
Component Analyse and Carcinogenic Performance Research after
Food Material Baked to Be Roasting
Liufeige Lu
Suzhou Foreign Language School, No 201 Zhuyuan Road, Suzhou New District, Suzhou, Jiangsu Province, China
Keywords:
Component Analyse, Food Material Baked, Carcinogenic Performance.
Abstract: Food cooking include the methods such as oil frying, baking, carbon baking, stewing. Among, oil frying,
baking, carbon baking and other method cooking at higher temperature and difficult to control. High
temperature cooking will caused the foods come to be roasting, many medias reported that burned in
roasting or oil fried foods easily carcinogenic. To proof and test the reliability of this conclusion and
research the true harm of this type foods, it selects the chicken, steam bun and celery as sample, baking the
samples under different temperature and time condition, the samples happened different degree burnt. It
obtained that the food happen carbonize after foods burned in roasting, the chemical structure of protein,
starch and cellulose all are changed, generated the acrylamide and conjugate aromatic ring chemical
compounds, thus generating carcinogenic performance to human body.
1 INTRODUCTION
More and more higher opportunity catch cancer in
the modern society, according to the report from
national tumour register center in 2013, the newly
happened cancer illness case exceed 3,000,000 per
one year (Liu, 2021). Much reason of cancer, many
medias reported that, oil frying, baking, carbon
baking and other methods cooked foods easily
caused cancer. The report said that baked meats
contain strong carcinogenic performance, the meat
and fish burned in roasting contain benzopyrene, the
average catch gastric caner ratio of the crowds who
frequently eat the baked meat type foods rising
twenty times (Ye, 2016). Additionally, for the plant
food like coffee and others, the content of
benzopyrene after burned in roasting also will has
extremely rising (Yin, 1980).
Our daily foods have meat, staple food type and
vegetable type. (1) The main component of meats
are protein, protein is one type biology big molecule,
formed by 20 types different natural amino acids.
The structure of natural amino acid mainly contain
the elements such as carbon, nitrogen, oxidize,
hydrogen, etc, additionally, R-perssad of some
amino acid contain the sulphur element. The amino
acid structure of meats been damaged after baked,
the protein happen property change, and caused
possible carcinogenic. (2) The food mainly include
wheat and rice, the main component is starch. The
form of starch main are three elements carbon,
oxygen and hydrogen. The starch burned in roasting
will generate strong carcinogenic matters, the
content of carcinogenic matters will higher than
meat type and vegetable, long time eating will
caused it amass in body and carcinogenic (Yiqi W,
2021). (3) The main components of most vegetables
are cellulose, it contain the elements such as carbon,
nitrogen, oxidize, hydrogen, etc. Because fewer
carbonhydrate and fat content, so the burned
vegetable will generate polycycline carcinogenic
matters (Chu, 2021).
Based on various reports of the medias, burned
food has carcinogenic performance, but still has
many report existing contradiction. Therefore, in this
research, it selected three foods chicken, steam bun
and celery in our test, the main components are
protein, starch, cellulose and other matters, baking
them under different temperature, further more adopt
infrared spectrum (FT-IR), scan electron microscope
(SEM), UV light spectrum (UV-Vis), fluorescence
spectrum and other method to to determine and
characterize the baked foods components. Finally
researched the carcinogenic performance of baked
foods through cell toxicity test.
70
Lu, L.
Component Analyse and Carcinogenic Performance Research after Food Material Baked to Be Roasting.
DOI: 10.5220/0012001900003625
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Food Science and Biotechnology (FSB 2022), pages 70-75
ISBN: 978-989-758-638-5
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

2 METHODOLOGY
2.1 Materials
The chicken, steam bun and celery all are purchased
from Suzhou HEMAXIANSHENG supermarket.
Purchased grow liquid, trypsase, Diphenyl tetrazole
bromide and glycocoll buffer liquid from Sigma
company, purchased dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)
from J&K scientific company.
2.2 Sample Preparation
Use knife cut the chicken, steam bun and celery into
small cube with size 1cm×1cm×1cm, use oven
(ACA TM33HT) baking them under 150℃ and
200℃ respectively, the baking time are 1 hour, 2
hours and 3 hours respectively, pick out the samples
from the oven after baked and process natural
cooling, prepare for characterize use.
2.3 Characterized Methods
(1) UV-Vis ultraviolet spectrophotometer method
Grind the baked samples to be thin and small
tiny pellets, weighing 1mg and dissolved into 10mL
deionized water and process ultrasound, convenient
to more better dissolve the samples. The dissolved
samples filtered by 0.45μm filtering film, make the
deionized water as reference ratio, use ultraviolet
spectrophotometer measure it after filtered
(Shimazu), measured wave length are 220~400nm.
(2) Fourier alternate infrared spectrum analyse
Use PerkinElmer Fourier alternate infrared
spectrum analyse instrument to process characterize
analyse (resolution ratio 4cm-1, wave length range
are 4000-400cm-1, scan 10 times).
(3) Fluorescence spectrum analyse
Use fluorescence spectrum instrument (Hitachi
F-7500), excite wave length 300nm, launch wave
length range are 220~400nm, width of excite and
launch narrow seam is 5nm.
(4) Surface pattern analyse
Adopt scan electron microscope (SEM, Hitachi
S4800) to process the surface pattern analyse the
samples chicken, steam bun and celery after baked at
different temperature, operating voltage is 1.0kV.
2.4 Cell Toxicity Test
Use foster base thinning the waiting test sample and
prepare different concentration, added into 96 holes
plate respectively, foster 24h at 37℃, then process
three times parallel determining at live cells
quantity. Then pick out empty 96 holes plate, each
one hole added 200μL foster base and 50μL MTT,
foster 4h at 37℃. Then added 200μL DMSO in each
one hole again. Finally added 25μL glycocoll buffer
liquid in each one hole, use enzyme standard
instrument record the completely absorb value at
570nm position.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Sample Preparation
The main components of chicken, steam bun and
celery are protein, starch and cellulose, put them into
oven and baking under different temperature and
time, the sample surface happened different degree
coking. It calculated the rest mass percentage after
samples baked, shown as the Table 1.
From the table it can see that, when same baking
time and temperature, the highest dewatering
quantity of celery, able to achieve 94% after baked 3
hours at 150℃, achieve 98% after baked 3 hours at
200℃, means water content of celery is the highest,
chicken at second, achieve 78% after baked 3 hours
at 200℃, lowest water content of steam bun, only
42% after baked 3 hours at 200℃. When baking at
the same temperature, example that baked at 150℃,
dewatering quantity of celery and chicken have a
certain rising along with rising baking time, but little
dewatering quantity change of steam bun. When all
samples baked at the same time, example all are
baked 3 hours, the dewatering quantity of same
sample after baked at 200℃ will bigger than
dewatering quantity after baked at 150℃.
Table 1: The dewatering quantity of chicken, steam bun and celery after baked at 150℃ and 200℃.
Dewatering quantity of different samples
baked different time at 150℃
Dewatering quantity of different
samples baked different time at 200℃
1h 2h 3h 1h 2h 3h
Chicken 70% 74% 76% 76% 78% 78%
Celery 88% 94% 94% 90% 96% 98%
Steam bun 38% 38% 38% 40% 42% 42%
Component Analyse and Carcinogenic Performance Research after Food Material Baked to Be Roasting
71
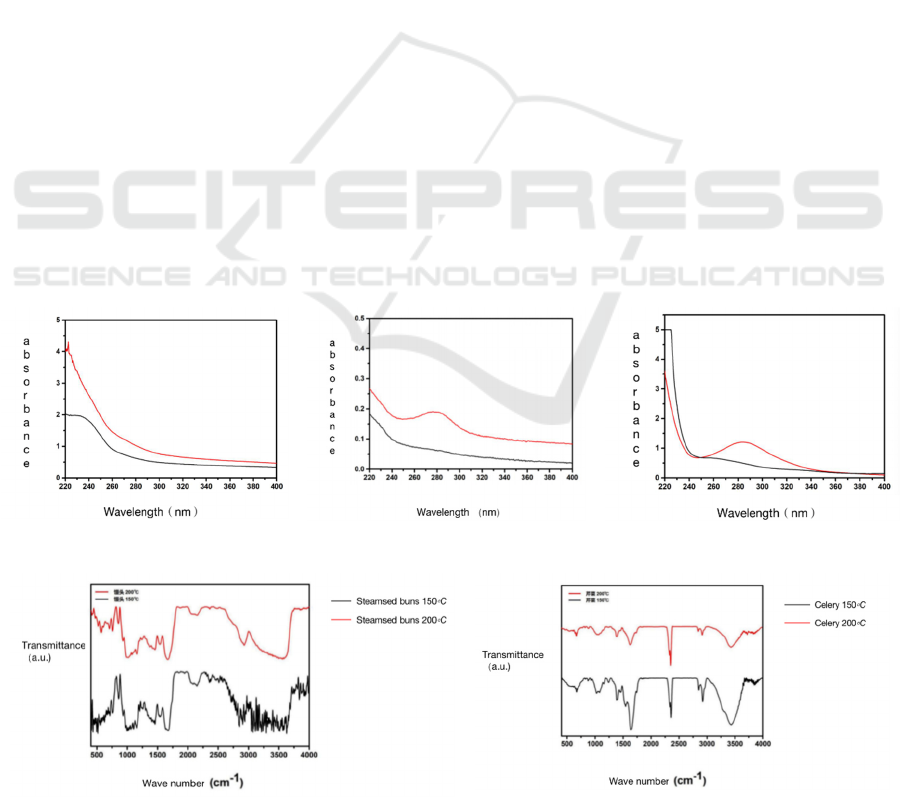
3.2 Sample Extinction Change After
UV-Vi Surface Characterize Baked
Figure 1 is the UV-Vis atlas of chicken, steam bun
and celery after baked 1h at 150℃ and 200℃
respectively. The chicken occur absorbing at
220~240nm position after baked at 150℃, occur
peak absorbing at 220nm after baked at 200℃, and
more higher peak absorbing strength, means the
generated matter quantity which able to ultraviolet
absorb increasing. The steam bun no peak absorbing
in the measured wave length range after baked, but
occur peak absorbing at 280nm position after baked
at 200℃. The celery occur one more higher peak
absorbing at 220nm after baked at150℃, but except
occur one peak absorbing at 220nm position after
baked at 200℃, also occur one absorbing at 290nm
position. The steam bun and celery all generated
absorbing at about 280nm after baked at 200℃,
generally, the absorbing at this position is the
continue conjugated alkene or aromatic chemical
compound with fewer rings. Through check the
documents, the peak absorbing of acrylamide at
280nm, means this matter maybe acrylamide (shown
as the below picture). According to report in
documents, starch and cellulose types matters easily
happen Maillard reaction under that heating under
high temperature condition and generate acrylamide
(Zhi-Jing N, 2021), through our test we found that,
the acrylamide generated by that baking steam bun
and celery at 200℃ more than baking at 150℃.
3.3 Fourier Alternate Infrared
Spectrum Characterize Result
Figure 2 is the Fourier alternate infrared spectrum of
steam bun and celery after baked 1h at 150℃ and
200℃. At the position 3500cm-1, the celery all have
one wide peak when baked 1h at 150℃ and 200℃,
this is stretch vibrating peak of oxhydryl of
glycoconjugate structure on cellulose, stretch vibrate
peak of -CH- at position 2900cm-1, stretch vibrate
peak of C=C and C=O double keys at position
1600cm-1. The function group of chemical structure
of celery baked 1h at 150℃ and 200℃ no obvious
changes. The infrared spectrum of steam bun after
baked 1h at 150℃ and 200℃ also no obvious
changes, this means the types of function group on
steam bun no changes.
3.4 Fluorescence Photometer Analyse
of Samples After Baked
Figure 3 is the fluorescence spectrum of chicken,
steam bun and celery baked 1h at 150℃ and 200℃.
The launched fluorescence light intensity about 2
times of that baked 1h at 150℃ after the chicken
baked at 200℃. At the same time, the launched
fluorescence spectrum of chicken after baked at
200℃ happen infrared shift compare to the sample
baked at 150℃, the max fluorescence strength of
samples after baked at 200℃ about 490nm, but the
max fluorescence strength of samples after baked at
Figure 1: UV-Vis atlas of chicken, steam bun and celery after baked 1h at 150℃ (black line) and 200℃ (red line).
Figure 2: The Fourier alternate infrared spectrum of steam bun and celery after baked 1h at 150℃ and 200℃.
FSB 2022 - The International Conference on Food Science and Biotechnology
72
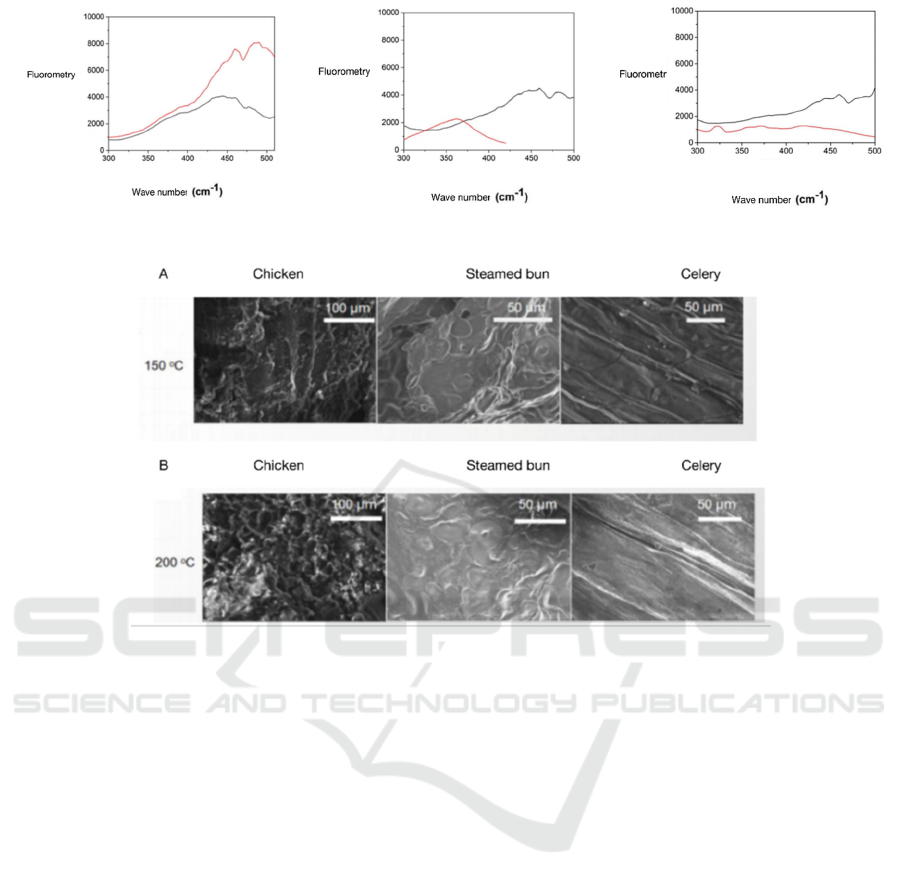
Figure 3: The fluorescence spectrum of chicken, steam bun and celery baked 1h at 150℃ (black line) and 200℃ (red line).
Figure 4: The SEM pictures of chicken, steam bun and celery after baked 1h at 150 and 200℃.
150℃ occur at about 445nm. Means that samples
baked at 200℃ maybe generate the related
conjugate structure. After the steam bun baked at
150℃ and 200℃, under the same excite light and
same sample concentration situation, the
fluorescence strength greatly reduced, the max
fluorescence strength of steam bun baked at 200℃
about half of chicken, at the same time, the longest
wave length of fluorescence launch spectrum also
only about 460nm. The fluorescence strength of
celery baked at 200℃ closes to the fluorescence
strength of steam bun baked at 200℃, and the
longest launch wave length of light spectrum also
closed, means the structure of celery and steam bun
baked at 200℃ are similar.
3.5 Scan Electron Microscope Observe
the Surface Structure After
Samples Baked
Figure 4 is the SEM pictures of chicken, steam bun
and celery after baked 1h at 150℃ and 200℃.
Firstly, the chicken samples occur holes after baked
at 150℃ and 200℃, especially that we can check
more bigger density of holes through scan electron
microscope after chicken baked at 200℃. Secondly,
sample surface of steam bun after baked looks more
flat, but still able to observe the celery internal fibre
tube structure of celery through SEM after celery
samples baked, this means that high temperature
baking still not destroy the internal fibre tube
structure of plant.
3.6 EDX Result of Chicken, Steam Bun
and Celery
Then it determined the EDX result of chicken, steam
bun and celery baked 1h at 150℃ and 200℃
respectively. To the chicken and steam bun, the
EDX spectrum chart after baked 1h at 150℃ and
200℃ all only contain elements C and O, and the
percentage of element C and O no obvious changes.
The component of celery baked at 150℃ and 200℃
has more obvious changes. Firstly, the celery self
contained more element types, except the elements
C and O, still contain the elements such as Na, Mg,
P, S, Cl, K and Ca, element types after baked almost
no changes, but percentage of each element has
Component Analyse and Carcinogenic Performance Research after Food Material Baked to Be Roasting
73
changes. Example, the percentage of elements C and
O a little reducing, the percentage of elements Na,
Cl and K a little rising, the reason maybe that high
temperature baked elements Na, Cl and K will not
form the volatilized matters and leave sample, so the
percentage has a little rising.
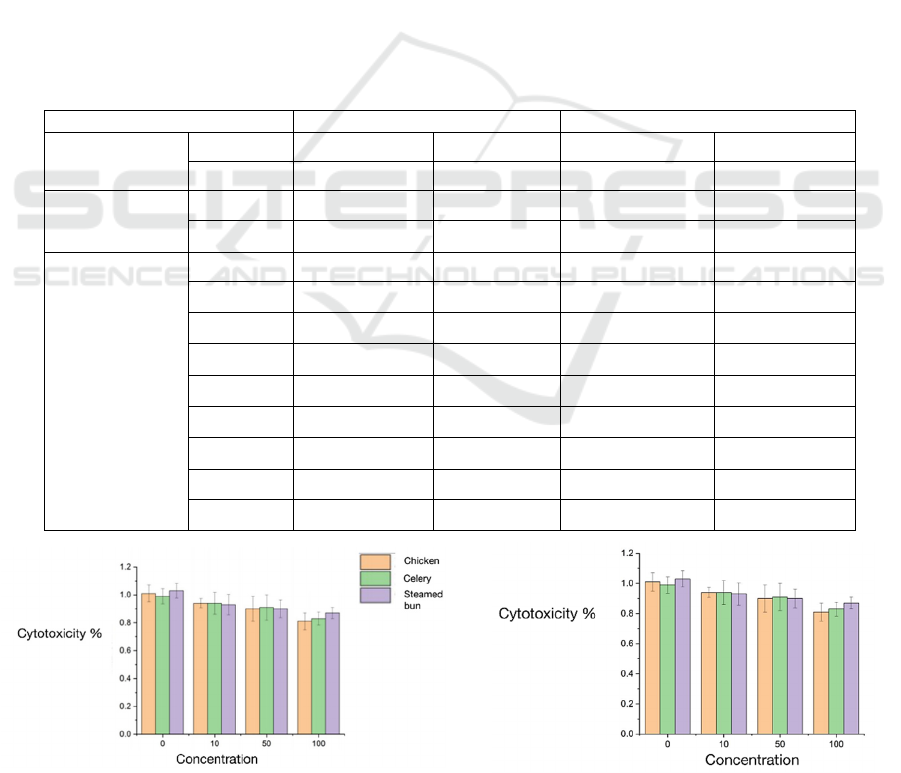
3.7 Cell Toxicity Test
Evaluating the cell toxicity of chicken, steam bun
and celery samples baked at different temperatures
and different concentration (0, 10, 50 and
100mg/mL) through MTT method. This test select
the mouse embryo fibroblast (NIH-3T3) to process
the cell toxicity test. From figure 5, we can know
that, through place the NIH-3T3 cells into sample
suspending muddy liquid and foster 2h, in
comparison, the cell toxicity of chicken, steam bun
and celery after baked at 200℃ more bigger than
samples baked at 150℃, the max cell toxicity of
samples when concentration at 100mg/mL.
4 CONCLUSION
Process characterization for the chicken, steam bun
and celery samples which baked at 150℃ and
200℃ through the test methods such as UV-Vis,
Fourier alternate infrared spectrum, fluorescence
spectrum, scan electron microscope and EDX
energy spectrum, found the foods after high
temperature baked will generate aromatic ring
chemical compound, acrylamide and other matters,
these matters all contain a certain toxicity. The cell
toxicity test result proof that, the baked foods will
generate a certain toxicity to cells under a certain
concentration. From here it can see that, no matter
meat types, starch types and vegetable types foods,
all shouldn’t be long time high temperature cooked
during the cooking process, if high temperature
cooking then will generate toxicity matters and harm
to human body.
Table 2: The EDX result of chicken, steam bun and celery baked1h at 150℃ and 200℃.
Element 150℃ 200℃
Chicken
C K 71.52 76.98 80.34 84.48
O K 28.48 23.02 19.66 15.52
Steam bun
C K 51.14 58.23 51.01 58.11
O K 48.86 41.77 48.99 41.89
Celery baked
C K 51.77 63.58 49.73 63.86
O K 31.12 28.69 25.51 24.59
NaK 02.72 01.74 05.01 03.36
MgK 00.80 00.49 00.69 00.44
P K 01.79 00.85
ClK 04.88 02.03 09.47 04.12
MoL 00.58 00.09
K K 03.59 01.35 07.35 02.90
CaK 02.89 01.06 01.66 00.64
Figure 5: The cell toxicity test of chicken, steam bun and celery samples baked 1h at 150℃ and 200℃.
FSB 2022 - The International Conference on Food Science and Biotechnology
74

REFERENCES
Chu Zhaoyin and Su Qing: the happen risk of
carbonhydrate and therioma. Shanghai medicine
science 2021, 44:286-292.
Liu Zongchao, Li Zhexuan, Zhang Yang, Zhou Tong,
Zhang Jingying, You Weicheng, Pan Kaifeng and Li
Wenqing: The globe cancer statistic report reading in
2020. Journal of Multidisciplinary Cancer
Management 2021, 7:1-14.
Ye Zhaoyu: fewer eating barbecue to prevent gastric
cancer. Food safety magazine 2016:51-52.
Yin Bing: quickly separate determine method of 3, 4-
benzopyrene in food. Oversea medicine science
(Hygiene science sub manual) 1980:53-54.
Yiqi W, Lian D, Xing Z, Yang J, Ying L, Lingling D,
Hong Y: Effect of long-term exposure to acrylamide
on endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in rat
cerebellum. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety
2021, 224.
Zhi-Jing N, Xiang L, Bing X, Long-Teng H, Kiran T,
Zhao-Jun W: Effects of sugars on the flavor and
antioxidant properties of the Maillard reaction
products of camellia seed meals. Food Chemistry: X
2021.11
Component Analyse and Carcinogenic Performance Research after Food Material Baked to Be Roasting
75
