
The Construction of Teacher TPACK Ability Evaluation System
Under the Ecological Environment of Smart Classroom
Hongyun Zeng
a
College of Computer and Information Science, Chongqing Normal University, China
Keywords: Smart Classroom, TPACK, AHP, YAAHP, Evaluation System.
Abstract: With the continuous innovation of information technology, smart classrooms have emerged from time to
time, which puts forward higher requirements for teachers' teaching ability. As a new knowledge structure
of teachers under the product of information technology, TPACK is the main basis for measuring teachers'
professional ability in the era of smart education, and an important means to improve teachers' ability to
integrate technology, teaching methods and content. Through the analysis of the smart classroom ecological
environment and TPACK theory, this study extracts the evaluation index of teachers ' TPACK ability in the
smart classroom ecological environment, and constructs the model of teachers' TPACK ability evaluation
system with the help of YAAHP software, and carries out matrix consistency test and data analysis.
Through the effective evaluation system to promote teachers to innovate teaching philosophy, improve
teaching methods and enhance teaching effective.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2658-9330
1 INTRODUCTION
‘Opinions on the Implementation of the National
Primary and Secondary School Teachers'
Information Technology Application Ability
Improvement Project 2.0’ (Ministry of Education
2019) clearly states that teachers should promote the
deep integration and innovative development of
information technology and their own education and
teaching. At the same time, the Education
Informatization'2.0 Action Plan (Ministry of
Education 2018) has promoted the model change
and ecological reconstruction of education supported
by emerging technologies such as artificial
intelligence, internet of things and big data. The
traditional classroom has gradually transitioned into
a smart classroom. The smart classroom has given
teachers a new role and put forward higher
requirements for teachers' information technology
application ability. Smart classroom involves all
aspects of computer technology and information
technology. It is necessary to break the barriers
between various technologies and solve the problem
of collaborative integration of interdisciplinary work
(Mukesh 2019). Smart classroom requires teachers
to have the consciousness of integrating technology,
the ability of using technology and the thinking of
innovating technology.
To promote development by evaluation, TPACK
is one of the bases to measure teachers' professional
ability. The construction of teachers' TPACK ability
evaluation system can positively motivate teachers
to improve TPACK ability. Nowadays, the
evaluation of teachers' TPACK ability still stays on
the teaching evaluation of traditional classrooms.
Zhang Lin (Zhang 2019) and others have explored
teachers' information-based teaching ability in
traditional classrooms, but this does not match the
evaluation required by teachers' TPACK ability in
the smart classroom ecological environment.
Therefore, this study aims to design the evaluation
index of teachers' TPACK ability in the ecological
environment of smart classroom, and explore the
ability of teachers to integrate information
technology in the teaching process in the ecological
environment of smart classroom with TPACK
theory as the core.
626
Zeng, H.
The Construction of Teacher TPACK Ability Evaluation System Under the Ecological Environment of Smart Classroom.
DOI: 10.5220/0011935800003613
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education (NMDME 2022), pages 626-631
ISBN: 978-989-758-630-9
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
2 THEORETICAL BASIS
2.1 Smart Classroom Ecological
Environment
With the continuous change of education, the
traditional classroom of single teaching mode has
been unable to carry the needs of modern teaching,
and the intervention of new technology has
promoted the emergence of smart classroom. With
the support of information technologies such as big
data and learning analysis, teachers can fully
implement diagnostic analysis and intelligent
resource push in the teaching process, and carry out
‘cloud + terminal’ learning activities and support
services. The smart classroom ecological
environment generally includes interactive screens,
freely assembled desks and chairs, tablets, cameras
and other hardware, as well as software such as
e-schoolbag systems and intelligent recording and
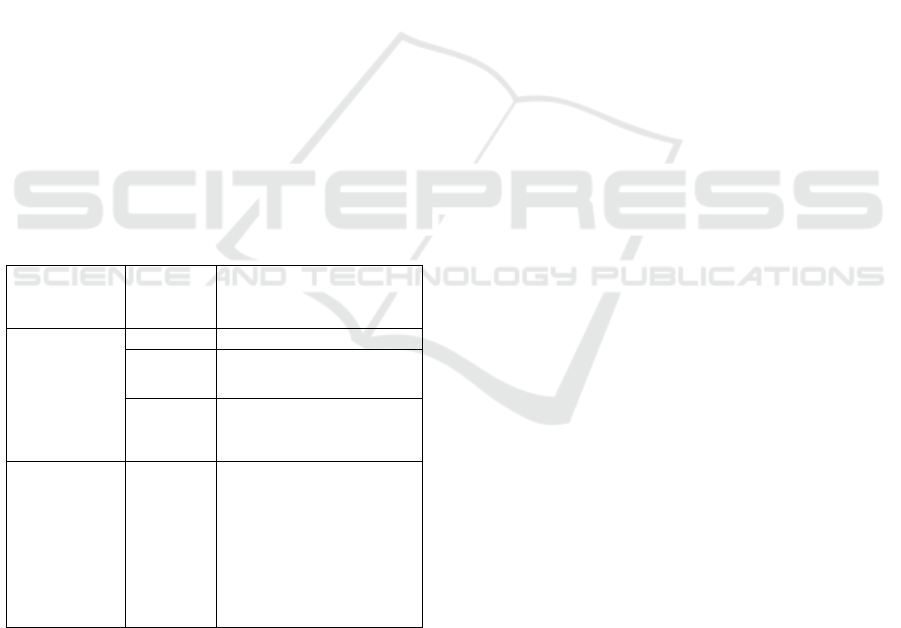
broadcasting systems (Li 2020),as shown in Table 1.
The intelligent teaching equipment of smart
classroom provides a new situation for teachers'
teaching and students' learning. Teachers can
simplify and optimize the three teaching processes
before, during and after class according to their
characteristics.
Table 1 Smart classroom software ecological environment
Component
Technica
l
su
pp
ort
Features
E-Schoolbag
System
Bi
g
date Rich sub
j
ect resources
Smart
push
Directional push job
exercises
Learning
analysis
Objective exercises
automatic correction,
instant feedbac
k
Intelligent
recording
and
broadcasting
system
face
recogniti
on,multi
media
technolo
gy
Support remote
broadcast, screen
switching,
teacher-student behavior
close-up, online editing,
intelligent inspection and
tracking of
teache
r
-student behavio
r
2.2 TPACK Element Analysis
The full name of TPACK is Technological
Pedagogical Content Knowledge (Charles R 2011),
which is translated into the subject teaching
knowledge of integrated technology. This theory
interprets the complex overlapping relationship
between teachers' knowledge structures, including
three core elements and four composite elements
generated by the interaction of core elements. The
core elements are content knowledge-content
knowledge of the subject taught by the teacher,
pedagogical knowledge-teaching related theoretical
knowledge, technical knowledge-related knowledge
about the use of information technology. The
composite elements are pedagogical content
knowledge-what kind of teaching theory knowledge
is used to impart subject content knowledge,
technical pedagogical knowledge -what kind of
information technology is used to present subject
content knowledge, technical content
knowledge-what kind of information technology is
used to support the development of teaching theory,
technical pedagogical content knowledge-
integrating technology, teaching method and
content, that is, changing teaching and learning in
some way through technology.
3 METHODS AND MATERIALS
At present, how to effectively and objectively
evaluate the TPACK ability of teachers in the
ecological environment of smart classroom is still in
the blank. In view of the above cognition of the
smart classroom ecological environment and
TPACK elements, this study establishes a
comprehensive evaluation index system to provide
reference for the evaluation of teachers' TPACK
ability in the smart classroom ecological
environment.
3.1 Construction Method of Evaluation
Index System
AHP, also known as analytic hierarchy process, is a
hierarchical weight decision analysis method that
decomposes the elements related to decision-making
into levels, index the indicators and assigns them
weights, and combines quantitative and qualitative
analysis (Xu 2018). AHP has the advantages of
systematization, simplicity, practicality and less
quantitative data, and is widely used in the
construction of evaluation index system. The general
process is to determine the research problem,
construct the hierarchical structure, construct the
judgment matrix and test the consistency of the
matrix, use the sum product method to calculate the
weight by column normalization, and finally draw
the corresponding conclusion.
The Construction of Teacher TPACK Ability Evaluation System Under the Ecological Environment of Smart Classroom
627

Generally speaking, the artificially constructed
judgment matrix is difficult to meet the consistency
requirements. It is often necessary to adjust and
correct the judgment matrix many times, and the
data processing process is complicated. The release
of YAAHP software solves this problem. Based on
the principle of analytic hierarchy process, YAAHP
software provides users with convenient hierarchical
model construction, judgment matrix data entry,
sorting weight calculation, calculation data export
and sensitivity analysis. It is flexible and easy to use
and simplifies the data processing process. This
study uses YAAHP software to process the data to
ensure the credibility, real-time consistency and
sensitivity of the entire model.
3.2 Construction Principle of
Evaluation Index System
The evaluation of teachers' TPACK ability in the
smart classroom can promote teachers to
consciously and actively integrate information
technology into the curriculum, so as to innovate the
educational concept and improve their TPACK
ability In the process of constructing the indicators
of the evaluation system, the following four
principles should be followed: First, the evaluation
objectives are clear, and the evaluation is based on
the wisdom classroom and TPACK theory.
Therefore, the evaluation objectives must be clear,
and the evaluation index system is only applicable to
the TPACK ability of teachers in the ecological
environment of wisdom classroom. Second, the
evaluation methods are diverse, smart classroom
evaluation is not limited to a single evaluation,
process evaluation, formative evaluation and
summary evaluation of integrated applications, from
a variety of evaluation methods, systematic and
complete construction of the entire evaluation
process; Third, the evaluation content is diverse.
Based on the TPACK framework, it can be seen that
teachers' ability is generated by the interaction of the
three elements of content, teaching method and
technology, so the evaluation content is based on the
three elements; Fourth, the evaluation design is
scientific. The construction of the evaluation index
system adopts the analytic hierarchy process, in
which the hierarchical structure is constructed by the
expert brainstorming method, the weights of the
indicators at all levels are determined by a small
amount of data, and the TPACK ability of teachers
is explored by combining quantitative and
qualitative methods, which is scientific.
3.3 Evaluation Index System Index
Based on the above elaboration of the ecological
environment and TPACK elements of smart
classrooms, it can be seen that smart classrooms are
more important than traditional classrooms in terms
of what technology to use, when and how to use
technology. This paper invites a total of 20 experts
at all levels and types, and uses the brainstorming
method to determine the evaluation index system as
four first-level indicators and twelve second-level
indicators, and forms the corresponding observation
perspective. The specific evaluation index system is
detailed in Table 2.
3.3.1 First Grade Indexes
Generally speaking, the smart classroom includes
three stages: before class, in class and after class
(Liu 2016). The concept of smart education runs
through the three stages. Before class, teachers
should understand the content knowledge, and on
this basis, select appropriate teaching strategies
according to the content knowledge, and list the
technical list, and finally form the teaching design,
which provides a blueprint for the whole teaching
implementation process. Teachers should
dynamically carry out the teaching process
according to the instructional design, use technology
to promote teacher-student interaction, support
learners' personalized learning, and optimize the
teaching process. After class, teachers should
review, evaluate and reflect on the teaching method,
content and technology to improve TPACK ability.
In summary, the first-level indicators are smart
classroom teaching philosophy, smart classroom
teaching design, smart classroom teaching
implementation, smart classroom teaching
evaluation.
3.3.2 Second Grade Indexes
Smart classroom teaching philosophy is the
cornerstone of smart classroom teaching. The
primary requirement of the traditional classroom
reform for the smart classroom is that teachers
should innovate the concept of self-teaching, from
the 'teacher-centered' in the traditional classroom to
the 'student-centered' in the smart classroom, and
always adhere to the 'student-centered' teaching
philosophy in teaching design, teaching
implementation and teaching evaluation. At the
same time, teachers should aim talents with high
intelligence and creativity as the goal (Zhu 2012), he
information age under the background of knowledge
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
628

learning is secondary, knowledge to ability is the
main, knowledge to ability transformation requires
students to have certain innovation ability.
Therefore, the secondary indicators under the
concept of smart classroom teaching are
student-centered and aimed at cultivating innovative
talents.
Intelligent classroom teaching design is an
important guarantee for intelligent classroom
teaching. At this stage, teachers should understand
the content of the subject, select teaching strategies
on the basis of understanding, and use technology to
build a personalized and diversified teaching
environment and resources for students, thus
forming a detailed teaching process. Therefore, the
secondary indicators under the design of smart
classroom teaching are the understanding of subject
content, the selection of teaching strategies, the use
of technology, and the relevance of subject content,
teaching strategies, and technology.
The implementation of smart classroom teaching
is the core of smart classroom teaching. Before the
implementation of teaching in the smart classroom,
teachers can use technology to make intelligent
diagnosis of students' learning situation, and carry
out accurate teaching dynamically according to the
diagnosis results. In the process of teaching, teachers
can use technology to promote teacher-student
interaction, support learners' personalized learning,
and carry out a series of activities to promote
students' innovative thinking. After implementing
the teaching process, teachers should intelligently
push appropriate resources according to students'
learning status, so as to promote students' ability to
transfer knowledge. In addition to the above three
points, there should be the embodiment of teachers'
basic teaching skills throughout the whole teaching
implementation process. Therefore, the secondary
indicators under the implementation of smart
classroom teaching are learning intelligence
diagnosis, learning activities, knowledge transfer,
teachers' basic teaching skills.
Smart classroom teaching evaluation is the
fundamental guarantee of smart classroom teaching.
Evaluation is an important means to ensure the
quality of personnel training and monitor the quality
of teachers' teaching, and to promote development
by evaluation. The evaluation here refers to the
organizational ability of teachers to evaluate the
teaching effect. Teachers should be able to make
evaluation scales scientifically according to the
learning situation. In view of the interaction between
TPACK elements to produce a variety of composite
elements, TPACK has a certain complexity. In order
to improve TPACK ability, teachers need to feel the
specific situation of teaching and learning in the
process of practice. After-school immediate
self-evaluation and reflection can effectively
improve teachers' TPACK ability. Therefore, the
secondary indicators of smart classroom teaching
evaluation are evaluation of organizational ability
and teacher self-evaluation.
3.4 Weight Calculation of Evaluation
Index System
This study uses analytic hierarchy process to
calculate the weight of each index, according to the
percentile conversion index weight score, the
specific score is shown in Table 2.
(1) According to the analytic hierarchy process
evaluation scale, the fixed quantitative value is
obtained by comparing the two factors, and the
judgment matrix A is constructed:
A11 A12
A21 A22
…… A1n
…… A2n
…… ……
An1 An2
…… ……
…… Ann
(2) The judgment matrix A is normalized by
column to obtain matrix B:
()
njjnii
A
A
B
n
i
ij
ij
≤=≤==
=
,1,,1
1
ij
(3) The weight value: ω:
),1(
n
B
ω
n
1i
ij
j
njj ≤==
=
(4) Weight multiplied by matrix:
()
=
≤=•=
n
ijj
niAA
1j
j
),1i(
ωω
(5) Find the maximum positive eigenvalue λ of
the judgment matrix A:
()
=
=
n
1j
j
j
n
A
ω
ω
λ
(6) Consistency test, if each layer index CR <
0.1, that the inconsistency of the matrix within
the allowable range, can determine the matrix
through the consistency test. On the contrary, the
judgment matrix should be modified until it
The Construction of Teacher TPACK Ability Evaluation System Under the Ecological Environment of Smart Classroom
629
passes the consistency test. The RI value comes
from the analytic hierarchy process RI value
table.
(7) From the above calculation process, it can be
known that the data processing process of the
analytic hierarchy process is cumbersome, which
is not conducive to the full play of the application
advantages of the analytic hierarchy process.
Using computer technology- YAAHP software,
you can quickly obtain accurate weights and
simplify data processing.
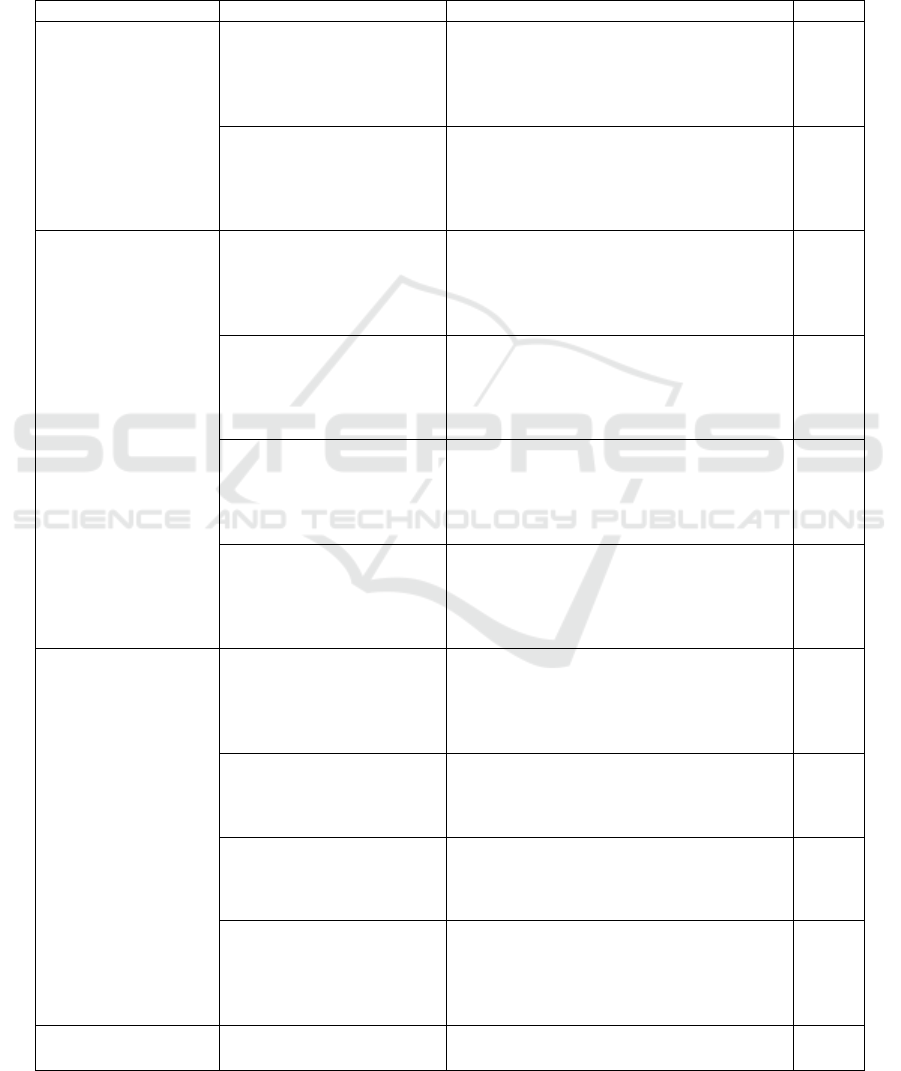
Table 2 Evaluation index system of teachers ' TPACK ability in smart classroom ecological environment
First
g
rade indexes Second
g
rade indexes Observation
p
ers
p
ective Grade
Intelligent Classroom
Teaching Concept(12
points)
student-centered(7
points)
Teachers can weaken self-role, highlight
students ' status and cultivate students '
autonomous learning ability
7
5
3
1
0
Aiming at Cultivating
Innovative Talents(5
points)
Teachers can make full use of
problem-based, project-based and STEAM
courses to stimulate students ' interest in
learning and promote their ability to solve
p
roblems
5
3
2
1
0
Intelligent Classroom
Teaching Design(28
points)
Understanding of subject
content(7points)
Teachers can fully understand the structure
of the subject content, the content and
extension of the concept, establish
three-dimensional teaching objectives
7
5
3
1
0
Selection of Teaching
Strategies(4points)
Teachers can select appropriate teaching
strategies according to the characteristics of
subject content
4
3
2
1
0
implementation of
technology(8points)
Teachers can list technology, that is, what
technology to use, when to use technology,
how to use technology.
8
6
4
2
0
The Suitability of Subject
Content, Teaching Strategy
and Technology(9points)
Teachers can fully consider the
characteristics of subject content, teaching
strategy and technology, use technology to
present subject content and support teaching
strateg
y
9
6
4
2
0
Intelligent classroom
teaching
implementation(41
points)
Intelligent Diagnosis of
Learning Situation
(8points)
Teachers can intelligently diagnose students
' learning based on the use of technology and
dynamically carry out precise teaching based
on diagnostic results
8
6
4
2
0
learning activities
(16points)
Teachers can create learning situations for
learners and carry out a series of activities to
promote students ' innovative thinking based
on innovative applied technical knowledge
16128
4
0
knowledge migration
(12points)
Teachers can push resources intelligently
according to students ' learning situation to
promote learners ' knowledge transfer ability
129
6
3
0
Teachers ' basic teaching
skills(5points)
Teachers ' language expression ability and
ability to deal with classroom crisis
5
3
2
1
0
Intelligent classroom
teaching evaluation
Evaluation of organizational
capacity(8points)
Teachers can formulate evaluation scale
scientifically according to students ' situation
8
6
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
630

(19 points)
and teaching content 4
2
0
self evaluation(11points)
Teachers can timely and effectively carry
out self-evaluation and reflection
118
5
2
0
Remarks : 90 points or more for level A, 80-90 points for level B, 70-80 points for level C, 60-70 points for
level D, 60 points or less for level E
4 CONCLUSIONS
With the support of emerging technologies such as
artificial intelligence, internet of things and big data,
hot spots such as smart classrooms and smart
education have impacted the education industry. The
education model has changed and the ecological
environment has been reconstructed. Smart
classroom puts forward higher requirements for
teachers' information technology application ability,
requiring teachers to have the consciousness of
integrating technology, the ability to use technology
and the thinking of innovative technology. As a new
knowledge structure of teachers under the product of
technology, TPACK is the main basis for measuring
teachers' professional ability in the era of smart
education, and an important means to improve
teachers' ability to integrate technology, teaching
methods and content. In the process of
implementing smart classroom teaching, teachers
can't treat all elements in isolation. They should
examine the shortcomings of self-ability through the
scientific TPACK ability evaluation system, and
actively seek promotion strategies, so as to realize
the high integration of technology, teaching methods
and content, and the deep integration of TPACK and
smart classroom.
All in all, the smart classroom is more urgent to
need appropriate evaluation methods to improve the
quality of teachers' teaching. This study uses the
brainstorming method to determine that the
evaluation index system is four first-level indicators
and twelve second-level indicators, and forms the
corresponding observation perspective. Through the
combination of quantitative and qualitative methods,
the scores of each index are calculated, and finally
an effective, objective and scientific evaluation
index system of smart class is formed. The table fills
the gap in the evaluation index system of teachers'
TPACK ability under the ecological environment of
smart class, and provides reference for the
evaluation of teachers' TPACK ability under the
ecological environment of smart class.
REFERENCES
[2019-03-21].http://www.moe.gov.cn/srcite/A10/s7034/20
1904/t20190402_376493.html.
Charles R, Graham. 2011. Theoretical considerations for
understanding technological pedagogical content
knowledge (TPACK). Computers & Education.
Volume 57, Issue 3, Pages 1953-1960, ISSN
0360-1315,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2011.04.010.
http://www.moe.gov.cn/srcite/A16/s3342/201804/t201810
425_334188.html.
Information Technology Application Ability Improvement
Project 2.0 [EB / OL].
Li Fengqing, Yin Miao, Shi Jie. The Construction of
Smart Classroom Ecosystem [J]. China Educational
Technology, 2020, (6): 58-64.
Liu Bangqi. Research on the Design and Implementation
Strategy of Smart Class Teaching in the Are of '
Internet + ' era [J]. China Educational Technology,
2016, 0 (10): 51-5673.
Normal University, 2019. DOI: 10.27149 /
d.cnki.ghdsu.2019.000088.
Ministry of Education. Opinions on the Implementation of
the National Primary and Secondary School Teachers '
Ministry of Education. Education Informatization 2.0
Action Plan [EB / OL]. [2018-06-20].
Mukesh Kumar Saini and Neeraj Goel. 2019. How Smart
Are Smart Classrooms? A Review of Smart
Classroom Technologies. ACM Comput. Surv. 52, 6,
Article 130 (November 2020), 28 pages.
https://doi.org/10.1145/3365757
Research on the cultivation of information-based teaching
ability of normal students [D]. East China
X. Xu, Y. Wang and S. Yu, "Teaching Performance
Evaluation in Smart Campus," in IEEE Access, vol. 6,
pp. 77754-77766, 2018, doi:
10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2884022.
ZHANG Lin. The Preparation of Student Teachers’ ICT
Competencv in China’s Normal Universities
Zhu Zhiting, He Bin. Smart Education: A New Realm of
Educational Informatization [J]. e-Education
Research, 2012 ( 12 ) : 5-13.
The Construction of Teacher TPACK Ability Evaluation System Under the Ecological Environment of Smart Classroom
631
