advantage as it can be used to pre-
dict the probability to belong a training sample (in our
case, tokenized and vectorized text) to one of the two
target classes.
4.2 CNN Model
CNNs are a class of DNNs that were originally de-
signed for image processing (LeCun and Bengio,
1998). But these models have shown their efficiency
for many other tasks, such as time series forecasting
(LeCun et al., 2015).
Kim (Kim, 2014) has shown that CNNs are ef-
ficient for classifying texts on different datasets. Re-
cently, they have also been used for various NLP tasks
(speech generation and recognition, text summariza-
tion, named entity extraction).
The architecture of CNNs consists of convolu-
tional and subsampling layers (figure 2).
Figure 2: Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) Architec-
ture for Text Processing (Kim, 2014).
The convolutional layer performs feature extrac-
tion from the input data and generates feature maps.
The feature map is computed through an element-
wise multiplication of the small matrix of weights
(kernel) and the matrix representation of the input
data, and the result is summed.
This weighted sum then passed through the
non-linear activation function. One of the most
common is the function ReLu, which is given as
ReLu(x) = max(0, x).
The pooling (subsampling) layer is a non-linear
compaction of the feature maps. For example, max-
pooling takes the largest element from the feature map
and extracts the sum of all its elements.
After max-pooling, feature maps are concatenated
into a flatten vector, which will then be passed to a
fully connected layer.
The input data for the most NLP problems is text
which consists of sentences and words. So we need
represent the text as an array of vectors of a certain
length: each word mapped to a specific vector in a
vector space composed of the entire vocabulary.
As these vectors, we can use word frequencies
(for example, obtained using the T F − IDF metric),
or pre-trained embeddings (Word2vec, GloVe, Fast-
Text).
M3E2 2022 - International Conference on Monitoring, Modeling Management of Emergent Economy
168
Unlike images processing, text convolution is per-
formed using one-dimensional filters (1D Convolu-
tion) on one-dimensional input data, for example,
sentences, using convolution kernels of different size
(widths).
Applying of multiple kernels widths and feature
maps is analogous to the use of N-grams.
For image processing, convolutions are usually
performed on separate channels that correspond to the
colors of the image: red, green, blue. Set of different
filters is applied for each channel, and the result of
this operation is then merged into a single vector.
For text processing as channels we can consider,
for example, the sequence of words, or words embed-
dings. Then different kernels applied to the words can
be merged into a single vector.
The final result of sentiment analysis is obtained
by applying Sigmoid activation function (binary clas-
sification task) or Softmax (in the case of multi-class
task).
4.3 LSTM and BiLSTM Model
Sequential information and long-term dependencies
in NLP traditionally performed with Recurrent Neu-
ral Networks (RNNs) which could compute context
information, for example, in dependency parsing.
The most common and efficient for many ML
tasks, including NLP, were architectures based on
LSTM (Long Short Term Memory) or GRU (Gated
Recurrent Unit) cells (Brownlee, 2017; Kamath et al.,
2019).
4.3.1 LSTM
LSTM model proposed by Hochreiter and Schmidhu-
ber (Hochreiter and Schmidhuber, 1997) introduces
the concept of a state for each of the layers of a RNN
which plays the role of memory.
The input signal affects the state of the memory,
and this, in turn, affects the output layer, just like in
a RNN. But this state of memory persists throughout
the time steps of a sequence (for example, time series,
sentence, or text document). Therefore, each input
signal affects the state of the memory as well as the
output signal of the hidden layer.
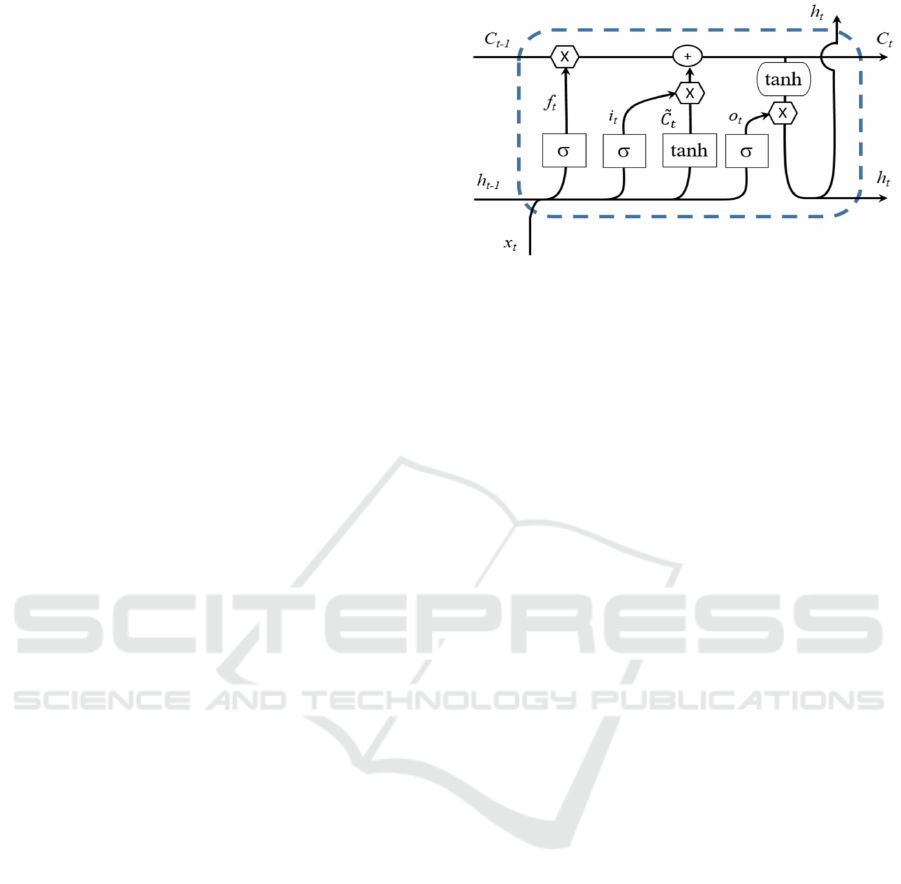
LSTM cell includes several units or gates: the in-
puts, output, and forget gates (figure 3). These gates
are used to control a memory cell that is carrying the
hidden state h
t
to the next time step.
The LSTM cell is formally defined as:
f
t
= σ(W
f
· (h
t−1
, x
t
) + b
f
, (7)
i
t
= σ(W
i
· (h
t−1
, x
t
) + b
i
, (8)
Figure 3: Diagram of a LSTM cell.
˜
C
t
= tanh(W
c
· (h
t−1
, x
t
) + b
c
), (9)
o
t
= σ(W
o
· (h
t−1
, x
t
) + b
o
), (10)
a
t
= i
t
⊗
˜
C
t
, (11)
C
t
= f
t
⊗C
t−1
+ a
t
, (12)
where x
t
– is the vector of input sequence at time
t; C
t−1
, h
t−1
– state (long-term content) and hidden
state in previous time step (t − 1) respectively; σ(·),
tanh(·) are the Sigmoid and Hyperbolic tangent ac-
tivation functions; ⊗ – the Kronecker product; W
f
,
W
i
, W
o
– the weight matrices for input, forget, out-
put of the gates respectively; b
f
, b
i
, b
o
– biases for the
gates.
The input gate i
t
determines which values need to
update. Then the hyperbolic tangent layer builds a
vector
˜
C
t
of new values that can be added to the state
of the cell C
t
.
The forget gate f
t
controls how much is remem-
bered (what part of the information is kept and what
is erased) from step to step. Decision what informa-
tion can be thrown out of the cell state is made by a
sigmoid layer.
The output gate o
t
receives an input signal (which
is the concatenation of the input signal at time step
t and the cell output signal at time step (t − 1) and
passes it to the output. Thus, this gate determines
which part of the long-term content C
t
should be
transferred to the next time step.
Each of these gates is a feed-forward neural net-
work layer consisting of a sequence of weights fitted
by the network with an activation function. This al-
lows the network to learn the conditions for forget-
ting, ignoring, or keeping information in the memory
cell.
Due its structure LSTM can learn and remember
representations for variable length sequences, such as
sentences, documents, and speech samples.
4.3.2 BiLSTM
Unidirectional (standard) LSTM only preserves in-
formation of the past because the only inputs it has
Sentiment Analysis of Electronic Social Media Based on Deep Learning
169

seen are from the past. Unlike standard LSTM, in
BiLSTM (Bidirectional LSTM) model the input flows
in both directions and it’s capable of utilizing infor-
mation from both sides.
So BiLSTM is a sequence processing model that
consists of two LSTMs layers: one taking the input
in a forward direction (from “past to future”), and the
other in a backwards direction (from “future to past”)
(figure 4).
Figure 4: Diagram of a BiLSTM model.
For example, if we want to predict a word by
context (the central word), the network takes a given
number of words to the left of it as the context – the
Forward layer performs it, as well as the words to the
right of it – Backward layer performs it.
Then we can combine the outputs from both
LSTM layers in different ways: as sum, average, con-
catenation or multiplication. This output contains the
information or relation of past and future word.
BiLSTM increase the amount of information
available to the network, improving the context.
It’s also more powerful tool for modeling the se-
quential dependencies between words and phrases in
both directions of the sequence than standard LSTM.
BiLSTM is usually used when we have the se-
quence to sequence tasks but it should be noted that
BiLSTM (compared to LSTM) is a much “slower”
model and requires more time for training.
4.4 CNN+LSTM Model
Both basic DNNs architectures CNN and LSTM have
own advantages and disadvantages. Thus, LSTM net-
works can capture long-term dependencies and find
hidden relationships in the data. CNNs are able to ex-
tract features using different convolutions and filters.
Therefore, the combination of convolutional and
recurrent layers in the model turns out to be effec-
tive in many applied problem such as simulation of
various natural processes, image processing, time se-
ries forecasting, and different NLP tasks (Chen and
Wang, 2018; Derbentsev et al., 2021; Islam et al.,
2020; Khan et al., 2022; Rasool et al., 2021; Shang
et al., 2020).
So we developed two models based on modifi-
cations of CNN+LSTM architecture which final de-
sign and hyperparameters settings are given in the
Section 6.
Our proposed models exploit the main features of
both LSTM and CNN. In fact, LSTM could accom-
modate long-term dependencies and overcome the
key issues with vanishing gradients. For this reason,
LSTM is used when longer sequences are used as in-
puts. On the other hand, CNN appears able to under-
stand local patterns and position-invariant features of
a text.
5 DATASETS AND SOFTWARE
IMPLEMENTATION
All developed DNNs (CNN, CNN-LSTM, BiLSTM-
CNN), and LR as the baseline, were implemented in
the Python 3.8 programming language using Scikit-
learn library for LR, estimation classification accu-
racy, and for designing DNNs models we used Keras
library and TensorFlow as backend.
We evaluate the performance of our models on
two datasets: Stanford’s IMDb dataset (Stanford’s
Large Movie Review Dataset), which contains 50,000
movie reviews as well as Sentiment 140 dataset (Kag-
gle, 2022) with 1.6 million tweets.
Both datasets are intended for binary classifica-
tion: they contain for each text (review or tweet) a
sentiment class binary label. They are also balanced,
i.e. contain the same number of texts for the positive
and negative classes.
6 EMPIRICAL RESULTS
6.1 Pre-Processing and Words
Embeddings
For text pre-processing the Python library package
NLTK (NLTK Project, 2022) was used, as well as cus-
tomers regular expressions.
The pre-processing stage included removing
punctuations, markup tags, html and tweet addresses,
removing stop words and converting all words to
lower case.
Tokenization was performed by using Keras pre-
processing text library. After tokenization we got the
length of the vocabulary in 92393 unique tokens for
M3E2 2022 - International Conference on Monitoring, Modeling Management of Emergent Economy
170

IMDb dataset and 507702 for Sentiment140 respec-
tively to which one token was added for representa-
tion out of vocabulary words.
It should be noted that the selected datasets are
characterized by different average length of texts
(number of words). Thus the length of most reviews
does not exceed 500 words, and tweets – 50.
Since DNNs work with fixed-length input se-
quences we padded zero tokens all reviews and tweets
which length are less than average to fixed length 500
and 50 words (tokens) respectively, and cut longer
texts to these fixed sizes.
For words vector representation was used GloVe
word embeddings with word vectors of dimension
100 provided by Gensim library (
ˇ
Reh
˚
u
ˇ
rek, 2022).
6.2 DNNs Models Design and
Hiperparameters Setting
To initialize the weights of the first layer (Embedding
Layer) for all models, pre-trained GloVe embeddings
of size 100 were used. These weights were frozen and
did not change during training.
The first model, CNN, consists of three sequential
Convolutional layers with filter sets of different ker-
nel widths. These layers are interspersed with Max-
pooling layers. Behind them are a Flatten and a Fully
connected (Dense) layer.
The second, CNN-LSTM model differs from the
CNN by the presence of an LSTM layer instead of
a Flatten after Convolutional and Maxpooling. The
base idea of such architecture is that CNN can be used
to retrieve higher-level word feature sequences and
LSTM to catch long-term correlations across window
feature sequences, respectively.
The third, BiLSTM-CNN model contains two
BiLSTM layers (forward and backward), followed by
a Convolutional and Maxpooling layers. After that,
two Fully connected layers were used to reduce the
output dimension and make prediction.
For all models Dropout layers were also used
to prevent overfitting. As the Loss-function Binary
Cross-Entropy (4) was chosen, which can be calcu-
lated as the average cross-entropy over all data sam-
ples (Geron, 2017).
The final parameters of DNNs architecture are
shown in table 1.
6.3 Evaluating Performance Measures
The datasets were divided in the proportion of: 64%
for training, 20% for validation, and 16% for test sub-
sets respectively.
All DNNs models were trained over 5 epochs with
a minibatch size of 256 and 1024 samples for IMDb
and Sentiment 140 respectively. To compare classifi-
cation performance of the developed models we used
the Accuracy metrics given by:
Accuracy =
T P + T N
P + N
× 100%, (13)
where T P and T N are the number of correctly pre-
dicted values of the positive and negative classes, re-
spectively; P and N are the actual number of values
for each of the classes.
We also calculated F1-score which is harmonic
average between Precision (the percentage of objects
in the positive class, which were classified as posi-
tive, are correctly classified), and Recall (percentage
of objects of the true positive class which we correctly
classified):
F1-score =
2T P
2T P + FP + FN
, (14)
Precision =
T P
T P + FP
, (15)
Recall =
T P
T P + FN
. (16)
Here FP (False Positive) and FN (False Negative) are
numbers of times (data samples) where the model in-
correctly classified these samples as belonging to the
positive and negative classes respectively.
The final results of classification performance are
presented in tables 2-3.
Classification performance on IMDb dataset for
all developed DNN models is better than baseline.
The best Accuracy metric was obtained using the
CNN model (90.09%). At the same time, mod-
els based on the combination of Convolutional and
LSTM layers showed an Accuracy of 2-3% less
(table 2).
It should be noted that obtained results are compa-
rable or even superior in accuracy to the results given
by other researchers (Haque et al., 2020; Quraishi,
2020; Ali et al., 2019) for IMDb dataset.
All models showed significantly lower accuracy
(on average 10% less) on the dataset Sentiment 140
(table 3). The best result was achieved for the
BiLSTM-CNN model – Accuracy 82.1%.
At the same time, the complication of models by
adding new layers did not lead to a significant in-
crease in accuracy, but prolonged the training time.
In our opinion, lower accuracy may be due to the
fact that Sentiment 140 dataset contains many slang
words that are out of vocabulary. So, if for IMDb
dataset the part of the missing words was about 30
percent, then for the Sentiment 140 this part was more
than 70.
Sentiment Analysis of Electronic Social Media Based on Deep Learning
171

Table 1: Final DNNs models hyperparameters setting.
Model Layers Parameters
CNN Embedding emb dim 100, sent len 500(50)
Dropout 0.3
Convolutional 1D 100 filters of size 2, act func ReLu
Max pooling pool size 2
Convolutional 1D 100 filters of size 3, act func ReLu
Max pooling pool size 2
Convolutional 1D 100 filters of size 4, act func ReLu
Max pooling pool size 2
Flattent
Dropout 0.3
Fully connected 1 neuron, act func Sigmoid
CNN-LSTM Embedding emb dim 100, sent len 500(50)
Dropout 0.3
Convolutional 1D 50 filters of size 2, act func ReLu
Max pooling pool size 2
Convolutional 1D 100 filters of size 2, act func ReLu
Max pooling pool size 2
Convolutional 1D 200 filters of size 2, act func ReLu
Max pooling pool size 2
LSTM 64 neurons, reccur dropout 0.3
Dropout 0.3
Fully connected 32 neurons
Fully connected 1 neuron, act func Sigmoid
BiLSTM-CNN Embedding Emb dim 100, sent len 500(50)
Dropout 0.3
Bidirectional LSTM with 100 neurons
Dropout 0.3
Bidirectional LSTM with 100 neurons
Dropout 0.3
Convolutional 1D 100 filters of size 3, act func ReLu
Global Max pooling 1D
Fully connected 10 neurons, act func ReLu
Fully connected 1 neuron, act func Sigmoid
Table 2: Classification performance on IMDb dataset,%.
Models Precision Recall F1-score Accuracy
LR (baseline) 86.62 85.54 86.08 85.90
CNN 90.04 90.31 90.18 90.09
CNN-LSTM 90.90 84.84 87.76 88.08
BiLSTM-CNN 83.08 93.25 87.87 87.03
Table 3: Classification performance on Sentiment 140
dataset, %.
Models Precision Recall F1-score Accuracy
LR (baseline) 71.61 74.63 73.09 74.23
CNN 76.17 79.47 77.78 77.24
CNN-LSTM 78.98 77.47 78.23 78.37
BiLSTM-CNN 79.54 84.41 81.91 82.10
7 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUDING REMARKS
Our research has shown that for sentiment analysis of
social media texts, at least for binary classification,
DNNs of relatively simple architecture with a small
number of layers provide, in general, a level of accu-
racy acceptable enough for practical use.
For the selected English-language datasets IMDb
and Sentiment 140, the classification accuracy using
the Logistic regression model (Baseline) was 85.9%
(74.23%), the CNN – 90.09% (77.24%), CNN-LSTM
– 88.01% (78.36%), and BiLSTM-CNN – 87.03%
(82.10%).
It should be noted that the accuracy of the clas-
sification can be increased if at the stage of pre-
M3E2 2022 - International Conference on Monitoring, Modeling Management of Emergent Economy
172

processing to execute lemmatization (or stemming)
which allow converting the words to their normal
form. This is especially true for tweets that contain
a large amount of user-generated vocabulary.
Also, it may be appropriate to use word embed-
dings weighted by their TF-IDF metric. It is also
possible for out of vocabulary words try to use the
weighted average value of the embeddings of the
neighboring words with a certain window length, or
replace the missing words with normalized TF-IDF
embeddings transformed using the principal compo-
nent method (SVD decomposition of the sparse TF-
IDF matrix to reduce its dimensionality).
In our opinion, a promising direction for carrying
out sentiment analysis of texts in social media is the
use of models based on deep convolutional networks,
or the synthesis of convolutional and recurrent net-
works, and applying the pre-trained embeddings (in
particular, based on GloVe, Word2vec, FastText mod-
els).
At the same time, the use of pre-trained embed-
dings allows to start learning DNNs not from ran-
domly generated values of model parameters, but al-
ready to some extent adapted to the task of text classi-
fication. Moreover, the learning process is accelerated
and the generalization abilities of classifiers based on
deep networks are improved.
REFERENCES
(2018). Natural Language Processing and Information Sys-
tems: Proceedings of 23rd International Conference
on Applications of Natural Language to Information
Systems, volume 10859 of Lecture Notes in Computer
Science. Springer Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/
978-3-319-91947-8.
(2021). Soft Computing in Data Science 6th International
Conference, SCDS 2021, volume 1489 of SCDS: In-
ternational Conference on Soft Computing in Data
Science. Virtual Event, Springer, Singapore. https:
//doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7334-4.
Alessia, D., Ferri, F., Grifoni, P., and Guzzo, T. (2015). Ap-
proaches, tools and applications for sentiment analysis
implementation. International Journal of Computer
Applications, 125(3):26–33.
Ali, N. M., El Hamid, M. M. A., and Youssif, A. (2019).
Sentiment analysis for movies reviews dataset using
deep learning models. International Journal of Data
Mining & Knowledge Management Process (IJDKP),
9(2/3). https://aircconline.com/abstract/ijdkp/v9n3/
9319ijdkp02.html.
Bengio, Y., Ducharme, R., Vincent, P., and Jauvin, C.
(2003). A neural probabilistic language model. Jour-
nal of Machine Learning Research, 3:1137–1155.
https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2000/file/
728f206c2a01bf572b5940d7d9a8fa4c-Paper.pdf.
Biesialska, M., Biesialska, K., and Rybinski, H. (2021).
Leveraging contextual embeddings and self-attention
neural networks with bi-attention for sentiment anal-
ysis. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems,
57:601–626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10844-021-
00664-7.
Bojanowski, P., Grave, E., Joulin, A., and Mikolov, T.
(2017). Enriching Word Vectors with Subword In-
formation. Transactions of the Association for Com-
putational Linguistics, 5:135–146. https://doi.org/10.
1162/tacl a 00051.
Brownlee, J. (2017). Develop Deep Learning Models for
Natural Language in Python. Deep Learning for Nat-
ural Language Processing. http://ling.snu.ac.kr/class/
AI Agent/deep learning for nlp.pdf.
Camacho-Collados, J. and Pilehvar, M. T. (2018). On the
role of text preprocessing in neural network archi-
tectures: An evaluation study on text categorization
and sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 2018
EMNLP Workshop BlackboxNLP: Analyzing and In-
terpreting Neural Networks for NLP, pages 40–46,
Brussels, Belgium. Association for Computational
Linguistics. https://aclanthology.org/W18-5406.
Chen, N. and Wang, P. (2018). Advanced combined lstm-
cnn model for twitter sentiment analysis. In 2018
5th IEEE International Conference on Cloud Comput-
ing and Intelligence Systems (CCIS), pages 684–687.
https://doi.org/10.1109/CCIS.2018.8691381.
Deng, H., Ergu, D., Liu, F., Cai, Y., and Ma, B. (2022). Text
sentiment analysis of fusion model based on attention
mechanism. Procedia Computer Science, 199:741–
748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2022.01.092.
Derbentsev, V., Bezkorovainyi, V., and Akhmedov, R.
(2020). Machine learning approach of analysis emo-
tion polarity electronic social media. Neiro-Nechitki
Tekhnolohii Modelyuvannya v Ekonomitsi, 9.
Derbentsev, V., Bezkorovainyi, V., Silchenko, M.,
Hrabariev, A., and Pomazun, O. (2021). Deep learning
approach for short-term forecasting trend movement
of stock indeces. In 2021 IEEE 8th International Con-
ference on Problems of Infocommunications, Science
and Technology (PIC S&T), pages 607–612. https:
//doi.org/10.1109/PICST54195.2021.9772235.
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., and Toutanova, K.
(2018). Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional trans-
formers for language understanding. https://arxiv.org/
abs/1810.04805.
Dhaoui, C., Webster, C. M., and Tan, L. P. (2017). So-
cial media sentiment analysis: lexicon versus machine
learning. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 34(6):480–
488. https://doi.org/10.1108/JCM-03-2017-2141.
Drus, Z. and Khalid, H. (2019). Sentiment analysis in so-
cial media and its application: Systematic literature
review. Procedia Computer Science, 161:707–714.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.11.174.
Durairaj, A. K. and Chinnalagu, A. (2021). Transformer
based contextual model for sentiment analysis of cus-
tomer reviews: A fine-tuned bert. International
Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Appli-
cations, 12(11). http://dx.doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.
2021.0121153.
Sentiment Analysis of Electronic Social Media Based on Deep Learning
173

Elzayady, H., Mohamed, M. S., and Badran, S. (2021). Inte-
grated bidirectional lstm-cnn model for customers re-
views classification. Journal of Engineering Science
and Military Technologies, 5(1). https://doi.org/10.
21608/EJMTC.2021.66626.1172.
Geetha, M. P. and Karthika Renuka, D. (2021). Improv-
ing the performance of aspect based sentiment anal-
ysis using fine-tuned bert base uncased model. In-
ternational Journal of Intelligent Networks, 2:64–
69. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/
S2666603021000129.
Geron, A. (2017). Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-
Learn and TensorFlow. O’Reilly Media, Inc.
Haque, M. R., Salma, H., Lima, S. A., and Zaman, S. M.
(2020). Performance analysis of different neural net-
works for sentiment analysis on imdb movie reviews.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343046458.
Hern
´
andez, N., Batyrshin, I., and Sidorov, G. (2022). Eval-
uation of deep learning models for sentiment analysis.
Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, pages 1–11.
https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-211909.
Hobson, L., Cole, H., and H.Hannes (2019). Natural Lan-
guage Processing in Action Understanding, analyz-
ing, and generating text with Python. Manning Publi-
cations.
Hochreiter, S. and Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long Short-
Term Memory. Neural Computation, 9(8):1735–1780.
https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735.
Iglesias, C. A. and Moreno, A., editors (2020). Sentiment
Analysis for Social Media. MDPI. https://doi.org/10.
3390/books978-3-03928-573-0.
Islam, M. Z., Islam, M. M., and Asraf, A. (2020). A
combined deep cnn-lstm network for the detection of
novel coronavirus (covid-19) using x-ray images. In-
formatics in Medicine Unlocked, 20:100412. https:
//doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2020.100412.
Jain, P. K., Pamula, R., and Srivastava, G. (2021). A
systematic literature review on machine learning ap-
plications for consumer sentiment analysis using on-
line reviews. Computer Science Review, 41:100413.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosrev.2021.100413.
Kaggle (2022). Sentiment140 dataset with 1.6 million
tweets. https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/kazanova/
sentiment140.
Kamath, U., Liu, J., and Whitaker, J. (2019). Deep Learn-
ing for NLP and Speech Recognition. Springer Cham.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-14596-5.
Karamollao
˘
glu, H., Do
˘
gru,
˙
I. A., D
¨
orterler, M., Utku, A.,
and Yıldız, O. (2018). Sentiment analysis on turkish
social media shares through lexicon based approach.
In 2018 3rd International Conference on Computer
Science and Engineering (UBMK), pages 45–49.
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8566481.
Khan, L., Amjad, A., Afaq, K. M., and Chang, H.-T. (2022).
Deep sentiment analysis using cnn-lstm architecture
of english and roman urdu text shared in social me-
dia. Applied Sciences, 12(5):2694. https://doi.org/10.
3390/app12052694.
Khoo, C. S. and Johnkhan, S. B. (2018). Lexicon-
based sentiment analysis: Comparative evaluation
of six sentiment lexicons. Journal of Informa-
tion Science, 44(4):491–511. https://doi.org/10.1177/
0165551517703514.
Kim, Y. (2014). Convolutional neural networks for sentence
classification. In Moschitti, A., Pang, B., and Daele-
mans, W., editors, Proceedings of the 2014 Confer-
ence on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Pro-
cessing, EMNLP 2014, October 25-29, 2014, Doha,
Qatar, A meeting of SIGDAT, a Special Interest Group
of the ACL, pages 1746–1751. ACL. https://doi.org/
10.3115/v1/d14-1181.
LeCun, Y. and Bengio, Y. (1998). Convolutional networks
for images, speech, and time series. In The Handbook
of Brain Theory and Neural Networks, page 255–258.
MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, USA.
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., and Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learn-
ing. Nature, 521(7553):436–444.
Li, H. (2017). Deep learning for natural language pro-
cessing: advantages and challenges. National Sci-
ence Review, 5(1):24–26. https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/
nwx110.
Mayur, W., Annavarapu, C. S. R., and Chaitanya, K.
(2022). A survey on sentiment analysis meth-
ods, applications, and challenges. Artificial Intel-
ligence Review, 55:5731–5780. https://doi.org/10.
1007/s10462-022-10144-1.
Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., and Dean, J. (2013).
Efficient estimation of word representations in vec-
tor space. In Bengio, Y. and LeCun, Y., editors,
1st International Conference on Learning Represen-
tations, ICLR 2013, Scottsdale, Arizona, USA, May
2-4, 2013, Workshop Track Proceedings. http://arxiv.
org/abs/1301.3781.
NLTK Project (2022). Natural language toolkit. https://
www.nltk.org/.
Pennington, J., Socher, R., and Manning, C. (2014). GloVe:
Global vectors for word representation. In Proceed-
ings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in
Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pages 1532–
1543, Doha, Qatar. Association for Computational
Linguistics. https://aclanthology.org/D14-1162.
Pozzi, F., Fersini, E., Messina, E., and Liu, B. (2016). Sen-
timent Analysis in Social Networks. Elsevier Science.
Priyadarshini, I. and Cotton, C. (2021). A novel lstm–
cnn–grid search-based deep neural network for sen-
timent analysis. The Journal of Supercomput-
ing, 77(12):13911–13932. https://doi.org/10.1007/
s11227-021-03838-w.
Quraishi, A. H. (2020). Performance analysis of ma-
chine learning algorithms for movie review. Interna-
tional Journal of Computer Applications, 177(36):7–
10. https://doi.org/10.5120/ijca2020919839.
Rasool, A., Jiang, Q., Qu, Q., and Ji, C. (2021). Wrs:
A novel word-embedding method for real-time sen-
timent with integrated lstm-cnn model. In 2021
IEEE International Conference on Real-time Com-
puting and Robotics (RCAR), pages 590–595. https:
//doi.org/10.1109/RCAR52367.2021.9517671.
ˇ
Reh
˚
u
ˇ
rek, R. (2022). Gensim: Topic modelling for humans.
https://radimrehurek.com/gensim/.
M3E2 2022 - International Conference on Monitoring, Modeling Management of Emergent Economy
174

Shang, L., Sui, L., Wang, S., and Zhang, D. (2020). Senti-
ment analysis of film reviews based on CNN-BLSTM-
attention. Journal of Physics: Conference Series,
1550(3):032056. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/
1550/3/032056.
Sudhir, P. and Suresh, V. D. (2021). Comparative study
of various approaches, applications and classifiers
for sentiment analysis. Global Transitions Proceed-
ings, 2(2):205–211. https://www.sciencedirect.com/
science/article/pii/S2666285X21000327.
Tabinda Kokab, S., Asghar, S., and Naz, S. (2022).
Transformer-based deep learning models for the senti-
ment analysis of social media data. Array, 14:100157.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.array.2022.100157.
Trisna, K. W. and Jie, H. J. (2022). Deep learning ap-
proach for aspect-based sentiment classification: A
comparative review. Applied Artificial Intelligence,
36(1):2014186. https://doi.org/10.1080/08839514.
2021.2014186.
Sentiment Analysis of Electronic Social Media Based on Deep Learning
175
