
A Method for Determining Hourly Generation Schedules of a Large
Hydropower Station with Monthly Trading Electricity
Xiaoyong Hu
1
, Jianjian Shen
2,*
, Xu Han
3
and Jianpeng Cheng
4
1
China Three Gorges Corporation Electricity Market Research Center, 100000, Beijing, China
2
Institute of Hydropower and Hydroinformatics, Dalian University of Technology,
Dalian 116024, People's Republic of China
3
Institute of Hydropower and Hydroinformatics, Dalian University of Technology,
Dalian 116024, People's Republic of China
4
China Yangtze Power Co., Ltd, 100000, Beijing, China
Keywords: Generation Schedule, Hydropower Station, Trading Electricity.
Abstract: The trans-provincial and trans-regional power transmission of the southwest giant hydropower station
involves complex multi-dimensional hourly generation curve decomposition with monthly energy demands.
This needs to consider complex power grid peak shaving and other needs, which is an important problem to
be solved urgently for the monthly power generation and operation of the hydropower station. This study
constructs a monthly contracted electricity curve decomposition model suitable for trans-provincial and
trans-regional power transmission giant hydropower stations. Considering the differences in electricity
prices of three types, i.e. guaranteed quantity and guaranteed price, guaranteed quantity bidding and
marketization, as well as the complex constraints of power grid peak shaving, market and power station
operation, this paper puts forward the secondary planning goal of maximizing the total revenue of multi
provincial and multi variety power generation, The mixed integer linear programming method is used to
solve the model efficiently. The model is verified through two different application scenarios of a real
hydropower station in dry season and flood season. The results show that under the boundary conditions of
peak load regulation that meet the requirements of the power grid, the power generation income of the
power station can be effectively improved by optimizing the multi-scale and multi variety power and output
distribution of the two provinces and giving priority to the distribution of market-oriented power to the peak
load and flat section.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since 2015, China has started a new round of
electricity market reform(Jia, et al., 2022; Shen et al.,
2022). A unified market and a two-level operation
mode of regional and provincial power grids, and
medium - and long-term trading operation
mechanism with sound systems and rules are
initially developed. In this case, how to ensure the
performance of the long-term traded electricity is
very important, especially for hydropower stations.
Due to the uncertainty of inflow and the boundary
restrictions of relevant dispatching constraints(Wang,
et al., 2019), the medium and long-term trading
electricity may not be fully implemented or the
traded electricity may not be traded but the power
plant is over generated. Performing the trading
electricity of hydropower plants is one of the key
issues to participate in the electricity market
transaction.
There are several difficulties in performing
long-term contract electricity. First, there are
restrictions on the proportion of electricity in all
power-receiving provinces, and the distribution
proportion of different types of electricity needs to
be controlled separately. Moreover, the load curves
of different provinces are discrepant, such as the
peak and valley loads. Second, the total distribution
proportion should be considered for the power of
multiple varieties, and the output distribution
process of all varieties should be equal to the total
power generation capacity of the hydropower plant.
In addition, this problem also involves various
complex constraints of hydropower operations, with
strong space-time coupling. Mathematically, it is a
very complex high-dimensional nonlinear
192
Hu, X., Shen, J., Han, X. and Cheng, J.
A Method for Determining Hourly Generation Schedules of a Large Hydropower Station with Monthly Trading Electricity.
DOI: 10.5220/0011956600003536
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment (ISWEE 2022), pages 192-197
ISBN: 978-989-758-639-2; ISSN: 2975-9439
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

optimization problem. At present, some research
works have focused on the decomposition of
transaction electricity curve. For example, some
works considered the short-term operation
constraints of cascade hydropower stations and
relevant constraints of the daily electricity contract
decomposition curve. In this work, the maximum
comprehensive income model of transaction
electricity decomposition is constructed(Xie, et al.,
2021; Xu et al., 2019). Another works developed an
optimization model based on the day-ahead actual
needs of power grids, taking into account the
objectives of power purchase economy, energy
conservation and consumption reduction, and
fairness of bidding and non-bidding unit
dispatching(Cheng, et al., 2020).
This study constructs a monthly contracted
electricity curve decomposition model suitable for
trans-provincial and trans-regional power
transmission giant hydropower stations. Considering
the differences in electricity prices of three types, i.e.
guaranteed quantity and guaranteed price,
guaranteed quantity bidding and marketization, as
well as the complex constraints of power grid peak
shaving, market and power station operation, this
paper puts forward the secondary planning goal of
maximizing the total revenue of multi provincial and
multi variety power generation, The mixed integer
linear programming method is used to solve the
model efficiently. The model is verified through two
different application scenarios of a real hydropower
station in dry season and flood season. The results
show that under the boundary conditions of peak
load regulation that meet the requirements of the
power grid, the power generation income of the
power station can be effectively improved by
optimizing the multi-scale and multi variety power
and output distribution of the two provinces and
giving priority to the distribution of market-oriented
power to the peak load and flat section.
2 CASE STUDY: XILUODU
HYDROPOWER STATION
Xiluodu hydropower station is the third largest
hydropower station in China. It is an important
backbone power supply for the "West to East Power
Transmission" in the main stream of Jinsha River. It
is equipped with 18 700MW-hydropower units,
equally distributed on the left and right banks
respectively, with a total installed capacity of 12600
MW. The power station is located at the junction of
Sichuan and Yunnan. During the wet season, all the
power is transmitted to Guangdong and Zhejiang. In
the dry season, when the electricity demand in
Yunnan and Sichuan is met, all the remaining
electricity will be sent out. According to the national
hydropower integration arrangement, during the wet
season, all the electric power of Xiluodu
Hydropower Station will be consumed by Zhejiang
and Guangdong at the ratio of 1:1. In the dry season,
30% of the retained electricity is consumed by
Yunnan and Sichuan at the ratio of 1:1, and the rest
by Zhejiang and Guangdong at the ratio of 1:1.
Considering the electricity replacement among
cascade hydropower stations in the lower reaches of
the Jinsha River, in the actual operation, 30% of the
retained electricity of Xiluodu hydropower station in
the dry season is consumed by Sichuan and Yunnan
at the ratio of 7:23.
Table 1 Scheme for absorbing energy production of Xiluodu Hydropower Plant.
Province Zhejiang Sichuan Guangdong Yunnan Total
Flood
season
Left bank 50% - - - 50%
Right bank - - 50% 50%
Dry
season
Left bank 35% 7% - - 42%
Right bank - - 35% 23% 58%
A Method for Determining Hourly Generation Schedules of a Large Hydropower Station with Monthly Trading Electricity
193
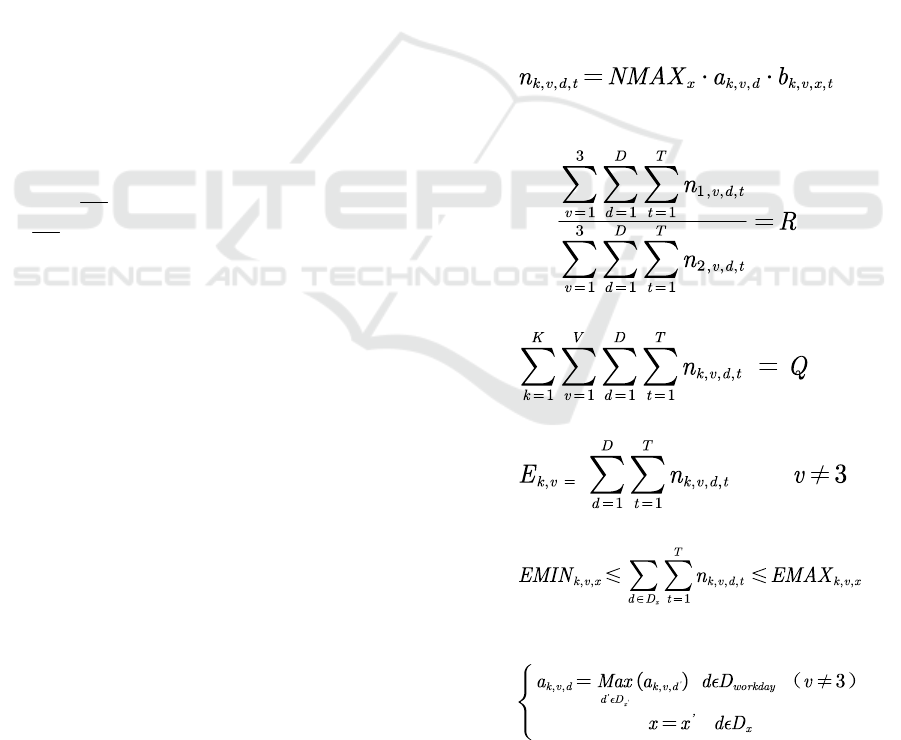
3 MATHEMATICAL MODEL
3.1 Notation
x
NMAX
Maximum power at a period
of ten da
y
s
R
Ratio of two power-
receiving
provinces(Guangdong and
Yunnan)
Q
Monthly energy demand
,kv
E
Trading electricity of variety
v at province
k
,,kvx
EMAX
,,kvx
EMIN
Maximum and Minimum of
trading electricity of variety
v at province k for each a
p
eriod of ten da
y
s
D
coef
A coefficient for non-work
da
y
,kh
c
,
,kh
c
Minimum and maximum of
hourl
y
coefficien
t
,kh
coef
A coefficient of normal
price for market electricity
in province
k
at period
t
,1k
P
,
,2k
P
,
,3k
P
Prices of three types of
electricity, namely, quantity-
price guarantee electricity,
quantity guarantee
electricity, and market
electricit
y
,,kvd
a
A daily coefficient for
variety v of province k in
da
y
d
,,,kvxt
b
A hourly coefficient for
variety v of province k in
p
eriod t o
f
the vth ten da
y
s
,, ,kvdt
n
Generation for variety v of
province k in period t of the
dth da
y
.
3.2 Objective
With the requirements for contracted electricity and
peak shaving of Guangdong and Yunnan Power
Grids, an hourly generation scheduling model with
maximizing the total power generation income is
developed. By optimizing the hourly generation
curves among provinces, ten days and varieties, the
monthly electricity income is maximized as far as
possible. Therefore, the objective function can be
described by the total income of three varieties, i.e.
quantity-price guarantee electricity, quantity
guarantee electricity, and market electricity.
1 ,1,,,1 ,2,,,2 ,3,,,3 ,
111
ax F ( )
KDT
kdtk kdtk kdtk kt
kdt
M
n P n P n P coef
===
=⋅+⋅+⋅⋅
(1)
3.3 Constraints
The above objective function is subject to important
operation constraints, listed in the following.
(1) Power balance constraint
(2)
(2) Energy production constraints
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(3) Other operation constraints
(7)
ISWEE 2022 - International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment
194

(8)
(9)
'
,,,
,,
,,,
1
()
kvxt
kt kt
T
kvxt
t
b
cc
b
Max
=
≤≤
‘
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
(14)
4 SOLUTION METHOD
Mathematically, the above trading electricity
decomposition model is a very complex large-scale
nonlinear optimization problem. It has high
dimensions and many nonlinear constraints, making
it difficult to solve. In order to realize the efficient
solution of the model, it is necessary to treat the
complex constraints equivalently. In the following,
the processing strategies of decomposition
coefficients of daily and hourly generation curves
are proposed, respectively.
Because the daily coefficient has a maximum
function, a temporal variable
is
introduced to describe the maximum of
at the
current ten days. The daily coefficient of each
province at each ten days should be limited in the
following.
(15)
(16)
(17)
For all provinces and varieties, the sum of
generation on working days should be equal to the
maximum power in current ten days, and there
should be a limit on non-working days.
(18)
(19)
Similarly, the hourly coefficients require
temporal variables
and to make the
model easily solve.
(20)
(21)
(22)
With the equivalent transformation of the above
constraints, the optimization model can be
transformed into a mixed integer quadratic
programming model and solved by a mathematical
solver.
5 CASE STUDY
This study takes the right bank of Xiluodu
hydropower station as the case study. Here, some
actual data are used to test the model. The monthly
trading electricity is set as 9.736*10
8
kWh. The ratio
of electricity for Guangdong Province and Yunnan
Province is set as 1.5.
According to the above solution method, we can
get hourly generation curve of each type of power
station in the first, middle and last ten days when the
hydropower station sends power to Guangdong and
Yunnan. Figure 1 shows the output process of the
power station in the first, middle and last ten days.
Figure 2 shows the hourly coefficients in ten days
for Guangdong and Yunnan, respectively. Figure 3
shows the generation schedules of the hydropower
station in two different days.
A Method for Determining Hourly Generation Schedules of a Large Hydropower Station with Monthly Trading Electricity
195
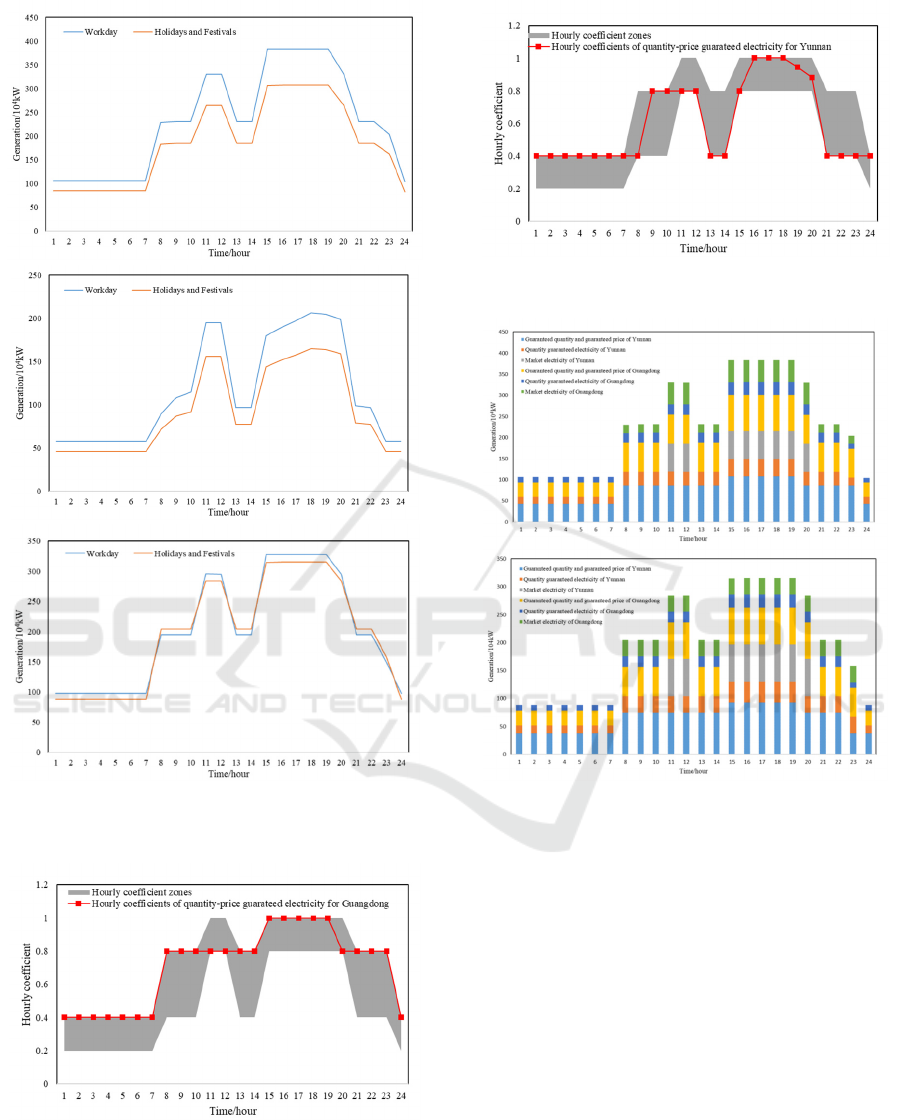
Figure 1: Typical generation schedules of the hydropower
station for three ten days.
Figure 2: Hourly coefficients for Guangdong and Yunnan
Figure 3: Generation schedules of different types of
electricity.
Firstly, the rationality is analysed. In the example of
dry season, the total monthly electricity in right bank
of Xiluodu is 973.6 million kWh, and the electricity
delivered to Guangdong and Yunnan is 584million
kWh and 389.6 million kWh respectively, meeting
the given requirements for cross provincial power
transmission ratio; The two priority electricity
varieties of guaranteed quantity and guaranteed price
and guaranteed quantity bidding are 725.6 million
kWh and 248.0 million kWh respectively, and the
results obtained are completely consistent with the
given parameters. At the same time, according to the
distribution proportion requirements of the two
provinces, the distribution results of electricity of
each variety are also consistent with the specified
power transmission proportion; The ratio of
guaranteed quantity, guaranteed price and
ISWEE 2022 - International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment
196

guaranteed quantity bidding electricity in each
province and each ten day period is within the
allowable fluctuation range of 20% above and below
the ratio of the monthly guaranteed quantity,
guaranteed price and guaranteed quantity bidding,
meeting the set boundary requirements; The time-
sharing coefficients of ten days in Figure 2 and
figure 3 are within the given purple value range,
meeting the peak shaving requirements proposed by
the power grid.
The efficiency of the model optimization results
is further analysed. According to the electricity
decomposition results in the dry season months, on
the premise of meeting the peak load regulation
requirements of the power grid, the market-oriented
electricity in the first ten days, the middle ten days
and the last ten days is basically distributed in the
load peak and normal sections with relatively high
electricity prices, of which 100% of Guangdong's
market-oriented electricity is distributed in the high
peak hours, because its market-oriented electricity
price is the highest in the peak hours, that is, 1.1
times of the benchmark price, so as to maximize the
power generation income, This distribution method
is reasonable. 63% of the market-oriented electricity
in Yunnan is distributed in the peak load and 37% in
the normal load section. The main reason is that the
market-oriented electricity price in Yunnan is lower
than that in Guangdong. Through the coordinated
distribution of multi varieties across provinces, the
market-oriented electricity will be preferentially
arranged in the peak period in Guangdong, which
has the highest electricity price. In this way, in order
to meet the requirements for the proportion of the
two varieties of electricity in Yunnan, i.e. the
quantity and price guarantee and the quantity and
bidding guarantee, Yunnan needs to arrange a large
proportion of priority electricity during peak hours,
so a part of market-oriented electricity is allocated at
periods with middle loads.
6 CONCLUSION
This paper mainly focuses on the hourly generation
scheduling model of a large hydropower station
when the monthly contract electricity is given. Using
monthly actual data, the following conclusions are
obtained. 1) The hourly generation scheduling model
can adapt to the power decomposition requirements
of multiple provinces, multiple market varieties and
multiple time scales. The dispatching scheme
obtained conforms to the actual production habits,
reflecting good adaptability and practicality. 2)
Taking into account the requirements of
differentiated peak shaving of multiple power grids,
and aiming at maximizing the monthly electricity
revenue of the hydropower station, it can effectively
take into account the interests of power grids and
hydropower enterprises. The hourly coefficients in
the middle and late ten days of the monthly
electricity declaration are consistent with the peak-
valley trend. Within the boundary conditions of peak
shaving, it is reasonable to arrange the market-
oriented electricity in the peak and flat load sections
with higher electricity prices as far as possible.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper is supported by scientific research
projects of China Three Gorges Corporation
(Contract number: 202003252).
REFERENCES
Ze Bin Jia, Jianjian Shen, Chuntian Cheng, et al. Optimum
day-ahead clearing for high proportion hydropower
market considering complex hydraulic connection.
International Journal of Electrical Power and Energy
Systems, 2022, 141:108211.
Jianjian Shen, Chuntian Cheng, Ze Bin Jia, et al. Impacts,
Challenges and Suggestions of the Electricity Market
for Hydro-Dominated Power Systems in China.
Renewable Energy, 2022, 187:743-759.
Jian Wang, ChunTian Cheng, Xinyu Wu, JianJian Shen.
Optimal Hedging for Hydropower Operation and End-
of-Year Carryover Storage Values. Journal of Water
Resources Planning and Management-ASCE, 2019,
145(4): 04019003.
Xie Mengfei, JIA Zebin, ZHANG Fan, et al. Method of
short-term scheduling for high-proportion hydropower
grid considering energy decomposition. Journal of
Hydroelectric Engineering, 2021, 40(01): 54-64.
Xu Chuanlong, ZHANG Lizi, CHEN Dayu, et al. A
Monthly Balancing Mechanism Based on Pre-bidding
and Its Multi-period Generation Schedule
Optimization Model. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019,
39(17): 5085-5094.
Cheng Xiong, TANG Yingling, SHEN Jianjian, et al.
Decomposition and Checking Method for Large-scale
Hydropower Plants Monthly Trading Energy in
Electricity Market. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020,
40(8): 2514-2524.
A Method for Determining Hourly Generation Schedules of a Large Hydropower Station with Monthly Trading Electricity
197
