
A Review of the Biomaterial Applications of Zein
Peng Liu, Ying Li and Wei Zhou
*
Shanghai Institute of Quality Inspection and Technical Research, Shanghai 200040, China
Keywords: Zein, Biomaterial Applications.
Abstract:
Plant protein has increasingly inspired the interest of researchers due to its safety, wide sources, and high
performance and low cost. Zein, an important member of plant protein was used by the US FDA as a safe
excipient for drug film packaging in 1985. In the past 20 years, reports on the application of zein in the fields
of drug sustained-release material and tissue engineer scaffold materials have been constantly emerging,
making the application of zein in the field of biomedicine a research focus. This review summarizes some of
the application forms of zein in biomedicine, including drug loading, sustained-release material, and tissue
scaffolding in the form of microspheres, fibers, and films. It is expected that this review will provide ideas for
the use of zein in biomaterials industry.
1 INTRODUCTION
Zein is a degradable, hydrophobic plant protein
originally isolated from whole white corn and named
by John Gorham in 1821. According to protein
solubility and sequence homology, it can be further
subdivided into α-zein (19 and 22 kDa), β-zein (14
kDa), γ-zein (16 and 27 kDa), δ - Zein (10 kDa), of
which α-zein has the highest content in corn, reaching
70-85% (
Curtis, 1991)
. The zein originates is more
hydrophobic attributed to its large number of
hydrophobic amino acid residues, such as leucine,
proline, alanine. The unique amino acid composition
makes zein only soluble in acetone, acetic acid,
aqueous ethanol and alkaline aqueous solution.
Early period, Zein was used to make regenerated
fibers, but it was quickly replaced by synthetic fibers.
Until 1985, the US FDA approved zein excipient for
drug film coating as a GRAS mainly used in tablets
(Anonymous, 1985). Thus, zein began to enter the
period of medicinal use. In recent years, with some
reports of the application of zein in drug delivery and
tissue engineering, the application of zein has
gradually become a hot spot in the field of materials.
Zein can be made in various forms for using, and
there are four commonly application: microspheres,
nanoparticles, nanofibers and zein films.
*
Corresponding author
2 APPLICATION OF ZEIN
MICROSPHERES
Microspheres with an average diameter of 1 mm are
designed for intravenous injection and oral
administration of drugs. In 2005, Xinming Liu (Liu,
2005) prepared zein microspheres encapsulating
ivermectin (IVM) drugs by using phase separation
technology. The microspheres were characterized by
scanning electron microscope and laser scattering
particle size analyzer. In vitro studies showed that
zein microspheres are suitable for the sustained
release of IVM, and the system is suitable for use on
some biologically active substances that require
sustained release, See Figure 1.
3 APPLICATION OF ZEIN
NANOPARTICLES
Particles with at least one dimension less than 1000
nm are defined as nanoparticles (Cristina, 2007),
which have great potential for improving
bioavailability and bioactivity due to their unique
physicochemical properties (Emilie, 2010). The
insoluble nature of zein in water makes it a good
choice for the development of slow-release
biopolymer nanoparticles.
Liu, P., Li, Y. and Zhou, W.
A Review of the Biomaterial Applications of Zein.
DOI: 10.5220/0012013400003633
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine (ICBB 2022), pages 77-81
ISBN: 978-989-758-637-8
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
77

Figure 1: Scanning electron micrographs of IVM-loaded zein microspheres (a) Before lyophilization (b) after lyophilization
(c) In vitro release profiles of IVM as a function of time from tabletted microspheres (d) from pepsin degraded tabletted
microspheres (Liu, 2005).
Cranberry proanthocyanidins (CPs) have
potential antioxidant functions and have certain
applications in reducing cardiovascular disease and
cancer. However, the oral bioavailability of CPs is
very low, which limits its further application. In 2011,
Tao Zou et al. (Zou, 2012) used an improved liquid-
liquid dispersion method to prepare cranberry
procyanidin-zein (CPs- Zein) nanoparticles, cell
culture experiments show that CPs encapsulated in
nanoparticles can reduce the toxicity to cells, See
Figure 2.
Figure 2: (A)Percentage of the cell viability, (B)the early stage of apoptosis (Zou, 2012).
Compounds with antioxidant effects have a
certain role in the prevention and treatment of some
cardiovascular diseases, tumors, etc., but most of
these antioxidant compounds have the characteristics
of low stability and low bioavailability, so the
development of new drug delivery methods for the
application of the compound is of great significance
(Huang, 2017). Gallic acid (GA) is an active
substance widely present in green tea, vegetables and
fruits, and has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory,
antibacterial and anti-tumor effects, but because
gallic acid is unstable under high temperature,
oxidation, light, etc., and the oral bioavailability is
low, so its application is limited (Wang, 2018). Jose
Agustin et al. (José, 2018) studied the preparation of
gallic acid-loaded zein nanoparticles by
electrospraying and demonstrated the potential
ability of such nanoparticles to protect gallic acid.
Figure 3. is the preparation process of gallic acid-
loaded zein nanoparticles.
ICBB 2022 - International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine
78
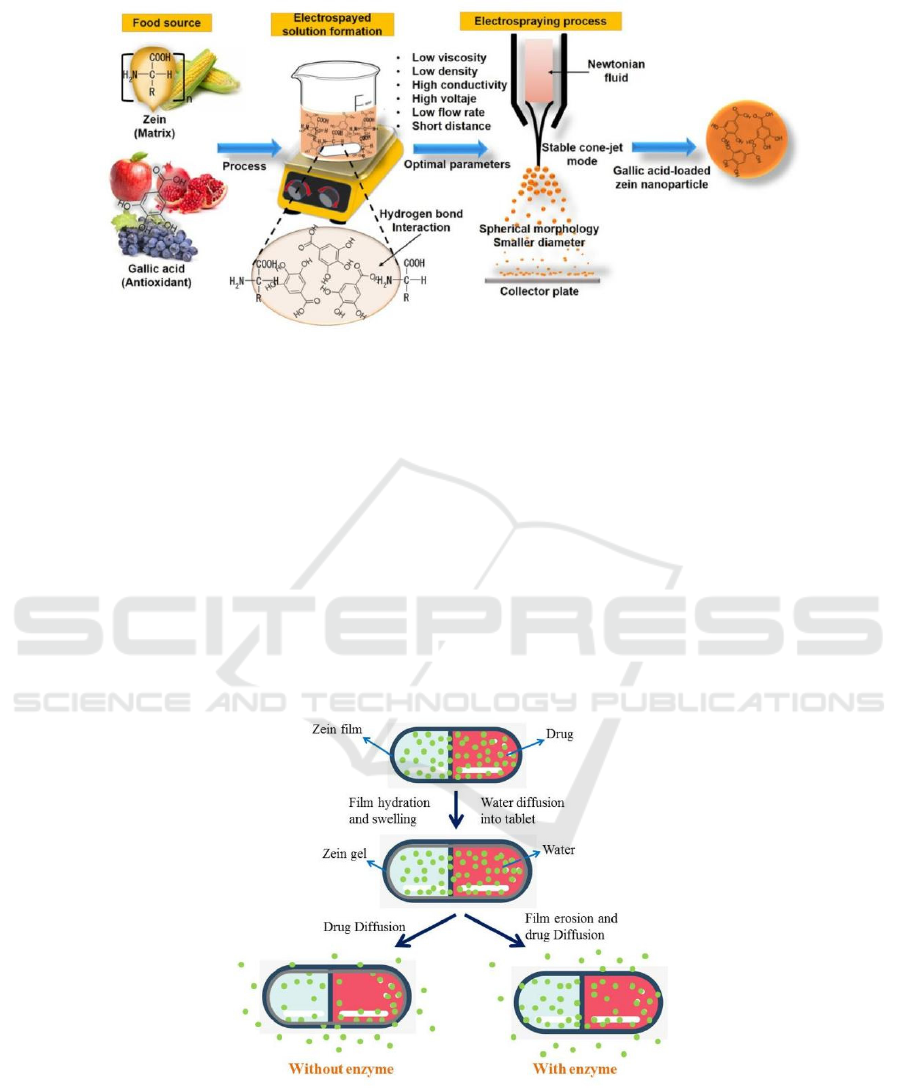
Figure 3: Preparation process of gallic acid-loaded zein nanoparticles (José, 2018).
4 APPLICATION OF ZEIN
NANOFIBERS
The use of zein as fiber has a very long history. As
early as more than 100 years ago, Ostenberg reported
the first patent for the production of fiber with zein.
Since then, various dry or wet spinning methods to
prepare micro-sized corn gluten fibers have appeared
one after another. In 2013, Weidong Huang et al.
(Huang, 2013) used an improved coaxial
electrospinning process to prepare ibuprofen (IBU)-
loaded zein fibers, and in vitro dissolution
experiments showed that the drug-loaded fibers could
diffuse through typical Fickian diffusion. and the
mechanism maintains sustained release in 10 hours.
W. Nie et al. (Nie, 2012) prepared zein-
polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) microfiber materials by
electrospinning technology, He used ketoprofen as a
model drug. Vitro dissolution experiments showed
that the drug dissolution rate was related to the ratio
of PVP, and fibers with different dissolution rates can
be obtained by adjusting the ratio of zein and PVP.
The drug sustained release model is shown in Figure
4.
Figure 4: Proposed drug release process of zein-coated tablets (Nie, 2012).
Afeesh Rajan Unnithan (Unnithan, 2014) mixed
cellulose acetate and zein, added streptomycin sulfate,
to obtain a nanofiber skeleton with antibacterial effect
utilizing electrospinning technology, applying
polyurethane as a substrate. The material has good
antibacterial properties, cytocompatibility, and
promotion of coagulation, this indicates the potential
application of this material in wound treatment.
A Review of the Biomaterial Applications of Zein
79
In addition to applications in drug delivery, zein
nanofibers have also begun to emerge as scaffolds for
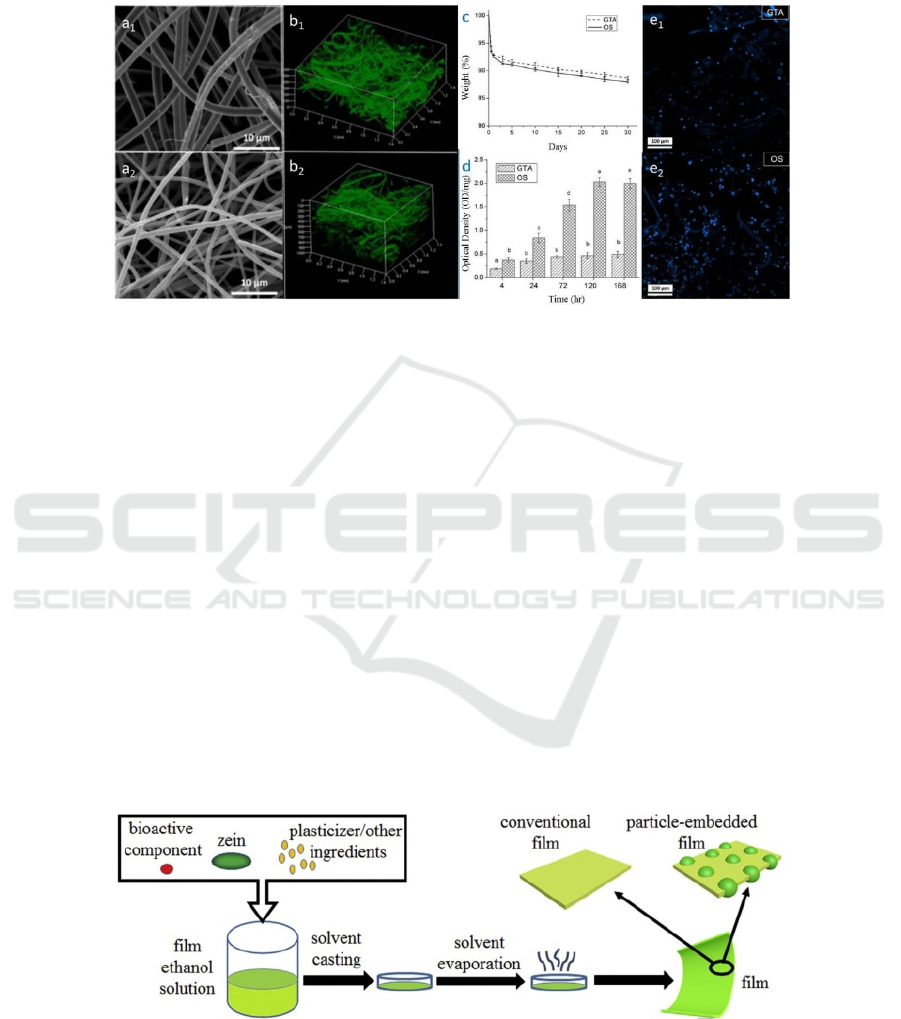
tissue engineering. In 2015, Peng Liu (Liu, 2015)
used oxidized sucrose as a cross-linking agent to
prepare a zein nanofiber scaffold using 3D
electrospinning technology. The development laid the
foundation, See Figure 5.
Figure 5. SEM images of the views (a1 and a2) ,and CLSM images of the top 45°view (b1 and b2) of the electrospun 3D
ultrafine fibrous zein scaffolds, Weight loss of electrospun 3D ultrafine fibrous zein scaffolds crosslinked with glutaraldehyde
(GTA) and oxidized sucrose (OS) (c), Growth of preosteoblast cells on electrospun 3D ultrafine fibrous zein scaffolds
crosslinked with OS and GTA(d), Spreading of MC3T3 cells on electrospun 3D ultrafine fibrous zein scaffolds crosslinked
with OS and GTA(e1 and e2) (Liu, 2015).
5 APPLICATION OF ZEIN FILMS
The preparation of zein film is relatively easy, and it
can be obtained by solution casting and extrusion
(Zhang, 2015). Zein is dissolved in water and organic
solvents, and dried at room temperature or under
specified conditions, and then through the
hydrophobic interaction within the protein molecule.,
hydrogen bonds, disulfide bonds, etc. work together
to obtain a zein film (Krochta, 1994).
To verify the compatibility between zein films
and cells, Jian Dong (Dong, 2004) prepared zein
films for culturing human hepatocytes (HL-7702)
and mouse fibroblasts (NIH3T3). The results show
that there is no significant difference between zein
film and Corning microplate cultured cells. This
preliminary test shows that zein is a material with
good biocompatibility, which can be used in the
development of tissue engineering. Yi-Long Han
(Han, 2014) obtained a zein film with a thickness of
50-100 μm by casting protein on a coverslip, and the
obtained film had good transparency in a dry
environment. In vitro experiments with NIH 3T3
cells showed that the film performed similarly to
culture plates, and this material has potential
applications in cell culture substrates and
microfluidic devices. Figure 6. exhibits the
preparation method of zein film.
Figure 6: Preparation process of cast zein film (Han, 2014).
Bacterial infection on implanted devices is an
important clinical problem and is associated with
bacterial adhesion, bacterial proliferation, and
biofilm formation. Traditional treatments include
both systemic and topical antibiotic administration.
However, the side effects caused by systemic
ICBB 2022 - International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine
80

administration are greater, so topical administration
has become an attractive means. Jian-Xi Fu et al. (Fu,
2009) prepared ciprofloxacin-loaded zein
microspheres by a phase separation method, and then
prepared zein microspheres containing the above-
mentioned. The solution of microspheres was poured
on the surface of a disc, and after the solvent
evaporated, a zein microsphere film (CF-MS film)
loaded with ciprofloxacin was obtained, and the
antibiotic-loaded zein film maintained antibacterial
activity for more than 6 days in experiments. The
material has potential application value in the
antibacterial of implanted devices.
6 CONCLUSION
Zein is an environmentally friendly and
biocompatible material. The promotion of its
industrial application contributes to the realization of
carbon peaking and carbon neutralization, so it has
been paid more and more attention by researchers.
Making zein in the form of particles, fibers and films
has been brilliant in the research fields of drug
delivery, drug sustained release, tissue engineering
scaffolds, etc. However, it should be noted that the
current research is basically still in the preclinical
stage, but we believe that through the continuous
efforts of researchers, zein will step into practical
clinical applications in the near future and benefit
mankind.
REFERENCES
Anonymous. (1985) Wheat gluten, corn gluten and zein
film: affirmation of GRAS status. Fed. Regist, 50:
8997–8999.
Curtis M, W. (1991) Multiple zeins from maize
endosperms characterized by reversedphase high
performance liquid chromatography. Plant Physiol,
95: 777–786.
Cristina, B., Ivan I, P., Kevin, R. (2007) Nanomaterials and
nanoparticles: sources and toxicity. Biointerphases, 2:
17-71.
Dong, J., Sun, Q.S., Wang, J.Y. (2004) Basic study of corn
protein, zein, as a biomaterial in tissue engineering,
surface morphology and biocompatibility.
Biomaterials, 25: 4691–4697.
Emilie, R., Frederic, L., Emmanuel, G., Jean-Pierre, B.
(2010) Biopharmaceutical parameters to consider in
order to alter the fate of nanocarriers after oral delivery.
Nanomedicine, 5: 287-306.
Fu, J.X., Wang, H.J., Zhou, Y.Q., Wang, J.Y. (2009)
Antibacterial activity of ciprofloxacin-loaded zein
microsphere films. Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 29: 1161–1166.
Han, Y.L., Xu, Q., Lu, Z.Q., Wang, J.Y. (2014) Preparation
of transparent zein films for cell culture applications.
Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces, 120: 55–62.
Huang, X.L., Dai, Y.Q., Cai J.X., Zhong, N.J., Xiao, H.,
McClements, D.J., & Hu, K. (2017) Resveratrol
encapsulation in core-shell biopolymer nanoparticles:
Impact on antioxidant and anticancer activities. Food
Hydrocolloids, 64: 157-165.
Huang, W.D, Zou, T., Li, S.F., Jing, J.Q., Xia, X.Y., Liu,
X.L. (2013) Drug-loaded zein nanofibres prepared
using a modified coaxial electrospinning process.
AAPS PharmSciTech, 14: 675-681.
José Agustín Tapia-Hernández, Francisco Rodríguez-Felix,
Josué Elías Juárez-Onofre, Saúl Ruiz-Cruz, Miguel
Angel Robles-García, Jesús Borboa-Flores, Francisco
Javier Wong-Corral, Francisco Javier Cinco-
Moroyoqui, Daniela Denisse Castro-Enriquez, Carmen
Lizette Del-Toro-Sánchez. (2018) Zein-polysaccharide
nanoparticles as matrices for antioxidant compounds: A
strategy for prevention of chronic degenerative
diseases. Food Research International, 111: 451–471.
Krochta, J.M., Baldwin, E.A., Nisperos-Carriedo, N.
(1994) Edible Coatings and Films to Improve Food
Quality. Technomic Publishing, Lancaster.
Liu, X.M., Sun, Q.S., Wang, H.J., Zhang, L., Wang, J.Y.
(2005) Microspheres of corn protein, zein, for an
ivermectin drug delivery system. Biomaterials,
26:109–115.
Liu, P., Xu, H.L., Mi, X., Xu, L., Yang,Y.Q. (2015)
Oxidized Sucrose: A Potent and Biocompatible
Crosslinker for Three-Dimensional Fibrous Protein
Scaffolds. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering,
300: 414-422.
Nie, W., Yu, D.G., Branford-White, C., Shen, X.X., Zhu,
L.M. (2012) Electrospun zein-PVP fibre composite and
its potential medical application. Mat Res Innov, 16:
14-18.
Unnithan, A.R., Gnanasekaran, G., Sathishkumar, Y., Lee,
Y.S., Kim, C.S. (2014) Electrospun antibacterial
polyurethane-cellulose acetate-zein composite mats for
wound dressing. Carbohydr Polym, 102: 884-892.
Wang, M., Fu, Y.Y., Chen, G.W., Shi, Y.G., Li, X.M.,
Zhang, H., & Shen, Y.L. (2018) Fabrication and
characterization of carboxymethyl chitosan and tea
polyphenols coating on zein nanoparticles to
encapsulate β-carotene by anti-solvent precipitation
method. Food Hydrocolloids, 77: 577–587.
Zou, T., Li, Z., Percival, S.S., Bonard, S., Gu, L.W. (2012)
Fabrication, characterization, and cytotoxicity
evaluation of cranberry procyanidins-zein
nanoparticles. Food Hydrocolloids, 27: 293–300.
Zhang, Y., Cui, L.L., Che, X.X., Zhang, H., Shi, N.Q., Li,
C.L., Chen, Y., Kong, W. (2015) Zein-based films and
their usage for controlled delivery: Origin, classes and
current landscape. Journal of Controlled Release, 206:
206-219.
A Review of the Biomaterial Applications of Zein
81
