
Methodology for Learning Programming Languages Through the
Use of Virtual Reality Resources
Christian Ovalle
1a
, Sandra Meza
2b
, Wilver Auccahuasi
3c
, Oscar Linares
4d
, Kitty Urbano
5e
,
Emilio Rosario-Pacahuala
6f
, Yoni Nicolas-Rojas
7g
, Aly Auccahuasi
8h
,
Tamara Pando-Ezcurra
9i
and Raúl Castro-Vidal
10 j
1
Universidad Tecnológica del Perú, Lima, Peru
2
Universidad ESAN, Lima, Peru
3
Universidad Privada del Norte, Lima, Peru
4
Universidad Continental, Huancayo, Peru
5
Universidad Científica del Sur, Lima, Peru
6
Universidad de San Martin de Porres, Lima, Peru
7
Escuela superior la Pontificia, Ayacucho, Peru
8
Universidad de Ingeniería y Tecnología, Lima, Peru
9
Universidad Privada Peruano Alemana, Lima, Peru
10
Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos, Lima, Peru
kurbano@cientifica.edu.pe, epacahuala@usmp.edu.pe, yoninicolas@elp.edu.pe, aly.auccahuasi@utec.edu.pe,
tamara.pando@upal.edu.pe, rcastrov@unmsm.edu.pe
Keywords: Programming, VR, Languages, Multi-Monitor, Development.
Abstract: New technologies are allowing us to have access to new tools, as is the case of Virtual Reality, education is
one of the areas where it is being used more frequently; in this sense we present a methodology to make use
of Virtual Reality in the teaching process of programming using the LabView programming language, which
has a fundamental characteristic, that of proposing two development environments, the first one related to the
design of the user interface through the use of virtual instruments and the second one related to the source
code through connections of the virtual instruments. As results, the necessary components to implement the
methodology are presented, as well as the exploitation and scaling of the methodology.
1 INTRODUCTION
The implementation of Virtual Reality technologies
requires the necessary technological infrastructure to
be able to be exploited without inconvenience.
Among the main necessary components are those
related to the connectivity of the devices, including
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5559-5684
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4650-1340
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8820-4013
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7952-9518
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2009-000X
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2421-548X
g
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6493-6084
h
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5069-0415
i
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0301-3440
j
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2901-0101
high-speed wireless networks with a stable signal. For
this purpose, it is a common consensus to work with
the communication protocols provided by the WIFI-
6 network (Auccahuasi, et al. 2021a), (Auccahuasi, et
al. 2021b). In using and exploiting Virtual Reality
technologies, some works used immersive virtual
reality (IVR) in student learning, for which concept
592
Ovalle, C., Meza, S., Auccahuasi, W., Linares, O., Urbano, K., Rosario-Pacahuala, E., Nicolas-Rojas, Y., Auccahuasi, A., Pando-Ezcurra, T. and Castro-Vidal, R.
Methodology for Learning Programming Languages Through the Use of Virtual Reality Resources.
DOI: 10.5220/0011962500003612
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing (ISAIC 2022), pages 592-596
ISBN: 978-989-758-622-4; ISSN: 2975-9463
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
maps will be used, related to the study of different
plants (Lee, Hsu, & Cheng, 2022).
Teaching processes are undergoing great changes,
originated by the use of new technologies, as is the
case of teaching courses related to different
programming languages (Srimadhaven, et al. 2020).
The power to bring these techniques to virtual
environments where students can experience new
ways, such as immersive media through virtual reality
(Saab, et al. 2021).
Industry 4.0, has originated new changes in
manufacturing and industrial processes, which is
complemented in proposing methods to perform
simulation processes, using the available technology,
in this task virtual reality helps to meet these
objectives (Kumar, et al. 2021). One of the areas is
related to learning processes to simulate birth
processes in order to train health personnel (Yu &
Mann, 2021).
We also found works for the teaching of the
English language with the intention of improving the
level of experimentation in order to improve the
teaching and learning processes (Barrett, Pack, &
Quaid, 2021). The use of virtual reality leads to
propose new ways to improve training processes, as
in the case of first aid training (Araiza-Alba, et al.
2021). Complementing the different medical
procedures that can be simulated using the techniques
described (Fealy, et al. 2019).
In this paper, we will address a methodology to
apply the techniques provided by Virtual Reality,
through the use of virtual reality glasses models
Oculus Quest II, for teaching programming
languages, applying to the development environment
that provides the LabView programming tool and the
INMERSED application, where the benefits are
exploited in order to improve the experience of
students to understand and understand programming
techniques.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The methodology we present is related to the use of
virtual reality glasses of the Oculus Quest II model,
as well as the use of the INMERSED application and
complementing it with the interaction of different
mobile devices such as computers and workstations,
then, we present the procedures to implement the
proposed methodology. According to figure 1.
Figure 1: Block diagram of the methodology.
2.1 Analysis of the Problematic Reality
on Programming Techniques
Some of the problems that are constantly presented in
programming classes, are related to explain and that
students can understand the programming logic,
which requires a lot of practice by students, and new
techniques that allow teachers and instructors can
explain the concepts of programming, one of the
modern programming tools related to programming
and industrial automation, is provided by the
development environment LabView, which presents
a new concept of programming thanks to the G
language, which presents a variation in the way of
programming, going from a classic form of
programming through lines of code, to a
programming based on objects and connections, this
form of programming is exploited by two
environments, one related to the development of the
graphical user interface and is the graphical
representation that the user will interact with the
system, and the environment related to programming
with objects and how they connect with each other, in
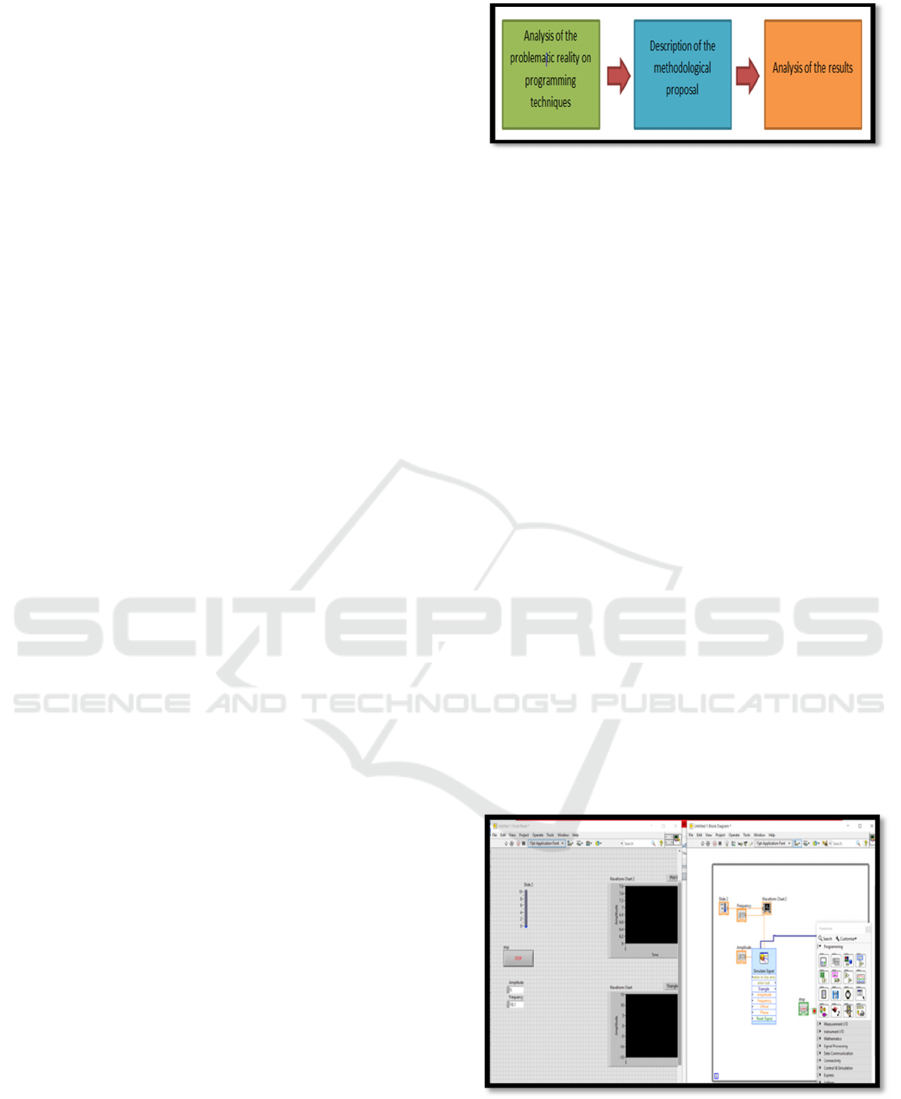
Figure 2, the development environment of the
programming language in LabView is presented.
Figure 2: Example of programming with Labview
language.
Figure 2 shows the LabView programming
language development environment, with the user
interface as well as the coding environment. In order
Methodology for Learning Programming Languages Through the Use of Virtual Reality Resources
593

to have a better learning experience, it is
recommended that each of the environments is
represented on an individual monitor, to be able to
understand and exploit the potential of the tool, in a
conventional situation the same monitor is shared
with the two development environments, which
hinders visibility and thus the analysis and
understanding of the exercises that are developed in
the teaching process.
2.2 Description of the Methodological
Proposal
The proposed methodology is based on the use of
virtual reality glasses of the Oculus Quest II model,
this first component exploits the potential offered by
virtual reality, because it allows us to visualize an
environment free of any distraction, the experience of
using these glasses is the abstraction and thus a
greater concentration when viewing your screen,
another advantage of the glasses is connectivity
through a wireless connection thanks to its WIFI
communication protocol, with which the glasses work
with a computer connected to a network, where you
can share resources. Figure 3 shows a graph of the
Oculus Quest II lenses where the connectivity with a
computer, the programming language and the user
and coding programming interfaces can be seen, the
power of the lenses provides all these features at the
time of being able to use it as an aid in the learning
process of programming languages.
Figure 3: Example of programming.
Another of the necessary components to be able
to exploit the VR glasses, is the INMERSED
application, with this tool we can interconnect the
glasses with the computer or workstation where the
application is installed; in order to exploit the
connectivity to the maximum, it is necessary that the
computer and the glasses are connected to the same
wireless network, so that what can be displayed on the
computer can be replicated on the glasses, as well as
to exploit all the benefits and profiles provided by the
application. One of the advantages is the option to
create virtual peripherals inside the glasses, as is the
case of monitors, keyboards and other peripherals, the
use of multiple monitors help in the learning process
because you can customize the different applications
and to visualize them inside the glasses, in Figure 4,
you can see the connectivity and interaction of the
INMERSED application and the different devices;
the application also provides an interconnection with
mobile devices to be able to share the content,
through which you can see on the glasses what is
displayed on the computer and on the mobile devices
you can see what is displayed on the glasses, so you
can experience the virtual environment on mobile
devices: to be able to exploit this advantage, it is
necessary that the mobile devices are also connected
to the same wireless network, as well as being able to
run the client of the INMERSED application to share
resources.
Figure 4: Methodology configuration diagram.
3 RESULTS
The results of the application of the methodology is
related to the exploitation of the method and the
configuration of the devices, in Figure 5, the final
configuration of the INMERSED application with the
glasses and the computer can be seen, in it you can
see what is observed in the virtual reality glasses, the
same thing that is projected on the glasses is projected
on mobile devices so the control can be decentralized.
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
594

An example of exploitation of the methodology
can be seen in a programming class, where there is
only 1 lens that the teacher can use to teach their
classes, the LabView program is installed on the
computer, so the manipulation of the computer is
through the glasses, also students can connect to the
network and thus can visualize what the teacher is
visualizing on the glasses, students can also
experience the experience if the cell phones are
connected to virtual reality glasses that use with
display element to mobile devices.
Figure 5: Methodology Set-Up.
The results we present are related to demonstrate
the experience of programming using the
programming language G, through the LabView
development environment, it is important to note that
in order to fully exploit the benefits provided by the
Oculus Quest II glasses and the INMERSED
application, it is necessary that they are configured on
the same network and on all devices connected to the
application installed on the computer.
Having configured the components, the
experience and the way to exploit the resources
provided by the methodology are described, being
complicated the capture of what is being visualized in
the glasses, the capture of the evidence was done
through one of the installed mobile devices.
Figure 6: Presentation of the user environment.
Figure 6, shows the environment for the creation
of the user interface, it is important to indicate that it
can be viewed on a single virtual monitor, also you
can see that you are immersed in a beach background
where it can give us a sense of tranquility, what you
see is what is displayed in the virtual reality glasses.
Figure 7: Presentation of user environment and code.
Figure 7 shows the user environment as well as
the code environment, each on a virtual monitor,
where you can see what is added in the user interface
and how it is coded in the coding environment, also
both monitors are configured in a sea background.
Figure 8: Configuration of virtual peripherals.
In Figure 8, we present how to add virtual
peripherals, where we add a virtual keyboard, with
which we can interact in this way, we have a physical
keyboard on the computer as a virtual keyboard inside
the glasses, with this configuration we increase the
interactivity in the management of the technologies
that virtual reality provides us, not only to be able to
visualize, but also to interact, with which we are
reaching a new milestone in the use and exploitation
of virtual reality technologies, where we not only use
it to visualize, but also to interact and to be able to
program in a virtual environment.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The conclusions we reached at the end of the
presentation and the description of the methodology,
is to increase the interactivity that Virtual Reality
allows us, thanks to it we can program in a virtual
environment, in the example we present, we use the
LabView development environment, being able to
Methodology for Learning Programming Languages Through the Use of Virtual Reality Resources
595

scale to the use of other programming languages such
as Python, R and others, always with the same logic,
the use of multiple monitors and the use of virtual
peripherals.
Thanks to the INMERSED application, we can
have access to the computer, we only need that the
glasses are connected to the same network as the
computer, so we can navigate through the computer
applications and be able to observe them on the
glasses, with this application we can perform multiple
tasks on the glasses, without the need to install the
programs on the glasses, so you can also expand the
range of visualization to various mobile devices, for
this these devices must be connected to the same
network.
Finally we can indicate that the methodology is
applicable and scalable to other educational
processes, in the particular case of engineering
careers, programming courses are the most difficult
to learn, so it is necessary to resort to new techniques
and methods to ensure the understanding and analysis
of programming techniques, One of them is the use of
Virtual Reality, the method can be improved using
other digital media that can be presented when using
the LabView language, as is the case of presentation
of manuals, video tutorials, among other mechanisms,
all of them can be displayed on a virtual monitor,
which improves interactivity and the level of
abstraction of students.
We can indicate as a way to discuss the results
obtained, with the works considered in the
introduction, that although most of the works describe
uses and applications of simulation models for
medical practice and industrial processes mainly,
which help to improve skills and improve practice;
our results are similar in the processes of learning the
LabView programming language, to improve the
level of abstraction and perception of the
programming logic and help to understand and
differentiate the use of the various virtual
instruments, which is one of the main features.
REFERENCES
Auccahuasi, W., Ovalle, C., Bernardo, G., Felippe, M.,
Pacheco, O., Lovera, D., ... & Ruiz, M. (2021a).
Connectivity pattern analysis for virtual simulation
design, based on high-performance game analysis.
Auccahuasia, W., Ovalle, C., Ayvar, Z., Aybar, J., Quispe,
R., Lovera, D., ... & Ruiz, M. (2021b). Methodology for
the optimization of resources, applied to virtual reality,
through the use of WIFI network 6.
Lee, SW-Y., Hsu, Y.-T. y Cheng, K.-H. (2022). ¿Los
estudiantes curiosos aprenden más ciencia en un
entorno inmersivo de realidad virtual? Explorando el
impacto de los organizadores anticipados y la
curiosidad. Informática y Educación, 104456.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2022.104456
Srimadhaven, T., Chris Junni, A. V., Harshith, N., Jessenth
Ebenezer, S., Shabari Girish, S., & Priyaadharshini, M.
(2020). Learning analytics: Virtual reality for
programming course in higher education. In Procedia
Computer Science (Vol. 172, pp. 433–437). Elsevier
B.V. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.05.095
Saab, M. M., Hegarty, J., Murphy, D., & Landers, M.
(2021). Incorporating virtual reality in nurse education:
A qualitative study of nursing students’
perspectives. Nurse Education Today, 105.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2021.105045
Kumar, V. V., Carberry, D., Beenfeldt, C., Andersson, M.
P., Mansouri, S. S., & Gallucci, F. (2021). Virtual
reality in chemical and biochemical engineering
education and training. Education for Chemical
Engineers, 36, 143–153.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ece.2021.05.002
Yu, M., & Mann, J. S. (2021). Development of Virtual
Reality Simulation Program for High-risk Neonatal
Infection Control Education. Clinical Simulation in
Nursing, 50, 19–26.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecns.2020.10.006
Barrett, A. J., Pack, A., & Quaid, E. D. (2021).
Understanding learners’ acceptance of high-immersion
virtual reality systems: Insights from confirmatory and
exploratory PLS-SEM analyses. Computers and
Education, 169.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2021.104214
Araiza-Alba, P., Keane, T., Matthews, B., Simpson, K.,
Strugnell, G., Chen, W. S., & Kaufman, J. (2021). The
potential of 360-degree virtual reality videos to teach
water-safety skills to children. Computers and
Education, 163.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2020.104096
Fealy, S., Jones, D., Hutton, A., Graham, K., McNeill, L.,
Sweet, L., & Hazelton, M. (2019, August 1). The
integration of immersive virtual reality in tertiary
nursing and midwifery education: A scoping
review. Nurse Education Today. Churchill Livingstone.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2019.05.002
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
596
