
Can the Implementation of the “Double Reduction” Policy Improve
the Satisfaction of Parents of Students at the Compulsory Education
Stage in Ethnic Minority Areas?
Analysis of Intermediary Effect based on Social Capital
Jia Tang
*a
and Yurong Zhu
b
Sichuan Agricultural University, College of Business and tourism, Dujiangyan, China
Keywords: “Double Reduction” Policy, Social Capital, Parents' Satisfaction, OLS Linear Regression Model, Structural
Equation Model.
Abstract: To explore the impact of the “Double reduction” policy on the satisfaction of parents of compulsory education
students in ethnic minority areas, and the mediating role of social capital in the impact of the “Double
reduction” policy on the satisfaction of parents of compulsory education students in ethnic minority areas. It
uses OLS linear regression model and structural equation model to make an empirical analysis of the
relationship between the implementation of the "Double reduction" policy in the stage of compulsory
education in ethnic minority areas and social capital, parents' satisfaction. The results showed that the
satisfaction of parents of compulsory education students in ethnic areas was higher, but there was a group
difference, and the implementation of the “Double reduction” policy could directly improve the satisfaction
of parents of compulsory education students in ethnic areas Social capital mediates the effect of the “Double
reduction” policy on the satisfaction of compulsory education parents in ethnic minority areas.
1 INTRODUCTION
For a long time, rat race's growing involvement in
education has not only increased children's academic
burden, but also created vicious competition in the
field of education. To 2021 this situation, the Central
Committee of the Communist Party of China (CPC)
and the state council have issued the "Opinions on
further reducing the workload of compulsory
education students and the burden of off-campus
training"(hereinafter referred to as the "Double
reduction" policy). The policy put forward the
working goal of "reducing students' excessive
homework burden and off-campus training burden,
family education expenditure and parents'
corresponding energy burden within one year,
achieving remarkable results within three years, and
significantly improving people's education
satisfaction". At present, the "Double reduction"
policy has been implemented for a year, the local
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7066-7095
governments, compulsory education schools have
responded, so that the burden reduction has a positive
effect, and parents' satisfaction has been rising. But
can the implementation of the "Double reduction"
policy improve the satisfaction of parents in ethnic
minority areas? Due to the natural, social and
historical reasons, the development of ethnic
education has many problems, such as high
complexity and difficulty, as a result, parents of
compulsory education students in ethnic areas are less
satisfied with the "Double reduction" policy.
Therefore, to explore whether the implementation of
the "Double reduction" policy can effectively
improve the satisfaction of parents of students
receiving compulsory education in ethnic minority
areas is helpful to understand whether the "Double
reduction" policy is "Acclimatization" in ethnic
minority areas.
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8634-3909
614
Tang, J. and Zhu, Y.
Can the Implementation of the â
˘
AIJDouble Reductionâ
˘
A
˙
I Policy Improve the Satisfaction of Parents of Students at the Compulsory Education Stage in Ethnic Minority Areas? Analysis of
Intermediary Effect Based on Social Capital.
DOI: 10.5220/0011935500003613
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education (NMDME 2022), pages 614-619
ISBN: 978-989-758-630-9
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

2 THEORETICAL BASIS AND
RESEARCH HYPOTHESIS
2.1 The Relationship and Hypothesis of
“Double Reduction” Policy,
Parental Satisfaction and Social
Capital
2.1.1 The “Double Reduction” Policy
Promotes the Satisfaction of Parents in
Ethnic Minority Areas
The implementation of the "Double reduction" policy
is beneficial to comprehensively improve the quality
of education in compulsory education schools, giving
full play to the main function of teaching and
educating people in schools, and thus enhancing the
satisfaction of parents. According to the working
objectives of the "Double-reduction" policy, the
existing research on the impact of the "Double-
reduction" policy on the satisfaction of parents can be
divided into four aspects: First, the "Double
reduction" policy promotes parent’s satisfaction in
ethnic minority areas by reducing students' excessive
homework burden (Zhao 2022). Second, the "Double
reduction" policy promotes the satisfaction of parents
in ethnic areas by improving the level of after-school
services. Third, the "Double reduction" policy can
improve parents' satisfaction in minority areas by
comprehensively regulating out-of-school training
behavior (Xue 2021). Fourth, the “Double reduction”
policy promotes the satisfaction of parents in ethnic
areas by improving the quality of school education
and the level of service (Xiang 2022). To sum up, the
“Double-reduction” policy on the ethnic areas of
student satisfaction with parents has an enhanced
role.
Based on this, we propose hypothesis 1: “Double
reduction” policy can improve the satisfaction of
parents in ethnic areas.
2.1.2 The “Double Reduction” Policy
Enhances the Social Capital Content
The impact of “Double reduction” policy on parents'
social capital is mainly studied from three
dimensions: social participation, social trust and
mutual benefit. In terms of social participation, the
“Double reduction” policy stresses the need to
improve the mechanism of home-school-community
collaboration during the compulsory education stage,
we can create a good social participation platform for
parents from different levels. In terms of Social Trust,
Social Trust is one of the prerequisites for the
formation of social capital (Zhang 2022). In the
process of building the community, parents can
cooperate with the school and social education
platform to establish a solid trust relationship, and
finally enhance the level of trust in the “Double
reduction” policy (Lu 2022). In terms of mutual
benefit, in order to enhance the quality of education
and teaching in schools, and to protect the basic rights
and interests of students, parents and parents, parents
and schools, parents and society should cooperate
with each other to urge the implementation of the
“Double reduction” policy to effectively reduce the
pressure of children's academic. (Li 2022, Zhang
2022) to sum up, the “Double-reduction” policy for
the parents of students to enhance the capital content.
The second hypothesis is that the policy of
“Double reduction” can improve the social capital of
parents.
2.1.3 The Accumulation of Social Capital
Contributes to the Improvement of the
Satisfaction of Parents of Students in
Ethnic Minority Areas
Social capital is an important social resource, which
can improve the satisfaction of parents in ethnic
areas. According to the different subjects connected
by social capital, we can divide the ways of
improving the satisfaction of students' parents into
three basic types. The first line of thinking is that
parents transmit educational expectations to their
children through a network of relationships within the
family (Xie 2017). The second way of thinking is that
social communication between parents and schools
can promote parents' understanding of schools and
teachers, and thus improve the satisfaction of
students' parents (Chu 2021, Zhou 2006). The third
approach concerns the role of social networks within
communities (Teachman 1997).
Based on this, this paper proposes hypothesis 3:
social capital helps to improve the satisfaction of
parents in ethnic areas.
Further, we propose hypothesis 4: social capital
mediates the effect of “Double-reduction” policy on
parents' satisfaction in ethnic areas.
3 RESEARCH DESIGN
3.1 Theoretical Model
Through the mathematical theory of the above
literature, according to the research purposes, a
theoretical model is put forward. Based on the above
literature review and research purposes, a multiple
Can the Implementation of the â
˘
AIJDouble Reductionâ
˘
A
˙
I Policy Improve the Satisfaction of Parents of Students at the Compulsory
Education Stage in Ethnic Minority Areas? Analysis of Intermediary Effect Based on Social Capital
615
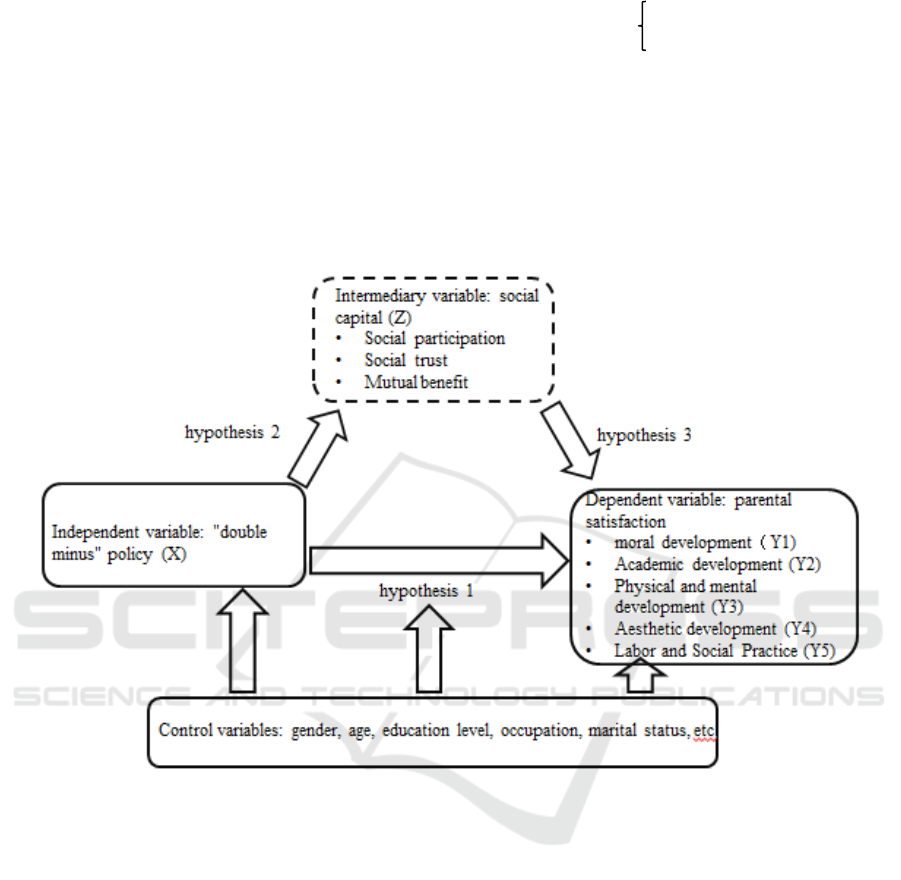
linear regression model is proposed:
Y= β
1
x
1
+ β
2
x
2
+···+ β
p
x
p
+ ε (1)
Among them, β
1
,β
2
, ···,β
p
is P unknowns, called
regression coefficient. Y is called dependent variable
(interpreted variable), while x
1
, x
2
, ··· , x
p
are p
general variables that can be accurately measured and
controlled, called independent variable (interpreted
variable). Formula (1) is called multivariate linear
regression model, ε is random error term, we often
assume the random error term
E(ε)=0 (2)
VA R ( ε ) = R
2
E(y)= β
1
x
1
+ β
2
x
2
+···+ β
p
x
p
+ ε (3)
is called a theoretical regression model.
On the basis of controlling the demographic and
socioeconomic variables, the influence mechanism of
"Double-reduction" policy and parents' satisfaction
(hypothesis 1), "Double-reduction" policy and social
capital (hypothesis 2), social capital and parents'
satisfaction (hypothesis 3) were analyzed.
Figure 1: Research theory diagram.
3.2 Sample Selection and Data Sources
This paper selected Sanzhou area in Sichuan province
as a typical case to carry out a questionnaire survey,
questionnaires were distributed to the parents of
students at the primary, junior and senior secondary
levels in 37 counties where Ganzi Tibetan
Autonomous Prefecture, Aba Tibetan and Qiang
Autonomous Prefecture, Liangshan Yi Autonomous
Prefecture ethnic minorities live through on-the-spot
research and online distribution. In this paper, 13658
valid samples were finally analyzed.
4 DATA RESULTS AND
ANALYSIS
4.1 The Relationship Between the
“Double Reduction” Policy, Social
Capital and Parents' Satisfaction
In this study, standardized mean scores were used to
measure the “Average parent satisfaction score,”
Cronbach's α coefficient of the scale was 0.967, and
the KMO of the whole data was 0.974 by exploratory
factor analysis, which indicated that the scale had
good reliability and validity.
After the primary analysis of the main variables,
the study hypotheses were tested one by one using
OLS multiple linear regression. The results of all the
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
616
regression model tests show that the VIF values of all
independent and control variables are between 1 and
3, indicating that there is no Multicollinearity
problem between these variables.
4.1.1 The Effect of “Double Reduction”
Policy on Parents' Satisfaction
According to Table 1, the satisfaction of parents after
the implementation of the "Double reduction" policy
was 6.16, 7.45, 6.79, 7.65 and 7.62 units higher than
that before the implementation of the "Double
reduction" policy. This fully shows that the
implementation of the "Double reduction" policy can
indeed improve the satisfaction of parents of students
in the compulsory education stage in ethnic minority
areas. Hypothesis 1 has been verified.
Table 1 Analysis results of the impact of “Double reduction” policy on parents' satisfaction in ethnic minority areas.
variable
M1 M2 M3 M4 M5
Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5
Policy 6.16*** 7.45*** 6.79*** 7.65*** 7.62***
Gender (1) 1.74* 1.77* 1.75* 1.81* 1.81*
Age -0.58 -0.54 -0.57 -0.48 -0.56
Edu
4.92
***
5.00*** 5.13*** 5.06*** 5.14***
Marriage -0.31 -0.33 -0.26 -0.26 -0.24
Work 1.41 1.40 1.42 1.41 1.39
Income 4.27*** 4.28*** 4.25*** 4.25*** 4.22
Gender (2) -1.03 -1.01 -1.01 -1.00 -1.01
Only child 25.87*** 25.83*** 25.96*** 25.86*** 25.89***
Boarding system -11.72*** -11.66*** -11.66* -11.61*** -11.65***
Left-behind -47.17*** -47.18*** -47.10*** -47.16*** -47.19***
Healthy 44.28*** 44.18*** 44.19*** 44.22*** 44.16***
Constant 32.04*** 32.36*** 31.94*** 32.65*** 32.09***
Sample 13654 13654 13654 13654 13654
R
2
0.896 0.897 0.896 0.896 0.897
Note: * * * represents P<0.001, * * represents P<0.05, and * represents P<0.1.
4.1.2 The Impact of the “Double Reduction”
Policy on Social Capital
As shown in Figure 1, The social capital of parents
after the implementation of the “Double reduction”
policy was 1.98 higher than that before the
implementation of the “Double reduction” policy.
This shows that the implementation of the “Double
reduction” policy can improve the social capital
content of the parents of students in the compulsory
education stage in ethnic areas. Hypothesis 2 has been
verified.
Table 2 Analysis Results of the Impact of the "Double
Reduction" Policy on Social Capital.
variable
M6
Social capital
Policy 6.88***
Gender (1) 2.95**
Age -2.95**
Edu 4.51***
Marriage 2.27*
Work 4.12***
Income 4.62***
Gender(2) -1.56
Only child 27.42***
Boarding system -13.44***
Left-behind -113.58***
Healthy 2.56**
Constant 85.83***
Sample 13654
R
2
0.8340
Note: * * * represents P<0.001, * * represents P<0.05, and
* represents P<0.1.
Can the Implementation of the â
˘
AIJDouble Reductionâ
˘
A
˙
I Policy Improve the Satisfaction of Parents of Students at the Compulsory
Education Stage in Ethnic Minority Areas? Analysis of Intermediary Effect Based on Social Capital
617

4.1.3 The Effect of Social Capital on
Parents' Satisfaction
According to Table 3, Social capital has a significant
positive effect on all dimensions of parents'
satisfaction. To be specific: for every unit increase in
social capital, the scores of the five dimensions
increased by 14.90,15.16,14.41,14.54,15.10 units
respectively in the compulsory education stage of
ethnic minority areas. To sum up, social capital can
help to improve the satisfaction of parents of
compulsory education students in ethnic areas,
hypothesis 3 is verified.
Table 3 Analysis Results of the Impact of Social Capital on Parents' Satisfaction in Ethnic Areas.
variable
M7 M8 M9 M10 M11
Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5
Social capital 14.90*** 15.16*** 14.41*** 14.54*** 15.10***
Gender (1) -8.59*** -8.48*** -8.59*** -8.44*** -8.42***
Age 3.55*** 3.71*** 3.69*** 3.84*** 3.72***
Edu 16.52*** 16.76*** 16.95*** 16.78*** 16.94***
Marriage
3.53
***
3.58
***
3.64
***
3.70
***
3.75
***
Work -4.74*** -4.77*** -4.64*** -4.72*** -4.70***
Income
3.24
**
3.21
**
3.17
**
3.21
**
3.15
**
Gender
(
2
)
0.78 0.87 0.83 0.95 0.91
Only child -3.21** -3.30** -3.06** -3.31** -3.24**
Boarding system -2.14** -1.99** -1.99** -1.90* -1.98**
Left-behind 10.55*** 10.74*** 10.81*** 10.91*** 10.62***
Healthy 10.23*** 10.12*** 10.19*** 10.28*** 10.11***
Constant -16.72*** -16.73*** -16.40*** -16.18*** -16.63***
Sample 13654 13654 13654 13654 13654
R
2
0.0694 0.0693 0.0675 0.0668 0.0683
Note: * * * represents P<0.001, * * represents P<0.05, and * represents P<0.1.
4.2 The Mediating Effect of Social
Capital in the Effect of “Double-
Reduction” Policy on Parents'
Satisfaction
This paper chooses structural equation model to
further analyze the intermediary effect of social
capital in the impact of “Double reduction” policy on
parental satisfaction. The analysis results are shown
in Table 4.
The coefficients of the indirect effects of the five
dimensions of parents' satisfaction were all
significant at the 1% level, the indirect effects of the
five dependent variables were 36.4%, 17.8%, 36.4%,
12.9%, 36.4% respectively. This suggests that social
capital does have a significant mediating effect
between the “Double reduction” policy and parental
satisfaction at the compulsory education stage in
ethnic minority areas.
Table 4 Analysis results of intermediary effect of social
capital.
dependent variable
Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5
Total
-
0.022*
*
0.045*
*
0.022
0.062*
**
0.022
Direct -0.014
0.053*
**
0.030*
*
0.070*
**
0.030
Indirect
-
0.008*
*
-
0.008*
*
-
0.008*
*
-
0.008*
*
-
0.008
**
Proporti
on of
indirect
36.4 17.8 36.4 12.9 36.4
Note: * * * represents P<0.001, * * represents P<0.05, and
* represents P<0.1.
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
618

5 CONCLUSION
As an important part of the compulsory education
reform, the “Double reduction” policy is an effective
means to enhance the satisfaction of parents of
students in ethnic minority areas at the compulsory
education stage. The main conclusions of this study
are as follows:
(1) the satisfaction of parents of compulsory
education students in ethnic areas is generally high;
But there are group differences: Middle aged, college
educated, married, non fixed occupation, non only
child families, girls as children, non boarding
children, non left behind children, and very healthy
children have higher parental satisfaction.
(2) the implementation of the “Double reduction”
policy can significantly improve the satisfaction of
parents of compulsory education students in ethnic
minority areas. Through OLS regression, it is found
that after adding control variables, the “Double
reduction” policy has a very significant effect on the
improvement of parental satisfaction, and the five
dimensions of parental satisfaction and the OLS
coefficient of the average score of parental
satisfaction are all positive significant. This shows
that the implementation of the “Double reduction”
policy is an effective means to improve the
satisfaction of students' parents at the compulsory
education stage in ethnic areas.
The implementation of the “Double reduction”
policy can improve the social capital of parental
satisfaction, and the social capital can significantly
improve parental satisfaction. The results of
structural equation model intermediary effect
analysis show that when the “Double reduction”
policy improves parental satisfaction, the indirect
effect of social capital is significant at the level of 1%,
indicating that it is an important intermediary variable
in the relationship between the two.
Based on the above conclusions, in the policy
aspect, it is suggested that: continue to promote the
implementation of the “Double reduction” policy in
ethnic minority areas, using the “Double reduction”
policy as an important means to enhance the
satisfaction of parents of students at the compulsory
education stage in ethnic minority areas, and making
use of the home-school-community coordination
mechanism to further clarify the responsibilities of
home-school education and foster closer home-
school communication, to enhance the enthusiasm of
parents for social participation, Foster Social Trust,
mutual benefit, harmonious and mutually supportive
social relations, and increase the social capital of
parents of students at the compulsory education stage
in ethnic minority areas, to further enhance the
satisfaction of parents.
REFERENCES
Chu Chao Hui. Implementation strategy of home-school-
community cooperative education [J]. People's
education, 2021(8): 33-36.
Lu Fang, Zhang Li, Zhai Youhua, etc.. Implementation,
problems and countermeasures of“Double reduction”
in primary and middle schools --an empirical analysis
based on Jiangsu province [J]. Journal of Tianjin
Normal University Science (Basic Education Edition),
2022, 23(4): 25-30.
Li Guanghai, Li Hailong. Block and solution of “Double
reduction” policy implementation from the perspective
of game theory [J]. Modern education management,
2022(06): 10-19.
Teachman, J.D.,K.Paasch,and K. Carver, “Social capital
and the generation of human capital,” Social Forces
75(1997): 1343-1359.
Xiang Xiaoqin, He Bo. The practical response of classroom
teaching in junior high school under the policy of
“Double reduction” [J]. Teaching and management
(secondary edition), 2022(1) : 29-31.
Xie Ailei, Hong Yanbi. The application of the concept of
social capital in educational research review and
comment [J]. Education Research, Tsinghua University,
2017,38(1) : 21-30.
Xue Haiping, Shi Huanhuan. A study on the impact of
education equalization on family shadow education
expenditure [J]. Journal of the National Institute of
Education Administration, 2021(8) : 14 -24.
Zhang Pin, Lin Xiaoshan. “Double reduction” and “Double
pinning”: parenting anxiety and family upbringing in
the revolution of educational policy [J]. Social
Construction, 2022,9(1) : 15-24.
Zhang Xiaoli, Zhang Yixiang, Du Xiayu. How can sports
participation improve the quality of life of urban
residents in China? The intermediary effect of social
capital [J]. Journal of Shanghai Institute of Physical
Education, 2022,46(4) : 28-39.
Zhao Decheng. Some thoughts on the evaluation of
students under the background of “Double reduction”
policy [J]. Classes. Textbooks. Sharia, 2022,42(1) :
140-146.
Zhou, M., and S. S. Kim, “Community forces, social
capital, and educational achievement: The case of
supplementary education in the Chinese and Korean
immigrant communities,” Harvard Educational Review
76(2006): 1-29.
Can the Implementation of the â
˘
AIJDouble Reductionâ
˘
A
˙
I Policy Improve the Satisfaction of Parents of Students at the Compulsory
Education Stage in Ethnic Minority Areas? Analysis of Intermediary Effect Based on Social Capital
619
