
Research on the Countermeasures of Life and Health Industry in
Zhejiang Province under the Background of Common Prosperity
Zhijian Lin
1
, Can Huang
2
, Yinjiang Cui
1,*
, Fei Fang
1
, Qiufei Qiu
1
, Xiaolu Chu
1
and Guochang Lv
1
1
Zhejiang Institute of Scientific and Technological Information, Hangzhou 310006, China
2
The Institute for Intellectual Property Management, School of Management, Zhejiang University,
Hangzhou 310058, China
Keywords:
Life and Health Industry, Biomedicine, Traditional Chinese Medicine, Healthcare Service, Common
Prosperity, Zhejiang Province.
Abstract:
Life and health industry has the obvious advantages of long industrial chain, high technological content and
large market demand. It has gradually evolved into one of the key industries on which the states and regions
rely to seek sustainable development. It is also the golden card of Zhejiang Province's high-quality
construction of “common prosperity demonstration area”. Zhejiang Province has made remarkable
achievements in the development of life and health industry, forming regional characteristics in the fields of
biomedicine, traditional Chinese medicine, healthcare services. This paper analyzed the development
characteristics and shortcomings of life and health industry in Zhejiang province, and puts forward a new path
to promote the development of life and health industry in Zhejiang province from the aspects of park layout,
industrial clusters, R & D services, digital empowerment and innovation elements.
1 INTRODUCTION
The life and health industry is a general term for a
series of related products and services based on
medical health, biotechnology, and life science, with
the goal of serving people's health, including medicine
and medical equipment industry, health care industry
and health management service industry, etc. (Zhang,
2021) As a strategic emerging industry, life and health
industry has huge market potential, which will drive
the coordinated development of upstream and
downstream industries (Ge, 2020). In 2021, Chinese
President Xi Jinping called on China to promote
common prosperity in a context of high quality
development. Focusing on continuing steady increases
in income and high quality development, common
prosperity aims to increase the size of middle income
groups, raise the earnings of low income groups.
(Michael Dunford 2022) In recent years, Zhejiang
Province has always adhered to the guidance of
scientific and technological innovation, and has
developed an innovative development path for life and
health industry that meets the requirements of the
central government, is full of Zhejiang characteristics
*
Corresponding author
and meets the needs of the masses. Life and health
industry has gradually become the golden card of
Zhejiang Province's high-quality construction of
“common prosperity demonstration area”. In order to
explore the development status, effectiveness and
deficiencies of life and health industry in Zhejiang
province, this paper conducts extensive investigations
into the fields with significant regional characteristics
in Zhejiang Province, such as biomedicine, traditional
Chinese medicine and healthcare services. On this
basis, the countermeasures and suggestions for the
innovative development of life and health industry in
Zhejiang province under the background of common
prosperity are put forward.
2 CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE
AND HEALTH INDUSTRY IN
ZHEJIANG PROVINCE
2.1 Biomedicine Industry
In 2020, the total industrial output value of
310
Lin, Z., Huang, C., Cui, Y., Fang, F., Qiu, Q., Chu, X. and Lv, G.
Research on the Countermeasures of Life and Health Industry in Zhejiang Province Under the Background of Common Prosperity.
DOI: 10.5220/0012020300003633
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine (ICBB 2022), pages 310-318
ISBN: 978-989-758-637-8
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

biomedicine in the Zhejiang province reached 215.1
billion yuan, with an average annual growth rate of
12.6% during the 13th Five-Year Plan period. At
present, a total of 5 enterprises have been selected as
provincial "Eagle Action" cultivation enterprises, 15
have been rated as provincial "invisible champions",
and 50 listed enterprises which accounting for 1/7 of
the country. In general, the development of the
biomedical industry in Zhejiang province presents the
following characteristics.
(1) Chain development of characteristic parks to
promote the development and clustering of block
economy
The magnetic attraction effect of the province's
biomedical industry has gradually emerged. It has
developed into an industrial pattern composed of 2
"Ten Thousand Mu and One Hundred Billion"
platforms of Hangzhou Qiantang District
pharmaceutical port and Shaoxing Binhai New Area,
pharmaceutical parks such as Linping District
Biomedical High-Tech Park and Hangzhou Bay New
Area Life and Health Industrial Park, as well as
Pan'an "Jiangnan Pharmaceutical Town" and Yuhang
Digital Health Town. Among them, the
pharmaceutical port has introduced and cultivated
more than 1,400 biomedical enterprises, and seven of
the world's top10 biomedical enterprises have settled
down, with an annual output value of 39.4 billion
yuan and an annual growth rate of more than 15%.
(2) Innovation and development in key areas
strongly support the construction of Science and
Technology Innovation Highland
A number of key enterprises and blockbuster
achievements have been gathered in key areas such as
biological drugs, chemical drug preparations and
medical devices. In the field of small molecule
innovative drugs, Icotinib won the first prize of
National Science and Technology Progress Award in
2015. Ganovo, the first domestic anti hepatitis C
Class 1 innovative drug was developed, which broke
the monopoly of the United States. In the field of
advanced medical devices, the R&D of cutting-edge
products such as implantable heart valves and
cochlear implants is leading in the country.
Meanwhile, new business formats such as AI +
medicine and Internet + medical treatment continue
to emerge, and new therapies such as gene therapy
and cell therapy have made substantial progress. In
2021, a total of 8 preparations in the province were
approved by ANDA, accounting for 10% of national
total.
(3) "Rainforest-style" ecology takes initial shape,
consolidating the foundation of world-class industrial
landmarks
Zhejiang Province has integrated multiple
resources and built a complete full-chain industrial
innovation support system. It has deployed high-level
scientific research platforms such as West Lake
University and Zhijiang Laboratory, gathered leading
CXO companies such as WuXi Biologics and
Tigermed, integrated clinical resources such as the
First Hospital of Zhejiang University. By focusing on
clinical transformation needs, the R&D and
achievement transformation effectiveness were
effectively improved.
(4) The launch of innovative drugs and clinical
trials have both reached new records, and the
momentum of innovation and entrepreneurship is
good
The R&D and registration of innovative drugs in
Zhejiang Province are active. In 2021, the proportion
of R&D investment in the province's regulated
pharmaceutical enterprises to operating income is
4.9%, which is higher than the national average.
Zhejiang Province received a total of 69 production
approvals, including 3 innovative drugs and 66
generic drugs and a total of 79 clinical approvals were
obtained in this year, including 61 innovative drugs.
The number of innovative drugs listed and clinical
trials had both hit a record high.
2.2 Traditional Chinese Medicine
Industry
The traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) industry is
one of the seven historical classic industries in
Zhejiang Province, with the following characteristics.
(1) Industrial agglomeration is accelerating
Zhejiang province takes Hangzhou, Jinhua,
Quzhou and Lishui as the core, vigorously promotes
the regional characteristic TCM industry cluster. It
has built a number of "Zhejiang Eight Flavor"
standardized planting demonstration bases and
authentic TCM gardens, including the Jinhua natural
drug production base, Lishui characteristic TCM
production area, Pan'an "Jiangnan Medical Town".
The development pattern of modern TCM industry
with industrial agglomeration, regional linkage and
distinctive features has basically taken shape. Five
leading enterprises such as CONBA and Jolly
Pharmaceutical were selected into the top 100
National TCM list, and seven TCM enterprises such
as Shouxiangu were successfully listed (ranking first
with Guangdong province), forming a number of
TCM varieties that enjoy high popularity in China,
such as Kanglaite Injection, CORBRIN capsule and
Capsule Dendrobii.
Research on the Countermeasures of Life and Health Industry in Zhejiang Province Under the Background of Common Prosperity
311

(2) The protection and utilization level of
authentic local resources has been significantly
improved
Zhejiang province is a province with large TCM
resources, known as the "treasure house of medicinal
plants in southeast China". There are 2385 kinds of
TCM resources in the region, with reserves of more
than 1 million tons. The number and total amount of
authentic local resources rank second in China. It has
the only "Dapanshan National Nature Reserve" in the
country, which focuses on protecting the germplasm
resources of wild medicinal plants, and the "East
China Pharmaceutical Botanical Garden", with the
most abundant ecological types, and many TCM
resource protection parks or bases. During the "13th
Five-Year Plan" period, 8 new varieties of TCM
materials such as Zhejiang Fritillaria, Zhejiang
Ophiopogon japonicus, Dendrobium officinale, and
Ganoderma lucidum were cultivated by utilizing the
advantages of authentic germplasm resources, and the
number of new varieties was listed at the national
advanced level.
(3) The cultivation of the new "Zhejiang Eight
Flavor" has achieved remarkable results
Zhejiang province is one of the key producing
areas of TCM in China, and has always been praised
by the industry for its authentic quality and numerous
varieties, among which "Zhejiang Eight Flavor" and
the new "Zhejiang Eight Flavor" are the most famous.
In 2020, the planting area of traditional Chinese
medicinal materials in the province was 802,000 mu,
with a total output of 262,000 tons and a total
agricultural output value of 6.38 billion yuan, an
increase of 38.5%, 46.7% and 20.6% respectively
over 2015. Among them, the planting area of
"Zhejiang Eight Flavor" and new "Zhejiang Eight
Flavor" is 216,000 and 270,000 mu, and the actual
agricultural output value of Dendrobium candidum is
2.69 billion yuan, and the output value of
Dendrobium officinale reaches 2.69 billion yuan,
which has effectively promoted industrial efficiency
and farmers' income. It has established 73 provincial-
level "Authentic TCM Garden" demonstration bases,
and Pan'an Xinwo, Chun'an Linqi and Yueqing
Dajing have become the national TCM characteristic
town. The standardization and intensive production of
TCM have been significantly enhanced.
2.3 Healthcare Service Industry
The healthcare service industry in Zhejiang Province
developed earlier and achieved remarkable results,
showing the following characteristics.
(1) An elderly care service system of "home-
based, community-supported, institution-
supplemented, and combination of medical care and
nursing care" is initially formed
Zhejiang province has continued to innovate and
develop healthcare services, and promoted the reform
and innovation of healthcare services in accordance
with the three main lines of ensuring the bottom type
of elderly care, expanding inclusive elderly care and
supporting socialized elderly care. A set of policy
systems and mechanisms have been formed to
promote the development of business industries, and
a home-based, community-supported, institution-
supplemented, and combined with medical care has
been initially established (Huang, 2017; Wang, 2020;
Han, 2021). The overall development level of elderly
care services is among the top in the country, the
layout of elderly care facilities has been basically
completed, the elderly care service policy has been
initially established, and the development concept of
elderly care services has been significantly changed.
(2) Both the quantity and quality of healthcare
services have increased, becoming the main way to
build an "Common Prosperity" demonstration area
In recent years, the number of health care services
in Zhejiang Province has made historical
breakthroughs, and the quality of services has entered
the road of transformation. By the end of 2020, there
were 2,485 elderly care institutions with 475,500
beds, including 252,000 nursing beds, accounting for
53%, and 1,689 private elderly care institutions,
accounting for 70% of the total number of elderly care
institutions (Zhou, 2021). There are 1106 home-based
care service centers in Zhejiang province, covering
more than 75% of towns and sub-districts. 7,511
families of the elderly in difficulty have been
retrofitted for aging, with an excess of 10%
completed. 111 health care joint ventures have been
launched, distributed 11 cities in the province. In
terms of urban and rural basic old-age insurance, by
the end of 2020, 43.55 million people in Zhejiang
province participated in basic endowment insurance,
and 55.57 million people participated in basic
medical insurance (Statistical Science and Practice,
2021), and the "Zheli Yang" smart endowment
service platform was developed with a framework of
"1+5+N". The main indicators are in the forefront of
the country, and it has been supervised and
encouraged by the State Council for two consecutive
years. The healthcare service system has become the
main way to build a "Common Prosperity"
demonstration zone.
ICBB 2022 - International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine
312

(3) The business model of elderly care services is
becoming clearer, and the enterprise track is
competitive
At present, Zhejiang's health care industry has
formed a relatively mature and diversified business
model, among which typical models include monthly
fee system, long-term rental single payment system,
membership system, property rights sales and
combination of financial products. Among them, the
monthly fee system is a typical business model
adopted by traditional elderly care institutions,
especially elderly care institutions that face just-in-
demand customers. The single-payment system for
long-term rentals is based on the monthly fee system.
Elderly care institutions receive a one-time fee for
beds ranging from 5 to 15 years, and thereafter,
according to the health status of the elderly, they
charge monthly nursing fees. The membership system
is an innovative model created by a large number of
companies entering the health care industry through
heavy asset investment. The elderly pay a certain
membership fee to lock in the rights to live in a senior
care institution, and then pay a monthly fee after
entering the senior care institution. Property rights
sales are the organic combination of the real estate
industry and the health care industry. After the
company sells the property rights of the old-age
housing, it provides old-age services to the elderly
and earns service fees on a monthly basis. The
combination of financial products means that the
elderly can purchase financial products, such as
insurance products or trust products, to lock in the
eligibility for occupancy in old-age institutions, and
enjoy insurance benefits and old-age services at the
same time (Anke Hassel, 2019; Gao, 2021). After
years of development, these five models have their
own advantages and disadvantages, and are suitable
for different types, backgrounds and positioning of
institutional pension projects.
3 DEFICIENCIES IN THE
DEVELOPMENT OF LIFE AND
HEALTH INDUSTRY IN
ZHEJIANG PROVINCE
3.1 Biomedicine Industry
(1) The magnitude and energy level of the industrial
cluster dimension needs to be further improved
In terms of cluster magnitude, the overall scale of
Zhejiang is less than that of Jiangsu and Shanghai,
and the gap will still be large in the future. In 2020,
the industrial scale of Zhejiang Province is 215.1
billion yuan, which is lower than Jiangsu's 448 billion
yuan. Suzhou proposed to build a world-class
biomedical industry landmark, and strive to exceed
400 billion yuan in 2025, which is twice the target of
Hangzhou. Shanghai proposed to double the
industrial scale during the "14th Five-Year Plan".
Zhejiang Province also lacks characteristic industrial
parks such as Shanghai Zhangjiang Medicine Valley,
Beijing Changping Zhongguancun Life Science Park
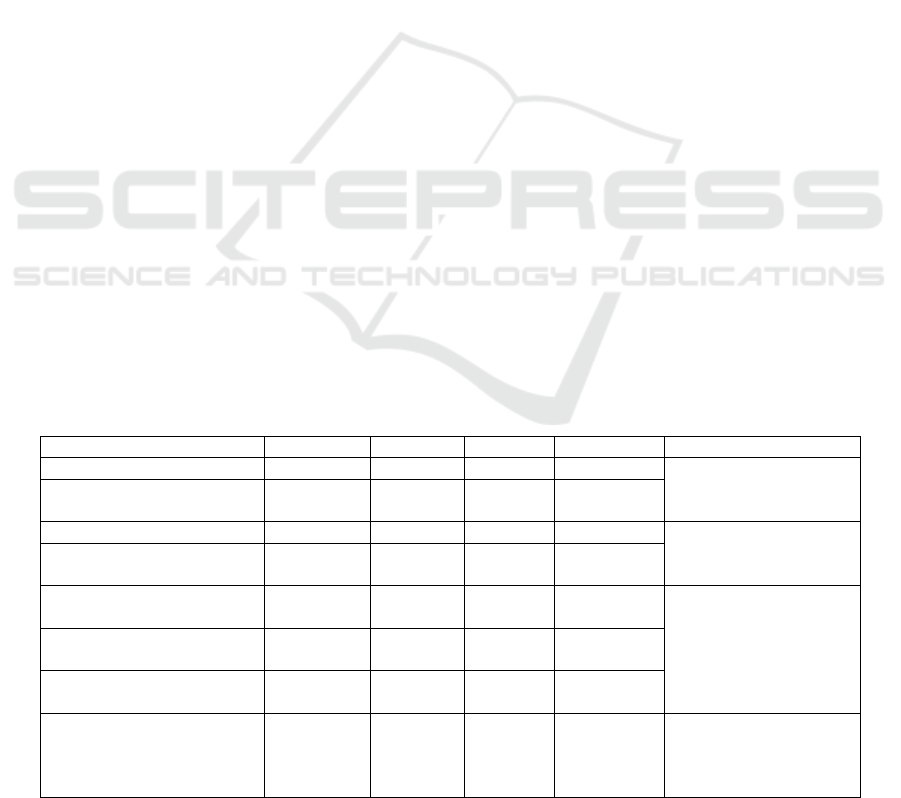
and Suzhou Biobay. In terms of the cluster level, the
layout and number of the national industrial clusters
in Zhejiang province need to be further increased. No
park in Zhejiang Province was selected into the Top
10 Comprehensive Competitiveness List of the "2020
China Biomedical Industrial Park Competitiveness
Evaluation and Analysis Report" released by the
China Biotechnology Development Center (see
Table1). Hangzhou High-tech Zone, the highest-
ranked in the province, only ranked 13th in the
country. In the "2021 Top 100 Biopharmaceutical
Industrial Parks" jointly released by CCID
Consulting's Pharmaceutical and Health Industry
Research Center and Sina Pharmaceuticals, only 3
parks in Zhejiang Province entered the Top50.
Hangzhou High-tech Zone ranked 18th in the list.
Table 1: List of national industrial clusters in the Yangtze River Delta.
Region
The strategic emerging
industry clusters of the
National Development
and Reform Commission
The innovative industrial clusters
pilot or cultivation of the Ministry
of Science and Technology
The advanced manufacturing
cluster of the Ministry of
Industry and Information
Technolo
gy
Zhejiang
Hangzhou biomedicine / /
Jiangsu
Suzhou biomedicine
Kunshan RNAi Innovative Industrial
Clusters, Taizhou Biomedicine
Innovative Industrial Clusters,
Suzhou National High-tech Zone
Medical Device Innovative Industrial
Clusters (all pilots)
/
Shanghai
Pudong New Area
biomedicine
Zhangjiang Biomedical Industry
Cluster (cultivation Class)
Zhangjiang Biomedical
Industry Cluster
Research on the Countermeasures of Life and Health Industry in Zhejiang Province Under the Background of Common Prosperity
313
(2) The cultivation of innovation resources in the
dimension of industrial innovation needs to be further
improved
In terms of talent aggregation, Zhejiang Province
has 910 provincial talents in the field of biomedicine,
which is lower than 1,517 in Shanghai and 1,061 in
Jiangsu. In terms of enterprise innovation ability,
Zhejiang province has 10,460 key enterprises (with
products and patents), lower than 16,240 in Jiangsu
province. Shanghai is favored by international
leading enterprises. At present, 18 of the world's top
20 pharmaceutical companies and 17 of the top 20
medical device companies have set up the China
headquarters or R&D headquarters in Shanghai. In
terms of corporate financing capacity, the number of
biopharmaceutical companies in Zhejiang Province is
lower than that of Jiangsu, and less than half of
Shanghai. The disclosed amount is 23.75 billion
yuan, which is only 53.5% of Shanghai's 44.35 billion
yuan. Lack of innovation resources has resulted in the
weaker innovation ability of life and health
enterprises in Zhejiang Province, and the less leading
enterprises. In the list of China's top100
pharmaceutical enterprises, the number of Zhejiang
companies has dropped significantly due to the lack
of innovation capabilities, from 13 in 2004 to 9 in
2019. There are few leading biomedical funds in
Zhejiang Province. Hillhouse, Sequoia, and Lilly
Asia Ventures (LAV) and other international capital's
Chinese headquarters are located in Shanghai.
(3) Clinical research capacity is weak, and the
policy support for innovative drug research and
development needs to be further strengthened
From the perspective of research ability, the top
experts in clinical research of innovative drugs
mainly work in Beijing, Shanghai, Guangdong and
other places. Zhejiang Province lacks experts with
national influence, especially in the field of tumor
drug research that is currently the most concerned.
Moreover, the number of research results of Zhejiang
Province is significantly less than Jiangsu and
Shanghai. By 2020, the innovative drugs applied in
Jiangsu and Shanghai were 3.2 and 2.7 times that of
Zhejiang respectively, and the number of “third class
medical devices” were 2.1 and 1.3 times that of
Zhejiang respectively. From the perspective of
investment, the cost of clinical research accounts for
the majority of new drug research and development.
In order to attract high-quality projects, local
governments have launched policies to increase
clinical research support in recent years. For example,
Guangzhou will increase the reward amount by 50%
for new drug projects commissioned by the city's
institutions to carry out clinical trials, up to a
maximum of 15 million yuan. In Shanghai, the
maximum support for innovative drugs that carry out
Phase I, Phase II, and Phase III clinical trials in China
is increased to RMB 5 million, RMB 10 million, and
RMB 30 million respectively.
In contrast, Zhejiang's policy only specifies
development plans, such as "providing support
through provincial key R&D programs for innovative
drugs that companies obtain registration certificates
and realize production or sales, as well as new drugs
that have been registered in the United States or the
European Union." Wait. It can be seen that the clinical
research foundation in Zhejiang Province is relatively
weak, and the strength and breadth of clinical
research support for innovative drugs needs to be
further improved.
Table 2: List of enterprise innovation achievements in the Yangtze River Delta.
Achievements
Zhe
j
ian
g
Jian
g
su Anhui Shan
g
hai Ex
p
lain
Clinical a
pp
lications
1708 5670 954 4651
Statistics by acceptance
number
As of 2020-12-31
Clinical applications
(innovative dru
g
s)
383 1228 58 1387
Clinical trials
3029 5171 1707 4437
Statistics by registration
number
As of 2020-12-31
Clinical trials (innovative
dru
g
s)
1014 1601 549 1572
Number of drugs
a
pp
roved
5336 8760 4228 3141
Statistics by approval
number
As of 2020-12-31
Number of innovative
dru
g
s a
pp
roved
8 42 5 10
Number of generic drugs
a
pp
roved
4995 8086 4066 3012
Number of Class III
medical devices approved
829 1772 76 1096
According to the
registration certificate
statistics
As of 2020-12-31
ICBB 2022 - International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine
314

3.2 Traditional Chinese Medicine
Industry
(1) The shortage of rural labor forces restricts the
production and cultivation of TCM
TCM industry is a labor-intensive industry. In
Zhejiang Province, the people engaged in the
cultivation of TCM are mainly the elderly, resulting
the prominent problems of labor shortage and
structural imbalance (Anke Hassel, 2019). This
restricts the large-scale development of TCM and
affects farmers' enthusiasm for planting. In addition,
TCM in Zhejiang are mainly planted in mountainous
areas. It is difficult to implement mechanical
replacement, and to popularize large-scale
machinery.
(2) Insufficient standardized management, heavy
metal and pesticide residues in some medicinal
materials exceed the standard
At present, China lacks pesticides suitable for
TCM, and there is little corresponding dose standard
"Chinese Pharmacopoeia" stipulates the limit
standard of 9 kinds of pesticide residues in TCM, but
the amount of pesticides used in production is far
greater than this number (Ma, 2018). It is the lack of
standards that makes it impossible to judge the real
situation of excessive pesticide residues in TCM. In
addition, there is also a problem that some pesticide
residue limits are too high. For example, in the
"Chinese Pharmacopoeia", the pesticide residue limit
of quinic acid is relatively high, which affects the
production and sales of Tongxiang Hangbaiju, and
also affects the market reputation.
(3) Insufficient production scale of Chinese patent
medicine
By 2020, there are 39 Chinese patent medicine
manufacturers and 76 decoction piece manufacturers
in Zhejiang province, accounting for 25% of the
pharmaceutical manufacturers. However, the revenue
and profit scale only account for 9.8% and 9.2% of
the drug production scale in the province,
respectively. In contrast, the revenue and profit of the
national TCM industry accounted for 29.1% and
25.0% of the pharmaceutical production,
respectively. Compared with other provinces, the
main business income of the processing of TCM
materials in Jiangsu Province alone reached 15.6
billion yuan, and the profit was 4.1 billion yuan,
which were 3.3 times and 13.2 times that of Zhejiang
Province respectively.
3.3 Healthcare Service Industry
(1) Insufficient implementation of policies and
relatively limited incentives
The government have introduced a large number
of policies and measures to encourage the
development of healthcare service industry, but the
implementation effect is not satisfactory. On the one
hand, the support policies of elderly care institutions
mostly focus on principle and macro guidance, and
lack specific implementation rules, which affects the
effectiveness of the policy to a certain extent. On the
other hand, the development of healthcare services
involves multiple departments, and there is a lack of
scientific and effective connection, interaction and
coordination mechanism between the policies of
different management departments, and sometimes
even falls into the embarrassing situation of mutual
preconditions, which affects the effective
implementation of policies (Huang, 2016). Compared
with public elderly care institutions, private
institutions are also faced with difficulties such as
lack of policy support and ineffective implementation
of support policies (Cui, 2017).
(2) High operating costs and insufficient sources
of funds
The construction costs, labor costs, maintenance
and management costs of various elderly care
services, the development and application costs of
smart and innovative elderly care products and
services, and the growing cost of personalized and
high-quality services are relatively high in Zhejiang
province. The imperfect capital security system,
including insufficient funding channels and low
capital operation efficiency, has become an important
reason for the lack of self-sustainable development
capabilities, operation difficulties, and inability to
achieve sustainable development of elderly care
enterprises, especially private elderly care
institutions. At the same time, there are problems of
policy arbitrage and serious deviation from the
original intention of the policy existing in some
investors.
(3) Lack of professional talents, and the level of
service standardization needs to be improved
The increase in the aging population has greatly
increased the demand for professional service
personnel in medical and health care, leisure health
care, trustee care, and domestic service. However, at
present, there is a relative shortage of professionals
and senior management talents such as doctors,
nurses, nutritionists, and rehabilitation specialists in
Zhejiang Province, and the service quality and
management level of the employees are not high
Research on the Countermeasures of Life and Health Industry in Zhejiang Province Under the Background of Common Prosperity
315

enough. Taking nursing care workers as an example,
there are only tens of thousands of people who have
obtained the professional qualifications of nursing
care in China, and less than 1,000 in Zhejiang
Province, which are far from meeting the pension
needs of different income groups in the society.
4 CONCLUSION
Based on the development status, effectiveness and
deficiencies presented above the conclusions are
obtained as below:
(1) Strengthen policy linkage and lead the layout
planning of the pharmaceutical park
The first, we should strengthen the guidance of the
layout and planning of pharmaceutical parks.
Establish a four-level work linkage mechanism of
province-city-district-park, and formulate the
development layout plan for the province's
biomedical industrial parks based on the development
foundation of each industrial park. The planning
should highlight the industrial characteristics of the
park, establish and improve the public service
platform and supporting upstream and downstream
enterprises, including intermediary service agencies.
The purpose is to promote industrial agglomeration,
enhance industrial service capabilities, build an
innovation and industrial ecosystem, and better attract
high-quality enterprises and projects. In addition,
attention should be paid to the development of high-
quality enterprises in the middle and late stages, and
individualized policy support and supporting services
should be provided for enterprises with the potential
to go public, so as to prevent the outflow of high-
quality enterprises in Zhejiang Province.
The second we should focus on advantages to
create a demonstration highland. Focus on increasing
support for regional parks with good industrial
foundation and characteristic advantages. For
example, the Yuhang Biomedical High-tech Park
located in Linping dstrict, with a total planned area of
21 square kilometers, has gathered more than 20
biopharmaceutical enterprises, including many
leading enterprises with wide coverage and strong
competitiveness. In particular, this park is close to
Shanghai and is in the core position of the Yangtze
River Delta metropolitan area. Under the situation of
comprehensively promoting the integrated
development of the Yangtze River Delta in the
province, it has strong advantages and potential. It is
recommended to give more attention and policy
support to such parks, and promote them to become a
first-class biomedical industry innovation highland in
the country.
(2) Focus on key areas, make overall planning and
construction of industrial parks to form a cluster
effect
The first is adhere to the leadership of leading
enterprises. Focus on the achievements of global
leading companies, industry invisible champions, top
talents in the industry and well-known scientific
research institutes in key fields such as
biopharmaceuticals, advanced medical device and
digital medicine, and increase efforts to introduce and
cultivate. With the help of the R&D innovation and
market development capabilities of key enterprises, it
will drive the improvement of innovation capabilities
of small and medium-sized enterprises and improve
the overall value chain.
The second is to guide the extension of the
industrial chain. We should carry out in-depth
industry-university-research cooperation, deploy
international frontier fields such as gene editing and
biomedical chips (Zhang, 2020). It is recommended
to make full use of the leading role of the provincial
scientific research special fund, encourage and guide
the resources and scientific research strength of
Zhejiang scientific research institutes, vigorously
support interdisciplinary research in the fields of
medicine, pharmacy, life science, artificial
intelligence, etc., and strengthen the joint effect of
government-industry-university-research.
(3) Focus on source innovation and build a first-
class R&D service system
The first is to speed up the overall system
infrastructure layout. Relying on research centers
such as West Lake University, Institute of Basic
Medicine and Oncology of the Chinese Academy of
Sciences, Liangzhu Laboratory, etc., and jointly with
Shanghai, Jiangsu and Anhui province, we should
commit to build advantageous disciplines and senior
talent think tanks. Deploy and construct major
scientific and technological infrastructure in frontier
fields such as brain science and synthetic biology in
advance, and strive to create national platforms.
Explore the establishment of a subversive technology
discovery funding mechanism to lead original
technological innovation breakthroughs.
The second is to innovate the full-chain
technological achievement transformation
mechanism. Accelerate the exploration of the
Zhejiang model for realizing the value of knowledge,
technology, data and other elements. Focus on
deepening the four-in-one cooperation of medical
institution, university, enterprise and financial
institution, establish an industrial technology
ICBB 2022 - International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine
316

innovation alliance, open up the whole link of
production, education, research and medicine, and
promote the development of core technologies and
the transformation and application of achievements.
Strengthen joint technical research and application in
the prevention and treatment of major infectious
diseases such as COVID-19, tumors, and
cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Encourage the research and development of
innovative TCM based on the Chinese classic
prescriptions. Accelerate the research and
development and industrialization of health care
products with TCM as raw materials, Chinese
medicine clinical diagnosis and treatment equipment,
and health care equipment (Jiao, 2018).
The third is to strengthen the construction of a
collaborative innovation platform for TCM. It is
necessary to establish a well-structured TCM
collaborative innovation system and mechanism, with
the national and provincial TCM scientific research
institutions as the core, with university, medical
institutions and TCM production enterprises as the
main body, and TCM scientific research bases and
TCM innovation platforms as the support (Bulletin of
The State Council of the People's Republic of China,
2016).
(4) Focus on digital empowerment, and develop
digital scenarios for the life and health industry
The first is to consolidate the resources of life and
health data and improve the analysis and computing
service capabilities. Zhejiang Province has strong
ability to process and analyze big data, but it is mostly
used in logistics and transportation fields, and the
application around life and health has just started. We
should further consolidate life and health data
resources, collaborate with existing digital life and
health-related institutions and innovation platforms,
bring together life and health digital resources and
technological advantages such as supercomputing
and digital processing, and build regional data
resource backup libraries to achieve upper and lower
linkages. It is necessary to break through the "stuck
neck" technologies such as high-performance
computing and mass storage, and realize the
application demonstration of digital life and health.
The second is to accelerate the integration of TCM
industry with advanced technologies such as big data,
Internet of things and blockchain. It is necessary to
combine big data, Internet of things, blockchain,
cloud computing, robotics and other technologies to
build an intelligent logistics system architecture for
Chinese herbal medicines, build a standardized,
intensive and traceable herbal medicine circulation
center for genuine herbal medicines, and promote
closer integration of the Internet of things system of
pharmaceutical circulation enterprises with the
quality traceability system (Jiao, 2018; Bulletin of
The State Council of the People's Republic of China,
2016). Chinese medicine hospitals at all levels are
encouraged to promote one-stop medical services
such as appointment registration, diagnosis and
treatment report and electronic prescription query, so
as to realize multi specialty joint diagnosis and
treatment through big data analysis and realize
precision medical treatment (Jiao, 2018).
The third is to enrich smart application scenarios.
It is necessary to further promote the digital reform of
healthcare services, and improve the ability of digital
service decision-making, service supervision, and
service supply and demand connection. Promote the
connection of healthcare service information with
information resources such as household registration,
medical care, social insurance, and social assistance,
improve the healthcare service payment system, and
realize a new leap in the digitalization of health care
services (Long, 2022; David, 2019; Pranav, 2021).
Health care service enterprises should make full use
of the smart elderly care information service
platform, undertake the content of elderly care
services purchased by the government, provide
professional and standardized services to the elderly
at home in the surrounding communities, and
establish a long-term mechanism for sustainable
development of the model (Han, 2021).
(5) Focus on the configuration of innovative
elements to build a full life cycle ecosystem
The first is to build a good ecological environment
for attracting and retaining talents. We should
optimize the ecological environment for innovation
and entrepreneurship, and speed up the construction
and improvement of biomedical parks. In terms of
taxation, house purchase, children's education and
other policies, it will be further refined according to
the talent levels to improve the attractiveness and
competitiveness of the policy. For example,
Hangzhou introduced a special reward policy for
high-level talents in November 2020. For qualified
high-level talents’ personal income tax, the portion
exceeding 15% will be rewarded by 80%-100% by
classification. After the implementation of the policy,
the social response has been good, and it is
recommended to promote it throughout the province,
and further increase the intensity and scope of tax
relief.
The second is to consolidate the intellectual
support of talents. We should vigorously implement
the "Kunpeng Plan" for top talents, draw a talent map
for the global life and health industry. It is necessary
Research on the Countermeasures of Life and Health Industry in Zhejiang Province Under the Background of Common Prosperity
317

to improve the talent supporting system and optimize
the "targeted and precise talent service". Focus on the
introduction and identification of professional service
and financial talents to ensure the talent needs of life
and health enterprises in the province. In addition,
policies should be formulated to encourage
enterprises to cultivate and introduce talents
spontaneously.
The third is to improve the construction of the
financial system. Provincial, municipal and district
governments should set up special industrial funds to
guide and gather domestic and foreign leading social
capital into Zhejiang. Learning from Shanghai
Zhangjiang Venture Capital, Suzhou Yuanhe Origin,
etc., we should cultivate and build local professional
life and health funds with national influence, and
improve the investment and financing system of the
province's life and health industry.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was financially supported by the National
Office for Philosophy and Social Sciences through
grant no. 21AZD010.
REFERENCES
Anke Hassel, Marek Naczyk. (2019) The political economy
of pension financialisation: public policy responses to
the crisis. Journal of European Public Policy,26(4):
483-500.
Cui Shuyi, Tian Yang. (2017) The "bottleneck" of the
development of elderly care institutions and their
solutions——based on a survey of 45 elderly care
institutions in Shandong province. Chinese Population
Science, 02: 115-125+128.
David C Mainenti. (2019) Big data and traditional Chinese
medicine: (TCM) What’s state of the art. 2019 IEEE
International Conference on Big Data (Big Data):1417-
1422.
Gao Yue, Yan Zhang. (2021) The current situation of the
development of domestic and international wisdom
pension service products and models. ISAIMS 2021:
Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on
Artificial Intelligence for Medicine Sciences: 252–256.
Ge Yanfei, Shen Junlong, Li Jie, et al. (2020)
Implementation Mechanism of Economic Value of
Traditional Chinese Medicine Under the Vision of the
Great-health Industry. Medicine and Society,33(06):
38-41+52.
Han Ye, Ji Ran, Fu Jiaping. (2021) Research on the
dilemma and countermeasures of the sustainable
development of private elderly care institutions.
Demographic Journal, 43(04): 89-97.
Huang Zhenzhen. (2017) Zhejiang Province strengthens the
construction of urban and rural home care service
centers. Zhejiang Daily, 2017-03-04: 007
Huang Chuang. (2016) Operation of private pension service
institutions: Self-development and support system.
Chongqing Social Sciences, 02: 66-72.
Jiao Yunlong. (2018) Promote the high-quality
development of Zhejiang characteristic TCM industry.
Zhejiang economy, 05: 52-53.
Long Y, Chu D, Wang H, et al. (2022) Blockchain-based
trace the source system for Chinese medicinal
materials. The 14th international conference on
measuring technology and mechatronics automation
(ICMTMA): 1007-1010.
Ma Lei, He Bowei, Xu Danbin. (2018) Zhejiang Province
Traditional TCM Industry Development Report. Rural
Science Experiment, 09: 107-109.
Michael Dunford. (2022) The Chinese Path to Common
Prosperity, International Critical Thought, DOI:
10.1080/21598282.2022.2025561
Notice of the state council on printing and distributing the
outline of the strategic plan for the development of
TCM (2016-2030) [J]. Bulletin of The State Council of
the People's Republic of China, 2016(08): 21-29
Pranav Ratta, Amanpreet Kaur, Sparsh Sharma, et al.
(2021) Application of blockchain and Internet of things
in healthcare and medical sector: applications,
challenges, and future perspectives. Journal of Food
Quality, 1:1-20.
Wang Wenxi. (2020) Report on the construction of the
provincial elderly care service system. Zhejiang
National People's Congress (Bulletin edition), 04: 128-
131.
Zhang Yiyi. (2021) Research on the Development of Life
and Health Industry in Wuxi Taihu Bay Science and
Technology Innovation Belt. Statistical Theory and
Practice,10: 43-46.
Zhou xiang, Zhu Xudong. (2021) The "13th Five-Year
Plan" of Zhejiang Province civil affairs work
documentary. Zhejiang Daily, 2021-01-19:009.
Zhejiang Province National Economic and Social
Development Statistical Bulletin. (2021) Statistical
Science and Practice, 03: 4-11.
Zhang K, Liu W. (2020) The Current status, trend, and
development strategies of Chinese biopharmaceutical
industry with a challenging perspective. SAGE
Open,10(1):1582440209.
ICBB 2022 - International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine
318
