
Determinant Factors Affecting Adherence of Hypertensive Patients to
Taking Antihypertensive Drugs
A. A. Bagus Suryantara
1
a
, I Gede Putu Darma Suyasa
1
b
, Ni Putu Kamaryati
1
c
and Ida Ayu Ningrat Pangruating Diyu
2
d
1
Magister of Nursing Program, Faculty of Health, Institute of Technology and Health Bali, Indonesia
2
Bachelor of Nursing Program, Faculty of Health, Institute of Technology and Health Bali, Indonesia
Keywords: Adult, Hypertension, Medication Adherence.
Abstract: A key success factor of hypertension management is adherence to taking hypertensive medications. However,
little research has been done to explore determinant factors of hypertension management in adult patients.
The study aimed to determine factors that affect adherence of hypertensive patients to taking antihypertensive
drugs. This study was a descriptive-analytic study with a cross-sectional approach. The research sample was
133 hypertensive patients from a Primary Healthcare Center selected using a simple random technique.
Inclusion criteria applied in sample selection were patients who visited Primary Healthcare Centers and were
aged 18 years and above. Ethical clearance for this study was granted by ITEKES Bali Research Ethics
Committee. Data collection was conducted in May 2022 using a valid and reliable questionnaire. Chi-square
analyses were conducted for bivariate analyses. Variables with a p-value of < 0.25 were further analyzed with
logistic regression. The results of bivariate analysis showed age, education, occupational, period of suffering,
motivation, and family support had a significant influence on adherence to taking antihypertensive drugs (p
< 0.05). The logistic regression test analysis showed that family support (p < 0.001; AOR: 14.050; 95% CI:
4.045-48.796) and age (p < 0.001; AOR: 0.038; 95% CI: 0.011 - 0.127) were significant determinant factors
affecting adherence to taking antihypertensive drugs. Health care professionals need to continue supporting
and educating families about hypertensive care.
1 INTRODUCTION
Hypertension is a major health problem.
Hypertension is an increase in systolic blood pressure
of about 140 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure of
about 90 mmHg. Hypertension shows no specific
symptoms, and thus being alert to this disease will
prevent hypertension. With the invisible symptoms,
hypertension is often called the silent killer
(American Heart Association, 2020).
Based on the report of the Basic Health Research
(2018), the number of people with hypertension in
Indonesia who routinely took antihypertensive drugs
(54.40%) was greater than those who did not take
medication regularly (32.27%) and did not take
medication at all (13.33%). Some areas of Bali
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3885-5456
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5817-8018
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3882-0683
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7522-1295
Province show percentages of people who adhered to
taking antihypertensive drugs. For example, Badung
Regency (41.75%) had 2,224 compliant patients;
Karangasem Regency (40.71%) showed 1,340
adhered patients, and Jembrana Regency (32.54%)
showed 910 compliant patients. (Riskesdas, 2018).
Data from the Badung Regency Health Office present
the highest prevalence of hypertension in the Mengwi
sub-district with 2,293 patients, followed by South
Kuta sub-district with 2,212 patients. Meanwhile, the
lowest of hypertension cases was found in the Petang
sub-district with 597 patients. The working area of
Mengwi I Primary Healthcare Center had the highest
number of hypertension cases amounting to 987
people (Dinkes Kabupaten Badung, 2020).
76
Suryantara, A., Suyasa, I., Kamaryati, N. and Diyu, I.
Determinant Factors Affecting Adherence of Hypertensive Patients to Taking Antihypertensive Drugs.
DOI: 10.5220/0011940700003576
In Proceedings of the 2nd Bali Biennial International Conference on Health Sciences (Bali BICHS 2022), pages 76-81
ISBN: 978-989-758-625-5
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
People with hypertension should take medication
every day regardless pain and symptoms. Treatment
adherence is aimed to control blood pressure of
patients and avoid complications (Utami &
Raudatussalamah, 2017). Uncontrolled consumption
of antihypertensive drugs can result in therapy
failures, one of which is unstable blood pressure,
complications and organ damage (Nurmainah et al.,
2014).
Research conducted by Pramana (2019), revealed
that age, gender, level of education, therapy, and
motivation affect adherence to taking
antihypertensive drugs. However, in a study
conducted by Handayani et al. (2019), age, gender,
occupation, motivation, family support, and
education have no relationships with adherence to
taking antihypertensive drugs. With these different
results, this study was focused on the identification of
determinant factors associated with adherence to
taking antihypertensive drugs.
2 SUBJECTS AND METHODS
This current study was quantitative with a cross-
sectional design. The research was conducted in May
2022 at the Mengwi I Primary Healthcare Center. The
population of this study was hypertensive patients
that were selected through the simple random
sampling with a sample size calculation
recommended by the World Health Organization. It
reached a total sample of 133 respondents after
calculation. The inclusion criteria of respondents in
this study were patients who were medically
diagnosed with hypertension by doctors and
hypertension patients who visited a primary
healthcare center for seeking treatment.
In data collection phase, this study used a
questionnaire consisting of the demographic
characteristics of the respondents, a motivation
questionnaire (Banifi, 2017), and a family support
questionnaire (Nursalam, 2015); additionally, the
MMAS-8 (Reynolds, 2012) questionnaire was used
to assess medication adherence. All statistical
analyses in this study were processed in SPSS version
21.0. Bivariate statistical analysis was performed
using the chi-square test. Multivariate binary logistic
regression was performed by inserting a predictor
with a p-value of < 0.25. This study was given an
ethical permission by the ITEKES BALI Ethics
Committee with the No. 03.0286/KEPITEKES-
BALI/III/2022 before data collection.
3 RESULTS
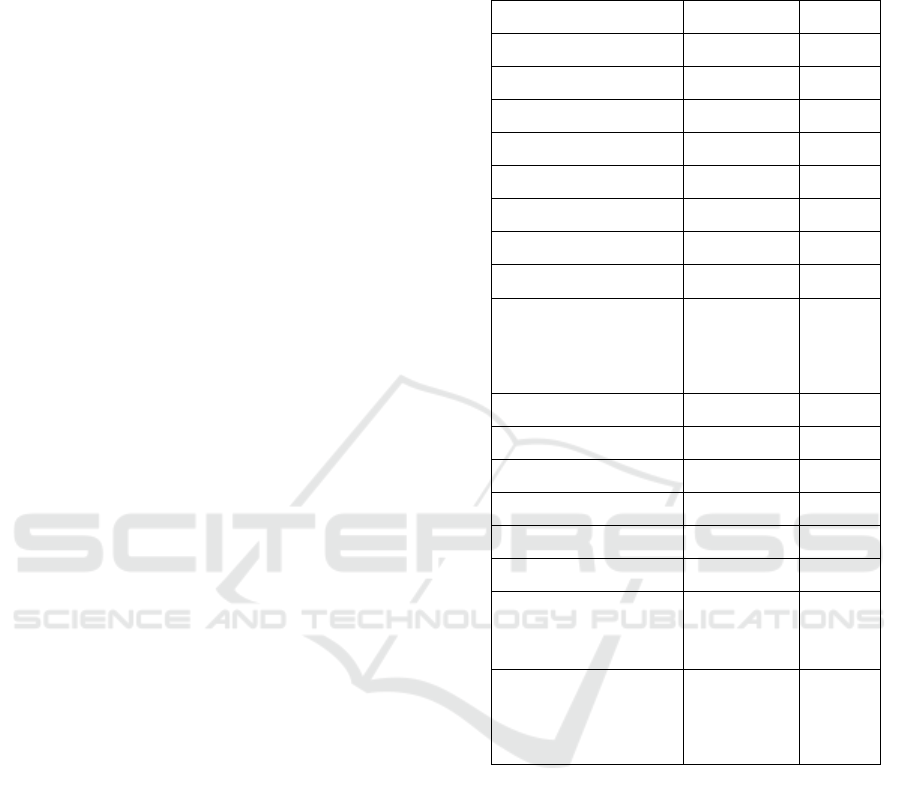
Table 1: Respondents’ Characteristics (n = 133).
Characteristics n %
A
g
e
Non-elderl
y
71 53.4
Elderl
y
62 46.6
Gender
Female 80 60.2
Male 53 39.8
Level of Education
Hi
g
h 93 54.9
Low
Occupational
Unemployment
Em
p
lo
y
ee
40
93
40
45.1
69.9
30.1
Period of sufferin
g
<5
y
ears 91 68.4
≥5 years 42 31.6
Motivation
High 70 52.6
Low 63 47.4
Family Support
Good
Poor
88
45
66.2
33.8
Adherence to taking
medication
Adherent
Nonadherent
79
54
59.4
40.6
Table 1 shows that most of the respondents are
non-elderly (53.4%) and women (60.2%). A half of
the respondents obtain higher education level
(54.9%), and most of the respondents had
unemployment status (69.9%). The majority of
respondents develop hypertension for less than five
years (68.4%) and have high motivation (52.6%).
Respondents mostly receive family support (66.2%),
and they took antihypertensive drugs regularly (59.4
%).
Determinant Factors Affecting Adherence of Hypertensive Patients to Taking Antihypertensive Drugs
77

Table 2: Relationships between respondents’ characteristics, motivation, and family support with adherence to taking
hypertension medication (n = 133).
Variable
Adherence to Taking
Antihypertensive Drugs
Total
P Value OR (CI 95%)
Nonadherent Adherent
f % f % f %
Age <.001 .020 (0.007-0.060)
Non-elderl
y
5 9.3 66 83.5 71 53.4
Elderl
y
49 90.7 13 16,5 62 46.6
Gender 0.862 1.065 (0.525-2.157)
Female 32 59.3 48 60.8 80 60.2
Male 22 40.7 31 39.2 53 39.8
Level of Education <.001 34.088 (12.640-91.929)
High 7 13.0 66 83.5 73 54.9
Low 47 87.0 13 16.5 60 45.1
Occu
p
ational <.001 7.795
(
2.806-21.652
)
Unemployment 49 90.7 44 69.9 93 69.9
Employee 5 9.3 35 44.3 40 30.1
Period of
sufferin
g
0.002 3.578 (1.543-8.341)
<5 Years 45 83.3 46 58.2 91 68.4
≥5 Years 9 16.7 33 41.8 42 31.6
Motivation <.001 5.958 (2.774-12.798)
Hight
15 27.8 55 69.6 70 52.6
Low
39 72.2 24 30.4 63 47.4
Family Support <.001 31.633 (11.367-88.029)
Good 15 27.8 73 92.4 88 66.2
Poor 39 72.2 6 7.6 45 33.8
In Table 2, this study presents that age (p =<
0.001), gender (p = 0.862), level of education (p =<
0.001), occupational (p =< 0.001), period of suffering
(p = 0.002), motivation (p =< 0.001), and family
support (p =< 0.001).
Table 3: Factors most related to adherence to taking antihypertensive drugs (n = 133).
Variables B S.E. Wald df P Value Adjusted
Odds Ratio
OR (CI 95%)
Lower Upper
Age -3.267 .615 28.216 1 <.001 .038 .011 .127
Level of
education
-.18.215
28162.1
50
.000 1 0.099 .000 .000
.
Ocupational
.350 .945 .137 1 0.711 1.418 .223 9.038
Period of
suffering
-786 .829 .717 1 0.397 .456 .074 2.812
Motivation
-.604 .639 .759 1 0.384 .547 .141 2.126
Family
Su
pp
ort
2.643 .635 17.306 1 <.001 14.050 4.045 48.796
Table 3 demonstrates that age (p =< 0.001) and
family support (p =< 0.001) were the most dominant
factors influencing adherence to hypertensive
medication. Level of education (p = 0.099),
occupational (p = 0.711), period of suffering (p =
0.397), and motivation (p = 0.384) are insignificant
factors that influenced adherence to hypertensive
medication.
Bali BICHS 2022 - The Bali Biennial International Conference on Health Sciences
78

4 DISCUSSION
4.1 Age and Adherence to Taking
Antihypertensive Drugs
This study shows age had a significant relationship
with adherence to taking antihypertensive drugs.
Around half of the respondents (53.4%) were non-
elderly aged <60 years old. They were more obedient
to taking antihypertensive drugs than the elderly
respondents (≥ 60 years). Research conducted by
Samsudin and Maharani (2020) found a relationship
between age and adherence to taking antihypertensive
drugs. Non-elderly have more stable organs and
sensory to respond to the treatment procedures.
However, age does not affect one’s compliance
with hypertensive medication. Elderly tends to
experience physical and cognitive decline which can
reduce their self-management in taking
antihypertensive drugs (Wahyudi et al., 2017).
4.2 Gender and Adherence to Taking
Antihypertensive Drugs
The results of this study show that gender did not
have a significant relationship with adherence to
taking antihypertensive drugs. This indicates that
both women and men have an awareness of health
regardless of their gender. Research conducted by
Puspita (2017) found a similar finding to this study.
Both women and men are equally concerned
about their health because they have the same social
equality or social status. The social status includes
education, which was equally distributed among male
and female respondents. Therefore, both women and
men have the same understanding and awareness of
adherence to hypertensive medication (Liberty et all.,
2018).
4.3 Level of Education and Adherence
to Taking Antihypertensive Drugs
Given the analysis of education variable, this study
found education level was significantly related to
compliance with medication. Most of the respondents
were highly educated (54.9%) and were more
obedient to hypertensive medication than low-
educated respondents. Research by Mardiana et al.
(2021) is aligned with this current study. Education
level is one of the factors that can affect one’s
adherence to treatment. A person who has higher
education level will likely understand the purpose of
the treatment, reinforcing their compliance with the
treatment.
Education level becomes the basic capital in
decision-making. Once a person holds higher
education degree, he/she will receive and understand
information at hand. As a result, she/he can develop
their self-management and awareness to comply with
medication (Pamungkas, 2015; Pratama & Ariastuti,
2016; Mahardika et al., 2021).
4.4 Occupation and Adherence to
Taking Antihypertensive Drugs
Besides age and education level, occupation was also
found to be significantly related to compliance with
medication. This study shows that most unemployed
respondents were more obedient to taking
antihypertensive drugs than employed ones.
According to previous research by Nurhani et al.
(2020), someone who works tends to have less time
to schedule their medication compared to someone
who does not work (Rajasati et al., 2018). Doctor’s
recommendations are not taken for further medication
as working patients infrequently visit primary
healthcare centers.
4.5 Period of Suffering and Adherence
to Taking Antihypertensive Drugs
The results of this study show that the period of
suffering had a significant relationship with
adherence to taking antihypertensive drugs. In this
study, the majority of the respondents (68.4%)
suffered from hypertension for <5 years and were
more compliant to taking antihypertensive drugs than
those who suffered from hypertension for >5 years. A
similar finding is stated in research conducted by
Balqis and Nurmaguphita (2018). Curiosity and
strong motivation to recovery make respondents
improve their awareness and efforts to comply with
the recommendations and prohibitions from
incompliance with medication (Wahyudi et al., 2018).
4.6 Motivation and Adherence to
Taking Antihypertensive Drugs
The results of this study show that a significant
relationship was found between motivation and
adherence to taking antihypertensive drugs. The
majority of respondents (52.6%) had high motivation
and were more likely compliant with taking
antihypertensive drugs compared to those who had
low motivation. Research conducted by Hanum et al.
(2019) reveals that intrinsic motivation i.e., hope and
Determinant Factors Affecting Adherence of Hypertensive Patients to Taking Antihypertensive Drugs
79

interest is the key factor for patient recovery and
compliance with treatment. Motivation comes from
family support (Nuratika et al., 2020).
4.7 Family Support and Adherence to
Taking Antihypertensive Drugs
Family support turns out to be associated with
adherence to taking antihypertensive drugs. The
results show that the respondents (66.2%) had high
family support and mostly adhered to medication
compared to respondents who had low family
support. Family support has a very important role to
provide emotional support and informational support
(Serinadi et al., 2021). Determining individual health
beliefs and values needs to be included into treatment
programs (Widowati, 2019). According to Kamaryati
and Malathum (2020), family support is very
effective in increasing medication adherence. Family
support can provide emotional and financial support
such as peace and compliance with medication.
Someone who has high family support will provide
peace and reduce burden of the patients. Family
support can control self-confidence in problem-
solving and self-management in medication
(Ningrum & Sudiasih, 2019).
5 CONCLUSION
Family support and age are the determining factors
that influence adherence to taking antihypertensive
drugs. A person with high family support has a
greater chance of adhering to taking antihypertensive
drugs than respondents with low family support.
Health workers need to provide support and education
about hypertensive treatment to families.
REFERENCES
Balqis, S., & Nurmaguphita, D. (2018). Hipertensi
merupakan penyakit yang memerlukan terapi jangka
panjang, sehingga diperlukan kepatuhan pasien dalam
menjalani pengobatan untuk mengontrol tekanan darah
dan menurunkan risiko komplikasi. Penelitian ini
bertujuan untuk mengetahui tingkat kepatuh. Jurnal
Kebidanan Dan Keperawatan Aisyiyah, 4(3), 1–5.
Banifi, A. S. (2017). Faktor-Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi
Penatalaksanaan Kontrol Tekanan Darah Pada Pasien
Hipertensi Di Puskesmas Gondokusuman II. IJNP
(Indonesian Journal of Nursing Practices), 1(2), 22–32.
Departemen Kesehatan RI. (2012). Profile Kesehatan
Indonesia 2012.
Dinkes Kabupaten Badung. (2020). Profil Kesehatan
Kabupaten Badung 2020.
Friedman, M. M. (2013). buku ajar keperawatan keluarga
riset, teori dan praktik. EGC.
Handayani, S., Nurhaini, R., & Aprilia, T. J. (2019). Faktor-
Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi Kepatuhan Pasien Dalam
Mengkonsumsi Obat Antihipertensi Di Puskesmas
Jatinom. Cerata Jurnal Ilmu Farmasi, 10(2), 39–44.
Hanum, sari, Puetri, N. R., Marlinda, & Yasir. (2019).
Hubungan Antara Pengetahuan, Motivasi, Dan
Dukungan Keluarga Dengan Kepatuhan Minum Obat
Pada Penderita Hipertensi Di Puskesmas Peukan Bada
Kabupaten Aceh Besar. Public Health Journal, 10(1),
1–23.
Hermanus, R. I. (2020). Dukungan Keluarga Dan
Kepatuhan Minum Obat Pada Pasien Hipertensi : Studi
Literatur Sebagai Evidence Based Promosi Kesehatan.
Nutrix Journal, 4(2), 1–8.
Ihwatun, S., Ginandjar, P., Saraswati, L. D., & Udiyono, A.
(2020). Faktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan
Kepatuhan Pengobatan Pada Penderita Hipertensi Di
Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Pudakpayung, Kota
Semarang. Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat (e-Journal),
8(3),352–359.
Kamaryati, N. P., & Malathum, P. (2020). Family Support:
A Concept Analysis. Pacific Rim International Journal
of Nursing Research, 24(3), 403-411.
Mahardika, I. M. R., Suyasa, I. G. P. D., Kamaryati, N. P.,
& Wulandari, S. K. (2021). Health literacy is Strongest
Determinant on Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose
(SMBG) Type 2 DM Patients During Covid-19
Pandemic at Public Health Centre in Tabanan Regency.
International Journal of Health & Medical Sciences,
4(3), 288–297.
Mardiana, sri siska, Faridah, U., Subiwati, & Wibowo,
badar daru. (2021). Hubungan Tingkat Pendidikan
Dengan Kepatuhan Minum. Jurnal Kesehatan, 2(1), 22–
30.
Ningrum, S. P., & Sudyasih, T. (2019). Hubungan
Dukungan Keluarga Dengan Kepatuhan Minum Obat
Pasien Hipertensi Di Puskesmas Seyegan Sleman
Yogyakarta.Muhammadiyah Public Health Journal, 3,
1–11. http://digilib.unisayogya.ac.id/4623/
Nurmainah, Fudholi, A., & Dwiprahasto, I. (2014).
Kepatuhan Penggunaan Antihipertensi Sebagai
Prediktor Laju Kejadian dan Biaya Rawat Inap. Jurnal
Manajemen Dan Pelayanan Farmasi, 4, 1–8.
Nursalam. (2015). Metodologi Penelitian Ilmu
Keperawatan: Pendekatan Praktis (Edisi 4). Salemba
Medika.
Osamor, P. E. (2015). Social support and management of
hypertension in South-West Nigeria. Cardiovascular
Journal of Africa, 26(1), 29–33.
Pramana, G. A., Dianingati, R. S., & Saputri, N. E. (2019).
Faktor-Faktor yang Mempengaruhi Kepatuhan Minum
Obat Pasien Hipertensi Peserta Prolanis di Puskesmas
Pringapus Kabupaten Semarang. Indonesian Journal of
Pharmacy and Natural Product, 2(1), 52–58.
Pratama, G., & Ariastuti, N. (2016). Faktor – Faktor Yang
Mempengaruhi Kepatuhan Pengobatan Hipertensi Pada
Lansia Binaan Puskesmas Klungkung 1. E-Jurnal
Bali BICHS 2022 - The Bali Biennial International Conference on Health Sciences
80

Medika Udayana, 5(1).
Pratiwi, W., Harfiani, E., & Hadiwiardjo, Y. H. (2020).
Faktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Kepatuhan
Dalam Menjalani Pengobatan Pada Penderita
Hipertensi Di Klinik Pratama GKI Jabar Jakarta Pusat.
Jurnal Profesi Medika, 2, 27–40.
Rasajati, Q. P., Raharjo, B. B., & Ningrum, D. N. A. (2018).
Faktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Kepatuhan
Pengobatan Pada Penderita Hipertensi Di Wilayah
Kerja Puskesmas Kedungmundu Kota Semarang.
Unnes Journal of Public Health, 4(3), 16–23.
Riskesdas. (2018). Laporan Nasional RIKESADAS 2018.
Reynolds, K. (2012). Propiedades sicométricas de la escala
morisky de adherencia a medicamentos específica para
osteoporosis (OS-MMAS) en mujeres
posmenopáusicas con osteoporosis nunca antes tratado
con bisfosfonatos. Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 46(5),
659–670.
Rusida, E. R., Adhani, R., & Panghiyangani, R. (2017).
Pengaruh Tingkat Pengetahuan, Motivasi dan Faktor
Obat Terhadap Kepatuhan Minum Obat Pasien
Hipertensi di Puskesmas Kota Banjarbaru Tahun 2017.
Jurnal Pharmascience, 4(2).
Serinadi, D. M., Suyasa, I. G. P. D., Nuryanto, I. K., &
Dharmapatni, N. W. K. (2021). Faktor-Faktor
Determinan Penerapan Tugas Keluarga Pada Lansia
Hipertensi Berdasarkan Family Centered Nursing
Theory. Jurnal Keperawatan, 13(1), 213–226.
Utami, R. S., & Raudatussalamah, R. (2017). Hubungan
Dukungan Sosial Keluarga dengan Kepatuhan Berobat
Penderita Hipertensi di Puskesmas Tualang. Jurnal
Psikologi, 12(2), 91.
Wahyudi, C. T., Ratnawati, D., & Made, S. A. (2018).
Pengaruh Demografi, Psikososial, Dan Lama
Menderita Hipertensi Primer Terhadap Kepatuhan
Minum Obat Antihipertensi. Jurnal JKFT, 2(2).
Determinant Factors Affecting Adherence of Hypertensive Patients to Taking Antihypertensive Drugs
81
