
Research on the Lake Health Evaluation based on Multi-Dimensional
Index System Taking Dongshan Lake as an Example
Zhaoxu Li
1,2
, Jianguo Wang
1,2,*
, Weijie Huang
1,2
, Wei Guo
1,2
, Xiaoping Zhu
1,2
, Qian Wu
1,2
,
Liehui Lei
1,2
and Yisi Liu
1,2
1
Pearl River Water Resources Institute, Pearl River Water Resources Commission, Guangzhou, China
2
Guangdong Provincial Engineering Technology Research Center for Life and Health of River & Lake, Guangzhou, China
Keywords: Research, Lake Health Evaluation, Multi-Dimensional Index System, Dongshan Lake.
Abstract: With the development of economy and society, the production and life of human beings gradually have a
negative impact on the water body of rivers and lakes. Restoring the health of rivers and lakes has gradually
become an important task. River and lake health evaluation is an important basic work to strengthen the
management and protection of rivers and lakes, and with the in-depth implementation of the River Chief
System (RCS) and the Lake Chief System (LCS), it has attracted more and more attention. In this paper,
focusing on the comprehensive management and protection of lakes, with the help of the multi-dimensional
index system of lake health evaluation in the Evaluation Guidelines and Technical Guidelines, the Dongshan
Lake in Guangzhou was taken as an example to study and determine the multi-dimensional health evaluation
index system. Utilizing the index system, the health evaluation and overall health characteristics analyzation
of Dongshan Lake were carried out, and the specific protection countermeasures and suggestions were given.
This research has a certain reference value for the systematic health evaluation and protection of lakes.
1 INTRODUCTION
There are many lakes in China. According to
statistics, there are 2,759 natural lakes larger than
1.0km
2
in the country, with a total area of
91019.63km
2
(Wang and Dou, 1998). Lake is one of
the natural units in the natural ecosystem on which
human beings depend for survival. As a unique
resource, lakes play a huge social and economic role
in water supply, flood control, aquaculture, tourism,
shipping, maintaining ecological balance and
environmental protection. With the increase of
population and the development of industrial and
agricultural production, the discharge of industrial
wastewater and domestic sewage is increasing, and
the lake ecosystem on which human beings depend is
degraded, especially the problem of eutrophication,
which has seriously threatened the sustainable
development of social economy and human health
(Pu et al., 2014). Therefore, studying the lake
ecosystem, establishing a lake ecosystem health
evaluation system and index thresholds, and ensuring
the water demand of the lake ecological environment,
not only can provide a comprehensive, authoritative
and operational decision-making basis for the rational
allocation of water resources and lake management,
but also be conducive to the sustainable management
and rational utilization of the lake ecosystem, as well
as the realization of ecological coordination of social
and economic benefits (Steedman, 1994; Hu et al.,
1998; Jones and Taylor, 1999; Ladhar, 2002) .
On January 12, 2012, the State Council issued the
Opinions of the State Council on Implementing the
Most Strict Water Resources Management System
(Guofa [2012] No. 3), which proposed to promote the
protection and restoration of aquatic ecosystems, to
study the index system establishment of ecological
water use and ecological evaluation of rivers and
lakes, to regularly organize the health assessment of
important rivers and lakes nationwide, and to
establish and improve the water ecological
compensation mechanism. On March 21, 2014, the
Ministry of Water Resources issued the Guiding
Opinions on Strengthening the Management of
Rivers and Lakes (Shuijianguan [2014] No. 76),
which proposed that by 2020, the river and lake health
security system should be basically established, the
river and lake management system and mechanism
should be established and improved, and the efforts
should be made to achieve no shrinkage of rivers and
Li, Z., Wang, J., Huang, W., Guo, W., Zhu, X., Wu, Q., Lei, L. and Liu, Y.
Research on the Lake Health Evaluation Based on Multi-Dimensional Index System Taking Dongshan Lake as an Example.
DOI: 10.5220/0011960600003536
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment (ISWEE 2022), pages 207-216
ISBN: 978-989-758-639-2; ISSN: 2975-9439
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
207

lakes, no degradation of functions, and no ecological
degradation.
In order to thoroughly implement the Opinions on
the Full Implementation of the River Chief System
(RCS) and the Guiding Opinions on the
Implementation of the Lake Chief System (LCS) in
Lakes by the General Office of the CPC Central
Committee and the General Office of the State
Council, guide all localities in carrying out river and
lake health assessment work and promote RCS and
LCS to be Famous, Realistic and Capable, the
Department of River and Lake Management of the
Ministry of Water Resources organized the Nanjing
Institute of Hydraulic Research and other units to
formulate the Guidelines for Health Evaluation of
Rivers and Lakes (Trial) (hereinafter referred to as the
Evaluation Guidelines ) , so as to provide a scientific
standard for testing the effectiveness of RCS and LCS
in various regions in China (Liu et al., 1999).
River and lake health evaluation is an important
content of river and lake management. It will provide
an important basis for determining the health status of
rivers and lakes, finding river and lake problems,
analyzing pathogeny, and proposing governance
countermeasures. It is an important basis for realizing
river and lake system governance and long-term
governance. This paper took the Dongshan Lake as an
example, and conducted health evaluation on the lake
according to relevant guidelines. On this basis, it
analyzed and evaluated the problems of the Dongshan
Lake from four aspects of health evaluation indices,
studied and put forward a systematic restoration
strategy for the lake to provide decision-making basis
for realizing long-term governance and effective
management of the lake.
2 MULTI-DIMENSIONAL
HEALTH EVALUATION INDEX
SYSTEM FOR LAKES
In August 2020, the River Directors Office of the
Ministry of Water Resources issued the Evaluation
Guidelines, pointing out that the health evaluation of
rivers and lakes is an important content of river and
lake management, and an important means to test the
Famous and Real of RCS and LCS. The results of
river and lake health assessment are an important
reference for the river and lake directors to carry out
the protection and management of rivers and lakes.
In May 2021, based on the Evaluation Guidelines,
the Office of the Leading Group for the
Comprehensive Implementation of the River Chief
System in Guangdong Province compiled the
Guangdong Province 2021 River and Lake Health
Evaluation Technical Guidelines (hereinafter referred
to as the Technical Guidelines), which combined the
characteristics of rivers and lakes in Guangdong
Province and the actual situation of river and lake
management, and condensed foreign and domestic
research results and practical experience, was used to
guide all localities to carry out river and lake health
evaluation .
For lake health evaluation, the technical
guidelines adopt a multi-dimensional health
evaluation index system, in which 22 indices are
involved in the evaluation of lakes from four criteria
layers including “Basin” (i.e. lake physical structure),
“Water” (i.e. lake water environment), Biology (i.e.
lake water ecology), and social service functions
(Table 1). All evaluation indices are divided into
Required Indices and Optional Indices based on lake
functions, index importance, difficulty in obtaining
index data, etc. These indices can scientifically and
comprehensively evaluate the performance of river
and lake governance from the perspective of river and
lake health.
ISWEE 2022 - International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment
208
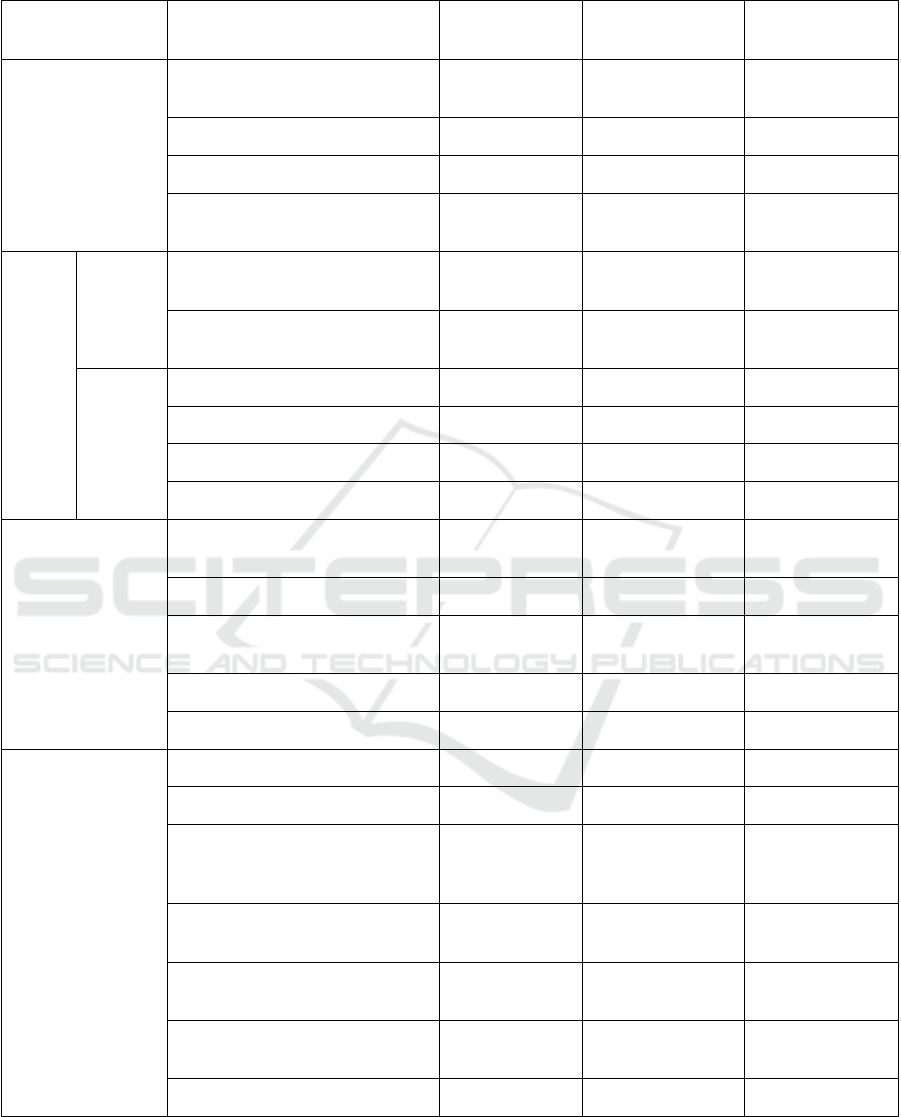
Table 1: Lake health evaluation index system and survey sampling scope.
Criterion layer Index layer Index type
Survey or sampling
monitoring scope
Specific location
“Basin”
Lake connectivity index Optional indice Evaluation Lake
River around the
lake
Lake area shrinkage ratio Required indice Evaluation Lake Water area
Natural conditions of shoreline Required indice Monitoring section Lakeshore zone
Degree of illegal development and
utilization of water shoreline
Required indice Evaluation Lake
Water area and
lakeshore zone
“Water”
Volume
Satisfaction degree of minimum
ecological water level
Required indice Monitoring point Water area
Variation degree of inflow Optional indice Evaluation Lake
River around the
lake
Quality
Quality of water Required indice Monitoring point Water area
Lake nutritional status Required indice Monitoring point Water area
Sediment pollution status Optional indice Monitoring point Water area
Water self-purification capacity Required indice Monitoring point Water area
Biology
Macrobenthic Invertebrate
Biological Integrity Index
Optional indice Monitoring point
Aquatic organism
sampling area
Fish retention index Required indice Evaluation Lake Water area
Water and bird conditions Optional indice Evaluation Lake
Water area and
lakeshore zone
Phytoplankton density Required indice Monitoring point Water area
Macrophyte coverage Optional indice Monitoring point Nearshore zone
Social Service
Functions
Flood control compliance rate Optional indice Evaluation Lake Lakeshore zone
Water supply guaranteed degree Optional indice Evaluation Lake Water area
Water quality compliance rate of
lake centralized drinking water
source
Optional indice Evaluation Lake Water area
Shoreline utilization management
index
Optional indice Evaluation Lake Lakeshore zone
Comprehensive benefits of Green
Road construction
Optional indice Evaluation Lake Lakeshore zone
Water and soil conservation rate of
watershed
Optional indice Evaluation Lake Catchment area
Public satisfaction Required indice Evaluation Lake Surrounding public
Research on the Lake Health Evaluation Based on Multi-Dimensional Index System Taking Dongshan Lake as an Example
209

3 GENERAL SITUATION OF
DONGSHAN LAKE AND
DETERMINATION OF ITS
HEALTH EVALUATION INDEX
SYSTEM
3.1 General Situation of Dongshan
Lake
The Dongshan Lake, built in 1958, is located to the
east of the North approach bridge of Haiyin bridge,
adjacent to the Pearl River in the south, connected
to Zhudao hotel in the East and Guigang business
district in the north. It is composed of the West
Lake, the Nanpian Lake and the Dongpian Lake,
and is one of the four largest artificial lakes in
Guangzhou. Its main functions are rain and flood
regulation and entertainment. The Dongshan Lake
receives the water from the upstream of the
Donghaochong River and the Xinhepu River in the
north, and is connected with the Ersha River
through two sluices (Sluice No. 6 and Sluice No. 8)
in the south, with a total rainwater collection area
of 4.48km
2
. The normal water storage level of the
lake area is 5.50m, the water surface area is
0.355km
2
, the water storage capacity is 410,700
m3, the current regulated storage control water
level is 6.80m, and the water storage capacity is
802,700 m3. The geographical location of
Dongshan Lake is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of the location of the
Dongshan Lake.
At present, the pollution interception of the
Dongshan Lake has been basically completed, and
the direct discharge pollution sources of industry,
agriculture and catering industry have been
basically eliminated. However, due to the impact of
various factors such as flood discharge and
drainage, sewage overflow, incoming water quality
and surface runoff, the water quality of the
Dongshan Lake fluctuates, which makes it difficult
for the Dongshan Lake to maintain a stable
monthly standard without the discharge of
surrounding pollution sources. Due to insufficient
exchange frequency with surrounding rivers, the
low flow rate and the poor water dynamics, the
water ecological environment of the Dongshan
Lake needs to be improved.
3.2 Determination of the Multi-
Dimensional Health Evaluation
Index System of the Dongshan Lake
This paper refers to the Technical Guidelines to
construct an index system for evaluating the health of
the Dongshan Lake, as shown in Table 2. From the
table it can be seen that there is a total of 18 evaluation
indices among the four criterion layers of the
Dongshan Lake health evaluation index system,
including 10 required indices and 8 optional indices.
ISWEE 2022 - International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment
210

Table 2: Health evaluation index system of the Dongshan Lake.
4 DONGSHAN LAKE HEALTH
EVALUATION, OVERALL
CHARACTERISTICS
ANALYSIS AND PROTECTION
COUNTERMEASURES
4.1 Dongshan Lake Health Evaluation
based on Multi-Dimensional Index
System
With reference to the evaluation methods and standards
of the Technical Guidelines, from the perspectives of
the four criterion levels of “Basin”, “Water”, biology,
and social service functions, the health evaluation
indices of the Dongshan Lake are assigned scores on the
basis of literature review, survey visits and field
investigations. According to the weight of each health
evaluation index of the Dongshan Lake, the index
layer and the criterion layer are weighted layer by
layer, and the specific calculation adopts Formula (1).
()
××=
mn
nrnwmw
ZBZBYMBRHI
i
(1)
In Formula (1), RHI
i
is the comprehensive score
of the lake health in the i-th evaluation Lake area;
ZB
nw
is the weight of the n-th index of the index layer;
ZB
nr
is the score of the n-th index of the index layer;
YMB
mw
is the weight of the m-th criterion layer.
According to the Technical Guidelines, the Dongshan
Lake set up three evaluation areas (Figure 2), i=3.
Criterion layer Index layer Index type
“Basin”
Lake connectivity index Optional index
Lake area shrinkage ratio Required index
Natural conditions of shoreline Required index
Degree of illegal development and utilization of water shoreline Required index
“Water”
Volume Satisfaction degree of minimum ecological water level Required index
Quality
Quality of water Required index
Lake nutritional status Required index
Sediment pollution status Optional index
Water self-purification capacity Required index
Biology
Macrobenthic Invertebrate Biological Integrity Index Optional index
Fish retention index Required index
Water and bird conditions Optional index
Phytoplankton density Required index
Macrophyte coverage Optional index
Social Service Functions
Flood control compliance rate Optional index
Shoreline utilization management index Optional index
Comprehensive benefits of Green Road construction Optional index
Public satisfaction Required index
Research on the Lake Health Evaluation Based on Multi-Dimensional Index System Taking Dongshan Lake as an Example
211
The comprehensive health score of Dongshan
Lake is calculated by formula (2).
()()
1
11i
−
==
×=
SS
R
i
i
R
ii
WWRHIRHI
(2)
In Formula (2), RHI is the comprehensive score
for the lake health; RHI
i
is the comprehensive score
for the lake health of the i-th evaluated lake area; W
i
is the water surface area of the i-th evaluated lake,
km
2
; Rs is the number of evaluated lake areas.
The final health evaluation result of the Dongshan
Lake was calculated, as shown in Table 3, Table 4,
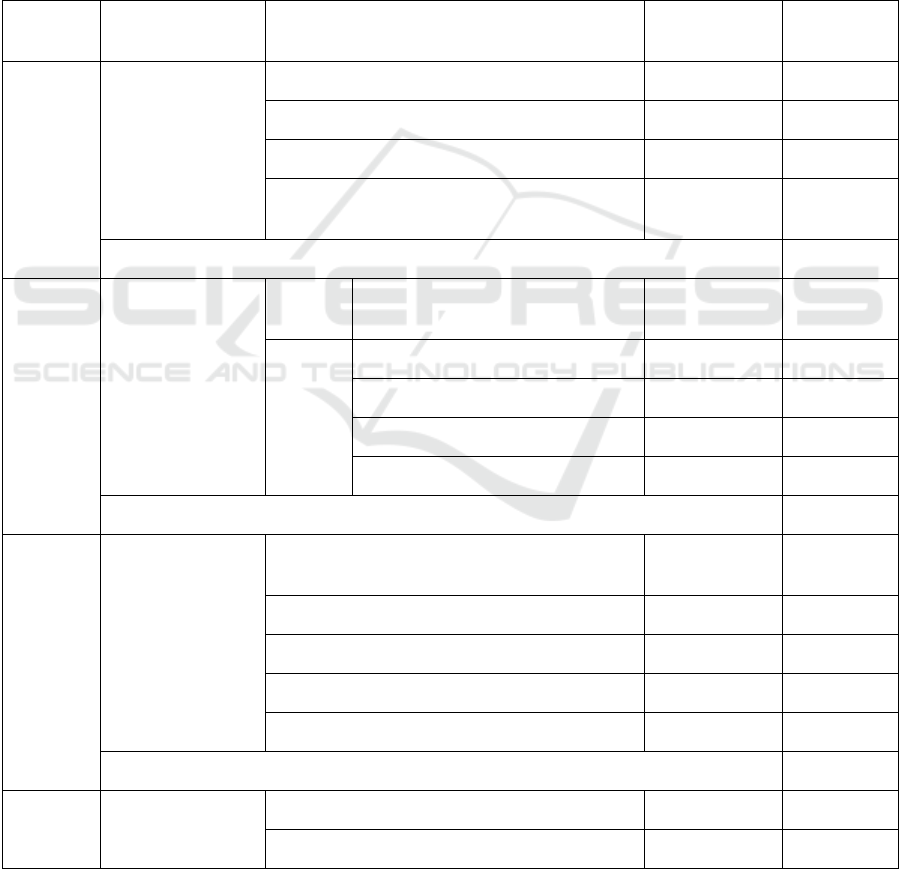
Figure 2 and Figure 3. It can be seen from Table 3 that
the overall scores of the four standard layers——Basin”,
Water, Biology, and Social Service Functions of the
Dongshan Lake are 86.85, 67.80, 39.37 and 97.07,
respectively. The Water standard tier scored 67.80,
which is lower, and the overall score of the criteria
layer is the lowest, only 40.46. The comprehensive
health evaluation score of the Dongshan Lake is
74.70.
Table 3: Multi-dimensional Index Assignment of the Dongshan Lake Health evaluation.
Criterion
layer
Criterion layer
weight (YMB
mw
)
Index layer
Index layer
weight (ZB
nw)
assigned
score (ZB
nr)
“Basin”
0.2
Lake connectivity index
0.19
45.00
Lake area shrinkage ratio
0.27 100.00
Natural conditions of shoreline
0.27 90.00
Degree of illegal development and utilization of
water shoreline
0.27 100.00
Overall score 86.85
“Water”
0.3
Water
volume
Satisfaction degree of minimum
ecological water level
0.30 75.00
Water
Quality
Quality of water 0.20 40.00
Lake nutritional status 0.20 49.00
Sediment pollution status 0.10 75.00
Water self-purification capacity 0.20 100.00
Overall score 67.80
Biology
0.2
Macrobenthic Invertebrate Biological Integrity
Index
0.18 15.00
Fish retention index 0.23 7.00
Water and bird conditions 0.18 75.00
Phytoplankton density 0.23 31.12
Macrophyte coverage 0.18 80.00
Overall score 39.37
0.3
Flood control compliance rate 0.24 100.00
Shoreline utilization management index 0.24 100.00
ISWEE 2022 - International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment
212
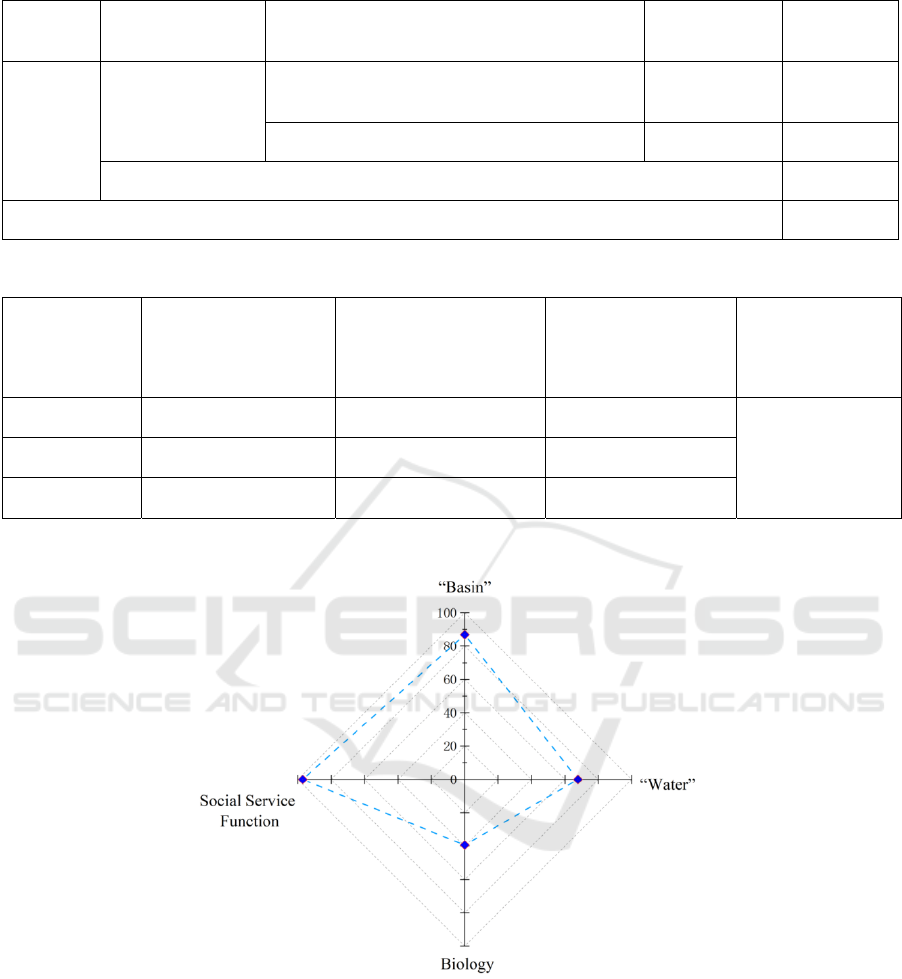
Criterion
layer
Criterion layer
weight (YMB
mw
)
Index layer
Index layer
weight (ZB
nw)
assigned
score (ZB
nr)
Social
Service
Functions
Comprehensive benefits of Green Road
construction
0.24 97.00
Public satisfaction 0.28 92.10
Overall score 97.07
Comprehensive health evaluation score of the Dongshan Lake ( RHI) 74.70
Table 4: Comprehensive health evaluation score of the Dongshan Lake.
Lake Zoning
Water surface area
(W
i
, km
2
)
Proportion of zoning area
to the total area
Zoning score
(RHI
i
)
Comprehensive
score
(
RHI
)
D1 0.09 25.71% 73.10
74.70
D2 0.10 28.57% 72.74
D3 0.16 45.71% 72.95
Figure 2: Health criteria layer of the Dongshan Lake scoring diagram.
Research on the Lake Health Evaluation Based on Multi-Dimensional Index System Taking Dongshan Lake as an Example
213
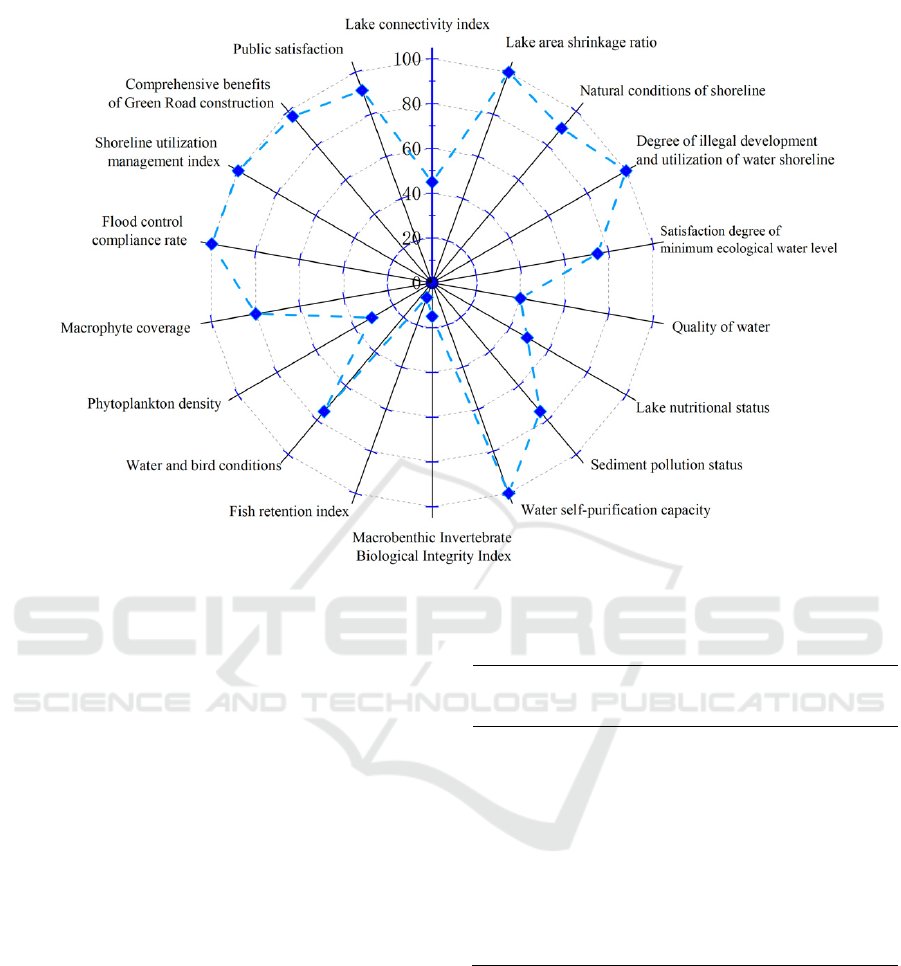
Figure 3: Health evaluation indices of the Dongshan Lake scoring diagram.
4.2 Analysis of the Overall Health
Characteristics of the Dongshan
Lake
From the perspective of each criterion layer of the
Dongshan Lake, the “Basin” criterion layer has a
score of 86.85, which is in a healthy state, the “Water”
criterion layer has a score of 67.80, which is in a sub-
health state, the biological criterion layer has a low
score of 39.37, which is in an unhealthy state; the
social service function criterion layer has a relatively
high score of 97.07, which is relatively healthy. The
Dongshan Lake has a total score of 74.70 in the health
evaluation which is between 60 and 75. It can be seen
that the Dongshan Lake has defects in water
ecological integrity and biodiversity, and its health
status is generally in a sub-healthy state. According to
the health evaluation indices, criterion layers and
comprehensive scores of the Dongshan Lake, and
referring to the lake health evaluation grading table in
the Technical Guidelines (shown in Table 5), the
Dongshan Lake was comprehensively assessed as a
Class-III lake.
Table 5: Classification table of the lake health evaluation.
Lake
classification
Health status
Scoring range
(RHI)
Class I Very healthy 90≤RHI≤100
Class II Healthy 75≤RHI<90
Class III Sub-healthy 60≤RHI<75
Class Ⅳ Unhealthy 40≤RHI<60
Class Ⅴ Inferior state RHI<40
4.3 Countermeasures and Suggestions
for the Dongshan Lake Protection
According to the results of the health evaluation of
the Dongshan Lake, it has defects in water ecological
integrity, anti-disturbance resilience and biodiversity,
and is in a sub-healthy state. It should strengthen daily
maintenance and supervision, take comprehensive
treatment and restoration measures, appropriately
increase ecological restoration projects, timely repair
local defects and eliminate hidden dangers affecting
ISWEE 2022 - International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment
214

health. Combining with the health evaluation of the
Dongshan Lake, several countermeasures and
suggestions for protecting the Dongshan Lake are put
forward.
Firstly, water environment treatment should be
consolidated. The pollution problem of the Dongshan
Lake can be fundamentally solved by adhering to the
water control policy of source control, pollution
interception, desilting, water replenishment and
management, implementing and promoting grid
water control, tackling difficulties in meeting the
standards of drainage units, and a series of practices
such as Three Sources, Four Washing and Five
Cleaning, which have been proven effective.
Secondly, the comprehensive treatment and
restoration measures of water ecology should be
strengthened. While doing a good job in the Three
Sources, Four Washing and Five Cleaning of the
Dongshan Lake, the ecological revetment project of
the Dongshan lake shoreline shall be implemented. At
the same time, focusing on the actual needs of
improving the water ecological integrity, anti-
disturbance elasticity and biodiversity of the lake, the
ecological restoration projects, such as the
implementation of biological manipulation,
multiplication and release measures, should be
appropriately increased.
Thirdly, the connectivity of the Dongshan Lake
should be restored. The Dongshan Lake should
implement the river and lake connectivity project to
ensure the overall connectivity of the lake. At the
same time, on the premise of ensuring flood control
safety, it should be optimized the linkage mechanism
of Dongshan Lake sluice and pump to realize the
small cycle of the Dongshan Lake, the Xinhepu River
and the Dongshan Lake, the large cycle of the Pearl
River, the Dongshan Lake, the Xinhepu River, the
Donghao River and the Pearl River, so as to make the
lake water truly live water (
Figure 1).
Fourthly, precise management should be
strengthened. Taking the implementation of the LCS
and the most stringent water resources management
system as the starting point, it should be strengthen
the protection of lake water resources, the
management and protection of lake water shoreline,
the prevention and control of water pollution, the
treatment of water environment and the restoration of
water ecology, etc., prepared and improved the “One
Lake, One Policy” plan on a rolling basis, promoted
the systematic governance of the whole basin and
effectively improved the management level of the
Dongshan Lake health.
At last, it is necessary to implement the
responsibility management system, strengthen the
assessment mechanism, and effectively improve
the management effectiveness, so as to protect the
health of the Dongshan Lake.
5 CONCLUSION
Rivers and lakes are important carriers of water
resources and have important ecological,
environmental and social service functions [11]. With
the rapid development of economy and society, many
river and lake ecosystems are gradually damaged or
even destroyed. Maintaining and restoring river and
lake health has gradually become an important task
and central work of lake management. River and lake
health evaluation is an important basic work to
strengthen the management and protection of rivers
and lakes, and it is an important means to test the
Famous and Real of RCS and LCS. With the in-depth
implementation of RCS and LCS, the health
evaluation of rivers and lakes has attracted much
attention. In this paper, focusing on the
comprehensive management and protection of lakes,
with the help of the multi-dimensional index system
of lake health evaluation in the Evaluation Guidelines
and Technical Guidelines, the Dongshan Lake in
Guangzhou was taken as an example to study and
determine the multi-dimensional health evaluation
index system. Utilizing the index system, the health
evaluation and overall health characteristics
analyzation of the Dongshan Lake were carried out.
According to the health evaluation indices, criterion
layers and comprehensive scores, the Dongshan Lake
was comprehensively assessed as a Class-III lake.
Finally, combined with the health evaluation of the
Dongshan Lake, this paper put forward relevant
countermeasures and suggestions for its management
and protection.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by the Open Research
Fund of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Water
Engineering Materials and Structures (GXHRI-
WEMS-2020-11), the
Special Foundation for
National Science and Technology Basic Research
Program of China (2019FY101900) and the National
Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.
5170929).
Research on the Lake Health Evaluation Based on Multi-Dimensional Index System Taking Dongshan Lake as an Example
215

REFERENCES
Cheng Y. H., 2019. Research on Health Evaluation of
Yamaguchi Lake Reservoir, Harbin: Heilongjiang
University Library, 1 p.
Hu W. ., Salomonsen J., Xu F. L., Pu P. M., 1998. A model
for the effects of water hyacinths on water quality in an
experiment of physico-biological engineering in Lake
Taihu, China. Ecological Model. 107: 171-188.
Jones M. L., Taylor W. W., 1999. Challenges to the
implementation of the ecosustem approach in the Great
Lakes basin. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Manag, 2(2):
249-254.
Ladhar S. S., 2002. Status of ecological health of wetlands
in Punjab, India. Aquatic Ecosystem Health &
Management, 5: 457-465.
Liu L. Y., Li Y., Wang X. G., 2020. The background and
significance in the issuance of the Guidelines for River
and Lake Health Assessment (Trial). China Water
Resources, (20): 1-3.
Pu P. M., Wang G. X., Li Z. K., Hu C. H., Cheng B. J.,
Cheng X. Y., Li B., Zhang S. Z., Fan Y. Q., 2001.
Degradation of healthy aqua-ecosystem and its
remediation: theory, technology and application.
Journal of Lake Sciences, 13: 193-203.
Steedman R. J., 1994. Ecosystem health as a management
goal. Journal of the North American Benthol Socience,
13: 605-10.
Wang S. M., Dou H. S. 1998. Lake records of China,
Beijing: Science Press.
ISWEE 2022 - International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment
216
