
Method to Improve Recovery Through Rehabilitation Techniques
Using Virtual Reality with Motor Imaging Techniques
Christian Ovalle
1a
, Sandra Meza
2b
, Wilver Auccahuasi
3c
, Oscar Linares
4d
, Kitty Urbano
5e
,
Gabriel Aiquipa
6f
, Yoni Nicolas-Rojas
7g
, Aly Auccahuasi
8h
, Tamara Pando-Ezcurra
9i
and Karin Rojas
10 j
1
Universidad Tecnológica del Perú, Lima, Peru
2
Universidad ESAN, Lima, Peru
3
Universidad Privada del Norte, Lima, Peru
4
Universidad Continental, Huancayo, Peru
5
Universidad Científica del Sur, Lima, Peru
6
Universidad Tecnológica de los Andes, Apurimac, Peru
7
Escuela superior la Pontificia, Ayacucho, Peru
8
Universidad de Ingeniería y Tecnología, Lima, Peru
9
Universidad Privada Peruano Alemana, Lima, Peru
10
Universidad César Vallejo, Lima, Peru
kurbano@cientifica.edu.pe, gaiquipa@utea.edu.pe, yoninicolas@elp.edu.pe, aly.auccahuasi@utec.edu.pe,
tamara.pando@upal.edu.pe, krojas@ucv.edu.pe
Keywords: Virtual Reality, Rehabilitation, Imagery, Motor Activity, Image, Video.
Abstract: The new technological tools provided by information and communication technologies are changing the
concepts and ways to perform certain actions, in the field of health, it is being applied to a great extent, we
can note that one of them is the Virtual Reality technology, in its different equipment and applications, one
of the related areas where you can take advantage of the immersion and abstraction, is related to
rehabilitation procedures, In this case we can indicate if you have any immobilization or absence of these
members, the rehabilitation processes of these situations, is highly aggressive in order to walk again in a
coordinated manner or a more serious case is when resorting to the use of a prosthesis, we must indicate that
when we walk, there is a harmony in the movement of the arms and legs, any absence or immobilization of
these, will affect the movement. In the present work we present a method applying Virtual Reality, which
uses the techniques of motor imagery, to help in the recovery through virtual therapies, the proposed method
uses three main elements, such as Virtual Reality glasses, which will be used by the patient and where he
will visualize the movements and images of the feet, arms, legs, among other images or videos to strengthen
self-confidence in the recovery process, Then we need a computer, which will be responsible for issuing and
controlling the sequence of images, a third element that is responsible for making possible the connectivity
and the ability to share images and videos, is the Virtual Desktop application, through this tool you can
share the computer screen to visualize the virtual reality glasses, we must consider that the equipment must
be connected to the same network.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5559-5684
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4650-1340
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8820-4013
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7952-9518
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2009-000X
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3755-7393
g
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6493-6084
h
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5069-0415
i
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0301-3440
j
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6867-0778
Ovalle, C., Meza, S., Auccahuasi, W., Linares, O., Urbano, K., Aiquipa, G., Nicolas-Rojas, Y., Auccahuasi, A., Pando-Ezcurra, T. and Rojas, K.
Method to Improve Recovery Through Rehabilitation Techniques Using Virtual Reality with Motor Imaging Techniques.
DOI: 10.5220/0011962700003612
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing (ISAIC 2022), pages 603-610
ISBN: 978-989-758-622-4; ISSN: 2975-9463
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
603

1 INTRODUCTION
Performing a literature review, we found works
related to the application of technological tools in
favor of patients, where it is evidenced that
presenting related images as the way of walking,
patients begin the retraining process (Auccahuasi, et
al. 2019). In rehabilitation procedures we can
evidence the level of behavior of patients, managing
to measure the level of concentration when they are
performing rehabilitation exercises, these
measurements are made thanks to techniques related
to the use of brain-computer interface (Auccahuasi,
et al. 2019). The use of technology is used for the
benefit of evaluating the gait aspect, seen in this way,
we find that gait is one of the main mechanisms of
the human being, so there is much concern that
people who have been affected, manage to recover
the ability to walk, for this opportunity through
inertial navigation systems can evaluate the behavior
of the center of gravity (Auccahuasi, et al. 2021).
We found works referred to robot-assisted
manual training applied to people who have suffered
stroke, with which you can perform practical
activities, with the use of a VR environment, so it
has been used to analyze about the robotic device on
the final effects of hand Amadeo used by improving
cognitive performance which is compared with the
amount of treatment that focuses on the hand which
is applied to 48 people with an average age 54.3 ±
10.5 years and the amount of women was 62, 5%
who have suffered an ischemic or hemorrhagic
stroke, which have been separated into 2 groups
called experimental group (GE) which were applied
the Amadeo Robotic Training and the control group
(CG) were subjected to occupational therapy
involving the upper limb, maintaining an evaluation
at the beginning and end of rehabilitation with a
neuropsychological battery, and motor function
tests, obtaining the results that in GE has been
obtained improvements in cognitive domains
including attention skills and executive functions,
hand motor, however robotic rehabilitation based on
VR showed improvements in both motor function in
the paretic arm and global cognitive skills in
cerebrovascular patients (Torrisi, et al. 2021).
We found works referred to VR technology used
in rehabilitation applied to people who have suffered
strokes, in order to analyze the effectiveness of VR
training without the use of glasses to improve motor
functions of the upper extremities applied to patients
who have suffered strokes for which 12 patients with
stroke have been considered for the process for 3
weeks, For this purpose, examinations were taken at
the beginning and end of the process in which the
evaluation was performed twice, including the Fugl-
Meyer upper extremity scale (FMS-UE), the
measurement of transcranial magnetic stimulation
(TMS) and the evaluation of movement from which
the results were obtained, which showed no
differences between the groups in the initial
evaluation, where after the intervention the FMS-UE
score showed superior improvement for the VR
group than for the control group, the TMS had a
significant difference on the latency of the cortex, on
motor conduction after the intervention, no
differences were shown on the amplitude of the
motor event potential (Xie, et al. 2021).
We found works referred to IT applied in patient
care and rehabilitation. We found works referring to
IT applied to patient care and rehabilitation, so a
review of the literature on games based on VR used
for motor rehabilitation was carried out. The
objective is to propose a methodology used to
improve the design and reporting process of clinical
trials using the search for publications on this type of
experiments, which were carried out in databases
such as Science and Medline (PubMed), which have
been evaluated. The publications about this type of
experiments were searched in databases such as
Science and Medline (PubMed), which have been
evaluated with the Downs and Black checklist, and
the following results were obtained: 86 studies were
identified in which the main tool used was the
Kinect, the EyeToy system and GestureTek IREX
based on VR games for rehabilitation which have
been tested in patients with cerebral palsy and stroke
focusing on posture control, limb exercises (Ayed, et
al. 2019).
We found works referred to multiple sclerosis
(MS) and diseases of the central nervous system
which affect motor, sensory, visual and cognitive
activities for which a review is made about the
virtual reality tools that can be used to perform
cognitive and motor rehabilitation for which an
analysis of studies between 2010 and 2017 searched
in PubMed databases is used, Scopus, Cochrane and
Web of Sciences with keywords such as "VR
rehabilitation" and "MS", where the results obtained
after the use of VR for rehabilitation can be seen an
improvement in motor and cognitive function, which
confirms the positive results about the improvement
of the outcomes of patients with MS (Maggio, et al.
2019).
We found works referred to advanced robotic
technologies (RT), virtual reality (VR) and
transcranial direct stimulation (TDC), in order to
make a combination of devices and apply them to
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
604

the recovery of hand-arm function based on the
hypothesis of functional reorganization of the
undamaged motor system, while early and intensive
motor treatment according to the patient's potential,
thus demonstrating that the application of new
technologies for rehabilitation is giving more
effective results in patients with cognitive deficits,
Therefore, the aim is to declare the application
criteria, limits and application procedures for which
a search and registration of post-stroke patients will
be used to undergo conventional rehabilitation and
rehabilitation with RT and TDC to then compare
them, which will be supported with virtual reality
(VR) methodology in the treatment of the paretic
upper limb after a stroke, obtaining the results of
superiority of VR methods compared to the classical
methodology (Pistarini & Maggioni, 2019).
We found works referred about VR applied in
the restoration of motor function in stroke patients
where the analysis was used in 45 patients with
acute stroke diagnosis, which were randomly
divided into 2 groups where the first group received
standard rehabilitation and neuro-trainer classes
while the other group only received standard
rehabilitation classes. Both groups were evaluated
according to Berg's balance test where the results
about the neurotransmitter showed an efficacy on the
15th to 19th day after the stroke, where re-sults can
be found superior to the beginning of training with a
neurotransmitter within days 5 to 9 after stroke (p =
0.022), with a degree of recovery about the
neurotransmitter (p = 0.001), reached within 3 to 5
sessions (Kate, et al. 2019).
We found works referred about VR exercises
implemented in motor rehabilitation on the lower
extremities applied in a Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
rehabilitation center where 12 patients with SCI and
10 control patients have been used, for which heart
rate and electromyographic activity of both legs
have been recorded, obtaining results about the
interactivity considered as the main interaction of
the participants, where it is considered that the
feedback is of vital importance for the improvement
of the patient assisted by robot (Steadman, et al.
2015).
We can indicate that within the rehabilitation
techniques, we find those related to the exercises
that are performed with a health personnel, this is a
traditional mechanism, one of the disadvantages is
the need to be able to travel to the health center, to
perform rehabilitation exercises, depending on the
resources available to patients, you can have access
to a health personnel to perform rehabilitation
exercises in a personalized way. We also have the
mechanisms where technology is applied, as is the
case of being able to use automated devices to
perform rehabilitation exercises, in this sense not all
patients can count on them, as well as health centers
do not have the necessary resources to be able to
acquire this equipment.
In retraining related to walking, involves
relearning how the movements of the arms and legs
are performed when the movement is being
performed, this technique uses videos and images of
the affected limbs to get to know them again, as well
as how they interact when walking, this technique is
known as motor imagery, which can be implemented
with the visualization of photographs or videos.
Having made a description of the state of the art
regarding the use of techniques related to the use of
technology in the health sector, as is the case of
virtual reality with emphasis on rehabilitation issues,
this paper develops a method that uses virtual reality
techniques to develop the technique of motor
imagery, organizing images and videos of the
components of the arms and legs and their
interaction in walking, through the projection of
these in the virtual reality glasses, with which you
can get patients to increase the level of concentration
and thus to recover their skills in the shortest time.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The materials and methods that we are presenting
have an important particularity, which is their
dynamics, based on being able to create different
scenarios according to the particularity and
preference of the patients, we can indicate that it is a
modular method organized with the intention of
being able to be replicated, for which we describe
the necessary components as well as their respective
integration plan and we end with previous results:
Figure 1: Description of the methodology.
Method to Improve Recovery Through Rehabilitation Techniques Using Virtual Reality with Motor Imaging Techniques
605
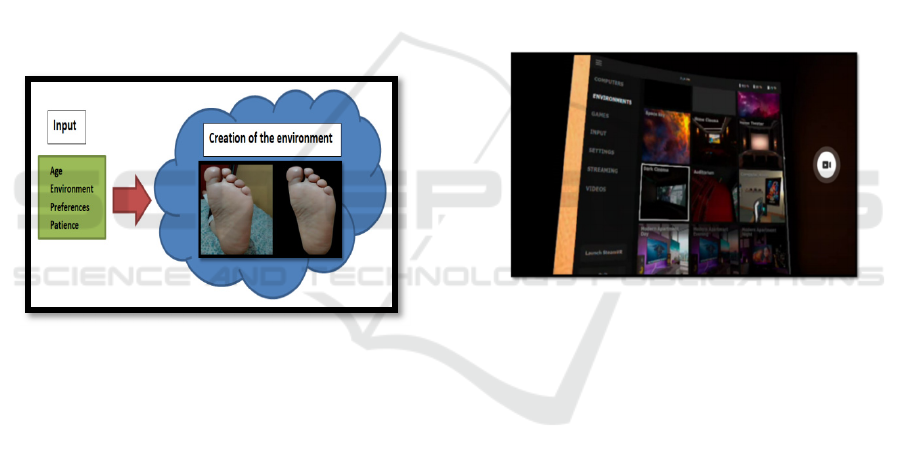
In Figure 1, we present the description of the
methods to be developed, starting with the definition
of the inputs, followed by the integration of
techniques and ending with the previous results, then
we develop the details:
2.1 Description of the Inputs
The inputs that we describe in the development of
the methodology, is characterized by the description
of the needs, we can indicate that in a real situation
we have two possible situations, the first in an
environment of a rehabilitation center, where we
have many patients, of different types of ailments
and rehabilitation therapies, as well as different ages
and a second environment can indicate that we are in
performing rehabilitation therapies performed in the
homes of patients, where we try to reinforce the
exercises performed in rehabilitation centers, or also
managing to have a particular staff to be able to
perform rehabilitation exercises.
Figure 2: Description of the inputs and creation of the
environment.
Figure 2 shows the approach of the inputs, which
result in the creation of the environment where the
sequence of images is represented, as well as the
representation of the background, this is one of the
characteristics of using virtual reality glasses,
because it not only presents the sequence of images,
but also a view of the depth, allowing the patient to
isolate himself from the physical place where he is
and can only visualize the scenarios provided by the
glasses, then we present what each of the inputs
consists of:
• The years, as the environment where it will
be presented will be implemented, to have a
better reception by the patient, the
background of the environment should be
developed according to themes related to
the patient's age, we must indicate that the
Virtual Desktop tool, allows us to select
different topics to be configured as
background of the scenario.
• In the environment, it is recommended that
the images and the environment are related
to the patient's activities, for example
sports, educational, work environments,
these help because they motivate the patient
in the recovery process.
• Preference is a very important aspect in the
process of personalizing the environment, it
would be ideal to know the preferences of
patients so we get a greater commitment of
the patient which would lead us to have
better results.
• Patience, one of the factors to take into
account and is related to age, this aspect is
very important to time the sequence in
which the images appear giving the
sensation that the patient is watching a
video.
Figure 3: Virtual Desktop application configuration mode.
In Figure 3, we present the screen to configure the
environment where the images corresponding to the
motor imagery technique are presented, where the
recommendations of the 4 described inputs are
applied, managing to select the environment
according to the tastes and preferences of the
patients, to achieve a better response from the
patients.
2.2 Integration Techniques
The integration that must be considered is related to
the necessary equipment to implement the model, as
hardware a computer is needed that has the task of
being able to present the sequence of images and to
control the sequence of images, it is necessary and
virtual reality device, such as glasses, for the
demonstration we use a virtual reality glasses model
Oculus Gest II, The function of the glasses is to be
able to replicate what is observed on the computer
screen, the total control is in the computer, an
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
606

additional mobile device can be considered, which
can be a cell phone, where you can replicate what is
displayed on the glasses, it also fulfills the function
of quality control to verify the operation of the
glasses.
As a software component, the Virtual Desktop
application is required, which provides connectivity
tools, with which we can share computer resources
and virtual reality glasses, we must indicate that it is
necessary that all devices are connected to the same
network, with which the application works as an
integrating agent, all devices must be registered with
the application that is installed on the computer. One
of the functionalities that this configuration allows
us, is to be able to work in a multiple configuration,
managing to configure several virtual reality glasses
connected to the same computer, with which the
therapy can be performed to several patients.
Figure 4: Description of the integration mode.
Figure 4 shows the integration mode between the
different components through the Virtual Desktop
application, the integration requirement is to be
connected to the same network and to be able to
register in the application installed in the computer.
Figure 5: Device connectivity.
Figure 5 shows the configuration in the Virtual
Desktop application, in the virtual reality glasses, the
virtual desktop client must be installed, when the
application is opened, it searches for the server that
can be connected in the same network, in our case,
we are connected in a laptop, so the application finds
and connects us to share resources.
2.3 Previus Results
For the case of the previous results, we present the
results that are observed in the virtual reality glasses,
as well as in the cellular equipment, we must
consider that what we observe in the cellular
equipment is the same image that is observed in the
glasses, so we can recommend as a quality control
mechanism, to only place the glasses on the patient
without any other action that may cause discomfort
to patients.
Figure 6: Verification of the connection with the simulated
cellular device.
In Figure 6, we present the connection of the cellular
device, where connectivity and access to the
computer is verified, what is displayed on the
cellular device is the same as what is displayed on
the virtual reality glasses.
Method to Improve Recovery Through Rehabilitation Techniques Using Virtual Reality with Motor Imaging Techniques
607
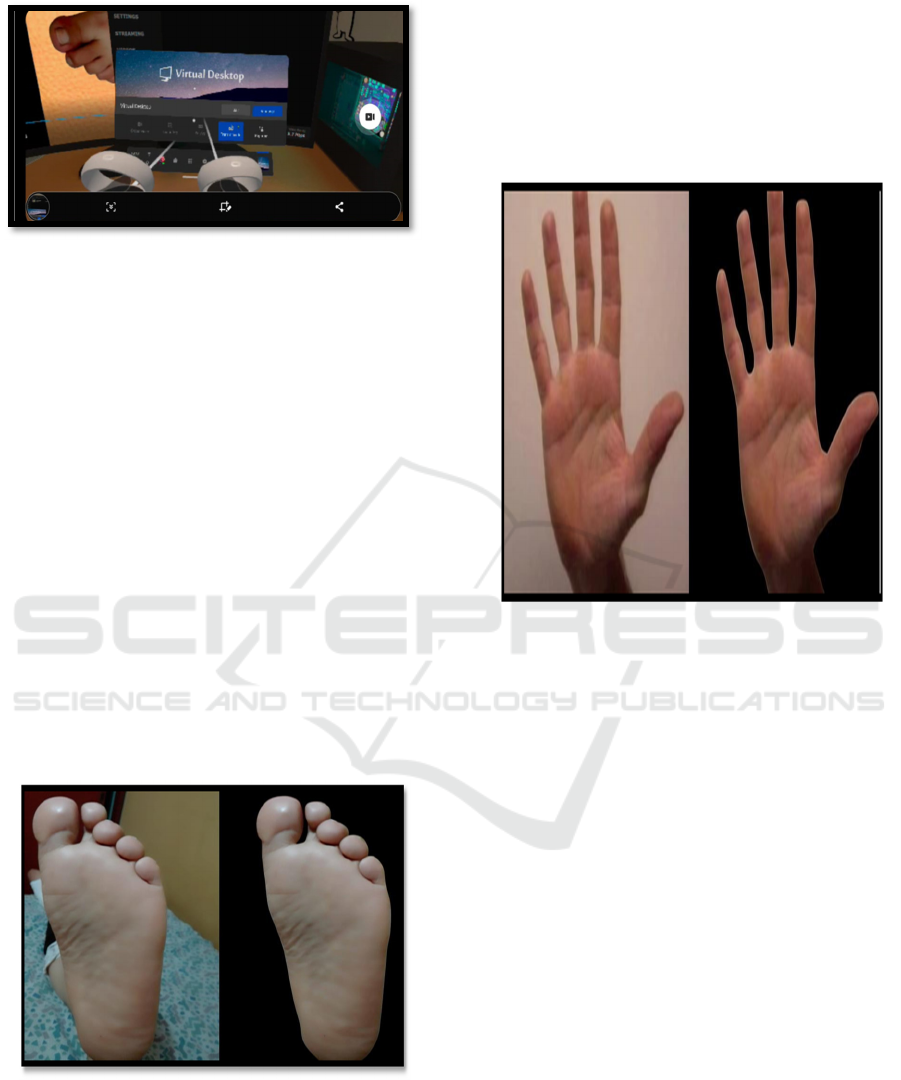
Figure 7: Virtual reality lens configuration.
Figure 7 shows the configuration of the Oculus Gest
II lenses, where the connection with the Virtual
Desktop application is shown, by means of which it
is possible to connect to the equipment as well as to
select the environment. The mode of use is through
the controls of the lenses, in the case of patient use,
the configuration is done before placing the lenses
on the patients.
3 RESULTS
The results that we present are related to the
implementation of the method and the results that
we obtain in each of the processes, the fundamental
idea of the publication is to explain how the method
can be implemented, as well as the results in each of
the stages. The results will explain the resulting
images in each process, similarly when replicated
the images can be used as a reference.
Figure 8: Generation of lower limb imaging sequence.
In Figure 8, we present the image generation
process, in this case we generate the images
corresponding to the feet, first we register the image
of the foot and then we eliminate the outline of the
foot, leaving the foot with a black background.
One of the recommended ways is to be able to
create your own sequence of images, the
recommended method is to be able to take pictures
of the limbs as appropriate, for a better reception of
patients, you can take images of the patient himself,
this way you have a better reception of the patient to
the therapy.
Figure 9: Generation of upper limb imaging sequence.
In Figure 9, we present, analogously to Figure 8,
how we generate the images of the hand, having the
hand with a commonly used background, and the
image of the hand with a black background.
Just as we made the collection of images of the
lower limbs, we present the sequence of images of
the upper limbs, for which we also recommend that
the image is of the same patient, you can take
several images as well as to rotate them in both
cases, to be able to reproduce them in sequential
form, so we can have more images.
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
608

Figure 10: Generation of image sequence.
The images shown in Figure 10 correspond to the
sequence of images generated, starting from the
same image we can add backgrounds, rotate them,
so that we can have a greater number of images.
Figure 11: Performance of motor imagery exercises.
In Figure 11, we present an example of the
application of the method, in which the patient is a
teenager who is performing the exercises, we can
observe the application of the method, by connecting
the computer, the virtual reality glasses and the
mobile device, the same image that is observed on
the computer is observed on the glasses and on the
cellular equipment.
Figure 12: Final visualization of the exercise.
In Figure 12, we present the final work mode, where
the recommendations of the method were applied,
the patient indicated is an adolescent who likes
movies, so the virtual environment was configured
to simulate a movie theater, the patient visualizes the
sequence of images as if he were in a movie theater,
improving the patient's perception, which would
help in their collaboration and thus improve
rehabilitation therapies.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The conclusions we reached at the end of the
research, is related to the implementation of the
method, as well as the benefits of the application, we
indicate from the perspective of the implementation
method, that the method is applicable because you
can perform exercises using the technique of remote
imaging, it is scalable, because it can be scaled
towards improvements in the images and replicable
because we present the procedures to implement the
method. The method can be applied in rehabilitation
centers using different equipment that provide a
virtual reality scenario, all of them connecting to the
same computer, and replicating it in all devices.
The benefits of using the motor imagery
techniques are related to the benefit of the patients
by reducing the recovery time, thus improving self-
confidence and eliminating all kinds of anxiety that
Method to Improve Recovery Through Rehabilitation Techniques Using Virtual Reality with Motor Imaging Techniques
609

is typical of patients, who try to recover as soon as
possible. Being able to control anxiety is very
important, increasing the motivation of the patients
themselves and generating confidence in their
recovery, using the method concentrating the patient
increases learning and performance at the time of
evaluating the patient's recovery.
The application of the method is related to
different types of patients, in which case they require
certain exercises to recover and perform daily
activities, can be applied to all types of patients,
adults, children, adolescents, workers, athletes,
although the technique of remote imagery helps in
recovery, to be complemented with the techniques
and advantages that provide us with virtual reality
helps to benefit the patient, using the proposed
method helps in the strategy for the recovery of the
patient.
Comparing traditional techniques with the
present proposal, they are related to the use and
exploitation of the different tools and techniques
provided by virtual reality, applied in the process of
learning how the arms and legs interact when
walking, known as motor imagery, being able to
provide patients with these images and videos in a
virtual environment, improve the perception and
attitude of patients, helping their recovery for the
benefit of recovering the mobility of patients, after
being immobilized by various factors.
REFERENCES
Wilver Auccahuasi, Monica Diaz, Juana Sandivar, Edward
Flores, Fernando Sernaque, Manuel Bejar, Ingrid
Ginocchio, and Nabilt Moggiano. 2019. Design of a
mechanism based on virtual reality to improve the
ability of graduated motor imagery, using the brain
computer interface. In Proceedings of the 5th
International Conference on Communication and
Information Processing (ICCIP '19). Association for
Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 119–
123. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1145/3369985.3370015
Auccahuasi, W., Flores, E., Sernaqué, F., Sandivar, J.,
Castro, P., Gutarra, F. y Moggiano, N. (2019,
noviembre). Técnica para la comparación de niveles
de concentración y meditación en la realización de
ejercicios de rehabilitación en bicicleta, utilizando
técnicas de realidad virtual e interfaz cerebro-
computadora. E-Health and Bioengineering
Conference (EHB) (págs. 1-4). IEEE.
Auccahuasi, W., Díaz, M., Sernaque, F., Flores, E., Aybar,
J. y Oré, E. (2021). Sistema de bajo coste en el análisis
de la recuperación de la movilidad mediante técnicas
de navegación inercial y realidad virtual. En
Paradigmas de atención médica en el ecosistema de
Internet de las cosas (págs. 271-292). Prensa
académica.
Torrisi, M., Maggio, M. G., De Cola, M. C., Zichittella,
C., Carmela, C., Porcari, B., … Calabrò, R. S. (2021).
Beyond motor recovery after stroke: The role of hand
robotic rehabilitation plus virtual reality in improving
cognitive function. Journal of Clinical
Neuroscience, 92, 11–16.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2021.07.053
Xie, H., Zhang, H., Liang, H., Fan, H., Zhou, J., Ambrose
Lo, W. L., & Li, L. (2021). A novel glasses-free
virtual reality rehabilitation system on improving
upper limb motor function among patients with stroke:
A feasibility pilot study. Medicine in Novel
Technology and Devices, 11, 100069.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medntd.2021.100069
Ayed, I., Ghazel, A., Jaume-i-Capó, A., Moyà-Alcover,
G., Varona, J., & Martínez-Bueso, P. (2019,
November 1). Vision-based serious games and virtual
reality systems for motor rehabilitation: A review
geared toward a research methodology. International
Journal of Medical Informatics. Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2019.06.016
Maggio, M. G., Russo, M., Cuzzola, M. F., Destro, M., La
Rosa, G., Molonia, F., … Calabrò, R. S. (2019).
Virtual reality in multiple sclerosis rehabilitation: A
review on cognitive and motor outcomes. Journal of
Clinical Neuroscience, 65, 106–111.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2019.03.017
Pistarini, C., & Maggioni, G. (2019). Virtual reality and
motor rehabilitation of the upper limb after CNS
damage. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 405,
39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2019.10.105
Kate, O. K. O., Zakharov, A., Khivintseva, H., & Kalinin,
V. (2019). Efficiency of virtual reality application as
an acceleration of motor rehabilitation in patients in
the acute period of stroke. Journal of the Neurological
Sciences, 405, 44.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2019.10.1634
Steadman, J., Donaldson, N., Kalra, L., Jbabdi, M.,
Boissy, P., Hamel, M., … Wansuk, L. (2015).
Reliability and concurrent validity of the Microsoft
Kinect V2 for assessment of standing balance and
postural control. Archives of Physical Medicine and
Rehabilitation, 94(3), 867–8. Retrieved from
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2012.12.010
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
610
