
Combined Ferric Chloride and Phanerochaete Chrysosporium
Pretreatment on Corn Stalk Degradation
Pin Zhang
1,*
, Jie Lu
2
, Shengyong Liu
2
, Jiong Wang
2
and Shuqing Zhang
1
1
Henan University of Animal Husbandry and Economy, Zhengzhou, 450011, China
2
College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, 450002, China
Keywords:
Corn Stalk, Pretreatment, Ferric Chloride, Phanerochaete Chrysosporium.
Abstract:
In order to shorten the pretreatment cycle of microorganisms and enhance the pretreatment effect, the corn
stalk was pretreated by means of metal ions and microorganisms, the effects of combined pretreatment of
ferric chloride and white rot fungi on the degradation of 40 and 80 mesh corn stalks were studied. The content
of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin changes and the yield of reducing sugar in the fermentation broth were
analyzed. The results showed that when the concentration of ferric chloride solution was 0.4mol/L, the solid-
liquid ratio was 1/20g/ml, and the 80 mesh corn stalk material was treated at 30 min at 100~108℃, the
cellulose content increased by 56.08%, the hemicellulose decreased by 13.06% and the lignin increased by
37.80%. When ferric chloride treated corn stalks were inoculated with Phanerochaete chrysosporium, the
reducing sugar content reached 2.52 mg/ml on the twelfth day, and the yield of reducing sugar was the highest
in the fermentation broth. The study opens up a new way for high efficiency, clean and low energy
consumption of biomass pretreatment technology of crop straw.
1 INTRODUCTION
China is rich in biomass raw materials, with an annual
output of approximately 700 million tons of crop
stalk, of which corn stalk accounts for approximately
35%. This represents a tremendous resource for
energy and environmental solutions in China. The
main components of crop stalk are cellulose,
hemicellulose, and lignin. Of these, hemicellulose
can be readily degraded into monosaccharides
(mainly xylose) and a small amount of arabinose,
mannose and galactose. Cellulose accounts for
approximately 40% of the total stalk weight; it
mainly consists of glucose, and its crystal structure is
difficult to degrade. Lignin is a phenolic polymer that
bonds cellulose to hemicellulose. To convert the
cellulose in corn stalk into fermentable sugars, the
stalk must be pretreated using a specialized method.
The lignin bound to the cellulose can only be broken
after the pretreatment, thus exposing the cellulose to
facilitate the subsequent enzymatic hydrolysis and
fermentation (Lissens, 2004; Palonen, 2004).
Pretreatment with metal ions is conducted under
normal conditions and is thus environmentally
friendly (Galbe, 2002; Bailey, 1996; Saricks, 1999),
with zero vapor pressure, high thermal stability and
catalytic function, and the pretreatment waste can be
recycled. The metal ion pretreatment reduces the
cellulose’s crystallinity, thus increasing its
accessibility and benefitting its subsequent
hydrolysis (Solomon, 2007). Lopez-Linares and
Romero of the University of Jaén, Spain, treated olive
tree biomass with metal ions at 0.265 mol/L for 30
min at 152.6 °C and achieved high rates of
hemicellulose removal and hydrolysis (López-
Linares, 2013). Zeng of Chongqing University,
China, treated biomass with 0.6 mol/L ferric chloride
solution for 15 min at 170 °C at a solid to liquid ratio
of 10:1 mL/g, increasing the relative cellulose
content by 72.19% and the reducing sugar yield by
131.6% (Zeng, 2013).
The biological treatment method has the
advantages of mild reaction conditions, low energy
consumption, environmental friendliness, and high
target product yield; thus, it has great potential for
development (Saha, 2016; Kim, 2008; Ranganathan,
2008; Henriksson, 2000). The degradation of lignin
by white rot fungi mainly uses peroxidase secreted by
white rot fungi to catalyze lignin oxidation. Lignin
peroxidase (LiP), manganese-dependent peroxidase
(MnP) and laccase (Lac) are the three main enzymes
for lignin degradation by white rot fungi (Wan,
Zhang, P., Lu, J., Liu, S., Wang, J. and Zhang, S.
Combined Ferric Chloride and Phanerochaete Chrysosporium Pretreatment on Corn Stalk Degradation.
DOI: 10.5220/0012013300003633
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine (ICBB 2022), pages 69-76
ISBN: 978-989-758-637-8
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
69

2012). White rot fungi not only have unique lignin
degradation ability, but also, like most other fungi,
have the ability to degrade cellulose and
hemicellulose to provide carbon source for their own
growth. The degradation of cellulose by white rot
fungi depends on the cellulase secreted by white rot
fungi, and the degradation of hemicellulose depends
on the hemicellulase secreted by white rot fungi.
Cellulase from white rot fungi is also composed of
Endoglucanase (EG, EC 3.2.1.4), Cellobiohydrolase
(CBH, EC 3.2.1.91) and beta-glucosidase (EC
3.2.1.21) (Kirk, 1997). Cellulose endonuclease
hydrolyzes the amorphous region of cellulose
microfibers and releases new end of cellulose chain.
Cellulose endonuclease hydrolyzes the next
cellobiose unit from end of cellulose chain in turn,
and finally hydrolyzes to glucose under the action of
beta-glucosidase. Xu et al. pretreated corn stalk with
Irpex lacteus CD2 at a cellulase dosage of 20 filter
paper units (FPU)/g dry matter for 25 days to achieve
hydrolysis and reached a saccharification rate of
66.4% (Xu, 2010). Sun et al. pretreated corn stalk
with Trametes hirsuta yj9 to increase total sugar
conversion from enzymatic hydrolysis (Sun, 2011).
However, due to the long period of microbial
pretreatment, it is difficult to apply in large-scale
industrial production, which restricts the further
application and development of biological
pretreatment. Ferric chloride solution achieves the
purpose of pretreatment mainly by destroying
hemicellulose of straw. The treatment cycle of straw
treated with ferric chloride and inoculated with white
rot fungi will be shortened and straw will be further
degraded to enhance the effect of pretreatment. In this
study, we investigated the effect of the process and
parameters of the pretreatment using ferric chloride
combined with Phanerochaete chrysosporium on the
reducing sugar content of corn stalk after enzymatic
hydrolysis. The pretreatment ability was determined
by the content change of cellulose, hemicellulose and
lignin and the yield of reducing sugar. It opens up a
new way for high efficiency, clean and low energy
consumption of biomass pretreatment technology of
crop straw.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Corn Stalk Raw Material
Corn stalk was collected from the experimental site
of the College of Mechanical and Electrical
Engineering of Henan Agricultural University, air-
dried, pulverized with a pulverizer, and sieved
through 40-mesh (0.425 mm) and 80-mesh (0.175
mm) standard sieves, and the siftage was dried at
75 °C to a constant weight. The main composition of
corn stalk was showed in Table 1.
Table 1. Main composition of corn stalk.
Raw material Cellulose (g) Hemicellulose (g) Lignin (g) Other (g)
40-mesh 0.252 0.315 0.127 0.306
80-mesh 0.255 0.314 0.127 0.304
Note: The total raw material weight used in the determination was 1.000 g.
2.2 P. chrysosporium Culture
P. chrysosporium (GIMCC No: GIM3.393) was
purchased from the Preservation Center of
Microorganisms of the Research Institute of
Microbiology of Guangdong Province. The
lyophilized P. chrysosporium mycelia were dissolved
in sterile water and revived. They were then
inoculated onto potato dextrose agar (PDA) slant
medium and cultured at 28 °C for 7 days, from which
the second-generation subculture was inoculated,
cultured for 7 days and then stored at 4 °C for later
use.
2.3 Ferric Chloride Pretreatment
Five grams of dried corn stalk powder sieved through
40-mesh or 80-mesh filters was placed into a 500-mL
Erlenmeyer flask, to which ferric chloride solution of
different concentrations (0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, or 0.5
mol/L) was added at a solid to liquid ratio (g/mL) of
1/10 (a) or 1/20 (b). The sample was then mixed
thoroughly and treated at 100–108 °C for 15 (c) or 30
min (d). The cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin
contents were determined after the above
pretreatment.
ICBB 2022 - International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine
70

2.4 P. chrysosporium Pretreatment
After rinsing to neutral pH, corn stalk siftage after the
ferric chloride pretreatments or 5 g of dried corn stalk
siftage sieved through 40-mesh or 80-mesh filters
was placed in a 300-mL Erlenmeyer flask, to which
distilled water was added at a solid to liquid ratio of
1:5. The flask was sealed with a sterile membrane and
treated at 121 °C for 1 h. Next, P. chrysosporium
growing in the logarithmic phase was punched with a
puncher, and several punch disks were inoculated
into 6 flasks and cultured at 28 °C. On days 6, 12, 18,
24, and 30 after inoculation, the reducing sugar
content was determined.
2.5 Determination Methods
The cellulose, lignin and hemicellulose contents in
the corn stalk were determined per the method of
Wang (Wang, 1987). The reducing sugar content in
the hydrolysate was determined using the 3, 5-
dinitrosalicylic acid colorimetric method on a Model
752 spectrophotometer (Ghose, 1987).
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Effects of Different Ferric Chloride
Pretreatment Conditions on
Cellulose and Hemicellulose Yields
The changes in cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin
contents of the 40-mesh corn stalk siftage treated
with ferric chloride are shown in Fig.1 After ferric
chloride treatment, the cellulose content increased in
all treatment groups, with little variation in
increments among the groups. The highest content
was 0.385 g, and the lowest content was 0.359 g,
which was a significant increase compared with the
original content of 0.252 g in the raw material. The
hemicellulose content for all treatment groups
decreased, while the lignin content increased because
the ferric chloride pretreatment destroyed the
scaffolding structure of the cellulose, lignin and
hemicellulose in the corn stalk, partially releasing
hemicellulose and increasing the cellulose content
while releasing more lignin. The cellulose and lignin
contents of the corn stalk treated with 0.5 mol/L ferric
chloride solution at 100–108 °C for 30 min at a solid
to liquid ratio of 1/20 g/mL increased significantly by
52.78% and 37.80%, respectively, relative to those of
the raw material, while the hemicellulose content
decreased by 12.06% compared with that of the raw
material.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
ac
cellulose conversion rate(%)
bd
ad
bc
ac
bd
ad
bc
ac
bd
ad
bc
ac
bd
ad
ad
bc
ac
bd
bc
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
hemicellulose conversion rate(%)
0
10
20
30
40
50
0.5 mol/LFeCl
3
0.5 mol/LFeCl
3
0.5 mol/LFeCl
3
0.5 mol/LFeCl
3
0.4 mol/LFeCl
3
0.4 mol/LFeCl
3
0.4 mol/LFeCl
3
0.4 mol/LFeCl
3
0.3 mol/LFeCl
3
0.3 mol/LFeCl
3
0.3 mol/LFeCl
3
0.3 mol/LFeCl
3
0.2 mol/LFeCl
3
0.2 mol/LFeCl
3
0.2 mol/LFeCl
3
0.2 mol/LFeCl
3
0.1 mol/LFeCl
3
0.1 mol/LFeCl
3
0.1 mol/LFeCl
3
lignin conversion rate(%)
0.1 mol/LFeCl
3
Figure 1: Conversion rate of each component of 40-mesh
corn stalk siftage treated with ferric chloride.
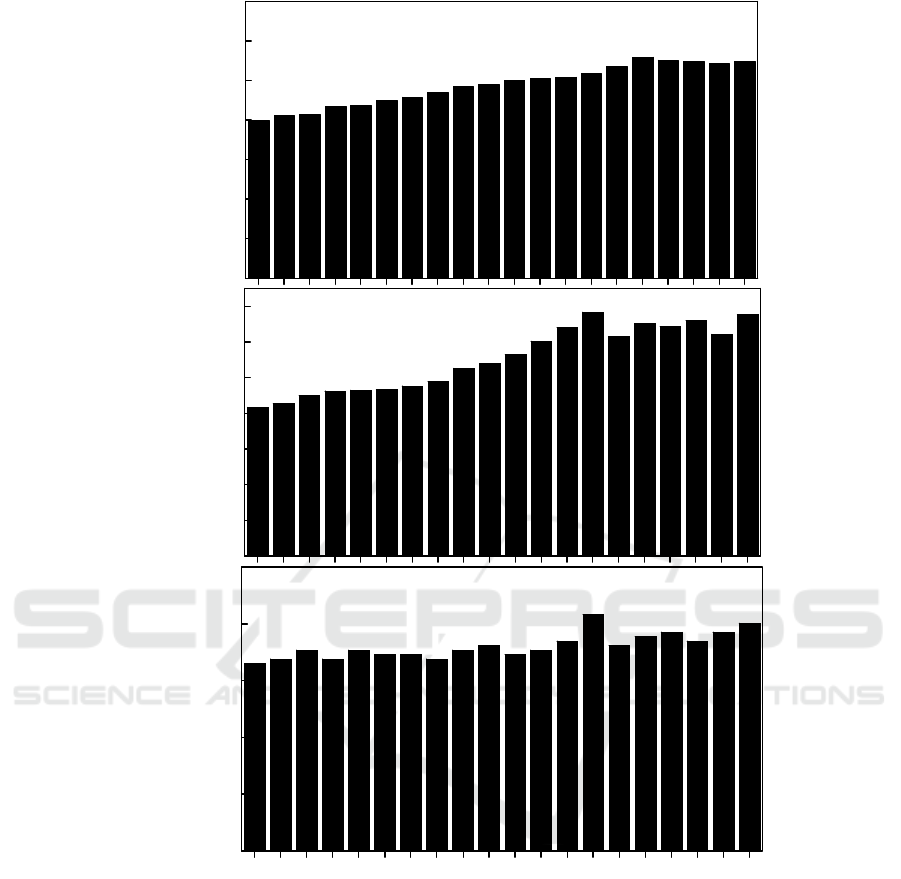
The changes in cellulose, hemicellulose and
lignin content of the 80-mesh corn stalk siftage
treated with ferric chloride are shown in Fig. 2 After
ferric chloride treatment, the cellulose content
increased in all treatment groups, and the increments
varied little among the groups. The hemicellulose
content decreased in all treatment groups, while the
lignin content increased. The cellulose and lignin
contents of the corn stalk treated with 0.5 mol/L ferric
chloride solution at 100–108 °C for 30 min at a solid
to liquid ratio of 1/20 g/mL increased significantly by
56.08% and 37.80%, respectively, compared with
those of the raw material, while the hemicellulose
content decreased by 13.06% compared with that of
the raw material. This treatment effect was the best.
Combined Ferric Chloride and Phanerochaete Chrysosporium Pretreatment on Corn Stalk Degradation
71
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
ac
cellulose conversion rate(%)
bd
ad
bc
ac
bd
ad
bc
ac
bd
ad
bc
ac
bd
ad
ad
bc
ac
bd
bc
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
hemicellulose conversion rate (%)
0
10
20
30
40
50
0.5 mol/LFeCl
3
0.5 mol/LFeCl
3
0.5 mol/LFeCl
3
0.5 mol/LFeCl
3
0.4 mol/LFeCl
3
0.4 mol/LFeCl
3
0.4 mol/LFeCl
3
0.4 mol/LFeCl
3
0.3 mol/LFeCl
3
0.3 mol/LFeCl
3
0.3 mol/LFeCl
3
0.3 mol/LFeCl
3
0.2 mol/LFeCl
3
0.2 mol/LFeCl
3
0.2 mol/LFeCl
3
0.2 mol/LFeCl
3
0.1 mol/LFeCl
3
0.1 mol/LFeCl
3
0.1 mol/LFeCl
3
lignin conversion rate(%)
0.1 mol/LFeCl
3
Figure 2: Conversion rate of each component of 80-mesh corn stalk siftage treated with ferric chloride.
After treatment with ferric chloride, the corn stalk
material’s morphology changed markedly (Fig.3).
The untreated 40-mesh corn stalk siftage showed a
smooth, flat, uniform, and undamaged surface, while
the treated corn stalk siftage showed a rough surface,
with disoriented surface structure texture, holes and
longitudinal fiber breakage. The treated 80-mesh
corn stalk siftage showed remarkable changes in
surface structure, with highly disarrayed texture in its
surface structure and holes in the partially fishnet-
shaped skeleton. The ferric chloride pretreatment not
only destroyed the surface structure of the corn stalk
raw material but also enlarged the size of pores on the
surface, thus increasing the specific surface area.
Compared with the 40-mesh corn stalk siftage treated
with ferric chloride, the 80-mesh corn stalk siftage
treated with ferric chloride showed more complete
and profound breakage, indicating that the lignin
ICBB 2022 - International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine
72

component was destroyed more effectively for the
smaller sized corn stalk.
(a) 40-mesh corn stalk (b) 40-mesh corn stalk siftage treated (c) 80-mesh corn stalk siftage
Siftage with ferric chloride treated with ferric chloride
Figure 3: Electron scanning microscopy of the corn stalk raw material.
After determining the cellulose, hemicellulose
and lignin contents of the 40- and 80-mesh corn stalk
siftages treated with ferric chloride, the optimal
combination of the treatment conditions was
determined and used in combination with the
subsequent P. chrysosporium treatment for corn stalk
degradation. The cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin
contents of the 40- and 80-mesh corn stalk siftages
treated with ferric chloride under the optimal
conditions are shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Optimal conditions for the ferric chloride treatment.
Stalk
particle
size
Ferric chloride
concentration
mol/L
Solid to
liquid
ratio
g/mL
Temperature/°C Time/min Cellulose/g Hemicellulose/g Lignin/g
40-
mesh
0.5 1/20 100–108 30 0.385 0.276 0.175
80-
mesh
0.4 1/20 100–108 30 0.398 0.273 0.175
3.2 Effect of P. chrysosporium
Pretreatment Conditions on the
Reducing Sugar Yield
Fig.4 shows the changes in the reducing sugar content
of the 40-mesh and 80-mesh corn stalk siftages
treated with P. chrysosporium over time. The
reducing sugar content first decreased, then
increased, again decreased, and finally stabilized.
This occurred because P. chrysosporium first
consumed small molecular carbon sources in the
substrate to propagate, thus decreasing the reducing
sugar content. After the mycelia matured, the fungus
began degrading the corn stalk, which increased the
reducing sugar content. As shown in Fig.4, on day 6
after fungal inoculation, the reducing sugar content
was high, peaking at 1.13 mg/mL for the fungus-
treated 40-mesh corn stalk siftage and at 1.20 mg/mL
for the fungus-treated 80-mesh corn stalk siftage,
although at this time, the stalk degradation was
incomplete. The reducing sugar content of the
fungus-treated 40-mesh corn stalk siftage reached its
lowest point at 0.39 mg/mL on day 12, while that of
the fungus-treated 80-mesh corn stalk siftage reached
its lowest point at 0.71 mg/mL on day 18. The
reducing sugar content in the corn stalk then rose
again, peaking at 0.97 mg/mL and 0.99 mg/mL for
the fungus-treated 40-mesh and fungus-treated 80-
mesh corn stalk siftages, respectively, on day 24, then
declined and gradually stabilized over days 24–30.
Combined Ferric Chloride and Phanerochaete Chrysosporium Pretreatment on Corn Stalk Degradation
73
0 6 12 18 24 30
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
Content of reducing sugar(mg/mL)
t(d)
40-mesh stalk siftage
80-mesh stalk siftage
Figure 4: Changes in the reducing sugar content in corn
stalks treated with P. chrysosporium over time.
Comparison of the fungus-treated 80-mesh and
40-mesh corn stalk siftages shows that on day 12, the
reducing sugar contents of the fungus-treated 40-
mesh and fungus-treated 80-mesh corn stalk siftages
were 0.41 mg/mL and 0.95 mg/mL, respectively,
with the largest gap at 0.54 mg/mL, likely because
the 80-mesh corn stalk siftage was smaller than the
40-mesh corn stalk siftage, which is conducive to
fungal growth. During days 6–12, the fungus grew
rapidly. On day 12, it had already finished degrading
the 80-mesh corn stalk siftage, yielding a higher
reducing sugar content.
3.3 Effect of the Combined Ferric
Chloride and P. chrysosporium
Pretreatment on the Reducing
Sugar Yield
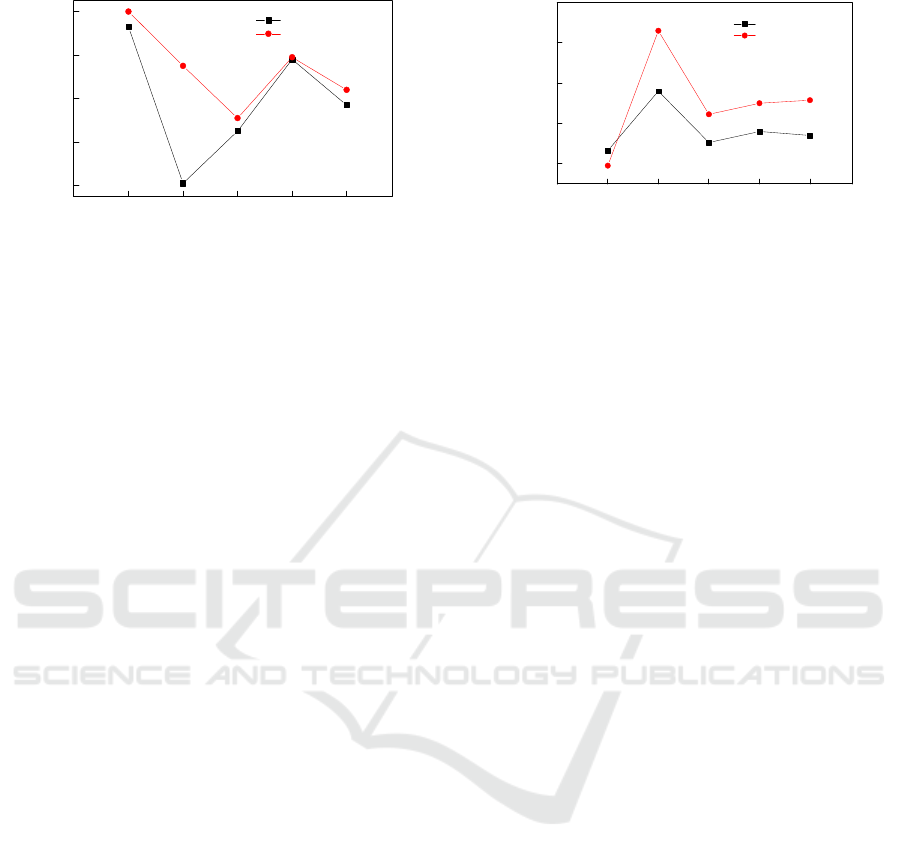
Fig.5 shows that as the treatment time increased, the
reducing sugar contents of the 40-mesh and 80-mesh
corn stalk siftages treated with the combined P.
chrysosporium and ferric chloride increased, then
decreased, and finally stabilized. This occurred
because on day 6, the fungus had already matured and
begun to degrade the corn stalk during days 6–12,
thus increasing the reducing sugar content in the
substrate. On day 12, the reducing sugar contents of
the 40-mesh and 80-mesh corn stalk siftages peaked
at 1.92 mg/mL and 2.52 mg/mL, respectively,
subsequently reaching their respective lowest points
at 1.41 mg/mL and 1.69 mg/mL on day 18. On day
24, the reducing sugar content of the 40-mesh corn
stalk siftage increased slightly and then stabilized,
while that of the 80-mesh corn stalk siftage showed
little change and remained stable during days 18–24.
0 6 12 18 24 30
1.2
1.6
2.0
2.4
2.8
Content of reducing sugars(mg/mL)
t(d)
40-mesh stalk siftage
80-mesh stalk siftage
Figure 5: Changes in reducing sugar content of the 40-mesh
and 80-mesh corn stalk siftage treated with the combined
P. chrysosporium and ferric chloride pretreatment over
time.
The reducing sugar contents of the 40-mesh and
80-mesh corn stalk siftages treated with combined P.
chrysosporium and ferric chloride differed little on
days 6, 12, 18, 24, and 30; however, on day 6, the
reducing sugar contents of the 40-mesh and 80-mesh
corn stalk siftages were 1.33 mg/mL and 1.18
mg/mL, respectively. The reducing sugar content of
the 40-mesh corn stalk siftage was higher than that of
the 80-mesh corn stalk siftage, likely because after
the ferric chloride treatment, the cell wall of the 80-
mesh corn stalk siftage was destroyed more
completely than that of the 40-mesh corn stalk
siftage, and the smaller particle size was more
conducive to mycelial propagation and growth. On
day 6, the fungus had already matured and begun to
degrade the 80-mesh corn stalk siftage. In summary,
after the combined pretreatment, the 80-mesh corn
stalk siftage produced more reducing sugars than did
the 40-mesh corn stalk siftage and showed the highest
reducing sugar content on day 12 after fungal
inoculation.
3.4 Effect of Different Treatments on
the Reducing Sugar Yield of Corn
Stalk
As shown in Fig.6, the reducing sugar contents of the
corn stalk with different treatments exhibited
different change trends. When treated with P.
chrysosporium alone, the reducing sugar contents of
the 40-mesh and 80-mesh corn stalk siftages first
decreased, then increased, decreased again and
finally stabilized. This occurred because shortly after
being inoculated into the corn stalk, the fungus fed on
the reducing sugars to grow while producing
reducing sugars by degrading the corn stalk. In the
combined treatment, the reducing sugar content of
ICBB 2022 - International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine
74

the treated corn stalk increased first, peaked on day
12, then decreased and finally stabilized. This
occurred because after being treated with ferric
chloride, the corn stalk’s cell wall structure was
destroyed, allowing the fungus to directly and rapidly
degrade the lignin and cellulose to form
polysaccharides. Therefore, after being treated with
ferric chloride, treating the corn stalk again with P.
chrysosporium significantly improved the reducing
sugar production yield and cycle.
0 6 12 18 24 30
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
Content of reducing sugars(mg/mL)
d(t)
40 mesh,p.chrysosporium alone
80 mesh,p.chrysosporium alone
40 mesh,combined treatment
80 mesh,combined treatment
Figure 6: Comparison of the reducing sugar content of the
corn stalk with different treatments
4 CONCLUSION
In this study, corn stalk was combined pretreated by
ferric chloride and P. chrysosporium. The reducing
sugar content of the P. chrysosporium-treated 80-
mesh corn stalk siftage previously treated with ferric
chloride was 2.52 mg/mL on day 12 after the fungal
inoculation when the reducing sugar content in the
fermentation broth was the highest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was sponsored by Science and technology
cooperation of Henan Electric Power Surveying and
Design Institute (2018015); National "863" project
sub-plan (2012AA051502-02) and 2019 PhD
research start-up funding of Henan University of
Animal Husbandry and Economy
(2019HNUAHEDF16); Scientific and technological
project of Henan Province (212102110228).
REFERENCES
Bailey, B. K., 1996. Performance of ethanol as a
transportation fuel. In:Wyman CE(ed) Handbook
on bioethanol: production and utilization. Bristol.
Galbe, M., Zacchi, G., 2002. A Review of the Production
of Ethanol from Softwood. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol
59, 618-628.
Ghose, T. K., 1987. Measurement of cellulase activities.
Pure Applied Chemical 59, 257-268.
Henriksson, G., Johansson, G., Pettersson, G., 2000. A
critical review of celliobiose dehydrogenases. Journal
of Biotechnology 78(2), 93-113.
Kim, Y., Hendrickson, R., Mosier, N. S., et al., 2008.
Enzyme hydrolysis and ethanol fermentation of liquid
hot water and AFEX pretreated distillers grains at high-
solids loadings. Bioresource Technology 99(12), 5206-
5215.
Kirk, T. K., Cullen, D., 1997, Enzymology and Molecular
Genetics of Wood Degradation by White-Rot Fungi.
Environmentally Friendly Technologies for the Pulp
and Paper Industry, John Wiley & Sons. 590-592.
Lissens, G., Thomsen, A. B., Baere, L. D., et al, 2004.
Thermal wet oxidation improves anaerobic
biodegradability of raw and digested biowaste.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 38, 3418-3424.
López-Linares, J. C., Romero, I., Moya, M., et al., 2013.
Pretreatment of olive tree biomass with ferric chloride
prior enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresource Technology
128, 180-187.
Palonen, H., Thomsen, A. B., Tenkanen, M., et al, 2004.
Evaluation of wet oxidation pretreatment for enzymatic
hydrolysis of softwood. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol.
117, 1-17.
Ranganathan, S. V., Narasimhan, S. L., Muthukumar, K.,
2008. An overview of enzymatic production of
biodiesel. Bioresource Technology 99(10), 3975-3981.
Saricks, C., Santini, D., Wang, M., 1999. Effects of fuel
ethanol use on fuel-cycle energy and green house gas
emission. Fuel Mixtures 65(1), 137-174.
Saha, B., 2016. Biological pretreatment of corn stover with
white-rot fungus for enzymatic hydrolysis and
bioethanol production. International Biodeterioration
& Biodegradation 109, 29-35.
Solomon, B. D., Barnes, J. R., Halvorsen, K. E., 2007.
Grain and cellulosic ethanol: History, economics, and
energy policy. Biomass and Bioenergy 31, 416-425.
Sun, F. H., Li, J., Yuan, Y. X., et al., 2011. Effect of
biological pretreatment with Trametes hirsuta yj9 on
enzy matic hydrolysis of corn stover. International
Biodeterioration & Biodegradation 65(7), 931-938.
Wan, C., Li, Y., 2012. Fungal pretreatment of
lignocellulosic biomass. Biotechnol. Adv. 30, 1447-
1457.
Wang, Y. W., Xu, W. W., 1987. Quantitative Analysis
Procedure of Hemicellulose, Cellulose and Lignin in
Lignocellulose Solid Matrix Fermentation.
Microbiology China 2, 82-84.
Xu, C., Ma, F., Zhang, X., Chen, S., 2010. Biological
pretreatment of corn stover by Irpex lacteus forenzy
Combined Ferric Chloride and Phanerochaete Chrysosporium Pretreatment on Corn Stalk Degradation
75

matic hydrolysis. Journal of Agricultural and Food
Chemistry 58, 10893–10898.
Zeng, G. M.; Wang, Y. L.; Zhang, M. L.; Zheng, Y. X.;
Xing, J.; Ma, Y. F.; Xu, H. J., 2013. Thermal
degradation and structural characteristics of corn stover
after ferric chloride solution pretreatment. Asian
Journal of Chemistry 25(5), 2431-2434.
ICBB 2022 - International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine
76
